Week 2
Terug: PRE_Groep2
Technische systemen voor tekstbewerking
Functies Nao op gebied van spraak
Op deze pagina staat een tutorial om Nao te laten spreken door middel van de codetaal Python:
file:///C:/Program%20Files%20(x86)/Aldebaran/Choregraphe%201.14.3.5/doc/naoqi/audio/altexttospeech-tuto.html#altexttospeech-tuto
De reden waarom we dit onderzoeken is omdat we een technisch systeem nodig hebben waarmee we een robot-stem aan kunnen passen. Nao leek ons hier een goed voorbeeld van. De vraag is alleen of Nao genoeg functies heeft om een robot-stem aan te passen naar de aspecten die een emotie heeft.
Er zijn een aantal aspecten die je door middel van deze taal aan kunt passen aan de stem van Nao. Hieronder volgt een opsomming daarvan:
- Een aantal modificaties aan de toonhoogte van de stem
- Double voice parameters kunnen worden gemodificeerd
- Wisselen naar een andere stem
- Het opslaan en ophalen van stem-voorkeuren
- Volume
- Toonhoogteverschuiving
De enige functies die we kunnen gebruiken voor ons onderzoek zijn volume en toonhoogte van de stem. Dit is niet genoeg om emoties aan een stem te kunnen geven. Daarom gaan we verder zoeken naar andere technische systemen die wel meer functies hebben. Dit kan bijvoorbeeld software zijn voor op een computer.
Tekst-spraak systemen
- eSpeak
informatie: http://espeak.sourceforge.net/
download: http://espeak.sourceforge.net/test/latest.html
Spreekt oa ook Nederlands. En volgens de bron kun je verschillende stemmen instellen, waarvoor je eigenschappen kan veranderen.
Om wav bestanden succesvol van espeak om te zetten naar Matlab en weer terug naar een wav bestand moeten we bij espeak 8k Hz, 16 bit mono instellen. Dit heeft te maken met het feit dat audio bestanden die in Matlab omgezet worden naar .wav bestanden gesampled worden met een sample frequentie van 8k Hz.
- festival
informatie & download: http://www.cstr.ed.ac.uk/projects/festival/
For queries regarding the Festival speech synthesis system email: festival@cstr.ed.ac.uk
- DECtalk
Informatie & download: http://facepunch.com/showthread.php?t=1323522
DECtalk is het systeem dat Steven Hawkins gebruikt.
Als je op de volgende link klikt kom je op een pagina over de master thesis van Janet Cahn (1989). Zij probeerde toen al emoties in een robotstem te krijgen en hiervoor gebruikte zij DECtalk3. Ze programmeerde zelf het programma 'Affect Editor'. Dit programma geeft twee strings. String één zet de intstellingen van DECtalk3 zodanig dat een bepaalde emotie wordt uitgedrukt, en string 2 is de tekst die dan wordt opgelezen door TTS. Op de pagina kun je geluidsfragmenten per emotie beluisteren en haar thesis terugvinden. http://alumni.media.mit.edu/~cahn/emot-speech.html
Janet Cahn schreef ook twee papers rondom het onderwerp:
- Cahn, Janet E., Generation of Affect in Synthesized Speech. Proceedings of the 1989 Conference of the American Voice I/O Society. Newport Beach, California. September, 1989. Pages 251-256. PS.GZ (29K)
Link: http://media.mit.edu/speech/papers/1990/cahn_AVIOSJ90_affect.pdf
- Cahn, Janet, From Sad to Glad: Emotional Computer Voices. Proceedings of Speech Tech '88, Voice Input/Output Applications Conference and Exhibition. New York City. April, 1988. Pages 35-37. PS (43K)
Wat gebruikt Amigo?
Amigo maakt gebruik van tts (text-to-speech) gemaakt door Philips, tts van Google en Ubuntu eSpeak.
Bron: http://bobbierobotics.nl/media/files/amigo_openspace_jmrvoncken_2013.pdf (pagina 7)
Audio bewerkingsprogramma's
Matlab wordt onder andere gebruikt voor signaal verwerking en analyse. http://www.music.mcgill.ca/~gary/307/week1/matlab.html
Example Matlab script and sound file: wavinout.m
Audio bestanden kunnen worden ingeladen en worden opgeslagen
Matlab heeft een Signal Processing Toolbox (dit zit standaard al in de Matlab versie R2012a) --> http://www.mathworks.nl/products/signal/
Key features:
- Signal transforms, including fast Fourier transform (FFT), discrete Fourier transform (DFT), and short-time Fourier transform (STFT)
- Waveform and pulse generation functions, including sine, square, sawtooth, and Gaussian pulse
- Transition metrics, pulse metrics, and state-level estimation functions for bilevel waveforms
- Statistical signal measurements and data windowing functions
- Power spectral density estimation algorithms, including periodogram, Welch, and Yule-Walker
- Digital FIR and IIR filter design, analysis, and implementation methods
- Analog filter design methods, including Butterworth, Chebyshev, and Bessel
- Linear prediction and parametric time-series modeling
We gaan nu kijken naar de begrippen die we al kennen waarmee je emoties kunt maken in geluid en of we deze toe zouden kunnen passen in matlab.
- Spreek tempo: vermenigvuldig de sample rate (fs) met de gewenste waarde om tempo te verhogen of te verlagen. i
- Gemiddelde spreekhoogte
- Spreiding spreekhoogte
- Intensiteit
- Stem kwaliteit
- Hoogte veranderingen
- Articulatie
Bronnen over de kenmerken van emoties
http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/summary?doi=10.1.1.52.5802
Het grootse probleem bij het vinden van geschikte bronnen is dat er meestal niet specifiek wordt ingegaan op verschillende emoties. Er worden belangrijke kenmerken genoemd om emoties te onderscheiden. Echter willen wij niet onderzoeken wat de waarde van een kenmerk is. We willen deze al hebben, zodat we het meteen kunnen implementeren in een programma. Ik heb dus veel meer bronnen gelezen, maar hieronder is een selectie van bronnen die van nut kunnen zijn.
"Emotional speech recognition: Resources, features, and methods"
Summary of the effects of several emotion states on selected acoustic features. The selected features are pitch, intensity and timing. The emotions that are used are anger, disgust, fear, joy anger. There are no values given to the different states, but the author gives indications whether an acoustic feature increases/decreces/etc. with an emotion.
"Emotion Recognition by Speech Signals"
http://www.isca-speech.org/archive/eurospeech_2003/e03_0125.html
Seems like an interesting article, but I have no access to the full text. For emotion recognition, the authors selected pitch, log energy, formant, mel-band energies, and mel frequency cepstral coefficients (MFCCs) as the base features, and added velocity/ acceleration of pitch and MFCCs to form feature streams.
"Emotions and Speech: Some Acoustical Correlates"
http://www.ohio.edu/people/leec1/documents/sociophobia/williams_stevens_1972.pdf
For the emotions anger, fear and sorrow some important acoustic features are summed up. These features are compared to a neutral from of speech. Examples of the acoustic features are fundamental frequency and duration of the syllables. Some of the features will be difficult to implement in a computer program.
"http://www.cvauni.edu.vn/imgupload_dinhkem/file/Chuyen%20De%20HCI/3_%20Analysis%20of%20Emotion%20Recognition%20using%20facial%20expression-speech.pdf"
Dit artikel is een overzicht van verschillende onderzoeken. Het is met name geschikt voor de bronnenlijst. Echter de bronnen die ik er tot nu toe mee heb gevonden zijn niet interessant voor ons onderzoek.
"http://www.fon.hum.uva.nl/praat/"
The most widely used speech cues for audio emotion recognition are global-level prosodic features such as the statistics of the pitch and the intensity. Therefore, the means, the standard deviations, the ranges, the maximum values, the minimum values and the medians of the pitch and the energy were computed using Praat speech processing software . In addition, the voiced/speech and unvoiced/speech ratio were also estimated. By the use of sequential backward features selection technique, a 11-dimensional feature vector for each utterance was used as input in the audio emotion recognition system.
"Prosody and Speaker State: Paralinguistics, Pragmatics, and Proficiency"
Jackson J. Liscombe, 2007
http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.135.7503&rep=rep1&type=pdf
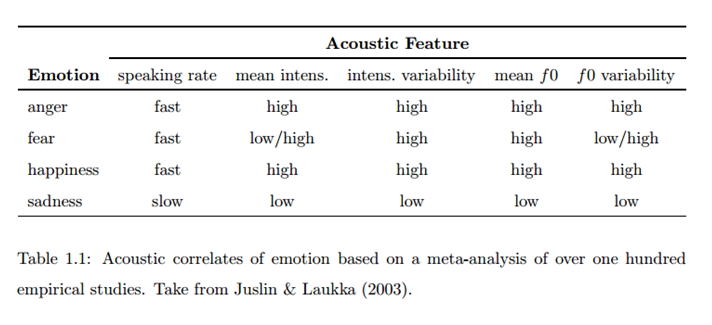
“Juslin & Laukka (2003) composed a meta-analysis of over one hundred studies conducted between 1939 and 2002.” (Liscombe, 2007) De uitkomst van deze meta-analyse is te zien in de tabel hier beneden. Uit al het onderzoek uitgevoerd tussen 1939 en 2002 komen een aantal kenmerken naar voren die specifiek zijn voor de emoties boos, angst, blij en verdrietig. Dit zijn de spreeksnelheid, de gemiddelde intensiteit en de variatie in intensiteit, de gemiddelde fundamentale frequentie en de variatie in deze frequentie. In de tabel is echter ook te zien dat boos en blij dezelfde specifieke kenmerken hebben, dus de vraag is hoe deze twee emoties dan te onderscheiden zijn. Ook angst kan verward worden met boos en blij, afgaande op deze kenmerken.
Om deze reden wordt emotie vaak opgedeeld in twee dimensies: activatie en valentie. Bovengenoemde kenmerken vallen onder activatie, en deze kenmerken alleen kunnen dus niet het verschil in boos, blij en verdriet verklaren. Daarvoor zou dus de tweede dimensie kunnen zijn. Er is echter geen overeenstemming tussen onderzoekers over wat deze dimensie bepaalt en of hij uberhaupt wel bestaat. “Some have suggested that voice quality may play a role (e.g, Scherer et al., 1984; Ladd et al., 1985; Zetterholm, 1999; Tato et al., 2002; Gobl & Chasaide, 2003; Fernandez, 2004; Turk et al., 2005), while others have suggested categorical intonation units (e.g., Uldall, 1964; O’Connor & Arnold, 1973; Scherer et al., 1984; Mozziconacci & Hermes, 1999; Wichmann, 2002; Pollermann, 2002).” (Liscombe, 2007)
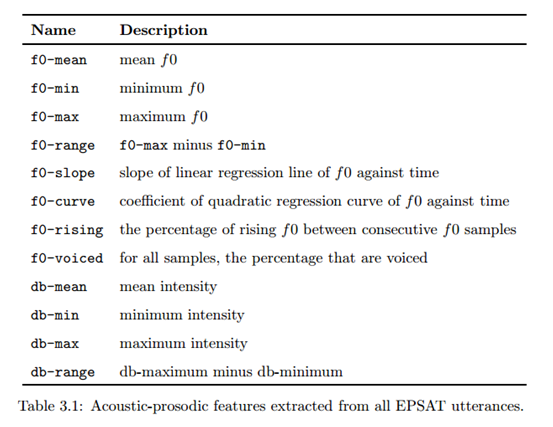
Liscombe (2007) voerde zelf ook een onderzoek uit naar emoties in spraak. Hierbij werden de parameters kenmerkend voor bepaalde emoties verkregen door het programma EPSAT (Emotional Prosody Speech and Transcript corpus). Data van spraak van 8 professionele acteurs werd gebruikt om deze parameters te vinden. De zinnen die gebruikt werden waren neutrale zinnen (dus geen woorden die gelinkt kunnen worden aan emotie) en 4 lettergrepen lang. Er werden 14 emoties en neutrale spraak opgenomen. De parameters die EPSAT genereerde zijn in tabel 3.1 te zien.
De kenmerken die het belangrijkst waren om onderscheid te maken tussen emoties waren: f0-mean, f0-min, f0-rising, db-min, db-range. Uit het onderzoek van Liscombe (2007) bleek dat op basis van deze kenmerken de volgende emoties van elkaar onderscheden konden worden: hot-anger, elation, happy, boredom, panic en neutral. De overige emoties die ze onderzochten konden in drie verschillende groepen van elkaar onderscheden worden, maar binnen die groepen niet.
"http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0167639302000821"
"These were synthesised using a formant synthesiser, and the voice source parameter settings were guided by prior analytic studies as well as auditory judgements."
Dus wellicht kunnen we een deel van de parameters voor de stem baseren op eerder onderzoek en een deel overlaten aan 'auditory judgements'.
"http://web.stanford.edu/dept/HPS/154/Workshop/Role%20of%20Emotion%20in%20Believable%20AgentsBATES.pdf"
Dit onderzoek gaat over de rol van emotie in de believability van agents. In de conclusie staat: Emotion is one of the primary means to achieve this believability, this illusion of life, because it helps us know that characters really care about what happens in the world, that they truly have desires.
Ik kom er nog niet helemaal achter of ze nu bewijs hebben dat emotie believability vergroot, of dat dit hier zomaar een aanname is.
"http://www.affective-sciences.org/system/files/biblio/1984_Scherer_JASA.pdf"
--> BELANGRIJK ARTIKEL!
Dit onderzoek komt ongeveer overeen met wat wij willen gaan doen.
Wat er o.a. gevonden is, is dat intonational categories alleen maar affect overdragen wanneer deze gecombineerd worden met grammaticale eigenschappen.
"http://scitation.aip.org/docserver/fulltext/asa/journal/jasa/93/2/1.405558.pdf?expires=1410524858&id=id&accname=2115293&checksum=7027346B3B61D918FCF324B061FCBCA5"
Op p. 1104 wordt er per onderzochte emotie uitgelegd welke parameters van belang zijn. Ook worden er verschillende waardes gegeven.
Samenvatting van de gevonden artikelen over kenmerken van emoties
"Emotions and Speech: some acoustic correlates"
Williams, C. E., & Stevens, K. N. (1972). Emotions and speech: Some acoustical correlates. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 52(4B), 1238-1250.
Below the fundamental frequency is stated for the emotions anger, sorrow and fear. We will not make use of the neutral emotion. The most important features of a sentence for each emotion is discussed and the fundamental frequency is compared between the different emotion.
We will briefly explain each graph. Anger: The contour shapes for utterances produced in anger situations showed an F0 that was generally higher throughout the utterances, suggesting that they were generated with greater emphasis. Furthermore, one or two syllables in each phrase were characterized by large peaks in F0, again indicating strong emphasis on these syllables. Although the excursions in F0 were quite great, there appeared to be a relatively smooth overall contour with one or two major peaks, but with no large discontinuities. Sorrow: The contouers for the utterances made in situations involving the emotion sorrow were relatively flat with few fluctuations, and the F0 was usually lower than that for neutral situations. For Voice B (fig.1), there was a slow falling contour during the first half of the utterance, and a more level contour towards the end. Fear: The contours for utterances made in fear situations often departed from the prototype shape for neutral situations. Occasionally there were rapid up-and-down fluctuations within a voiced interval, as in cluster 4 for voice B. Sometimes sharp discontinuities were noted from one syllable to the next. In the graph below the median fundamental frequency is stated of the three emotions based on the recordings of three voices. This can be seen as a recap of the results that they find on the fundamental frequency.
In the next table the mean rate of articulation for each emotion is shown.
Some of the findings of the article were difficult to interpret because the pictures of the findings were not always readable. However at the end of the article there was a summary of the findings for each emotion. This will be discussed below. Anger: the most consistent and striking acoustic manifestation of the emotion anger was a high F0 that persisted throughout the breath group. This increase was, on the average, at least half an octave above the F0 for a neutral situation. The range of F0 observed for utterances spoken in anger situations was also considerably greater than the range for the neutral situations. Some syllables were produced with increased intensity or emphasis, and the vowels in these syllables had the highest fundamental frequency. These syllables also tended to have weak first formants, and were often generated with some voicing irregularity (i.e., irregular fluctuations from one glottal pulse to the next). The basic opening and closing articulatory gestures characteristic of the vowel-consonant alternation in speech appeared to be more extreme when a speaker was angry. The vowels tended to be produced with a more open vocal tract (and hence to have higher first-formant frequencies), and the consonants were generated with a more clearly defined closure.
Fear: The average F0 for fear was lower than that observed for anger, and for some voices it was close to that for the utterance spoken in neutral situations. There were however occasional peaks in the F0 that were much higher than those encountered in a neutral situation. These peaks were interspersed with regions where the pitch the F0 was in a normal range. The pitch contours in the vicinity of the peaks sometimes had unusual shapes and voicing irregularities was sometimes present. The duration of an utterance tended to be longer than in the case of anger or neutral situations. As was observed for anger, the vowels and consonants produces in fear situation were often more precisely articulated than they were in a neutral situation. Although these various characteristics were found for some of the utterances of some voices, observations of spectrograms revealed no clear and consistent correlate for the emotion fear. Sorrow: The average F0 observed for the actors speaking in sorrow situations was considerably lower than that for neutral situations and the range of F0 was unusually quite narrow. This change in F0 was accompanied by a marked decrease in rate of articulation and an increase in duration of an utterance. The increased duration resulted from longer vowels and consonants and from pauses that were often inserted in a sentence. Perhaps the most striking effect on the wide-band spectrogram was voicing irregularity. On occasion the voicing irregularity reduced simply to noise: i.e., the voiced sounds became whispered in effect.
"Analysis of Emotion Recognition using Facial Expressions, Speech and Multimodal Information"
Busso, C., Deng, Z., Yildirim, S., Bulut, M., Lee, C. M., Kazemzadeh, A., ... & Narayanan, S. (2004, October). Analysis of emotion recognition using facial expressions, speech and multimodal information. In Proceedings of the 6th international conference on Multimodal interfaces (pp. 205-211). ACM.
In this article there are no specific measurements given to program certain emotions. However they do state which characteristics are mostly used in by other researchers to determine an emotion. We will list these characteristics, because it is useful to know where we should emphasize on in a sentence.
Most researchers have used global suprasegmental/prosodic features as their acoustic cues for emotion recognition, in which utterance-level statistics are calculated. For example, mean, standard deviation, maximum, and minimum of pitch contour and energy in the utterances are widely used features in this regard. Dellaert et al. attempted to classify 4 human emotions by the use of pitch-related features. They implemented three different classifiers: Maximum Likelihood Bayes classifier (MLB), Kernel Regression (KR), and K-nearest Neighbors (KNN). The main limitation of those global-level acoustic features is that they cannot describe the dynamic variation along an utterance. To address this, for example, dynamic variation in emotion in speech can be traced in spectral changes at a local segmental level, using short-term spectral features. 13 Mel-frequency cepstral coefficients (MFCC) were used to train a Hidden Markov Model (HMM) to recognize four emotions. Nwe et al. used 12 Mel-based speech signal power coefficients to train a Discrete Hidden Markov Model to classify the six archetypal emotions. The average accuracy in both approaches was between 70 and 75%. Finally, other approaches have used language and discourse information, exploring the fact that some words are highly correlated with specific emotions.
We tried all researches that are listed in the text above. Some of them we were not able to find or we could not have access to them. Others turned out to be unusable for our research. However we did found some useful articles, for example the article that was discussed earlier.
"Emotive Qualities in Robot Speech"
Breazeal, C. (2001). Emotive qualities in robot speech. In Intelligent Robots and Systems, 2001. Proceedings. 2001 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on (Vol. 3, pp. 1388-1394). IEEE.
Fearful speech: is very fast with wide pit& contour, large pitch variance, very high mean pitch, and normal intensity. I have added a slightly breathy to the voice as people seem to associate it with a sense of trepidation.
Angry speech: is loud and slightly fast with a wide pitch range and high variance. We've purposefully implemented a low mean pitch to give the
voice a prohibiting quality. This makes sense as it gives the voice a threatening quality.
Sad speech: has a slower speech rate, with longer pauses than normal. It has a low mean pitch, a narrow pitch range and low variance. It is softly spoken with a slight breathy quality (it gives the voice a tired quality). It has a pitch contour that falls at the end.
Happy speech: it is relatively fast, with a high mean pitch, wide range, and wide pitch variance. It is loud with smooth undulating inflections.
There were other emotions discussed, but we are not going to implement those emotions. Therefor they were not stated here.
"Emotions in the voice: humanising a robotic voice"
Bowles, T., & Pauletto, S. (2010). Emotions in the voice: humanising a robotic voice. In Proceedings of the 7th Sound and Music Computing Conference, Barcelona, Spain.
In this article three important characteristics are stated. They will be explained below.
Phrase duration: Figure 1 shows the average duration of each phrase. Higher bars indicated longer duration and, when comparing the four emotional versions of the same phrase, a slower speech rate, whereas shorter bars indicate a shorter duration and, when considering different versions of the same phrase, a faster speech rate.
We looked at how each emotional phrase deviates from its neutral version and we noted that the phrases involving only monosyllabic or short words saw the greatest reduction in duration for the angry and happy phrases (-20% and below the duration of the neutral phrase). In the cases of phrases 1, 3 and 8, the average angry and happy phrases were slower than their equivalent neutral voices. Half of the sad phrases saw over a 20% increase in duration, whereas the short words phrases (phrases 5, 6 and 7) saw an increase in duration between 10-20%. The average length of pauses per phrase was also measured. The sad phrases saw the longest overall pauses with 5 out of the 8 sad phrases having the longest phrase duration. Half of the happy phrases contained pauses that were longer than the angry equivalent, whereas only angry phrases 2 and 5 contained pauses that were longer than their happy equivalent
Pitch analysis: In order to investigate the emotional changes in pitch, the maximum peak in fundamental frequency (F0), the number of pitch contours (or pitch variations) per phrase and the direction of pitch contours were examined. Figure 2 shows the average maximum peak of F0 for each phrase
For all phrases, anger and happiness have high F0 peaks, while sadness has low F0 peaks. With the exception of phrase 4, anger phrases have the highest peak fundamental frequency of the 3 emotions. The average maximum peak frequency range of the angry phrases sits between 246Hz-281Hz, with 6 out of the 8 phrases averaging above 250Hz. The happy phrases have a range of 225Hz-269Hz, with 2 of the 8 phrases averaging above 250Hz. The sad phrases have lowest fundamental frequency peaks, operating within a range of 143Hz-186Hz. Overall, the variation in the number of pitch contours was dependent on the type of phrase. Some of the angry phrases saw the greatest increase in the number of pitch contours, while the happy phrases showed greater variation between increases and decreases, from phrase to phrase. The sad phrases generally saw a decrease in the number of pitch contours, with two exceptions. The average direction of pitch contours per phrase was calculated by counting every upward curve as a positive value (+1) and every downward directed contour as a negative value (-1). The result for each phrase was totaled and an average obtained. The majority of the neutral phrases contained downward directed pitch contours. The majority of the angry phrases contained more downward directed pitch contours, whereas the happy phrases varied between having upward directed or downward directed pitch contours. The majority of the sad phrases contained downward directed contours.
Amplitude analysis: Figure 3 shows the average maximum amplitude peak for each of the 8 phrases based upon the actors’ performances.
We can see that for all the phrases, anger and happiness have the high peaks, while sadness have low peaks. The sad phrases had the lowest maximum amplitude peaks, with all of the sad phrases peaking below 95dB. All the angry phrases and 7 out of 8 happy phrases had peaks that exceeded 100dB.
Meeting donderdag 11-09-2014
Tijdens onze bespreking op donderdag 11 september kwamen we erachter dat het onderzoek wat wij wilden uitvoeren niet echt vernieuwend is. Onze onderzoeksvraag was: In hoeverre is het mogelijk om emoties te geven aan een robotstem? Uit literatuuronderzoek bleek dat dit mogelijk is, er zijn al veel onderzoeken gedaan naar welke kenmerken bepalend zijn voor bepaalde emoties en er is getest of mensen de emoties kunnen herkennen. De nauwkeurigheid waarmee mensen dit kunnen herkennen ligt voor de meeste emoties al rond de 70 procent. De vraag is of wij dit percentage kunnen verbeteren in zo'n korte tijd, en wij denken van niet. Onze huidige plan is daarmee dus niet echt vernieuwend en we vroegen ons af wat ons onderzoek dan bij zou dragen. Om deze reden zijn we verder gaan brainstormen over wat we dan wel kunnen onderzoeken. De volgende ideeën kwamen hieruit naar voren:
- Meer focussen op het user-onderzoek. En dan niet alleen kijken naar of mensen emoties kunnen herkennen in een robotstem, maar ook of dit invloed heeft op hoe ze tegenover de robot staan/ of ze het fijner vinden dat een robot met emoties praat.
- Wat we tot nu toe uit de literatuurstudie hebben gehaald is dat er op dit moment alleen getest is of mensen emoties kunnen herkennen in neutrale zinnen (waarin de context niet verwijst naar emotie). In de toepassing van emoties van een robotstem is het echter waarschijnlijker dat een robot een zin met emotie wil uitspreken als deze ook in de context emotionele waarde heeft. Mogelijk onderzoek wat wij kunnen doen is dan kijken of emotie toevoegen aan een zin die emotionele context heeft, een versterkend effect heeft op hoe de luisteraar de zin ervaart.
- De emoties boos en blij zijn nu nog moeilijk te onderscheiden in robotspraak. We zouden kunnen kijken of wij dit kunnen verbeteren. Het is alleen onwaarschijnlijk dat wij dit wel kunnen.
Uiteindelijk hebben we voor de tweede optie gekozen, waardoor onze nieuwe onderzoeksvraag wordt:
In hoeverre is het mogelijk om een zin van een robotstem met een emotionele betekenis te versterken?
We verwachten de emotionele betekenis te kunnen versterken door signaaltechnische aanpassingen van de robotstem.
Planning aankomende tijd
| Voorkennis | |
| Robotstem programmeren | |
| Onderzoek opstellen | |
| Onderzoek uitvoeren | |
| Onderzoek verwerken |
| Week | Dag | Datum | Tijd | Omschrijving | Wie? | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | vr | 12 sept | 3 uur | Aspecten per emotie op een rijtje zetten (eventueel met waardes) | Meike | |||||
| 2 | za | 13 sept | 2 uur | Uitzoeken of ons onderzoek al eerder is uitgevoerd | Iris | |||||
| 2 | za | 13 sept | 4 uur | Presentatie slides maken | Meike | |||||
| 2 | zo | 14 sept | 2 uur | Aspecten per emotie aanvullen en uitzoeken of ons onderzoek al eerder is gedaan | Suzanne | |||||
| 3 | zo | 14 sept | 3 uur | Planning overzichtelijk uitwerken voor op de presentatie | Floor | |||||
| 3 | ma | 15 sept | 1,5 uur | Bespreking voortgang | Floor + Meike + Suzanne + Iris | |||||
| 3 | ma | 15 sept | 0,5 uur | Persoonlijke feedback | Floor + Meike + Suzanne + Iris | |||||
| 3 | ma | 15 sept | 2 uur | Presentatie | Meike | |||||
| 3 | ma | 15 sept | 2 uur | Luisteren naar presentaties | Floor + Suzanne + Iris | |||||
| 3 | ma | 15 sept | 5 uur | Uitzoeken hoe de specifieke kenmerken toegepast kunnen worden in matlab | Iris + Floor | |||||
| 3 | di | 16 sept | 4 uur | Opzet onderzoek maken | Suzanne | |||||
| 3 | di | 16 sept | 7 uur | Kenmerken per emotie toepassen | Iris + Floor | |||||
| 3 | wo | 17 sept | 4 uur | Opzet onderzoek maken | Meike | |||||
| 3 | wo | 17 sept | 3 uur | Kenmerken per emotie toepassen | Iris + Floor | |||||
| 3 | do | 18 sept | 6 uur | Kenmerken per emotie toepassen | Iris + Floor | |||||
| 3 | do | 18 sept | 8 uur | Ideeën opzet onderzoek samenvoegen | Suzanne + Meike | |||||
| 3 | vr | 19 sept | 6 uur | Kenmerken per emotie toepassen | Iris + Floor | |||||
| 3 | za | 20 sept | 3 uur | Buffer | Floor + Meike + Suzanne + Iris | |||||
| 3 | zo | 21 sept | 3 uur | Buffer | Floor + Meike + Suzanne + Iris | |||||
| 4 | ma | 22 sept | 1,5 uur | Bespreking voortgang | Floor + Meike + Suzanne + Iris | |||||
| 4 | ma | 22 sept | 0,5 uur | Persoonlijke feedback | Floor + Meike + Suzanne + Iris | |||||
| 4 | ma | 22 sept | 2 uur | Meeting Coach | Floor + Meike + Suzanne + Iris | |||||
| 4 | ma | 22 sept | 6 uur | Robotstem afmaken | Floor + Iris | |||||
| 4 | di | 23 sept | - | - | - | |||||
| 4 | wo | 24 sept | 4 uur | Geluidsfragmenten verwerken in enquête | Suzanne + Meike | |||||
| 4 | do | 25 sept | - | - | - | |||||
| 4 | vr | 26 sept | 5 uur | Enquête afmaken | Floor + Meike + Iris | |||||
| 4 | vr | 26 sept | 5 uur | Enquête rondsturen | Floor + Meike + Iris + Suzanne | |||||
| 4 | za | 27 sept | 3 uur | Buffer | Floor + Meike + Suzanne + Iris | |||||
| 4 | zo | 28 sept | 3 uur | Buffer | Floor + Meike + Suzanne + Iris | |||||
| 5 | ma | 29 sept | 1,5 uur | Bespreking voortgang | Floor + Meike + Suzanne + Iris | |||||
| 5 | ma | 29 sept | 0,5 uur | Persoonlijke feedback | Floor + Meike + Suzanne + Iris | |||||
| 5 | ma | 29 sept | 2 uur | Meeting Coach | Floor + Meike + Suzanne + Iris | |||||
| 5 | di | 30 sept | - | - | - | |||||
| 5 | wo | 1 okt | 6 uur | Inleiding en methode schrijven | Meike + Suzanne | |||||
| 5 | do | 2 okt | 6 uur | Inleiding en methode bespreken + plan opstellen om resultaten te verwerken | Floor + Meike + Suzanne + Iris | |||||
| 5 | vr | 3 okt | - | - | - | |||||
| 5 | za | 4 okt | 3 uur | Buffer | Floor + Meike + Suzanne + Iris | |||||
| 5 | zo | 5 okt | 3 uur | Buffer | Floor + Meike + Suzanne + Iris | |||||
| 6 | ma | 6 okt | 1,5 uur | Bespreking voortgang | Floor + Meike + Suzanne + Iris | |||||
| 6 | ma | 6 okt | 0,5 uur | Persoonlijke feedback | Floor + Meike + Suzanne + Iris | |||||
| 6 | ma | 6 okt | 2 uur | Meeting Coach | Floor + Meike + Suzanne + Iris | |||||
| 6 | di | 7 okt | 8 uur | Resultaten verwerken + discussie en conclusie schrijven | Floor + Meike + Suzanne + Iris | |||||
| 6 | wo | 8 okt | 4 uur | Resultaten verwerken + discussie en conclusie schrijven | Floor + Meike + Suzanne + Iris | |||||
| 6 | do | 9 okt | 8 uur | Presentatie maken en voorbereiden | Floor + Meike + Suzanne + Iris | |||||
| 6 | vr | 10 okt | 4 uur | Presentatie voorbereiden | Suzanne | |||||
| 6 | za | 11 okt | 3 uur | Buffer | Floor + Meike + Suzanne + Iris | |||||
| 6 | zo | 12 okt | 3 uur | Buffer | Floor + Meike + Suzanne + Iris | |||||
| 6 | zo | 12 okt | 4 uur | Presentatie bespreken en laatste aanpassingen doen | Floor + Meike + Suzanne + Iris | |||||
| 7 | ma | 13 okt | 2 uur | Afronden project | Floor + Meike + Suzanne + Iris | |||||
| 7 | ma | 13 okt | 2 uur | Final presentation | Suzanne | |||||
| 7 | ma | 13 okt | 2 uur | Luisteren naar presentaties | Floor + Meike + Iris |
Presentatie maandag 15-09-2014
File:Presentatie 15-09-2014.pdf
Slide 2: Vorige week
Iris en Floor hebben onderzoek gedaan naar welke mogelijkheden er zijn op het gebied van spraakprogramma’s. Uiteindelijk hebben we nu het idee laten varen om de NAO robot te gebruiken in ons onderzoek, omdat we ons alleen op de spraak richten en dat NAO niet per se een toegevoegde waarde heeft. Daarnaast hebben text-to-speech programma’s die je op je laptop af kunt spelen een grotere mogelijkheid om dingen aan te passen in het geproduceerde geluid. We hebben ervoor gekozen om Matlab te gaan gebruiken, hier kunnen veel dingen in aangepast worden en hier hebben we al eens eerder mee gewerkt.
Suzanne en Meike zijn aan de slag gegaan met het vinden van meer informatie over aspecten die kenmerkend zijn voor emotie in de stem en welke waardes deze dan hebben. We kwamen erachter dat het onderzoek wat wij wilden uitvoeren niet heel vernieuwend is, en dat het erg lijkt op wat onderzoekers voor ons ook al gedaan hebben.
Slide 3: Aanpassingen onderzoek
Daarom hebben we ervoor gekozen om onze onderzoeksvraag iets aan te passen en ons meer te gaan richten op het in de praktijk testen van onze applicatie. Uit het literatuuronderzoek bleek dat er op dit moment vooral is getest of mensen emoties kunnen herkennen in een stem met neutrale zinnen. In de praktijk is het echter waarschijnlijker dat emotie in een robotstem wordt gebruikt bij emotionele zinnen. Daarom willen we onderzoeken of het wel echt toegevoegde waarde heeft als een robotstem bij emotionele zinnen emotie gebruikt. Onze nieuwe onderzoeksvraag is daarom:
In hoeverre is het mogelijk om een zin van een robotstem met een emotionele betekenis te versterken?
In hoeverre is het mogelijk om een zin met emotionele betekenis, uitgesproken door een robotstem, ook emotioneel te laten klinken?
Om deze onderzoeksvraag te beantwoorden gaan we via Matlab een robotstem maken die een emotionele zin neutraal uitspreekt en een emotionele zin met emotie uitspreekt. We willen een online enquete af gaan nemen waarin de deelnemer de ontwikkelde geluidsfragmenten moet beoordelen m.b.v. een Likert schaal. Aan de hand van de resultaten willen we dan kijken of het toevoegen van emotie aan de stem een betere perceptie van de emotie met zich meebrengt.
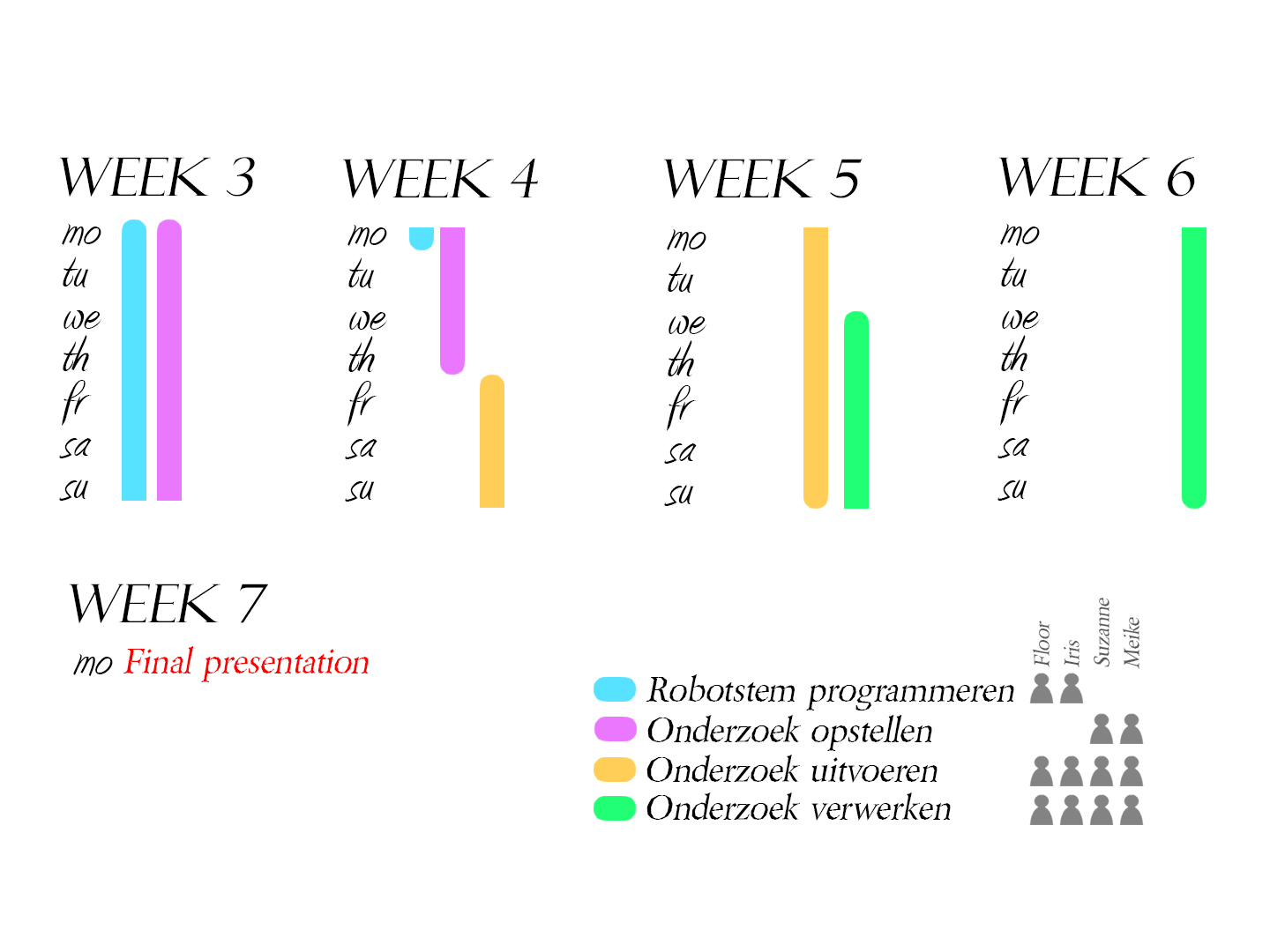
Slide 4, 5 en 6: Globale en gedetailleerde planning
Om dit voor elkaar te krijgen hebben we de volgende planning opgesteld. Komende week gaan Iris en Floor met behulp van de gevonden waarden uit vorig onderzoek, een paar zinnen met en zonder emotie programmeren. Het ligt er een beetje aan hoe snel dit programmeren gaat, hoeveel emoties we gaan onderzoeken. Tegelijkertijd zullen Suzanne en ik gaan werken aan de opzet van het uit te voeren gebruikersonderzoek. Als de robotstem af is zullen we deze geluidsfragmenten in de enquête verwerken. Aan het einde van week 4 gaan we de enquête versturen en promoten om zo veel mogelijk deelnemers te krijgen. In week 5 worden de enquêtes ingevuld en beginnen we met ons eindverslag. In week 6 zullen we de resultaten van de enquête verwerken en de eindpresentatie gaan voorbereiden.
Slide 7: Milestones en deliverables
Concreet zullen onze milestones en deliverables als volgt zijn:
- Op maandag 22 september zijn de robotstemmen met en zonder emotie af.
- Op vrijdag 26 september is de enquête af en kan deze in het weekend rondgestuurd worden.
- Op donderdag 9 oktober zijn de resultaten verwerkt en is de uitkomst van ons onderzoek bekend.
- Op maandag 13 oktober is de eindpresentatie.
Feedback presentatie maandag 15-09-2014
- De vraag of eSpeak de zinnen emotieloos uitspreekt is zeer belangrijk. Het kan namelijk goed zo zijn dat dit programma al bepaalde functies toepast op bepaalde zinnen/woorden.
- Hoe ga je de context toepassen in de survey? Je zou de participanten zich eerst in kunnen laten leven in de situatie.
- Zoek bronnen over scales of andere methodes die bij soortgelijke onderzoeken zijn gebruikt. Hiervoor kunnen we bijvoorbeeld naar Jaap Ham.
- Hypotheses opstellen aan de hand van bronnen.
- We hebben een sterk verhaal en een goede vraag. Er zijn geen twijfels dus we krijgen een GO!
Persoonlijke feedback week 2
Algemeen:
- Tip: Reactie in de whatsapp mag in het weekend wat meer.
Meike:
- Top: Fijn dat je de presentatie hebt gemaakt en aandachtig hebt gekeken naar de planning
- Top: En goed gediscussieerd
- Tip: maak je verslag van de week uitgebreider, dan komt je werk overeen met de uren die je hebt gemaakt
Suzanne:
- Top: Veel inzet tijdens de bespreking donderdag.
- Top: Goede samenvatting gemaakt dit weekend.
- Top: Je hebt dingen gezegd waar je mee zat en je goed uitgesproken.
Floor:
- Top: Een mooi overzicht van de planning gemaakt
- Top: productief gewerkt aan de speech programs
- Tip: Van te voren even aangeven als je niet bereikbaar bent vanwege omstandigheden.
Iris:
- Top: Fijn dat je bronnen had gezocht.
- Top: fijne samenwerking over het algemeen.