PRE2024 3 Group14
Group members
| Name | Student ID | Current Study Programme |
|---|---|---|
| Chantal Smits | 1689339 | Electrical Engineering |
| Julien Rodriguez | 1829599 | Computer Science and Engineering |
| Mihail Abramov | 1813978 | Applied Mathematics & Computer Science and Engineering |
| Anbiya Popal | 1838849 | Electrical Engineering |
| Danila Bogdanovs | 1782746 | Electrical Engineering |
Introduction
A lot the streets of big cities are full of litter. This is something that is noticed and bothers a lot of people. The litter is often washed away by rain and eventually ends up in our oceans. Therefore we are designing a robot that roams the Eindhoven citycenter streets and collects this litter. Currently this is done by people once a day which is not only labour intensive, but also means that the litter can be on the streets for up to 24 hours, which means that the trash is more likely to end up in the sewers, and eventually the oceans.
For this project we want to plan out the design of the robot, both it's hardware and software. We are focussing this project on the people that will use it and therefore we are basing our requirements on both our own experiences in the eindhoven center and on a few interviews with other people.
Approach
Phase 1 - research
Define the topic of the project and the approach taken. Perform literature research on the topic.
Phase 2 - requirements
Collect user requirements through interviews. Specify the requirements.
Phase 3 - implementation
Write the algorithm and make design of the robot. Build a prototype and perform simulations.
Phase 4 - finalization
Test the prototype and finalize both code and design. Give a presentation.
Planning
Based on the chosen approach the planning of the project was created. The four phases of the project were split into more specific tasks and the timing for each task is specified. The planning is summarized in the following Gantt chart below:
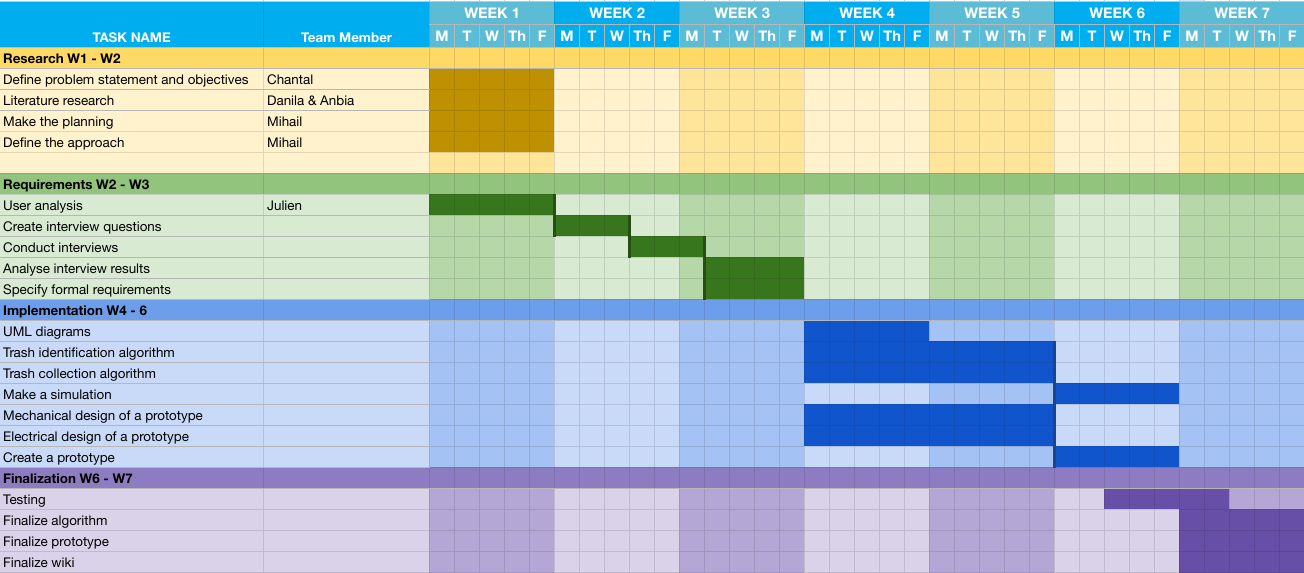
The research should be performed in the first two week. The requirements identification will be performed up to week 3. Having the results from research and requirements phases, the implementation phase will be performed. Implementation will span from week 4 to week 6. The finalization phase concludes the project in weeks 6 and 7 after the implementation is completed.
Milestones
End of...
Week 1 - having a plan for the project
Week 2 - finishing the research
Week 3 - finishing analysis and specifying user requirements
Week 5 - completing algorithm and design for the prototype
Week 6 - making a simulation and building a prototype
Week 7 - tested the prototype and presented the project
Literature Review
Autonomous trash collecting robots are designed to identify, collect, and dispose of waste materials efficiently. Many of these robots use computer vision, AI-based object detection, and autonomous navigation to function effectively.
Sivasankar et al. (2017) describe an early-stage autonomous trash robot capable of collecting garbage using a predefined route. Nagayo et al. (2019) further enhance this concept by incorporating a wireless charging system, ensuring that the robot remains operational for extended periods in a campus environment.
A more advanced model by Kulshreshtha et al. (2021) integrates YOLOv4-tiny, a deep-learning-based object detection model, enabling higher accuracy in trash detection. Othman et al. (2020) contribute by designing an automated trash collector that uses sensors to improve object detection and classification.
Furthermore, Nayak et al. (2009) introduce the "TailGator", a semi-autonomous trash-collecting system designed for outdoor environments. These studies show how new waste management systems are powered by artificial intelligence in some way. Recent studies also researched multi-robot systems, where drones and ground robots collaborate to identify and collect litter. Milburn et al. (2023) present the Tandem Rover and Aerial Scrap Harvester (TRASH) system, which integrates a ground robot and a drone to collect waste more efficiently. Together with the aerial mapping waste detection system presented by Akbari et al., these two systems represent a state-of-the-art, multi-robot waste management approach. Integrating the two would result in a fully autonomous, intelligent waste collection system that detects waste using drones, maps and classifies waste with computer vision and GPS data and deploys a ground robot to collect waste, optimizing routes based on the drone’s findings.
Trash robots contribute significantly to environmental sustainability. MacLeod et al. (2021) highlight the global plastic pollution crisis, emphasizing the need for employing robots in waste collection. He et al. (2022) discuss microplastic pollution, noting how robotic trash collectors could aid in reducing the spread of plastic waste.
In urban settings, robotic solutions have been proposed to address litter issues caused by nightlife and tourism. Becherucci & Pon (2014) compare waste accumulation in nightlife-dense areas, while Fallahranjbar et al. (2018) propose urban planning strategies combined with robotic waste collection. Burlakovs et al. (2020) propose the use of IoT-based smart waste bins which help optimize waste collection schedules using AI-based analytics. These studies give sufficient grounds on which one could say that deploying robotic trash collection systems in highly polluted urban spaces has social and environmental benefits.
However, these technological advancements are having several challenges that complicate the adoption of trash robots. Firstly, most trash robots rely on battery power, limiting the time for which one such robot could operate. A solution could be deploying multiple robots that could work in “shifts”, but this sparks another challenge: high costs and scalability issues. Sunil & Shanavas (2023) discuss how autonomous office waste collection robots face financial and technical barriers in deployment, meaning that financial struggles are to be expected when deploying such systems on city scale. Lastly ethical concerns set in, particularly around labor displacement and public safety (Jamil et al., 2023). Additionally, regulatory frameworks must be developed to standardize the deployment of trash robots in urban settings.
To summarize, current technological advancements allow for trash detection, autonomous navigation and multi-robot collaboration. This has the potential of reducing plastic pollution and optimizing urban and tourist area waste management. Future research needs to be done on more energy-efficient designs, lowering costs of the robotic solutions and policy and regulation frameworks.
Littering remains a significant issue in cities across Europe, impacting environmental well-being and living standards among the people. A survey conducted by the Clean Europe Network indicates that large cities such as Brussels, Copenhagen, Edinburgh, Helsinki, Oslo, Stockholm, and Zurich all experience the same city litter issues. The one-day survey, carried out in various urban settings such as popular landmarks and public parks, showed that litter is prevalent in all these municipalities. The findings point out the necessity for comprehensive national policies against littering, as stipulated by EU legislation mandating the adoption of such policies.
Innovative solutions at the municipal level also have been implemented to minimize littering. In Amsterdam, mini-gardens were installed at the locations where trash bins were placed to make such places look attractive and put individuals off from littering. The measures saw little litter around such bins, showing how the design of urban spaces influences people's behavior.
In the Netherlands, also, efforts by the citizens have been an important reason for addressing litter. Anti-litter activist Dirk Groot, who is otherwise called "Zwerfinator," has played a big role in raising awareness for littering with his extensive data collection. Groot invested careful time measuring and collecting over 700,000 items of litter across the nation, and in doing so, highlighting how common littering is and citizen science's capacity to assist with solving environmental problems.
Specific to Eindhoven, Groot's fieldwork reflected certain litter patterns. His studies revealed that specific places, such as shopping areas and public spaces, were found more frequently littered. Data also revealed the average litter of cigarette butts and snack waste, providing informative material for targeted interventions in the city.
Urban litter has been known to have negative effects on urban residents' quality of life. A Keep Britain Tidy survey of the country concluded that only 10% of English streets and parks are litter-free. "A Rubbish Reality," a report, concluded that areas in the most disadvantaged areas were three times more likely to be littered. The common litter consisted of cigarette butts, sweet wrappers, and drink cans. The research emphasized the negative effect of litter on the mental well-being of residents, sense of security, and community economic growth, with most of the respondents hesitant to invest in areas with litter.
User and stakeholder analysis
The primary users of our product include city waste management departments, cleaning staff, urban residents, local businesses and tourists. City waste management teams wish to lower operational costs and improve street cleanliness but have to deal with high manual labor expenses and workforce limitations. The robot addresses these issues by offering round-the-clock cleaning. Municipal cleaning staff reap benefit from reduced physical efforts as the robot can perform repetitive tasks and leave more complex tasks for the staff. In addition, regular waste collection will improve the quality of life of the city’s residents who desire cleaner streets for hygienic and aesthetic reasons, local businesses who depend on tidy surroundings to attract their clientele and tourists who want to enhance their overall experience and who can build a good reputation for the city.
The stakeholders, parties indirectly affected by the robot’s implementation include city officials/ urban planners and environmental agencies. City officials and urban planners must take into account public perception, cleanliness standards, and budgeting, with the potential benefit of improved waste management and city image. Environmental agencies vouch for pollution reduction and sustainable waste disposal, which the robot could support through eco-friendly features, like being fully electric. Additionally, waste management companies must be able to integrate the robot into their existing collection systems, improving operations and facilitating collaboration.
Interviews
Requirements
Following from the interviews, the safety features the robot is required to have are as follows: advanced collision avoidance system, using LiDAR, ultrasonic sensors and computer vision to effectively identify people in its path and safely navigate around them without pushing into crowds and causing inconvenience. Speed control systems and smooth, predictable movement patterns to avoid inconsistent acceleration, sudden stops and potentially unsettling movements. Non-intrusive sound and light signaling, meaning no loud sounds or bright, flashing lights. Instead, it should use subtle sounds and light indicators similar to those of regular vehicles to communicate its movement and stops. From the interviews, the robot should keep a distance of at least one meter away from pedestrians for them to feel safe and comfortable. Lastly, the robot must show environmental and context awareness. It should dynamically adjust its route based on pedestrian density data, moving to quieter streets if necessary.
Adressing the vandalism issue, the robot should have a low center of gravity to make it difficult to be toppled. Furthermore, a tough frame and casing and an alert system that notifies authorities in case of damage or theft attempts is in order. Finally, considering privacy issues, a reasonable compromise is having the system store only the last 15 minutes of camera data. This balances the the need for security and reduces the risk of mass surveillance or misuse of long-term data. Another possibility is trigger-based storage, where the robot only saves footage when relevant instead of recording constantly. This can be improved upon by having an AI model be trained on these snippets of recordings that allows it to learn when an activity is suspicious, a potential threat or neither. This solution is also potentially better from a hardware standpoint.
| Index | Description |
| 1.1 | The robot shall be equipped with a camera |
| 1.2 | The robot shall have 4 wheels |
| 1.3 | The robot shall be equipped with a speaker |
| 1.4 | The robot shall have a container for trash |
| 1.5 | The robot shall have rotating sweepers |
| 1.6 | The robot shall have a vacuum mechanism |
| 1.7 | The robot shall be equipped with GPS |
| 1.8 | The robot shall be connect to the internet |
| 1.9 | The robot shall be equipped with LEDs |
| 1.10 | The robot shall be equipped with a rechargeable battery |
| 1.11 | The robot shall have a body casing to hold all electrical components |
| 1.12 | The robot shall be shorter than 1.5 meters |
| 1.13 | The robot shall be taller than 0.5 meters |
| 1.14 | The robot shall not be wider than 1 meter |
| 1.15 | The robot shall not be longer than 2 meters |
| 1.16 | The robot shall be able to store at least 30 liters of trash |
| Index | Description |
| 2.1 | The robot shall detect trash on the ground |
| 2.2 | The robot shall compute distance to detected trash |
| 2.3 | The robot shall detect people |
| 2.4 | The robot shall compute distance to detected people |
| 2.5 | The robot shall be able to suck trash directly beneath it |
| 2.6 | The robot shall move using its wheels |
| 2.7 | The robot shall be able to cross sidewalks |
| Index | Description |
| 3.1 |
| Index | Description |
| 4.1 | The robot shall detect when a person touches it |
| 4.2 | Upon a person touching the robot, it shall notify a person to stop touching it |
| 4.3 | The robot shall detect when a person approaches too close |
| 4.4 | Upon a person approaching too close to the robot, it shall notify a person to keep distance |
| 4.5 | The robot shall detect when it is being kicked |
| 4.6 | The robot shall detect when it is being overthrown |
| 4.7 | The robot shall detect when its components are being damaged |
| 4.8 | Upon being kicked or overthrown or damaged the robot shall make an loud signal notifying people to stop vandalization |
| 4.9 | Upon being kicked or overthrown or damaged the robot shall contact the security |
| 4.10 | The robot shall keep the footage at most 1 week |
| 4.11 | The footage shall be accessed only in case of robot being vandalized |
| Index | Description |
| 5.1 | The robot shall not move faster than 5km/h |
| 5.2 | The robot shall not move closer than 1 meter to people |
| 5.3 | The robot shall not make noise louder than 60 db |
| 5.4 | The robot shall not pass the same place more often than once in 30 minutes |
| 5.5 | The robot shall work for at least one day without human maintenance |
Specification
Mechanical design
Electrical design
Trash identification algorithm
Trash collection algorithm
Simulation
Discussion and Further research
Conclusion
Planning
| Week | Student | Work Done | Total Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Julien | Brainstorm meeting + planning (2h)/ Wrote User and stakeholder study (1h) | 3h |
| Mihail | brainstorm meeting + planning (2h), described approach and planning of project (3h) | 5h | |
| Chantal | Introduction lecture (1h) brainstorm meeting + planning (2h) problem statement & objectives (1h) | 4h | |
| Danila | Introduction lecture (1h) brainstorm meeting + planning (2h) literature review (4h) | 7h | |
| Anbiya | brainstorm meeting + planning (2h) literature review (4h) | 6h | |
| 2 | Julien | group meeting (2h), taking pictures of stratum (1h) | 3h |
| Mihail | group meeting (2h), refined interview questions (1h) | 3h | |
| Chantal | group meeting (2h), write interview questions (1h) | 3h | |
| Danila | group meeting (2h) | 2h | |
| Anbiya | research into cleaning companies and email (1h) group meeting (2h) | 3h | |
| 3 | Julien | Group meeting (5h), Conducted interviews (3h) | |
| Mihail | group meetings (4h), redesigning the idea (3h), making new interview questions (1h),
Conduct interviews (3h), specific requirements (3h) |
14h | |
| Chantal | group meeting (4h) Conduct interviews (3h), extract user opinions from interviews (2h) | 9h | |
| Danila | group meeting (5h) interviews (1h) extending literature review (2h) safety features (1.5h) | 9.5h | |
| Anbiya | |||
| 4 | Julien | ||
| Mihail | |||
| Chantal | |||
| Danila | |||
| Anbiya | |||
| 5 | Julien | ||
| Mihail | |||
| Chantal | |||
| Danila | |||
| Anbiya | |||
| 6 | Julien | ||
| Mihail | |||
| Chantal | |||
| Danila | |||
| Anbiya | |||
| 7 | Julien | ||
| Mihail | |||
| Chantal | |||
| Danila | |||
| Anbiya |