PRE2020 1 Group2
Group Members
| Name | Student Code | Email address |
|---|---|---|
| Pleun Hutten | 1310925 | p.m.hutten@student.tue.nl |
| Jeroen Bakermans | 1007330 | j.bakermans@student.tue.nl |
| Rik Nietsch | 1244044 | r.nietsch@student.tue.nl |
| D.Kim | 1258893 | d.kim@student.tue.nl |
| E.W. Pardijs | 1257811 | e.w.pardijs@student.tue.nl |
Introduction
The measures taken for prevention of the spread of the coronavirus financially affect all sorts of enterprises. Employees are obligated to work from home, children suddenly had to follow online education, thousands of people lost their jobs et cetera. From one moment to the other, there was a lockdown and it wasn’t allowed to leave your home if it wasn’t for a crucial job, grocery shopping or for a run (on your own). Social distancing is the new norm.
The Netherlands is slowly building up the ‘1.5m-society’; hotels, restaurants, cafes, gyms, museums, education facilities, offices et cetera are allowed to welcome people again, provided that its visitors keep 1.5m distance at all times. However, there is one sector that is still deeply suffering from the measures taken concerning the coronavirus: the event branch. It is not (and will not be in the near future) allowed to organize events with large numbers of people. Festivals, expositions, fairs, markets, mass sports events are all removed from the calendars. But might there be innovative solutions that would nevertheless make such events possible again? That’s exactly what we are going to focus on during this project!
Idea 1
We are going to develop a device that makes sure all visitors of events always keep safe distance of 1.5m between each other. The principle is rather simple: everybody wears this gadget and when two (or more) come into a radius of 1.5m of each other, an alarming signal will go off. This will serve as a warning to the visitors to remain distanced from each other. Furthermore, the violation of the social distancing rules of this specific individual will be registered. The event-organizers could decide to intervene after for instance five warnings.
Idea 2
We are going to find and create/model a way to make dance-events possible again in corona-times. It will look as follows: attendees of the event can 'hire' a circular island with their household. All 'island-inhabitants' wear headphones through which music sounds. The visitors are allowed to move freely as long as they remain on their islands. The distance of every attendee to the middle of the circle is continuously tracked. Once the distance from the attendee to the reference point exceeds the radius he/she will be warned. An annoying beep will disturb the music, stimulating the attendee to go back to his/her island. This way customers will remain in their bubble and households will not get mixed up. This idea will be further elaborated below and will be referred to as a second idea.
Objectives
The current COVID-19 situation only allows for sit-concerts and -festivals. The event branch is financially hit and does not have any certainty about when the usual events will be allowed again. Interviews with the festival branch revealed that the sit-festivals are okay according to the circumstances, so here are no substantial problems. However, there is a big wish for being able to move freely and dance. This is not allowed at the moment because keeping distance while dancing is hard and therefore unrealistic. Therefore, the goal of this project is to come up with an innovative and safe way to make the organization of dancing festivals possible in times in which the coronavirus is lurking.
Before specifying the target group, it is important to discuss the current COVID-19 situation and the expectations for the future. At the time this wiki-page was created, the rising number of infections was alarming; the government spoke of a ‘second wave’. As a consequence, new measures were taken: horeca had to be closed at 10 pm, the maximum group size was 30 inside and 40 outside and face masks became an urgent advice. Before the second wave things started to get back to normal (at a distance): horeca and sport clubs were opening their doors, people could go to work, schools restarted physical education et cetera. However, the event branch was still deeply suffering from the consequences of the pandemic. As mentioned earlier, dancing events were not allowed and the capacity was drastically reduced. With the necessary new measures for stopping the second wave, the organization of events became even more impossible (because of the new maximum group size). This has the following consequences for our project: even if we come up with a safe tool that serves its goal, it would not be realistic to assume that dancing events would be allowed again on short term. Additionally, it is expected that the virus keeps hitting hard when a lot of our activities are moved inside because of the weather. Therefore, our product could not be used on short term, but whenever groups are allowed to be bigger again. It is expected that such events without a maximum group size (of course a 1.5 meter distance) will be allowed again by springtime (first outdoors). In the …-section we will discuss how to handle the uncertainty regarding the pandemic and the measures. Moreover, our product is specifically based on the demand on the Dutch market, as the measures differ in each country.
More concretely: we focus on indoor and outdoor festivals of many music genres. From pop, to electronic dance music, to house, to jazz: all festivals where dancing is desirable. However, this tool will not be suitable for music events where attendees usually go romping and mosh pitting (creating an open space in the audience and then run into it all at the same time). It is only suitable and desirable for events where attendees approximately stay at the same place to dance. The target group is very varied: from teenagers, to headbangers, to salsa dancing grandfathers. Depending on the applying measures, the maximum number of people might be prescribed or maximized for a certain terrain or hall. Our tool can be used at a small scale-events but can also be upscaled to larger music events.
We limit the use of this tool to concerts and festivals, because people buy a ticket with the main goal of enjoying the music. It could be argued that this is also the case in bars and night club. However, bars serve another goal: you go there to catch up with friends after a week of work. If our tool would implemented in bars, it would be useless as headphones will be taken off more frequently.
Deliverables
At the end of this project we want to have the following deliverables:
- In order to make sure that there is a demand for this product on the market a feasibility study will be performed. This means that we will contact as many stakeholders as possible to gain information and feedback on our plan. In the next section we will discuss who the stakeholders actually are. Another part of the feasibility check is the calculating the cost-effectiveness and verifying the technical aspects of the design.
- A company plan. In this document not only the problem statement and solution, but also the target market, competition on the market, marketing and a financial plan will be discussed.
- A wiki page documenting:
- The why and goal of our project.
- The literature studies performed.
- An extensive documentation on the communication with all sorts of stakeholders.
- A detailed description of the idea and its requirements, constraints and preferences.
- A detailed description of the technical aspects.
- The feasibility check and company plan will also be included.
- A (video) presentation on our feasibility study and company plan.
Stakeholders
Users
Visitors of events
The direct users will be the visitors of music events. When you visit an event at which this technology will be used, you will have no choice but to accept the terms. A downside for the introduction of the social distancing dancing device may be that a ticket for an event will get more expensive, as for every customer a gadget must be rented. However, hopefully this idea will allow dancing parties in the first place and then it will be worth it (we will come back to this).
Event organizers
The event organizers are suffering from the current measures. As of August of 2020 the measures installed to prevent the spread of the Covid-19 led to cancellations of practically all events. Since the start of the outbreak in the Netherlands the event sector has suffered from a 85% loss of revenue. [1]
Our tool can make corona-proof dancing events possible again and can even enable safe upscaling outdoors. Downside of this tool for event organizers is the extra costs (obviously we will get back to this) and the extra working hours for the installation of the technique.
Artists
Artists would also indirectly profit from a tool that allows for events to happen again, with all the cancelled events it is logical that the artists performing at these events are also losing revenu. Additionally, only a select portion of artists benefits from the existing sitting concerts. Some genres like House and Dance are much more catered to dancing, a sitting concert for music in these genres makes little sense. Therefore there are also artists benefiting from a solution to this problem.
Society
Community
Not many articles have been written on the effects of the quarantine, social distancing and social isolation, as life is far from back to normal. Once more time has gone by, the real psychological impact will become clear. However, there are some first researches in which provisional psychological effects have become clear. The lockdown-measures prevented the virus from spreading on a large scale, but the consequences for isolated individuals will be a problem in the future. Research of Hiremath et al showed that the measures causes psychological problems like depression, anxiety and panic disorder [2]. There have even been reported suicides due to psychological effects of social isolement and all other inconveniences [3]. General research on social isolation also reveals that social isolation evidently harms mental health [4]. Naturally, we need social interaction, which is exactly what was deprived from us in lockdown. Coming together and making fun at a concert or sports event could significantly contribute to minimizing the psychological problems that are caused by the corona crisis. Of course, events are already possible in an adapted version. However, the majority of the festival sector will remain highly restricted as long as visitors are not allowed to stand and move freely.
Local authorities
The local authorities are responsible for deciding which events can take place in their region and which ones are not allowed to take place. The municipality could also decide to conduct an experiment that will reveal whether the idea works out the way it was aimed. [5]
Government
First of all, if a social distancing gadget for dancing events will be nationally introduced, the government will definitely have a say about it. The government of course has to power to keep such a product from the market. However, suppose the gadget will be approved by the government, then it will be up to the local authorities to decide whether to allow events during the corona crisis, as the government has given the responsibility for the regulation of events to the local authorities. [5] However, if the number of infections (and/or hospital admission and deaths) rises significantly, the government has the power to cancel all events (from a certain number of people, for instance 250 people), like it did in the beginning of the corona crisis. The government thus can always take control. Besides this, the government also has control over the subsidies and the financial support in COVID-19 times for the cultural sector. If this tool would allow for more safe events, it could decide to reduce the financial support.
Enterprise
Manufacturers
Obviously, if this device gets through the testing phases and it is approved by all governmental institutions, it must be manufactured on a larger scale.
Rental companies
After the product has been manufactured, it will by supplied to event organizations by rental companies. In our company plan, we will take the point of the rental companies. We will substantiate this choice further below.
Security
The introduction of this gadget will affect security companies. These last months the number of security employees in places where many people come together has risen significantly. The introduction of this product might change the role of security at events. They no longer have to enforce within the 'bubbles', but mainly show the attendees the walking routes and signing towards the bar and bathrooms.
User Needs
Customers
Although restaurants and cafés are opening their doors and summer-evenings are being spent on the terrace, the festival-summer is entirely cancelled. The social isolation is deeply affecting not only children and young adults, but also the elderly. [6].
Everybody longs for entertainment, like we were used to. Therefore, it would be a relief, not only economically, but also psychologically for the society if the event sector could resume activities.
For the users it was decided that a survey would be a good way to determine what the users’ needs are. The survey contained 10 questions about events and the idea of being monitored by the organization. The target group is attendees of events. The survey was done anonymously and online via SurveyMonkey.
Results
1. How often, in a normal year, do you attend an event?
| Answers | Percentage | Number reactions |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0% | 0 |
| 1 to 2 | 22.22% | 8 |
| 2 to 5 | 41,67% | 15 |
| 6 + | 36.11% | 13 |
| Total | 100% | 36 |
This question’s purpose was to get to know the respondents. Our respondents usually go to an event in a normal year. This is good news because those people are our target group. So, all the data that is gathered in this survey is relevant for our user study.
2. How many events did you attend this year?
| Answers | Percentage | Number reactions |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 33,33% | 12 |
| 1 to 2 | 47.22% | 17 |
| 2 to 5 | 13,89% | 5 |
| 6 + | 5.56% | 2 |
| Total | 100% | 36 |
Here a shift is noticed. Some respondents did not go to any event this year. Still most of the users did go to an event this year. The follow up question was what kind of measurements the event took to maintain the distance and safety of the attendees.
3. If you went to an event this year. What measurements did they take regarding Covid-19?
Here an error was found in the question. Three respondents answered the question with the fact that the events were before the outbreak of covid-19. So those answers were not useful. The most notable answers are that the events are a lot smaller, users had to stick to a fixed table with 4 people. One extreme was that the temperature was measured before entering the event. Almost every answer contained disinfection.
4. If you went to an event this year. Could you keep enough distance to the other attendees? And did you actively pay attention to keeping distance?
For the first question of 21 respondents 17 said yes to this question. So, keeping distance was possible due to their being enough space. The remaining respondents said that there was not enough space. Some noted that in the room there was enough space but when entering the toilet this was impossible to do. To the second question 5 respondents said that they actively paid attention to the distance. The remaining respondents noted that after some alcohol consumption they did care less about the distance. This resulted in not paying attention and violating the rule of keeping 1.5 meters distance.
5. Would you wear a device which measures your distance to others to attend an event?
| Answers | Percentage | Number reactions |
|---|---|---|
| Yes | 72,22% | 26 |
| No | 27.78% | 10 |
| Total | 100% | 36 |
Surprisingly most of the respondents would wear a device that would measure the distance. This gives room to design such device.
6. May this wearable give you warnings, via vibrations, when you come to close?
| Answers | Percentage | Number reactions |
|---|---|---|
| Yes | 72,22% | 26 |
| No | 27.78% | 10 |
| Total | 100% | 36 |
Same results as with question 5. This seems logical due to the fact that the same respondents find it a good idea.
7. Can you think of other feedback systems you would like?
This question was added to get some feedback from the respondents. It is possible that they have a good idea that was not accounted for by the research team. Most of the respondents answered no to this question.
8. After receiving three warnings the security will come and will ask why you are not adhering to the rules, without a good reason you will be removed from the festival. Would you as an attendee agree with these terms?
| Answers | Percentage | Number reactions |
|---|---|---|
| Yes | 56,56% | 20 |
| No | 44.44% | 16 |
| Total | 100% | 36 |
9. When answered no. Why not?
A lot of respondents said that this is too harsh. It is very error sensitive in the sense that if someone else comes close to you are you then to blame for his or her mistake. So, how can this problem be solved that it is fair to every user. The respondents said it is fair when this is accounted for but otherwise most of them would not support such a system. This is something the research time should think about. 3 people did not support it at all, this because of the money lost.
10. Would you prefer such a system over standing in a given spot which you cannot leave? Why?
| Answers | Percentage | Number reactions |
|---|---|---|
| Yes | 70,97% | 22 |
| No | 29.03% | 9 |
| Total | 100% | 31 |
The main reason was the feeling of more freedom at a festival. The remaining respondents liked the fixed spot because of the safety advantages they thought it had. It cannot go wrong when your spot is fixed.
Conclusion
To conclude this user research it can be noted that most of the respondents would like such a device that gives them more freedom. Some respondents are skeptical about if this is a system that can be maintained by an organization, however, they are open to the idea. One problem to take away from this research is how to make it fair when somebody has to be removed from the event. This is of course error sensitive and this has to be looked at by the research team.
Raw data: [1]
Event organizers
In this crisis it becomes clear that many sectors profit from the organization of events. Sport athletes, artists, bands, orchestras, catering and all organizations that are responsible for the setting up of events suddenly were busy cancelling their events and paying back people’s money instead of making money. Many enterprises are in deep crisis or already went bankrupt [7].
To find out what the exact problem is in the event sector (it could be the lower number of customers, the social distancing, the hygiene et cetera) we contacted some event agencies, festival organizers and concert halls. This is a summary of the answers we received to the questions via mail.
Response via mail
In this project we are focussing on big events out in the open air with a larger number of people. If adhering to the social distancing and hygiene rules, what is/are the problem(s) that make(s) the organisation of these events so hard? Is this for instance the social distancing at the entrance/exit or the bar or at the stages. Or is it something else?
An employee of an event agency says that he doesn't believe in 1.5 meter-events. At a festival you ought to be able to freely dance, sing and drink. He refers to a research of Mojo concerts, in which the main conclusion was that events without keeping distance out in the open air are not as dangerous as is being thought. It states that more than 96% of the infections happens inside and that super spreading events also always happened inside [8]. He argues that festivals and concert should be allowed without social distancing, as the chance of getting ill is very little if you're younger than 45 years. Everybody has to take responsibility and when in doubt: stay home.
The organizer of the festival Bontgenoten confirms that organizing events with 1.5 meters distance is almost impossible. He also mentions another problem: standing is not allowed. Furthermore, capacity drops drastically. Another problem is alcohol consumption: during the day the 1.5 meters is mostly respected. However, when it gets dark and the alcohol kicks in, visitors are having a harder time respecting the distance.
Do you have any ideas about how to control the crowd in order to make sure the 1.5 meter distance is being respected? You can think of cameras, an app or other sorts of gadgets.
The organizer of Bontgenoten says that they haven't thought of crowd control. They use security to make the visitors aware of the social distancing rules and motivate visitors to adhere to these. He says that this is a cheaper way than using electronics for crowd control.
Do you consider the following gadget desirable at a festival? All customers get a gadget when they enter the festival. This gadget continuously tracks the distance to other gadgets of other people. If two (or more) gadgets come within a radius of 1.5 meter an alarming signal will go off. Too many warnings for violating the social distancing rules means exclusion from the festival. Another function of this gadget could be that we would program it in such a way that people from the same household do not have to keep 1.5 meter distance. What do you think?
The employee of the event agency worries about friends: they are not from the same household, but probably do not want to keep 1.5 meter distance.
Do you have any other ideas how we could possibly help the eventbranch?
The employee of the event agency mentions a quick coronatest. Everyone has to undergo a coronatest, of which the result is known in two minutes. Everyone that tests negatively is allowed to enter, the rest has to go home.
The organizer of Bontgenoten also thinks of a scan that can detect whether a visitor has (had) the coronavirus and/or has been vaccinated. Another idea is a 'body wash' that every customer has to do before entering the terrain.
Interview
This was all feedback we got via email. We also had an appointment with an employee of the Effenaar, an (indoors) event location in Eindhoven. She gave us insight in problemsome situation they are in at the moment. A summary of the conversation is written below.
What do you consider to be the biggest problem for organizing events in the current covid-19 situation?
In short, the following measures and its consequences are killing for the Effenaar:
First of all, the 1.5 meter distance rule drastically brings down capacity. In their biggest hall they can normally receive 1300 guests. The government now has the policy that indoor locations can receive as many people as possible provided that enough distance is kept. For the Effenaar, this means that they can sell 50 duo-tickets. Obviously, this makes shows far from profitable. They need at least 900 guests to be cost-effective. The cancelling of shows and the lower capacity has lead to dismissal of more than half of the staff.
Secondly, the 1.5 meter has to be respected at all times, also at the entrance, exit, bar and bathrooms. The Effenaar has introduced walking routes and signing. However, guests are having a hard time following these routes. The Effenaar also organized some outdoor events on 1.5 meters with a larger number of people. This raises one more challenge: crowd control. How do you boost the flow of guests?
Furthermore, at all events guests have to sit. It is not allowed to stand, because violation of the social distancing is more likely when standing. Although these sitconcerts might not be the biggest problem for singer-songwriters, a dance-, house- or hardstyle-concert without being able to dance is almost unimaginable.
We also talked about the tracking device (first idea). This is the feedback we received on that:
Just beeping or lightening up is not enough. The lightening can be ignored easily and the beeping might not be heard because of the music. Therefore, vibrating is the better option.
How do we make sure that people do not take off the bracelet? On the other side, making sure that the bracelet can't be taken off might give an anxious feeling. Do guests have a choice?
About the idea of this device, she said the following: guests book a ticket for entertainment, relaxation. Continuously being buzzed because you accidently pass someone in the toilets is far from relaxing. Also when extra features are added such as only alarming the person that is responsible for violating the distance rule (by tracking movements) and raising the threshold of seconds for receiving a warning visitors will still have an uncomfortable feeling continuously being tracked. A better alternative would be to send the warnings to security, who can approach the guests and remind him or her of the rules.
Last but not least, it is useful to design this tool? It is now possible to organize events with the current measures. Such a tool would only be useful if it would enable the Effenaar to scale up capacity or when standing concerts would be allowed. This device will probably not have an added value at this moment.
An alternative she came up with is to make this tracking device not for the audience but for the artists. They also have to maintain 1.5 meter distance at the stage. Moreover, the distance between the singer and the audience must always exceed 3 meters.
In conclusion, the most pressing issue is the downfall of the capacity, which is unfortunately something we can not solve as long als the social distancing rules are in effect. Moreover, the sit concerts are 'okay' right now. This can be regulated satisfactorily. However, thinking ahead and making dancing events possible again would absolutely make a difference for event organizers! Together we came up with the following idea:
In order to enable dancing at a distance stationary dance-islands can be created. This means that every guest gets a circle in which he or she can freely move. Those circles will of course be 1.5 meters apart from each other. In the middle of the circle will be a reference point and the customer will wear a tool that continuously tracks the distance to the reference point. If this distance exceeds the maximum radius of the circle a warning will be given. As light and sound can be easily missed/ignored at a festival, another way needs to be found to make sure that the behaviour of the user is influenced. To this end, headphones will be introduced (just like they are used now in silent disco's). When exceeding the radius of your circle an annoying sound will disturb your music or the music will even be paused compeletely. When going to the bar or toilet, you can take off your headphones and security knows that you are heading to the bar or toilet. The annoying sound/pausing the music discourages leaving your island. It is also possible to make the radii of the islands a bit bigger and allow more people of one household in one circle. This way you can scale up and make it more fun for visitors.
Second survey
Because the idea has shifted to using stationary islands to track the attendees it was decided to do a new user research. Again, via a survey.
Results
When attending events. Do you usually walk around a lot or do you stay more at a fixed location at the stage? Choose the option according to your normal behaviour that resembles you the most.
| Answers | Percentage | Number reactions |
|---|---|---|
| Walk around | 51,6% | 16 |
| Stay at a fixed location | 48,4% | 15 |
| Total | 100% | 31 |
The results are slightly curved to the walking around option. Desirable for us would be that the attendees would like to stay at a fixed location. Although this result was expected, a festival is an experience so getting food, drinks and sitting somewhere with your friends is all part of the experience. However, it is almost fifty-fifty.
Would you like to attend an event where you have to stay in your predefined area in which you can freely move?
| Answers | Percentage | Number reactions |
|---|---|---|
| Yes | 83,9% | 26 |
| No | 16,1% | 5 |
| Total | 100% | 31 |
Surprisingly most respondents answered yes to this question. This shows that the respondents are open for a different kind of event.
Would you like to attend an event where you have to wear headphones that monitors your movement?
| Answers | Percentage | Number reactions |
|---|---|---|
| Yes | 77,4% | 24 |
| No | 22,6% | 7 |
| Total | 100% | 31 |
As can be seen 7 people did not like the idea of being monitored. When asked why not they responded that they do not like the feeling of being monitored. One person did not like the idea that there will be no interaction with others.
When leaving the given spot the music, via your headphones, will stop playing. Would this encourage you to stay in your spot?
| Answers | Percentage | Number reactions |
|---|---|---|
| Yes | 73,3% | 22 |
| No | 26.7% | 8 |
| Total | 100% | 31 |
22 people out of the 31 answered yes to this question. The biggest problem was that some wanted to stop listening to the music. When, for example, getting beer or talking to other people. This needs to be looked at. It is undesirable for the organization that everybody puts off their headphones to just talk with other attendees.
How would you experience an island which you cannot leave? With exception to going to the toilet or the bar
| Answers | Percentage | Number reactions |
|---|---|---|
| The feeling of it being a good solution | 41,9% | 13 |
| The feeling of being mildly restricted | 32,3% | 10 |
| The feeling of being in a cage | 25,8% | 8 |
| Total | 100% | 31 |
As can be seen most respondents think it is a good idea. Although it is a small majority. Some have the feeling of being mildly restricted. And 8 of the 31 respondents have the feeling of being in a cage. This last group is undesirable. Attendees should never have the feeling of being caged. The responses vary. Some say that the attendees have no choice. It is this kind of festival or nothing. Another one responded that he or she gets very anxious if he or she needs to stay at a fixed location. So two groups can be seen here. On the one hand there is the group that just accepts the fact there are no other options. The other group does not like the feeling of being restricted in their movement behaviour. These are things to consider. The organization should be clear on the amount of tracking that is done and make the attendees feel comfortable with the idea.
Are you willing to pay an extra 5 to 10 euros to make such events happen?
| Answers | Percentage | Number reactions |
|---|---|---|
| Yes | 70% | 21 |
| No | 30% | 9 |
| Total | 100% | 30 |
21 of the 30 respondents responded yes to this question. The reasons why some would not pay the extra 5 to 10 euros were that these restrictions do not benefit towards the fun factor. Some claimed that events are already expensive enough and this would mean paying extra for a worse event.
With how many people would you like to attend such events? (including yourself)
| Answers | Percentage | Number reactions |
|---|---|---|
| 2 people | 6,7% | 2 |
| 4 people | 26,7% | 8 |
| 6 people | 66,7% | 20 |
| Total | 100% | 30 |
Most respondents answered that they would like to go with 6 people. This would be the best option for the festival organizers too. This way the festival ground can be arranged most efficiently.
What is your general idea about this solution?
Most respondents said they liked the idea. Some respondents were skeptical about if it really was going to work. Others totally disagreed with the idea. At last some have pitched other ideas to make the event more fun. For example, making the cost of the ticket higher because of the costs of the tracker but in return offer a free beer. Attendees will have more eye for the free beer.
Conclusion
To conclude it is seen that there are two groups. One that agrees with the terms and are eager to party again, so they will accept the rules. Others still do not like this kind of event and they just want to have normal parties again.
Second interview at de Effenaar
Consequences of new measures (28-9-2020): it is no longer allowed to receive more than 30 guests inside. And because they are a horeca-place they have to close the door at 10 pm. They are in consultation with the local authorities to try to get a permission for receiving 100 guests and closing the door at 10 pm.
First of all, we explained our overall goal and our concrete plan. We told Tinka that we want to go to the local authorities with a concrete plan to hear their opinion on it. She came with some very helpful tips on how we should approach the municipality and who we should contact before doing so.
First some general remarks on the concrete plan: work with an app such as Airchip. This is an app for ordering drinks at a distance to avoid queues at the bar. This way you can minimize time outside the islands! Moreover, make sure that the reference point is not be easily removed or replaced! About our target group: our gadget is not suitable for all sorts of music. If attendees want to do a mosh pit, our tool is of course worthless.
Some practical things: it is possible to do a live concert with headphones. Furthermore, attendees are not allowed to sing or yell. Obviously, only thing we can do about this is to ask people to adhere to the rules. This is not a problem that we can solve
Although Tinka liked the idea, she remarked justly that organizing the dancing-festivals outdoors would solve two problems instead of one. Indoors we can only solve the problem of sitting. However, outdoors we can not only solve the problem of not being able to dance, but we can also maximize capacity by arranging a bigger terrain.
Before contacting the local authorities it would be useful to also contact organizers of corona-proof events, such as the StadsOase in Eindhoven, but also other pop podia, such as 013. StadsOase is an outdoors horeca-place, where you can book a table with your household and have drinks while enjoying music. This resembles the atmosphere of a festival, while sitting at a table. How do they justify households that are friends pretending to be a household? What are the deals they made with the local authorities? And contact other festival organizations that are still organizing festivals in times of COVID-19. What do they think of our idea?
If we set next summer as a target for organizing dancing events, there is enough time for finding investors, talking with the stakeholders and getting permission
On our concrete plan for the municipality Eindhoven: we have to substantiate why people need this tool to respect the rules. The local authorities might argue: ‘why is this tool needed when you draw islands on the ground? People can use their common sense right?’ We have to describe precisely what would go wrong if you do not monitor this.
On the financial aspect. We expressed our concern on not being certain that working with our tool will be profitable for festival organizations. We asked Tinka what she thinks of this and whether de Effenaar would be willing to organize an event without profit.
For de Effenaar there is no benefit in organizing an event that is not profitable for them. The only reason they did not completely sweep their calendar is for retaining the subsidies from the municipality. Organizing an event with our tool would require more working hours for staff, which makes the preparations more expensive. However Tinka was enthusiastic and said she was willing to consider organizing a dancing event if they would not make a bigger loss on it than they are doing at the moment, be it for fun.
More on the financial aspect: contact organizations that help young entrepreneurs with finding investors, such as Young Creators and the start-up challenges of the local authorities. They can also give us advice on contacting other stakeholders and how to approach the municipality.
Rental Companies
To research the feasibility of a solution the companies that rent out silent disco systems have also been interviewed, as our product is a modification of a silent disco system these companies offer a good insight as to the feasibility of our product. This information is obtained from phone interviews with two rental companies and email correspondence with another company.
All three rental companies have been significantly hit by the corona crisis, with the business to business market grinding to a halt. This is of course a direct result of the impact of corona on the event sector itself. There have been some creative solutions to keep business going throughout the coronacrisis, using the headphones for drive-in cinemas for example. The business to customer market has also seen an increase during the corona crisis, people rent the headphones for a garden party together with neighbors for example. The loss of the business to business market however is greater then the gains, getting the business to business market going again would be very important for this stakeholder.
Our proposed solution would come with an increased cost, an additional cost almost doubling the price of the base headphones. Even with this cost however our modification is still generally seen as worth it, this depends however on if our product will be necessary to hold dancing events during the corona crisis. If these modified headphones are completely necessary and widely accepted by both users and stakeholders the demand for the headphones would be significant enough to make the additional cost worth it. Some of this additional cost must however be carried over into an increased rental costs for the event organizers. For reference: the current rental cost is around €3.50 to €5.00 depending on the size of an order.
It would also help greatly if our modification the headphones could be undone after the coronacrisis is over. If headphones could be restored to their original functionality the risk would be far smaller for the rental companies. This could also relieve the financial strain due to the sensors used in our solution still keeping a percentage of their value.
Therefore, if governments would be more willing to let events happen if our headphones are used and if a significant demand would be created for the headphones due to this, then headphone companies definately view our product as feasible.
RPC's
Requirements
- Notifying the user that he or she left their island.
This can be done via turning off the music on the headphones. The event being a silent disco event the user will probably notice when the headphones are off. There is some room for errors here. For example, putting the headphones off.
- It should not be possible to ignore the signal.
Making the event a silent disco event ensures this. When users put their headphones off they cannot listen to the music anymore. Again, the same problem arises as with requirement 1. The user may want to stop listening to music for a minute or so.
- Center of the island should be stationary.
Otherwise people would move around too much. When creating dynamic islands, there will be many violations, be it coincidentally.
- Center of the island should not be easily removable.
Otherwise people might want to grab it with them and move to another location. Again, this will result in more violations and potentially messing up the system.
- Attendees should not be able to switch islands.
When this would be possible everybody can just switch with each other when they want to talk to someone else. The group with whom you attend stays the same for the entire event.
- It should not be possible to tamper with the tracker by the attendees.
This to prevent false data or potentially turning of the tracker.
- The tracking system should adhere to the privacy rules.
Tracking attendees can come with complications regarding maintaining the privacy of the attendees. It should be clear to the attendees what the festival is doing with their data and the attendees should agree with these terms.
- The tracker should be able to measure distance to island-members of the same household.
The anchor in the center of the island should only be able to detect the members of the household of that island.
- It should help the event organizers in making events more affordable.
In the long run the festival organizers should benefit from the investment. This can be accomplished via various ways. For example, via money but it could also be via positive publication.
- The tracker should be able to stop the music of the attendees who are violating the rules.
The tracker should be able to stop the music. By stopping the music at the source or switching of the headphone.
- The organizers of the event should be able to see who is violating the rules.
When an attendee violates the rules too often he or she needs to be removed from the event.
- The visitors should not feel uncomfortable being tracked when not violating the distance rule.
The visitors should not have the feeling of being followed. They should have a feeling of being free to move, although this is restricted.
- It should be legal to stand at an event.
The local authorities should approve the idea of making standing possible at events again.
Preferences
- A device to order drinks that then can be brought to the island.
This to reduce the amount of wandering by the attendees.
- Having an error rate of zero.
This is hard to realize in 8 weeks.
- Making a physical product.
It is more fun and better to make a physical model. However, due to time being restricted and meeting physically is hard due to covid-19 this seems not doable.
- Making it possible that friends can go together without being in one household.
This is not up to us to decide. The government needs to make this possible. It is tolerated at the moment.
- A device that people could use to let the staff know that they went to the toilet.
This is not so hard to make. However, the attendees should not be able to abuse this button. This is hard to realize.
- Finding inventors to make the plan feasible.
To realize the production investors need to be found.
Constraints
- Only 8 weeks to design a solution.
This project only lasts 8 weeks. There is so much you can do in 8 weeks, this means that the solution would almost certainly not be perfect.
- Privacy laws regarding monitoring attendees.
It is not possible to just track visitors according to the GDPR. It should be clear to the attendees what is done with the data the organizers gather.
- Costs to produce such product and setting up a business.
Being a student team it is not possible to order the best tracking systems resulting in a suboptimal design.
- Covid-19 law
For events it is forbidden to let attendees stand. They have to sit at a table. This needs to be changed to realize our business.
Detailed description of idea
Festival organizations that use this tool do not sell individual tickets, but group-tickets. If you are from the same household you can book a dance-island. This island is a stationary circle with a table in the middle, the periphery of this island is indicated on the ground. The islands are positioned in the venue such that whilst inside of this island the members of this household are guaranteed to not come within 1.5 meter of people inside other islands. Every attendee listens to the music through a pair of headphones just like in the preexisting silent disco systems. Our idea concerns an addon to these headphones, the headphones are coupled to the reference point in the middle of the table on their island. The distance between the headphones and the reference point is continuously measured. If this distance exceeds the radius of the circle, the wearer of the headphone is positioned outside of the island and therefore the music will be muted. This encourages visitors to stay inside of their island. Of course, you are permitted to leave your island to go to the bar or toilet, provided that you adhere to the walking routes. Security will enforce this. Attendees going to the toilet or bar pass the perimeter and the music through their headphones will be muted. When going to the toilet they can either leave their headphones at their island or hang them around their neck. This way security can recognize attendees heading for a drink of for the bathrooms. In conclusion, this tool will focus on what happens on the islands and not on what happens outside. This is because festivals organizations have already taken steps to manage the crowd outside of the circles, with for example security and premarked walking routes.
What has to be added here?
- Radius
- How many islands?
- Sketch
Number of people per island
We talked with multiple parties about the number of people per island. A music venue we talked to said they only sell 2-person tickets, but they have a few exceptions e.g. a cancelled concert that is scheduled later again. Because of limits to practical implementation the music venue is aiming at offering only 2-person tickets in the future. But it would be nice if they could sell grouptickets for e.g. 4 or 6 people. The music venue told us they cannot check whether groups saying they are a household are actually a household.
After talking with the music venue, we went to a bar and asked them about handling ‘fake households’. They told us they make sure there is always place to keep enough distance and security enforces that people do not sit on each other’s lap and that they keep seated.
In the food and beverage outlets in the Netherlands it is the case that only people from the same household are allowed to be within less than 1.5 meter or of each other [9]. Group of 2 people are also an exception to the distance rule, but for the rest everyone needs to respect the distance rule of 1.5 meter. Of course, food and beverage could abuse this rule and a group of friends that do not form a household could lie and then the food and beverage outlets cannot be held accountable for acceptance of the group. Therefore we could argue to organize the festival terrain for the venues or organizations using our product to maximize the number of people, i.e. making quite a lot of 6 person islands.
We have contacted multiple parties and one of them told us that most people (by far) that go to a music festival go there with their friends. Not with their household. We do not expect this to be different during the coronatimes.
As the director of Koninklijke Horeca Nederland Dirk Beljaarts said (paraphrased): “do not go look for loopholes in the rules, because that could come back as a boomerang and then the food and beverage outlets get into trouble”. [10]
We agree with Beljaarts and feel the urge to act in a safe and moral way. With this experiment we want to show what is possible with keeping safety in mind. We want to represent the event branch and do not want to hurt the branch’s reputation by acting in an unsafe and immoral way.
Allowing 6 people households while we know that most people go to festivals with friends and not with their household is therefore not an option. Therefore we cannot organize the terrain such as the respondents of the second survey have said they wanted. About 6% responded they want to visit in couples, 27% with 4 persons and the vast majority with 67% answered 6 persons. We would love to do this, but given the current rules it is irresponsible and unrealistic. Since we want to cooperate with the government, we do not want to consciously violate their rule, although it could be legally allowed.
Then there is also the issue of enforcement. Suppose we would allow for 6-person groups. Then it is also harder for security to know who belongs to which group. It is for example allowed for 2 people who are not from the same household to have less than 1.5 meter distance [11]. This way it is easy for security to enforce the distance rule: if there are more than 2 people not respecting the 1.5 meter distance, then security can intervene. However, if groups of 6 people are allowed then how should security enforce this? We belongs to which (self-declared) household? People could mingle up in different groups of 6 people and then we would only make the job of security harder, while we want the opposite: help security with our product.
Therefore we have chosen to make only 2-person dance islands. Suppose families would be interested in our events or other currently unforeseen developments will happen, then we could always scale up the number of islands in cooperation with the authorities.
Design
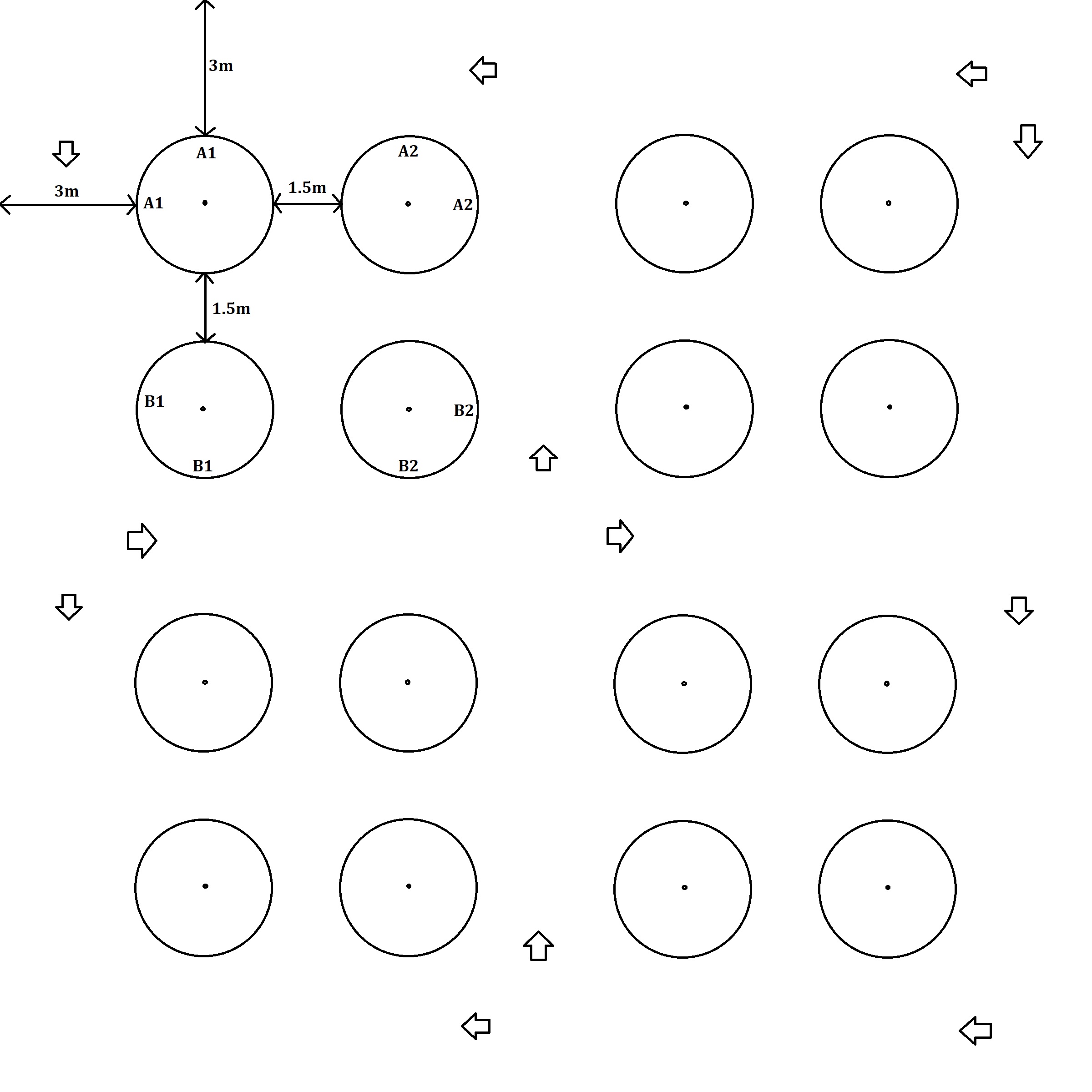
Figure1. Abstract design of the dancing island.
/*It will be added once I know the parameters more. */
In order to design the size of dancing island circles, the approximate movement range when a human dance is needed. Instead of looking for a paper, what size a company who has a dancing related product recommends as a dancing movement. Home. (2019, September 16).[12] The company says a person needs at least 0.836 square meters.
Then the calculation to get a size of different dancing islands circles is as follows:
For 1 person: 0.83612 square meters = x^2. So for one person, x = 0.91 meters should be a diameter.
For 2 person: 1,67225 square meters = x^2. So the circle diameter should be, x = 1.4 meters.
For 4 person: 3,34451 square meters = x^2. So the circle diameter should be, x = 1.8 meters. We will increase this to 1.9 meters.
For 6 person: 5,01676 square meters = x^2. So the circle diameter should be, x = 2.3 meters. We will increase this to 2.5 meters.
/* I calculated without putting a table in the centre, if we put a table within each circle, then the radius should be increased as much as the table's radius. */
/* Question: How many will there be of each dancing islands for 6 people, 4 people and 2 people? Because I think people would come with a lot of people, so the number of islands that allowing 4 and 6 will be more? */
/* Terrain size could be 10000m^2. However, we can scale it up from 100 meters by 100 meters. */
Detailed description of the technical aspects
Distance measurement
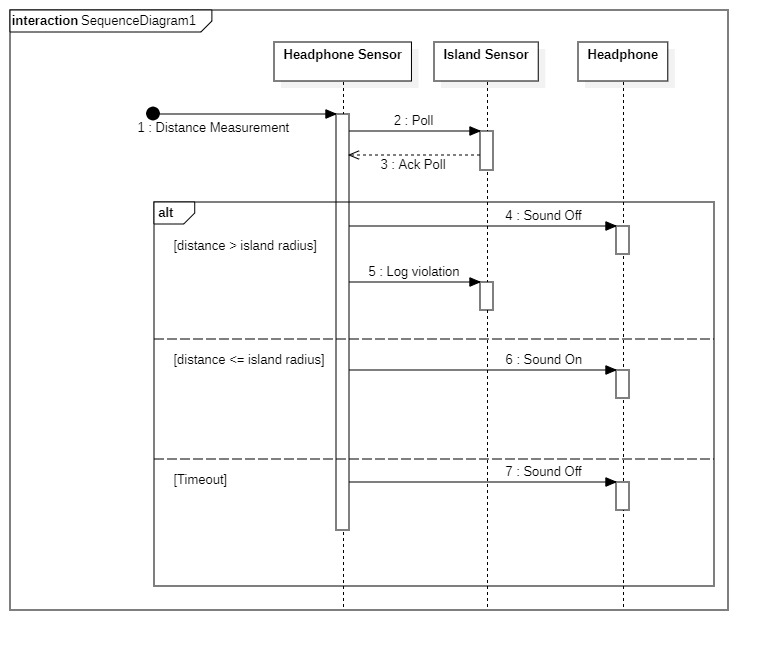
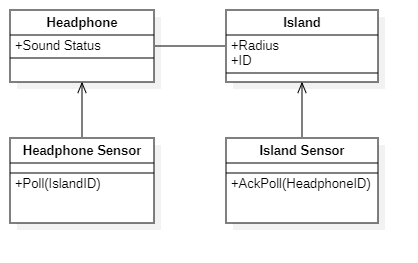
We need to be able to measure the distance between each headphone and the center of the island that headphone belongs to. To accomplish this we’ll make use of ultrawideband transceivers, one on every headphone and island center. Multiple ways of measuring the distance exist, the two that would make sense for our use case are by measuring the time of arrival or the round trip time of a transmission between a headphone and the island center.[13] From this time we can calculate the distance between the two, since the propagation time of a transmission through air is a constant. To measure the time of arrival, one transceiver would transmit to all headphones the time of transmission, each headphones would compare this to the time of arrival. Such calculation would require a synchronized clock between the two which is not likely to be available in our case. Thus we calculate the round trip time: the headphones poll the island sensor to which the island's center responds. By comparing the time from the transmission of the poll request and the island's center response, the RTT and thus the distance to the island's center can be calculated. If no response is received from the island within a certain threshold we can assume that the headphone is too far away and thus still outside of the boundaries of the island. RTT measuring introduces more room for error however due to the time taken to handle a message weighing twice as much when compared to TOA measuring.
There are multiple headphones to each island and multiple islands to each event. It is therefore necessary that a headphone sensor’s poll request is responded to by the right island’s sensor and that an island sensor’s poll acknowledgement is also handled by the correct headphone sensor. Therefore each island and headphone should be identifiable by an unique identifying number. Polling requests will be accompanied by the sending headphone’s ID and the accompanying island’s ID, the same holds for polling acknowledgements. A device will only handle a received transmission if their ID matches up to the ID in a transmission, be it a headphone listening for an acknowledgement or an island's center listening for a polling request. Therefore it is ensured that communication between sensors is only between the intended sensors, it can't happen that the wrong island responds to a polling request or that a polling acknowledgement is handled by the wrong headphone.
Headphone Behavior
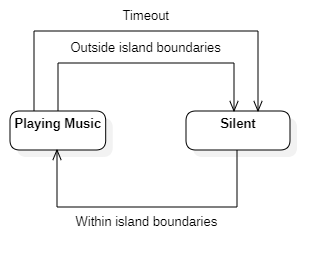
The headphone has only two real states, silent or playing music. How this state is decided is incredibly simple and is depicted in the following State Diagram.
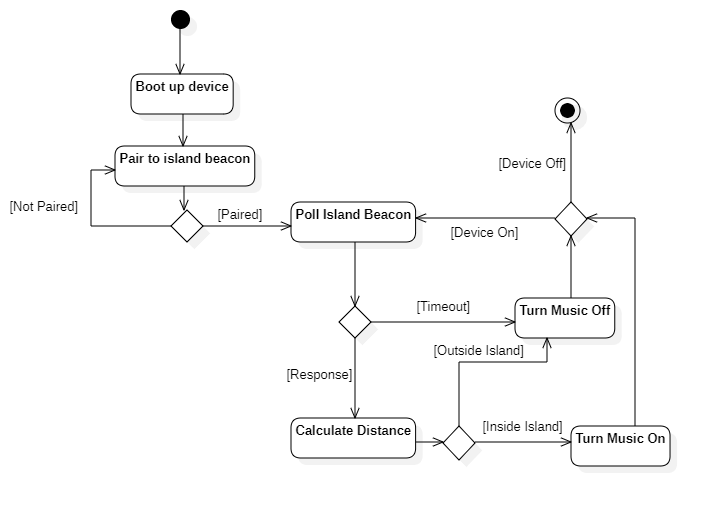
The sequence of activities for a headphone between turning on and turning off is depicted in the following activity diagram. Firstly the device will boot up, the program will be loaded and sensors started up, after this the headphone must be paired to an island beacon. After the headphone is paired it will continuously measure the distance to the island beacon, depending on the result of this measurement the music will be either turned on or off. The headphone will endlessly loop until it is turned off.
Further considerations
The development of this product requires some more depthly thinking about the pros and cons of this technology and about possible problems that might come up when implementing it.
The advantages for the users have been described above. The social distancing gadget will make standing events possible again in times in which corona is amongst us, which means that customers can have entertainment, while event organizers and artists profit from this.
Not only the advantages, but also the ethical disadvantages must be paid attention to. Obviously, this tool only gives the desired result if every visitor on the terrain carries a device. As a consequence, each visitor must accept to wear a gadget and remain within his/her circle as much as possible. This means that someone who does not want to be monitored all the time, cannot be admitted to the festival terrain. So customers have no choice but to compromise to wearing this gadget, otherwise they will be excluded form the event. It can be argued that this not entirely ethically neat. However, we think that this is the only way to make (dancing) events fully corona-proof (with of course extra measures for hygiene). For the second questionnaire: are attendees willing to wear such a headphone that constantly monitors your movements?
Secondly, the dance-islands might feel like 'cages'. Second questionnaire: ask how users would experience this?
Besides the ethical considerations, some practical things must also be paid attention to. Obviously, festival organizations have to buy these technologies or rent them. What are the consequences for the users? Second questionnaire: are they willing to pay an extra 5/10 euros?
Additionally, how do we make sure that attendees do not switch headphones and this way switch islands? The goal of the dance-islands and the distance in between these islands is that households do not mix up. All headphones are coupled to a specific reference point. This way it can be verified at the exit whether you have the right headphones. By asking a deposit (of 10 euros) at the entrance and checking whether you hand in the right headphones, switching headphones will hopefully be reduced. Furthermore, security will of course keep an eye on the headphones and will intervene if they see attendees exchanges headphones.
Lastly, to make sure that customers do not remove the tracker we attach them to their headphones. When going to a festival you want to hear the music so the tracker will be part of the deal. We expect that attendees will not mess with their headphones as they risk losing their music. We also hope that the tracker being on the headphones will give a less anxious feeling of 'Big Brother is watching you' than the tracker being around your wrist, as you can take of your headphones when going to the bar or toilet. The deposit that is charged on the headphones will also restrain tampering with the tracker. Moreover, the reference point in the middle of the island should also not be easily tampered with. To this end, it will be hidden and tightened to the table in the centre of the island. Additionally, the switch-off button will be not be easily accessible. Festival organisators can also chose to ask a deposit for this too.
What has to be added here?
- Cost-effective
- Extra costs for users
Legal aspect
Face mask duty
From the 5th of August till the 31st of August 2020 there was a face mask duty in certain busy spots in Amsterdam and Rotterdam. [14] [15]. This rule was implemented by the mayors of the two cities. According to professor of law and society Jan Brouwer of the state university of Groningen and professor of constitutional law Wim Voermans of the university of Leiden the face mask duty is legally not possible. [16]. According to Voermans the duty is in violation of article 10 of the Dutch Constitution, the right to privacy. As Wim Voermans says “all colleagues agree: this is not possible”. However, in public transport in the Netherlands there is a face mask duty. As Brouwer says: “The Passenger Transport Act of 2000 contains a separate part on the basis of which the carrier can impose requirements on the wearing of a face mask. It is the private carrier who take the initiative.” [17] According to mr-online.nl an employer could impose the face mask duty to his/her employees based on the right to instruction. Provided that this is reasonable and the employee has no (constitutional) objections to this. It could be seen as an extra dress code. [18] It is unclear if it would be possible for an event organization to impose a face mask duty onto its visitors. However, regarding the coronabeeper duty, it is also possible to work with wristbands duty as a way of entering the festival and for e.g. getting alcohol, so it might be possible to enforce a coronabeeper duty.
Enforcement of coronabeeper duty
The problem with enforcement by security workers of the festival is that they are limited in available resources. BOA’s are already having a difficult time in the Netherlands regarding enforcement because of rebellious citizens, so security workers can get a difficult time as well. Especially when people are drinking alcohol, they could be less cooperative regarding the social distancing. Then there is also the support base which can decrease and can be unstable. When the incident with minister Grapperhaus happened for example, a lot of people where angry and this incident made enforcement more difficult for policemen and BOA’s. The same could apply for security workers. Just like with restaurants and bars, it is possible for the government to keep the restaurants and bars responsible for making sure all guests follow the distance rules. Out of fear that bars and restaurants would get fines, some bars and restaurants decided to not open up again. [19] If these restaurants and bars have difficulty with enforcement, imagine having a festival with way more people. That would be more difficult and it is imaginable that festival organizations would be even more afraid of getting fines. And suppose such controls would take place and the government inspectors say the rules cannot be enforced then it is not only the case that the organization gets a fine. It might also be the case that the festival has to end. Of course this would be a huge disappointment for the visitors and a lot of costs for the organization e.g. not being able to make money from visitors buying drinks, but being tied to contracts with caterers, security etc. Also prior to all of this, visitors might not go to a festival as easily when they know they might be send away because of people not adhering to the rules and government inspection with a closure as a result. Furthermore, the government has to give permission for the festival to take place and given that reinforcement is so difficult, the government will probably not give permission.
Costs of the distance islands
The music festival industry is very diverse. The festivals can be distinguished in the groups public, nonprofit and private festivals [20]. There are private festivals, like Coachella that made a gross profit of $114.6 million in 2017 [21], but this was the first festival to earn more than $100 million. There are also a lot of festivals that are nonprofit. In general profits are not very high in the festival industry and it is a risky business, since ticket sales can differ dependent on weather circumstances for example [22]. In the Netherlands there were about 18.2 million festival visitors in 2018 [23] and about 1.4 million music festival visitors in 2015, of which about 450.000 pay an entrance fee and 950.000 visit a free festival [24]. The free festivals rely a lot on sponsoring and subsidies. There are also quite a few non-profit festivals in the Netherlands, that make use of these subsidies, one of them is Woo Hah!, a hiphop festival in Tilburg. In 2015 it sold 5500 tickets and made a revenue of €611.000 and had costs of €610.700 [25]. In the case that this festival would be organized with much lower visitor numbers, the festival would need a huge increase in sponsoring and subsidies, which is unlikely to happen.
TODO possibly higher prices per ticket, since more ‘exclusive’ (because capacity) and people could not go to a festival for a very long time?
Silent disco rental companies
There are quite a lot of silent disco rental companies. These companies rent out their headphones for prices around €3.50 - €5 per headphone. Suppose festival organizations would pass on these prices in their tickets there would be no additional cost for the festival organization. However, our product also has a price tag. The Dutchbands’ Watpod alone costs €75 and that is without the added value of our product. But even if this price can be passed on to the customer as well, the question of dealing with lower visitor numbers remains. There will be less visitors, but a big terrain size remains, while there is less income for food, merchandise, camping etc. Under normal circumstances, without corona, there are already a lot of uncertainites for festival organizers. Only the weather can have a big influence on the number of tickets sold. With corona, uncertainty has only increased. Normally prices can be based on willingness to pay by the customers, but right now it is very hard to get to know this willingness, since it is unknown how festivals can look like with the 1.5m so it is hard to estimate willingness and therefore it is hard to come up with good prices to finance the whole festival. Besides willingness to pay, there is the issue with permits. Suppose a festival could get a permit to organize a festival in a few months’ time, but then the number of infections increases in this time and with that the measures. Could the permit be withdrawn or actually could the permit be given out in the first place?
TODO find out criteria for permits and period between receiving permit and organizing event
All this uncertainty makes it very unattractive to organize festivals in these times. Our product will probably not add any value in that cas
Cost of production
Prototype Cost
For the prototype of our product the following parts with the corresponding prices are required. Here the cost required to produce one headphone and one island beacon is mentioned, note that in the actual product only 1 island beacon will be necessary for every 4 to 6 headphones.
One headphone prototype:
| Part | Price |
|---|---|
| RF-309 Headphones | 17.03 |
| Arduino Nano | 2.83 |
| DWM1000 | 17.54 |
| Relais, Resistors, Wiring | 2.00 |
One island beacon prototype:
| Part | Price |
|---|---|
| Arduino Nano | 2.83 |
| DWM1000 | 17.54 |
Mass Production cost
The cost of the product when mass produced is also determined, for such a product the Arduino can be replaced by the cheaper ATMega328 microprocessor and the wiring will be replaced by a printed PCB plate. Invoices for these parts have been made for different quantities.
One headphone prototype:
| Part | Price (100x) | Price (1000x) | Price (10000x) |
|---|---|---|---|
| RF-309 Headphones | - | - | - |
| ATMega328 | - | - | - |
| DWM1000 | - | - | - |
| PCB print | - | - | - |
One island beacon prototype:
| Part | Price (100x) | Price (1000x) | Price (10000x) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ATMega328 | - | - | - |
| DWM1000 | - | - | - |
State-of-the-art
Due to the outbreak of global pandemic COVID 19, there have been many efforts to keep up to date with technologies to enhance devices or systems e.g. Analysis of big data, Artificial intelligence, Blockchain. Stuff that has been already made are such as a real-time tracking map, modelling studies of the viral activity in each country using a database, active communication between people and public institutes using social media platforms, the thermal imaging–enabled facial recognition system[26] and algorithms running on positive cases of COVID 19. [27] Our group's projects also want to follow the technological trend according to the pandemic. This project is aimed at developing a wristband/watch that can alert and remind the reasonable social distance (1.5m) between people at a festival or an event venue.
Technologies for social distancing
A social distancing has been introduced to reduce the spread of the pandemic at the early stage. [28] However, there have been difficulties to implement a social distancing in large-scale measures. To mitigate these difficulties, a lot of effective technologies are used to facilitate social distancing in practice. e.g. AI, thermal, computer vision, Inertial sensors, ultrasound and visible light. The referenced paper above also contains information about wireless technologies and open issues. Other than this, there is an enhanced technology regarding deep learning framework for monitoring social distancings.[29] This framework uses YOLO v3 detection model and Deepsort to separate people from the background at a surveillance camera and tracking people with IDs and boxes. However, it is hard to implement on a small device we are planning to make. Thus, this idea is not going to be used in our project.
Ultra-wideband for location detection
This paper[30] conducts research about a comparison with Bluetooth low energy (BLE) and Ultrawide-band (UWB) technology. There are two main reasons for using Ultrawide-band(UWB) instead of Bluetooth(BLE) on this paper. The first reason is that the UWB time of flight is better than the BLE receive signal strength indication. The paper shows the second reason by stating an industrial trend in using location technology at the company, Apple. Nevertheless, the company has been promoting for BLE for years, it has replaced IBeacon BLE technology by UWB. This is because UWB has brought the possibility to use more applications and higher quality. Also, the location accuracy and data rates are higher than BLE since UWB operates in a wide frequency range (approximately 500 MHz) while BLE does in around 2 MHz.
The paper[31] introduces a concept of indoor positioning technique and provides an analysis of SWOT which is strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. Also, it states various positioning technologies e.g. Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) - which can be replaced or improved by UWB[32] -, Infrared (IR), Ultrasonic, Zigbee, Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN), Cellular Based, Bluetooth, Dead Reckoning, Image-Based Technologies and Pseudolites and it explains why UWB has gained attention as a positioning skill. At the intro part, it compares Indoor positioning systems (IPSs) and Global Positioning System (GPS). IPSs keeps updating data continuously in real-time but signals attenuate and scatter to go through solid obstacles using GPS. With our project, it is stated that the product is aimed at an outdoor event or festival. However, assuming that data can be updated more quickly and that people's movements are not as extensive as military operations or satellite orbits in space, IPSs would be more suitable to apply than GPS. Furthermore, in terms of the cost, UWB is also cheaper than other technologies and consumes less power.
UWB has an accuracy of 5 to 10 cm compared to roughly 5m accuracy for Wi-Fi and Bluetooth. The data rate of UWB has been adjusted to 6 to 8 MB/s in contrast to the past in which it was 100 MB/s, for better use for mobile devices. Also UWB consumes less power than Wi-Fi. However a disadvantage of UWB is that Wi-Fi and Bluetooth are better at interacting with mobile devices. [33]
Dual patch microstrip antenna
Dual patch microstrip antenna [34] does not require a physical connection between the antenna compartment and the feed line. Also, a combination of slot coupling technique and the two-layer electromagnetically coupled patch (EMCP)antenna offers advantages that the device can be used in wideband and experiences a low cross-polarisation. The impedance bandwidth of the microstrip could be improved when a modest horizontal displacement between the two patches are given.
Ultrasonic sensor
Al-Mahturi, Ayad & Rahim, Ruzairi. (2016). ULTRASONIC SENSOR FOR DISTANCE MEASUREMENT
One technique that can be used to measure the distance between different objects is with ultrasonic sensor. This technique is based on measuring the pulse reflection time. So, how long it takes to get the echo from the original sound. Ultrasonic sound is not hearable by humans. Usually a normal ultrasonic sensor can measure a maximum distance of 2.5 meters. A downfall of this technique is that the refresh rate of the sensor is low.
GPS
Shen, J. S., Bao, Y., Gan, W., Guo, W., Zhang, M., & Wang, G. (2018). Millimeter-accuracy structural deformation monitoring using stand-alone gps: case study in beijing, china. Journal of Surveying Engineering, 144(1). https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)SU.1943-5428.0000242
N. Idris, A. M. Suldi, J. R. A. Hamid and D. Sathyamoorthy, "Effect of radio frequency interference (RFI) on the Global Positioning System (GPS) signals," 2013 IEEE 9th International Colloquium on Signal Processing and its Applications, Kuala Lumpur, 2013, pp. 199-204, doi: 10.1109/CSPA.2013.6530041.
GPS is another technique to determine the distance between multiple users. The precision of the GPS technique is around the 5-7 mm in this study. Dual frequency GPS is preferable. A dual-frequency GPS does not use one signal but uses two signals to improve the accuracy and reduce disturbance from Radio frequency interference (RFI). An example of such interference could be that from Bluetooth other sources could be that from wireless networks. So, this can be hard to realize when one would like to organize a festival with many attendees. Another problem can a multipath error. This means that the signal bounces of buildings or obstructions leading to making the GPS confused. However, in an open field at a festival this would not be the case.
Bluetooth
Cho, Hosik & Ji, Jianxun & Chen, Zili & Park, Hyuncheol & Lee, Wonsuk. (2015). Measuring a Distance between Things with Improved Accuracy. Procedia Computer Science. 52. 10.1016/j.procs.2015.05.119.
Another technique that can be used to measure distance is with a Bluetooth low-energy sensor. Via the signal strength distance can be estimated. The downfall is that the outcomes of such measurement comes with an high error rate, almost 50%. This can be reduced by self-correcting beacons these are placed at an fixed position. This point will act as an reference point for the others to measure from. This reduces the error rate to 10% within a distance of 1.5 meters. Without this extra beacon estimation can be made on how close someone is but no real precise numbers can be given.
Bluetooth (BLE) is about proximity sensing, not measuring distance per se. Measuring distance can be done using signal strength, however that might not be a good indicator. For example there could be an object in the way. To overcome this, a technique called “fingerprinting” could be used. Fingerprinting makes several measurements to several fixed beacons and then chooses the distance to be the closest distance to a beacon. [35]
Combining technologies
Instead of using a single medium to estimate the locations of the targets, positioning technologies can be combined to get the best of both worlds. For example, the SVG system combines WLAN and UWB. WLAN has the advantage of covering large area, while UWB can give highly accurate position estimated in some small required areas. [36]
Plan
Approach
In order to produce a solution to our problem we will use the following approach. First of all we’ll do the necessary research required to come up with a design for our product. This will be research into the current state of our problem, the technological aspects of the problem and also the societal implications of a solution. We will formalize the requirements, preferences and constraints of our product and possibly interview stakeholders related to our problem, we will then create a preliminary design from which we will develop a detailed design. From the design we will develop a functional prototype that can be used to help maintain a distance of 1.5m between people, this functional prototype will be tested with a predetermined test plan. All throughout the course we aim to actively maintain the wiki page to document the design process, a presentation will also be made.
In the planning below it can be seen how we aim to divide the process over the weeks.
Planning
| Week | Tasks | Milestones |
|---|---|---|
| Week 1 | Form groups, choose a subject, document problems statement, start planning and research. | |
| Week 2 | Continue research, formalize RPC's of product and possibly get in contact with stakeholders. | |
| Week 3 | Create preliminary design, decide the necessary hardware and obtain it | Complete preliminary design |
| Week 4 | Detailed design, create test plan, breadboard prototype | Complete design |
| Week 5 | Work on prototype and document full design on wiki | |
| Week 6 | Work on wiki and finish the prototype and perform test plan. | Working prototype |
| Week 7 | Document results on wiki page, produce presentation video | |
| Week 8 | Last touches on wiki and video | Complete wiki, complete presentation |
Literature study
Position Measurement using Bluetooth, by Sheng Zhou and John K. Pollard
Using bluetooth there is an position error of about 1.2m indoors. Outdoors this is generally less, however in the case of strong multipath interference there can still be errors.
Distance Sensing with Ultrasonic Sensor and Arduino, by N. Anju Latha , B. Rama Murthy, K. Bharat Kumar
An Arduino microcontroller in combination with an ultrasonic sensor can be used to measure distance. Ultrasonic sensor are popular, since they are cheap and have a precision of less than 1 cm in distance measurements of up to 6m. The most common method for measurement is the time of flight measurement, which measures the time between departure and arrival of a signal. A disadvantage of this way of measurement is that the target to be measured should be perpendicular to the plane in which the signal travels. It also the case that the bigger the target, the more accurate the distance will be measured.
The Impact of Covid 19 on Event Management Industry in India, By Mr. Anup M Gajjar & Dr. Bhaveshkumar J Parmar
The event management sector is the fastest growing industry in India. This industry has a lot of damage because of Covid-19, but it is not easily quantifiable how much, since the industry does not come under one ministry or one department, in contrast to e.g. Germany. A lower growth of India’s economy will mean a lower growth of the event industry and a lot of jobs are at stake. The event management sector are now advised to organise events such that information is up-to-date, spaces are well designed to prevent crowd stupidities, communication is clear and event managers are urged to plan for finance and make hand-washing more accessible. It is not possible the identify the loss accurately, but it is certain that because of travel fear and public gathering fear it will take time to recover.
Were Stay-at-Home Orders During Covid-19 Harmful for Business? The Market’s View, by Chen Chen , Sudipto Dasgupta, Thanh D. Huynh, Ying Xia
Stay-at-Home orders were actually good for business. In states without Stay-at-Home orders businesses were worse off. In the U.S., where the research was conducted, it is found that the effect is seen more vividly in counties with a high number of infections and for firms in essential industries. Although the short-term effects of a lockdown seem bad for business, the long-term effects are positive. A reason for this might be that the measures are seen as necessary for stopping the spread of the virus and making labour participation possible.
COVID-19 impact on city and region: what’s next after lockdown? bY Myounggu Kang , Yeol Choi , Jeongseob Kim , Kwan Ok Lee , Sugie Lee , In Kwon Park , Jiyoung Park & Ilwon Seo
Density does not play a big role in the spread of the virus. On the contrary, cities have benefits, such as response times or hospitals being nearby that could be taken advantage of. Essential services should also be close by and there should be enough cheap housing. Furthermore, economics structures like global trade should be restored to keep jobs. Also privacy concerns should not be underestimated and transparency and voluntary consent should be premised. Last but not least we should make sure prejudice and hatred do not develop, which means a great deal of social effort should be made.
Other useful links:
Arduino with an ultrasonic sensor and a buzzer. If an object gets too close to the sensor, the buzzer goes off.
https://www.instructables.com/id/ARDUINO-DISTANCE-BUZZER/
Using Bluetooth:
https://create.arduino.cc/projecthub/tanishq/diy-bluetooth-proximity-sensor-c82265
LIDAR:
https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/lidar-lite-v3-hookup-guide/all
15-25 cm accuracy(?)
https://www.getmapping.com/support/height-lidar-data/how-accurate-height-data-and-lidar
Experiment plan
Make dancing possible again. That is our goal, but how do we achieve that? Currently it is mandatory for food and beverage occasions to assign the guest to a fixed seat at a table or at the bar [37]. This also includes music venues and festivals. By conducting an experiment we want to show the Dutch government that using our product it is possible to safely dance at music venues and festivals again and convince the government to change the seating rule.
Necessity for this experiment
In the weekend of 7 till 9 August 2020 Finally Fiesta took place in Alkmaar. There were shifts per day with 250 people per shift. That meant a total of 1500 tickets were sold. [38]. “Eating and drinking was only allowed when you sat down, while dancing was allowed when standing at the table”, organizer Jos Mechielsen said.

“We have three meter pathways with one-way traffic”, Mechielsen said. The tables are at least 1.5m apart and in between the tables people can walk to go to the toilet or the bar. However, people at a music festival like to have fun and do not want to constantly check whether they are close to their table. They can easily forget when they are having a good time. With our product, the guests do not have to constantly think about the distance. Our product does that job for them! With the experiment we want to show that people will respect the distance rule when using our product.
A reason why people want our product, is that people like dancing. You get happy when you’re dancing and especially when dancing together with friends or family. In these hard corona times, people like to be distracted from the pandemic and would love to go to a festival, maybe even more than before the pandemic. Therefore our product is an important contribution to society. Also youngsters can be bored during these corona times. We have seen that youngsters are more aggressive to BOA’s and police and we want to give these people a way of having fun again.
Concrete plan for the experiment
TODO what was the reason De Effenaar only sell couple tickets? Was this regarding legal aspect? “Voor 250 mensen per shift hebben we 125 statafels nodig en 250 barkrukken, ieder groepje krijgt een cirkel waarbinnen je mag staan.”, https://3voor12.vpro.nl/artikelen/overzicht/2020/augustus/Alkmaar-coronaproof-dansen-festival-finally-fiesta.html
There is a small dancing event (max. 250 people) at a music venue or an outdoor location.
A guest arrives and his ticket is being scanned. He enters the building or the area and gets the headphones, after which he goes looking for his island. Before receiving the ticket, he pays a deposit for the headphone with our technology. The islands are separated with 1.5 meter in between. There are also pathways where guests can walk. These paths have signs on them, so guests do not cross.
There is a reference point in the middle of the island. This reference point contains a sensor that measures the distance to the tracker that is attached to the headphone. The reference point is taped on the ground and attached to cables for power. When a guest tries to remove the reference point, the reference point will not get any power and the music will stop. It will be communicated beforehand to the guests that they are not allowed to remove the reference point and that they will not get the deposit back when trying to remove the reference point.
This way staff can relatively easily remove it, while guests cannot, since they would be seen by security and get a warning to stop. When everybody has been directed to their island the music starts. People start dancing and would like to have a drink. However, when attendees leave their island their music will stop. To minimize the time spent outside the island, the suggestion for using Airchip will be made to the event organizer. This is an app for ordering drinks at a distance to avoid queues at the bar.
When the drink is ready and there are no people waiting at the bar before him, the guest gets a notification on his phone to pick up the drinks. The guest steps outside his circle and stops hearing any sound on his headphones. He will walk on the one-way pathways to the bar and pick up his drinks there. He walks back and as soon as he steps into the island, he starts hearing music again.
A suggestion for the event organizer would be to install a big green or red light near the toilets. The light is green when there are toilets available and the light is red when all toilets are occupied.
When the music event ends, the music will stop and a nice waiting song will be heard again. Guests put off their headphones and personnel will collect the headphone at the island and give the deposit back. The personnel going to the islands prevents a queue at the exit.
At this moment, this experiment can not be conducted (oktober 2020) as the current maximum group size is 40 people. It is impossible to tell whenever it is possible to conduct this experiment, but that actually doesn’t really matter. This technology is applicable whenever larger groups are allowed to come together while keeping distance. As soon as the maximum group size is raised, our tool will become relevant as the distance rule will assumably will still be the case.
Experiment map
Above you see the map of how the terrain where the experiment would be performed looks like. There will be islands with a radius of 2m. This way 2 persons can dance freely in their dance area. For simplicity luminous tape or something will be placed on the area so people roughly know how big their circle is. Of course these straight lines could be extended with more tape to show the area of the circle better. We leave this up to the event organizer. At the two places where guests are allowed to enter their dance island the name of their island is marked on the ground (e.g. A1 on the top and left pathway). We have chosen to group the dance islands in groups of 4 with 1.5 meter in between of the islands to safe space. In between the groups of islands there will be 3 meter to make sure people walking in the pathways are guaranteed to have 1.5 meter to the island right and left of them.
Hypothesis
As can be seen in the results from the survey 17 out of 21 attendees that went to an event during COVID-19 could keep sufficient distance to other attendees. However, only 5 out 21 respondents said they actually actively keep this distance. It was concluded from this that just common sense is not enough to make sure that attendees stay at a safe distance and that extra extra measures are necessary at a festival terrain. The results from the survey also showed that attendees are willing to wear headphones that track their movement if that makes dancing possible. Additionally, respondents endorse that they will be stimulated to stay in their circles if the music will be paused when crossing the lines. From the input that was received from attendees and stakeholders it became clear that it has appeared to be very complicated for attendees to follow the signing and to respect the distancing rules at toilets and bars. Therefore, the following hypothesis is formulated:
Participants will adhere to the distancing rules, but possibly not to the right pathway direction. Some participants will leave the dance island, but when they stop hearing music they will all go back.
Note: also regarding alcohol. behaviour during corona in general e.g. people at supermarkets forget about 1.5m
Discussion
A disadvantage of this experiment is that it is a controlled environment. Because of safety, we would prefer to have more security available, but then people might start behaving differently. Also the average person that is willing to participate in this experiment might behave differently than the average person that will visit events with our technology in the future. People who want to voluntarily participate in a study are often more willing to cooperate than people who simply want to dance and have a fun night out. (TODO support this further)
What will be done with the outcomes of the experiment?
If the experiment would actually take place, then the outcomes wil first of all be shared with the local authorities. If everything went right and the attendees and local authorities are satisfied, these results will be used to introduce the product nationally to the academic world and the music venue and festival industry. Depending on their reaction, it will be proposed to the government to allow standing events with this product.
Business plan
Executive Summary
Problem Summary
We would like to make dancing possible again at a festival or event venue and help the related stakeholders by minimizing the loss caused by COVID-19. To achieve this goal, our company must solve how to make dancing possible while keeping the “social distancing”. And how to deal with the financial part and regulation by the government.
Solution Summary
We make sure that people keep the distance by assigning two people in a circle, called a dancing island so that the circle can be 1.5 meters away from other circles. Also, we deal with the uncertainty regarding corona by making sure that our add-on(extra sensors) on the headphones can be undone. And, we conducted interviews with authorities and festival organizers and did surveys with users.
Market
Our main target customer is a headphone rental company.
Competition
There are three alternatives. A corona proof party suit with a helmet A wristband that detects a distance to other people and gives a signal A non-technological deck
Why Us?
We are students who major in a computer, biomedical and psychology and could be financially supported by the Bright move, an initiative of the TU/e, Brainport Development and BOM. As a team, our multidisciplinary team is a big advantage to develop this product. We have considered both the technical part of our product and the human factor which can affect the user-friendliness. The technical part is done by software modelling with UPPAAL and specific diagrams aided by research on sensors. And the practical implications have been researched through multiple interviews, conversations and surveys. Also, our ultimate ambition is to see when people can relish dancing at a festival or event place again which brings a positive effect on their mental health as well. [40]And this desire leads to the competent development of our product.
Forecast
Once the current situation is improved and the regulation on COVID-19 is loosening, we plan to rent this technology to our customers. Yet, we try to have a test phase from January or February in 2021. Because we could apply our technology to a few events as a test case in advance and attempt to prevent illegal parties more. There exists a regulation on an event, nonetheless, some illegal parties are taking place throughout the world, for example, France, China, America.[41][42][43] With trial and error, we could gain extra assessments from event visitors or our customers and adjust details for an actual demonstration in May or June. We aim to sell our idea to festival headphone companies. Also, if this pandemic situation is over, we give an option for our customer to detach sensors from the headphone. And then sell the sensors or rent the headphones as before. So there would not be much loss for all involved parties.
Opportunity
Problem Worth Solving
Whether they are private companies or public authorities, it becomes onerous to hold an event or festival at this moment. An example of an associated adverse impact is that the economic situation of related companies[44] and individual mental status have deteriorated [45]. Thus, as soon as this pandemic situation is improved guided by the government's policy, our business would like to make dancing possible again at a festival or event venue and support the related stakeholders by minimizing the loss caused by COVID-19. To achieve this goal, our company must solve how to make dancing possible while following the pandemic guideline (i.e. social distancing). Since people do not want to feel that they are in a cage, it was necessary to come up with a solution to implement this social distancing in a natural atmosphere. However, we have to notice that people perceive an exceptional restriction as effective. [46] Thus, assigning people in a different circle does not make people feel extremely restricted. Also, we would like to work on the uncertainty problem of this business when COVID-19 is over. That is when the add-on of the headphone is not desired anymore. Regarding the financial section of private companies, we trust that our customers would like to compensate for the loss by continuing the business rather than closing the event permanently. Thus, that is also one of our motivations that we would like to manage dancing possible. Furthermore, the last problem to solve is negotiating the current law with local authorities and discussing further with the government.
Our Solution
Our solution for solving the problem is as follows. A guest arrives and his ticket is being scanned. He enters the building or the area and gets our headphones, after which he goes looking for his island. Before receiving the ticket, he pays a deposit for the headphone with our technology. We first create dancing islands with a diameter of 2 meters and assign two people on the same island. The sizes of the dancing islands would be big enough considering the minimum dancing movement range which is 0.5 - 0.9 square meters[47]. It can be drawn with duck tape or plastic material. A distance of 1.5 meters will be maintained between islands. But a guest does not need to keep a distance inside the island because we assume people from the same group are from the same household. There are also pathways where guests can walk. These paths have signed on them, so guests do not cross. There is a reference point in the middle of the island. People would not take the reference point off from the centre because it will stop the music completely. The distance of a headphone from this reference point is constantly measured. When a person goes out of the circle, then the ultra-wideband sensor (UWB) inside the headphone and the reference point would recognize that and send a warning to the staff. About using a bar and toilet, it is completely up to a festival/event organizer how to host this. But our suggestion would be to use an application called Airchip to order food in order to prevent a queue at the bar. Also, the organizer could use green and red light to indicate if the toilet is available or not. In order to reduce the cost for our customers, we would like to move forward in the direction of applying our technology to the original headphone rental company instead of making our own headphones. Also, we deal with the uncertainty when the COVID-19 is gone by making sure that our add-on(extra sensors) on the headphones can be undone. We use sensors with proper quality from original manufactures in case our customers would decide on not using those sensors anymore and return or sell them. In this way, customers do not dissipate the cost. Also, in order to deal with the regulation problem on a festival and event, we have conducted interviews and contacted people who are related to opening festivals such as organizations and authorities. Also, we did several surveys to meet the festival visitor’s needs as well. The uniqueness of our product would be scalability and an ability to restrict the behaviour of the crowd in a natural way. Since we will know how many people would come as a group and already know the size of dancing islands, it is handy to fit the size in the area of any festival venues. Also, if we would allow guests as an individual without assigning them on an island, it would be difficult to control their behaviours.[48] And they would feel less responsibility to keep the distance with each other.
Target Market
Market Size & Segments
Our main target customer is a headphone rental company in the Netherlands. We first would like to sell our technology in the Netherlands, and then expand our business range to a global market once the size of the business gets bigger. The size of festivals or events using headphones is quite big in the Netherlands. One example that can show the number of demands of headphones is the Lowlands festival. This is the world’s biggest silent disco. With the number of headphones supplied, there have been 10000 headphones in 2017, 20000 headphones in 2018 and 30000 headphones in 2019. [49] Also, we have searched the number of headphone rental service companies to figure out the market size in the Netherlands. There would be more companies if we include other keywords. But there are around 63 headphone rental service companies in the Netherlands searched on Google with the keyword, “silent disco koptelefoons huren”. [50] Doing research on the revenue of this industry was done by a specific business website. [51] The range of research has been done 8 silent disco organizer/rental companies where 1 company is in the Netherlands, others are in Australia and the UK.[52] There was a limit to know the revenue of large samples. Therefore, we included research about other countries' cases as well. The revenue varies from $192,000 to $5 Million. With the population size of 8, the median is calculated as $506,000.
Competition
Current Alternatives
There are three types of alternatives to our technology. First, Micrashell that is a Corona proof party suit with a helmet.[53] This product is equipped with LED, sensors, speaker, camera and resonator system. Second, a wristband that can detect a distance and give a signal.[54] Last, a non-technological deck where 5 people from the same household can go on.[55] And the distance between decks is 6 feet which are approximately 1.8 meters. This was implemented in August at Virgin Money Unity Arena in Newcastle of England. And 2500 tickets were sold out in minutes.
Our Advantages
We would like to introduce our advantages to each alternative. The first product has equipped several sensors, cameras and some technology systems. For a good quality camera and speaker, it would already cost a lot of money for only one suit. Our product is more cost-effective since we only need one external sensor on an existing headphone. Also, we would assume wearing the suit would not be user friendly since there are some statistics that people who find wearing a mask is already burdensome. [56]Although the research is limited to Americans, we could assume it happens to any countries. The second product would not be ideal for a festival. There are two reasons. First, people tend to lose control more in a bigger crowd than a smaller sized group. Our product has subgroups inside the crowd which leads to better control on people to make them keep the distance. The last reason is people can easily ignore the subtle LED/vibration/sound indication in a noisy environment and that indication comes out when they do not keep the distance.[57] Our product makes use of a headphone which enables a natural controlling on people by stopping the music. The third alternative way would not be ideal for a bigger scaled festival or indoor event. If the festival is on a huge scale, then people who are far away from the stage would not enjoy the music as the people who are close to the stage. Also, there are way fewer people for an indoor event unless it is an exceptionally huge dome or arena. Furthermore, one of the interviewees that we contacted said, the company has to hire people to build up the deck for those fewer people and it might be difficult to build the deck and reuse the material. With these advantages over those three alternatives, we believe our product is strongly competitive.
Execution
Marketing & Sales
As defined above our target market is rental companies of silent disco headphones. To reach those companies advertisement needs to be done. This can be done in various ways, for example via mailing the companies ourselves. In the beginning stage of our company we will try to contact many companies who rent out these headphones, tell them about the idea we have and try to convince them of the goal we have. It is likely when these companies like the idea we will investigate in marketing campaigns. These marketing campaigns will be directed to the companies that are in this business. This will probably be via email. We will send out emails and send letters to the rental companies, trying to convince them of our idea. Furthermore, when the company has launched we assume to be noticed by other rental companies. At the end of the line the event branche will use our product the most. When the event branch likes the idea, which we already have had some feedback on, they can order more of the distance headphones which ultimately results in more sales for us. The event branche wants to organize events again. This will likely increase the chance that the rental companies want to do business with us because they are getting convinced from both sides, from our side and from the event branche.
Position of our company
The covid-19 pandemic started this year. Parties are not given in the way that we know. In the Netherlands parties are only allowed when the visitors stay seated. We want to change this in making dancing allowed and manageable for the organizers. So, the market is fairly new, which gives the company a good position in the market. We are the first company with this idea which also increases the position of the company. WATpod is a dutch company who already looked into measuring distance in covid-19 times. However, WATpod focused more on businesses, how to maintain distance from workers. Also to use the WATpod on events is hard to realise, visitors could easily tamper with the WATpod. We changed this idea and made it into an easy to use design for events. The goal of the company is to launch as fast as possible, our aim is to launch our company in the beginning of may. The research and test phase should be finished by then. The pandemic is an uncertain time. How long this pandemic stays is uncertain and to reduce the risk it is important to launch as early as possible.
Pricing
The normal price margin for normal growth is around 5%. However, the aim is to go higher with our price margin. This is preferable for a company like us because we are probably a “hype company”. Meaning that we will rise fast and sadly die out when the pandemic is over. To maintain enough profit the prices will be higher than the normal 5% on the costs. This is also possible because the company is one of a kind. There are not a lot of companies operating in our field, which gives us a good position. Rental companies already responded well to our design and although the costs for them would maybe be high they think it is worth it in the end. This foreshadows a good future for the company.
The costs of the product are:
‘’The distance tracker on the headphone’’
| Component | Price per 1000 | Price per 5000 | Price per 10000 | Price per 50000 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Assembly (pcbcart) | $0.24 | $0.15 | $0.08 | $0.03 |
| PCB print (pcbcart) | $0.25 | $0.25 | $0.25 | $0.25 |
| DWM1000 (semiconductorstore.com) | $15.65 | $15.65 | $15.65 | $15.65 |
| ATMEGA328 (AVNET) | $1.26 | $1.21 | $1.20 | $1.20 |
| Relay (AVNET) | $0.68 | $0.54 | $0.53 | $0.48 |
‘’The beacon”
| Component | Price per 1000 | Price per 5000 | Price per 10000 | Price per 50000 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Assembly (pcbcart) | $0.24 | $0.15 | $0.08 | $0.03 |
| PCB print (pcbcart) | $0.25 | $0.25 | $0.25 | $0.25 |
| DWM1000 (semiconductorstore.com) | $15.65 | $15.65 | $15.65 | $15.65 |
| ATMEGA328 (AVNET) | $1.26 | $1.21 | $1.20 | $1.20 |
Public relations
As a team from the University of Technology we benefit from being in a great position. Companies are more inclined to talk to us due to the fact that our university is a well known establishment in the Netherlands. It is easier to get a prominent review from professors who are well known in the scientific world as well. This can strengthen our position in the market if we get approval of a university so well known in the Netherlands. Furthermore, contact with many event branches and rental companies are already made. Most of them responded enthusiastic about the idea. These relationships are good for the company, they could be our test cases to find out if this is a healthy business and that the company can make profit selling these tracking devices to the rental companies. This can all be done before the big launch resulting in lowering the risk of losing capital.
Operations
Sourcing and fulfillment
The individual components will be sent to us from various places around the world. There are three main companies where the components will come from. The sensor DWM1000 will come from semiconductorstore.com. Furthermore, the microprocessor will come from the company AVNET. The assembly of the parts will be done by PCBcart. The assembly of the product to the headphone will be done by us. These companies are trustworthy and quality of the components are guaranteed. These products can be bought in bulk which lowers the price. However, first the precise demand needs to be established and a testphase must be held to establish this.
Technology
The product is an add-on device for silent disco headphones to track attendees of an event. The silent disco headphone that is used the most are the RF-309 Headphones. The events could differ from large festivals to small festivals. The technique is scalable so when the terrain is large enough more islands can be made. The technique measures the distance from a reference point, this is called the anchor. This is done via ultrawideband which is accurate enough to measure the distance that we prefer, scalable for short distances. The processing of the data is done by an ATMEGA328. This is a small microprocessor meaning that it can be hidden nicely within the headphone. These two ultra wideband sensors, one at the reference point, the anchor, and one on the headphone let's call that the receiver. The anchor and the receiver continuously communicate with each other measuring the distance from the reference point to the headphone. When a visitor of the event exits his or her area the music will be paused at the headphone. The visitor can resume listening to the music only when he or she returns to the area he or she should be. The microprocessor will give a signal and short circuit the music, this will result in pausing the music. The idea is that visitors are actively reminded to adhere to the rules. The rules, being, staying in your designated area. When investors want more details on how it works they can contact us. When both parties come to an agreement the technique can be explained more in detail. At this moment the precise working is company secret.
A diagram how the technique work can be seen below:
Milestones & Metrics
Milestones
The major milestone is to start testing in january. At this time the company needs to have enough investors and confidence to really start working. The aim to start on a larger scale is in the beginning of May. When, in the process, we find out this can be realized earlier. We want to be ready before the festival season begins so we can utilize this season the most. Other milestones are finding investors and our first rental company who wants to work with us. After mailing a lot of rental companies, the first companies are already found. This is already a great milestone because tests can already be done to find out how profitable this will be. Furthermore, participating in innovation challenges and winning them are milestones the company is hoping for. To get more investments winning prize money is a goal.
Key Metrics The key metric that will be followed is how much profit there will be made in a year. Another one is how many companies we are working with. It is a good measurement to see how healthy the company is. The aim is to order in two batches from the manufacturers in China. First a test phase, in which the profit and how healthy the company is are established. In the second phase a large amount of components will be ordered. From the test phase it is predicted how many components are needed to get the company through the festival season. This will be the biggest phase. There could be a third phase when the pandemic is not over yet. If this is the case the second phase will be repeated until the pandemic is over. The technique is usable outdoors and also indoors. So, in the winter when the festival season is over the company can continue selling the devices.
Key assumptions and risks The biggest assumption the company takes is also the biggest risk. It is about the covid-19 pandemic. The company is based on this pandemic and the problem that there is no good alternative to organize parties in these times. So, there was an assumption made that the pandemic stays for at least until the end of the summer of 2021. The risk that comes with that is that we can never be certain if this would be the case, the future cannot be predicted. So, when the pandemic stops before this deadline our company will have no market resulting in not being able to sell the product. The costs that are at that moment already made are dependent on when the pandemic ends. If the pandemic stops early on in December the loss will be minimal, the test phase has not even been started at that point. However, if the pandemic stops just before May the loss will be bigger, the components are already ordered and assembled. The second assumption that we made is the fact that the government will not allow large festivals where attendees can come close to each other. We assume this will be banned until the end of the summer of 2021. This is because our product is useless if festivals are allowed again. However, it is assumed that in the spring of 2021 larger groups can attend festivals with the 1.5 meters distance from each other. The last assumption is that event organizers have made a lot of loss during the pandemic and they are eager to try new ideas. This assumption, however, is almost a certainty with all the feedback from the different stakeholders.
Company
Team
The team consists of 5 students from the university of technology in Eindhoven. We are a multidisciplinary team with majors in biomedical engineering, computer science and engineering and psychology & technology. This gives us a big advantage because we can work simultaneously on different aspects of the problem. This results in fast results and letting every team member excel in their specialty. The structure of the team is that every team member is equal. We, as a team, decided to rotate the role of chairmen and minute taker. This to also train the team members in different skills such as chairing a meeting. This results in good discussions and, again, letting our full potential flourish.
We are a young team full of energy and a drive to tackle problems. This makes us an energetic and modern company. The character of the company is open. We are always open for feedback and easy to work with. We easily adapt ourselves to new partners which benefits us in maintaining good relationships with the companies we work with.
Advisors
We are advised by a team consisting of two professors of the University of technology in Eindhoven. There are weekly meetings on Monday and in these meetings the process is discussed and they guide us through the process of setting up this business.
They are not our only advisors; we also got some feedback from multiple companies and event organizers. They guided us through some problems and came up with ideas where we as a team were stuck. Furthermore, a rental company came up with our final idea. The idea of making an add-on system for the headphones. This way we could tackle the problem when the corona crisis would end. This being, if the corona pandemic ended we are out of business. With this small change investors can invest in us with less risk which results in more investors.
Mission statement
The main goal of this business is to make festivals or events possible in times of corona. To be more clear, the ultimate goal is to make dancing possible at events. The rules have changed since Corona came into the picture. To make events possible the government decided that all the visitors have to stay at their table. This to reduce movement of the visitors. Sitting at a party is less fun in our view, so we wanted to change this. Furthermore, this view is shared with many event organizers and visitors after the research we have done.
Slogan
Business structure
We are a team of 5 students who are equal to each other in the process. In meetings we shuffle between who is the chairman or woman and who is the minute taker. This way everyone is equal to each other. This makes us a unique company. The business has 3 weekly meetings. In which we discuss multiple problems and try to come up with solutions for the problems we encounter. The remaining time in the week we work on tasks we have come up with in the meetings. In the meetings we also discuss our results of these tasks.
Company history
The company is in the early launch stage. This means that an idea is formed and are trying to get investors and making moves against the local authorities to make our goal possible. The company started on 31 august 2020 when the course project robots everywhere started.
Location
The company is located in Eindhoven. This is a great location for our business because Eindhoven is seen as the technology capital of the Netherlands. The district we operate in is called Brainport Eindhoven. Brainport Eindhoven is a collective of companies who strive to innovate and make the future better, safer and cleaner. This is accomplished with technology playing a key role. The innovative strength of Brainport Eindhoven is that they work with multidisciplinary teams to reach goals. This is in line with our goal and our way of working and thinking. Companies and the university work together. We as a beginning company can see the benefits of such location and mentality. For example, the process of working with various music organizers. They did not hesitate to work with us to reach our goal. Especially in times of corona, Brainport Eindhoven searches to help each other get through this time together. This is the main reason why this location is so good for a company like us.
Financial plan
To startup the company needs to find funding. The first option is to get investors aboard. One big investor is bright move. Bright move is an initiative of the TU/e, Brainport Development and BOM. Their aim is to help starting, innovative entrepreneurs in the region of Eindhoven to accomplish their goals. The company has applied for funding and we are still waiting for the response. This funding can range from 15000 to 50000 euros. This will be enough to invest in our initial aim which is buying the products for 200 headphones. Another option is to use dropshipping. This method is beneficial for us because the customers first need to buy the product after which we order it. This way we do not need any funding. A small starting capital is needed to make a website with the information of the company. This can be made via jouwweb.nl. This costs 8 euro per month. Payment options are included like IDeal which makes it easy to manage the payments. The company has to register itself in the KVK. This consists of a one time payment of 50 euros. The company address will be one of the owners addresses. This because a warehouse is not needed the products can be sent directly to the rental companies or can be sent to one of the owners. After which we distribute it ourselves. This distribution will be done with Peugeot van. The van runs on diesel the gas needs to be paid for too. Both tables are based on a first batch of 200 headphones. Table based on going with fundings
| Debit | € | Credit | € |
|---|---|---|---|
| Funding | €15000 to €50000 | Components | €4527.15 |
| - | - | Registration KVK | €50 |
| - | - | Website | €8 |
For the time being, we have to look more into dropshipping if this is really an option. Because we need to add the product to the headphones.
Logbook
Week 1
| Name | Total Hours | Tasks |
|---|---|---|
| Jeroen | 9.5 | Meetings (1.5 hrs), brainstorming (1 hr), literature study on state of the art (7 hrs) |
| Pleun | 10.5 | (Preparing and) meeting (2 hrs), reading other wiki's and brainstorming (1.5 hrs), writing on introduction, objectives, stakeholders, users needs and ethical considerations (5 hrs) and literature research psychological part (2 hrs) |
| Dayeong | 11.5 | Meetings (1.5 hrs), looking up wikis of previous projects + searching for 8 technology literature (6 hrs), Reading papers and making a summary on State-of-the-art (4 hrs) |
| Rik | 10 | Meetings (1.5 hrs), researching for subject, reading and summarizing papers regarding the technical aspect of our product and the financial impact of Corona |
| Erik | 9 | Meetings (1.5 hrs), meeting prep, brainstorming and looking through previous wikis, writing on plan, looking for more relevant papers |
Week 2
| Name | Total Hours | Tasks |
|---|---|---|
| Jeroen | 5.5 | Meeting (1.5 hrs), Working on survey (4 hrs) |
| Pleun | 7 | Meeting (1.5 hrs), mailing and calling event agencies and festival organizers, working out answers from them |
| Dayeong | 4 | Metting 0.5 hrs + 1 hr + Wristband research 1 hr + contact(WATPod) + modelling(meeting) 0.5 hrs + brainstorming research 1 hrs |
| Rik | 5.5 | Meeting, researching legal aspect on forced use of face masks, coronabeepers etc., coming up with ideas for making festivals possible again and talking with Van Klink who knows about legal aspects on enforcement of the distance rule, model meeting |
| Erik | 9.5 | Meetings (1.5hrs) Brainstorm ideas and requirements (2hrs) Creating first sketch of UPPAAL Model of Wristband (5.5hrs) Meeting on model (0.5hrs) |
Week 3
| Name | Total Hours | Tasks |
|---|---|---|
| Jeroen | 0 | Tasks here |
| Pleun | 10 | Group meetings, meeting at the Effenaar, relistening Effenaar-talk and writing a summary, brainstorming on new idea, updating wiki-page |
| Dayeong | 7 | Meetings, Doing research about new ideas, Making a diagram |
| Rik | 7.5 | Group meetings, meeting at De Effenaar, formulating requirements and coming up with ideas based on the Effenaar talk, work on model |
| Erik | 0 | Tasks here |
Week 4
| Name | Total Hours | Tasks |
|---|---|---|
| Jeroen | 0 | Tasks here |
| Pleun | 9 | Meeting, working on Wiki (intro, objectives, rpc's, detailed description of idea), prepping interview Effenaar, contacting festival organizations, overthinking weaknesses/concerns/solutions. |
| Dayeong | 15 | 1.5 hr (meeting) + 4 hrs (design, researching on a terrain and human movement area, calculating the estimates of circles) + 5 (making activity diagram, use case diagram) + 1.5 hrs (Wiki) + 1 hr (meeting, documenting) + 1.5 hr (contacting to 12 festival organizers) + 0.5 hr (Researching irritating sensation as a punishment) |
| Rik | 8 | Meetings, working on cost effectiveness, thinking about and researching concerns and alternatives, cleaning up legal aspect section |
| Erik | 0 | Tasks here |
Week 5
| Name | Total Hours | Tasks |
|---|---|---|
| Jeroen | 0 | Tasks here |
| Pleun | 15h | Tutor meeting (30m), meetings, brainstorm on continuation, preparation meeting for de Effenaar (1h), talk at de Effenaar, processing interview and writing summary on it, contact corona-proof events in Eindhoven, contacting festival organizations, contacting YoungCreators, creating overview on mail-response, working on wiki (objectives, deliverables, stakeholders), |
| Dayeong | 14.5h | 3 hr (meeting) + 8 hr (researching relevant parts + documenting, creating a business plan) + 0.5 hr (contacting festival organizer) + 1.45 hr (meeting) + 1 hr (meeting + wiki) |
| Rik | 14h45 | Tutor meeting (30m), brainstorm on continuation (3h), preparation meeting for De Effenaar talk (1h), talk at De Effenaar (1h), working on experiment plan, reviewing objective, coming up with questions and remarks, searching for startup challenges, meeting (1h45m), tidy up meeting minutes (15m), discussion Whatsapp (15m), Finding relevant contacts, contacting Smart Distance Lab, music venues, Ministerie van Economische Zaken, Rijksdienst voor Ondernemend Nederland (2h30m) |
| Erik | 0 | Tasks here |
Week 6
| Name | Total Hours | Tasks |
|---|---|---|
| Jeroen | 0 | Tasks here |
| Pleun | 13h | meeting, contacting stakeholders, working on experiment plan, thinking about slogan, marking all assumptions, updating planning, placing comments, working on household problem, working on an index |
| Dayeong | 15hr | 1.5 hr (meeting) + 3 hr (researching / contacting manufacturers to know the bulk price / marketing cost) + 2.5 hr(editing business plan and linking academic papers) + 1.5 hr (meeting) + 5 hr (reading feedback + editing business plan + correcting errors + researching event equipment service or silent disco headphones rental market) + 0.5 hr (discussing financial part) |
| Rik | 11h30 | Tutor and group meeting (1h30m), Working on Experiment plan (1h45m), Reacting to e-mails, looking at Pleun’s comments on the Experiment plan, reading up on SSAs and Business Plan (2h), Group meeting (1h30m), Reading, researching, thinking about business plan, sending e-mails Veiligheidsregio Brabant Zuidoost, Koninklijke Horeca Nederland, researching, thinking, writing, discussing number of people per island (2h20m), Whatsapp discussion on number of people per island, funding for business plan, costs (1h15m), Making experiment sketch (1h15m) |
| Erik | 0 | Tasks here |
Week 7
| Name | Total Hours | Tasks |
|---|---|---|
| Jeroen | 0 | Tasks here |
| Pleun | 7 | meetings, contacting Effenaar, writing Development of Ideas section, placing comments |
| Dayeong | 0 | Tasks here |
| Rik | 0 | Tasks here |
| Erik | 0 | Tasks here |
Week 8
| Name | Total Hours | Tasks |
|---|---|---|
| Jeroen | 0 | Tasks here |
| Pleun | 0 | Tasks here |
| Dayeong | 0 | Tasks here |
| Rik | 0 | Tasks here |
| Erik | 0 | Tasks here |
References
- ↑ [Harm Teunis, Mathijs Smit (2020, August 14) ‘Zonder nieuwe steun verdwijnt helft banen evenementensector’. RTLnieuws
- ↑ [Pavan Hiremath, C S Suhas Kowshik, Maitri Manjunath, and Manjunath Shettara. COVID-19: Impact of lock-down on mental health and tips to overcome]
- ↑ [J.M. Gonzalez_Diax, J.F. Cano, V. Pereira-Sanchez. Psychosocial impact of COVID-19-related quarantine: refelections after the first case of suicide in Colombia. https://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0102-311X2020000607001&tlng=en]
- ↑ [Rohde, N., D’Ambrosio, C., Tang, K.K. et al. Estimating the Mental Health Effects of Social Isolation. Applied Research Quality Life 11, 853–869 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11482-015-9401-3]
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 CCV. (2020). Evenementenbeleid. Retrieved from https://www.raadsledenenveiligheid.nl/veiligheidsthemas/evenementenbeleid
- ↑ Kaparounaki, Chrysi & Patsali, Mikaella & Mousa, Danai-Priskila & Papadopoulou, Eleni & Papadopoulou, Konstantina & Fountoulakis, Konstantinos. (2020). University students’ mental health amidst the COVID-19 quarantine in Greece. Psychiatry Research. 290. 113111. 10.1016/j.psychres.2020.113111
- ↑ [Sarah Moon. Effects of COVID-19 on the Entertainment Industry. https://www.idosr.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/IDOSR-JES-51-8-12-2020.-P2.pdf]
- ↑ [ I.Helsloot, J. Groenendaal, J. Vis, 2020. Wat weten we nu eigenlijk precies van het coronavirus en wat betekent dit voor evenementen? https://crisislab.nl/wordpress/wp-content/uploads/Wat-is-er-bekend-over-corona-def-24-8-2020.pdf?fbclid=IwAR1SU-AAqsZB1uc1iaGLnhSi_fgNvEpbkuInxO3aZfgTXRxQmVEgTSG94mI]
- ↑ [ Het coronavirus en de horeca en evenementen, Rijksoverheid, https://www.rijksoverheid.nl/onderwerpen/coronavirus-covid-19/ondernemers-en-bedrijven/horeca ]
- ↑ [ Mensen uit zelfde huishouden hoeven in horeca geen 1,5 meter afstand te bewaren, Misset Horeca, https://www.missethoreca.nl/horeca/nieuws/2020/05/mensen-uit-zelfde-huishouden-hoeven-in-horeca-geen-15-meter-afstand-te-houden-101335773 ]
- ↑ [ Het coronavirus en de horeca en evenementen, Rijksoverheid, https://www.rijksoverheid.nl/onderwerpen/coronavirus-covid-19/ondernemers-en-bedrijven/horeca ]
- ↑ [Retrieved from https://www.greatmats.com/how-big-of-a-dance-floor-do-i-need.php]
- ↑ [Hossain, Iqbal & Minhas Talat (2012). Distance Measurement Using Ultra Wideband.]
- ↑ [Mondkapje gaat op in Amsterdam en Rotterdam, maar waar precies?, RTL Nieuws, https://www.rtlnieuws.nl/nieuws/nederland/artikel/5175421/mondkapje-coronavirus-plicht-drukke-gebieden-amsterdam-rotterdam]
- ↑ [ Amsterdam en Rotterdam stoppen met mondkapjesplicht, NOS nieuws, https://nos.nl/artikel/2345715-amsterdam-en-rotterdam-stoppen-met-mondkapjesplicht.html]
- ↑ [Deskundigen: verplicht dragen mondkapje is wettelijk niet mogelijk, NOS nieuws, https://nos.nl/artikel/2342362-deskundigen-verplicht-dragen-mondkapje-is-wettelijk-niet-mogelijk.html]
- ↑ [Hoogleraar recht: algemene mondkapjesplicht kan juridisch gezien niet, Omrop Fryslan, https://www.omropfryslan.nl/nieuws/978741-hoogleraar-recht-algemene-mondkapjesplicht-kan-juridisch-gezien-niet ]
- ↑ [ Mondkapjes op de werkvloer, verplichten, verbieden of toestaan?, Mr-online.nl, https://www.mr-online.nl/mondkapjes-op-de-werkvloer-verplichten-verbieden-of-toestaan]
- ↑ [ Zorgen om naleving coronaregels in horeca: meerdere zaken gesloten, AD, https://www.ad.nl/binnenland/zorgen-om-naleving-coronaregels-in-horeca-meerdere-zaken-gesloten~a8b19d9d/ ]
- ↑ [ Festival Ownership. Differences between Public, Nonprofit and Private Festivals in Sweden, TOMMY D. ANDERSSON & DONALD GETZ, https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/pdf/10.1080/15022250903217035?needAccess=true ]
- ↑ [ How Music Festivals Became a Massive Business in the 50 Years Since Woodstock, BY MAHITA GAJANAN, https://time.com/5651255/business-of-music-festivals/ ]
- ↑ [The cost of staging a music festival: 'We spent £30,000 on the waste', Eamonn Forde, https://www.theguardian.com/music/2015/jul/09/cost-of-staging-music-festival ]
- ↑ [ FESTIVAL OVERZICHT 2018, EM Cultuur, https://www.em-cultuur.nl/festival-overzicht-2018/ ]
- ↑ [ Aantal festivals in Nederland groeit hard, muziekfestivals meest in trek, by Consultancy.nl, https://www.consultancy.nl/nieuws/14191/aantal-festivals-in-nederland-groeit-hard-muziekfestivals-meest-in-trek ]
- ↑ [ BEGROTING: WOO HAH!, Ruud Lemmen, http://www.brabantc.nl/site/wp-content/uploads/2016/01/bijlage-1-WOOHAH_BEGROTING.pdf ]
- ↑ [Van Natta, M., Chen, P., Herbek, S., Jain, R., Kastelic, N., Katz, E., Struble, M., Vanam, V., & Vattikonda, N. (2020). The rise and regulation of thermal facial recognition technology during the COVID-19 pandemic. Journal of law and the biosciences, 7(1), lsaa038. https://doi.org/10.1093/jlb/lsaa038]
- ↑ [Ting, D.S.W., Carin, L., Dzau, V. et al. Digital technology and COVID-19. Nat Med 26, 459–461 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-020-0824-5]
- ↑ [Nguyen, C. T., Saputra, Y. M., Van Huynh, N., Nguyen, N. T., Khoa, T. V., Tuan, B. M., ... & Chatzinotas, S. (2020). Enabling and Emerging Technologies for Social Distancing: A Comprehensive Survey. arXiv preprint arXiv:2005.02816.]
- ↑ [Punn, Narinder & Sonbhadra, Sanjay & Agarwal, Sonali. (2020). Monitoring COVID-19 social distancing with person detection and tracking via fine-tuned YOLO v3 and Deepsort techniques.]
- ↑ [Colmer, Morgan. (2019). UWB Vs BLE Whitepaper.]
- ↑ [Alarifi, A., Al-Salman, A., Alsaleh, M., Alnafessah, A., Al-Hadhrami, S., Al-Ammar, M. A., & Al-Khalifa, H. S. (2016). Ultra Wideband Indoor Positioning Technologies: Analysis and Recent Advances. Sensors (Basel, Switzerland), 16(5), 707. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16050707]
- ↑ [D. Dardari, R. D'Errico, C. Roblin, A. Sibille and M. Z. Win, "Ultrawide Bandwidth RFID: The Next Generation?," in Proceedings of the IEEE, vol. 98, no. 9, pp. 1570-1582, Sept. 2010, doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2010.2053015.]
- ↑ [What’s The Difference Between Measuring Location By UWB, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth? By Ciaran Connell, https://www.electronicdesign.com/technologies/communications/article/21800581/whats-the-difference-between-measuring-location-by-uwb-wifi-and-bluetooth ]
- ↑ [T. M. Au, K. F. Tong and K. M. Luk, "Analysis of offset dual-patch microstrip antenna," in IEE Proceedings - Microwaves, Antennas and Propagation, vol. 141, no. 6, pp. 523-526, Dec. 1994, doi: 10.1049/ip-map:19941545.]
- ↑ [What’s The Difference Between Measuring Location By UWB, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth? By Ciaran Connell, https://www.electronicdesign.com/technologies/communications/article/21800581/whats-the-difference-between-measuring-location-by-uwb-wifi-and-bluetooth ]
- ↑ [A Survey of Indoor Positioning Systems for Wireless Personal Networks Yanying Gu, Anthony Lo, Senior Member, IEEE, and Ignas Niemegeers]
- ↑ [ Het coronavirus en de horeca en evenementen, Rijksoverheid, https://www.rijksoverheid.nl/onderwerpen/coronavirus-covid-19/ondernemers-en-bedrijven/horeca ]
- ↑ [ Hoe organiseer je legaal een coronaproof feest?, Timo Pisart, https://3voor12.vpro.nl/artikelen/overzicht/2020/augustus/Alkmaar-coronaproof-dansen-festival-finally-fiesta.html ]
- ↑ [ Finally Fiesta, Simon Pannekoek, Partyflock, https://photo.partyflock.nl/970417/main/Finally-Fiesta-23.jpg ]
- ↑ [Lakes, K. D., Marvin, S., Rowley, J., Nicolas, M. S., Arastoo, S., Viray, L., Orozco, A., & Jurnak, F. (2016). Dancer perceptions of the cognitive, social, emotional, and physical benefits of modern styles of partnered dancing. Complementary therapies in medicine, 26, 117–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctim.2016.03.007]
- ↑ [Hermesauto. (2020, August 23). The party goes on for French ravers, despite Covid-19 pandemic and police warnings. Retrieved from https://www.straitstimes.com/world/europe/the-party-goes-on-for-french-ravers-despite-covid-19-pandemic-and-police-warnings]
- ↑ [Wuhan pool parties bring post-coronavirus relief in China. (2020, August 19). Retrieved from https://apnews.com/article/334d491bc894f2add48dd327542650e4]
- ↑ [Photo: twitter/lawler50/Reuters. (2020, June 01). Opinion | The People Are Ahead of Leaders on Covid-19. Retrieved from https://www.wsj.com/articles/the-people-are-ahead-of-leaders-on-covid-19-11591037724]
- ↑ [Baldwin, R., & Weder di Mauro, B. (2020). Economics in the Time of COVID-19.]
- ↑ [Pfefferbaum, B., & North, C. S. (2020). Mental Health and the Covid-19 Pandemic. New England Journal of Medicine, 383(6), 510-512. doi:10.1056/nejmp2008017]
- ↑ [Mækelæ, M. J., Reggev, N., Dutra, N., Tamayo, R. M., Silva-Sobrinho, R. A., Klevjer, K., & Pfuhl, G. (2020). Perceived efficacy of COVID-19 restrictions, reactions and their impact on mental health during the early phase of the outbreak in six countries. Royal Society Open Science, 7(8), 200644. doi:10.1098/rsos.200644]
- ↑ [Retrieved from https://www.greatmats.com/how-big-of-a-dance-floor-do-i-need.php]
- ↑ [Doukas, S.G. (2006). Crowd management: past and contemporary issues. The sport journal, 9.]
- ↑ [World's biggest silent disco hits 30,000 headphones. (2019, December 10). Retrieved from https://avmanagement.net/worlds-biggest-silent-disco-hits-30000-headphones/]
- ↑ [ ]
- ↑ [Hit Your Number. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://www.zoominfo.com/]
- ↑ [ ]
- ↑ [Micrashell. (2020, September 18). Retrieved from https://production.club/micrashell]
- ↑ [Social Distancing Wristband Wearables. (2020, August 06). Retrieved from https://www.mokosmart.com/social-distancing-wristband-wearables/?gclid=CjwKCAjwzvX7BRAeEiwAsXExo0NsgyjpCwymgNDEFtRBbO64tVZ21_XGuItvGrKc-N9fIjrnqjx98hoC994QAvD_BwE]
- ↑ [Virgin Money Unity Arena. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://virginmoneyunityarena.com/]
- ↑ [Vargas, E. D., & Sanchez, G. R. (2020, August 31). American individualism is an obstacle to wider mask-wearing in the US. Retrieved from https://www.brookings.edu/blog/up-front/2020/08/31/american-individualism-is-an-obstacle-to-wider-mask-wearing-in-the-us/Figure 1]
- ↑ [Tronstad TV, Gelderblom FB. Sound exposure during outdoor music festivals. Noise Health. 2016;18(83):220-228. doi:10.4103/1463-1741.189245]