Mobile Robot Control 2020 Group 4: Difference between revisions
| Line 76: | Line 76: | ||
===Interfaces=== | ===Interfaces=== | ||
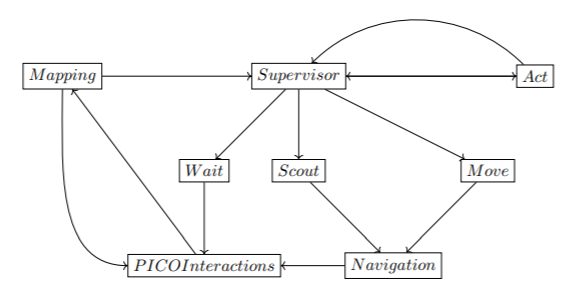
Keeping the aforementioned functionalities in mind, and given that the modes of the Supervisor module are represented here as separate locations for clarity’s sake, a rough depiction of the proposed system structure is shown in Figure 3 below. | Keeping the aforementioned functionalities in mind, and given that the modes of the Supervisor module are represented here as separate locations for clarity’s sake, a rough depiction of the proposed system structure is shown in Figure 3 below. | ||
[[File: | [[File:InterfacesDesignReport.png|center|thumb|Figure 3: State Machine Representation]] | ||
===Components=== | ===Components=== | ||
Revision as of 12:24, 12 June 2020
Group Members
| Name | Student Number | |
|---|---|---|
| M. Katzmann | 1396846 | m.katzmann@student.tue.nl |
| B. Kool | 1387391 | b.kool2@student.tue.nl |
| R.O.B. Stiemsma | 0852884 | r.o.b.stiemsma@student.tue.nl |
| A.S.H. Vinjarapu | 1502859 | a.s.h.vinjarapu@student.tue.nl |
| D. van Boven | 0780958 | d.v.boven@student.tue.nl |
| R. Konings | 1394819 | r.konings@student.tue.nl |
Introduction
Welcome to the wiki page of group 4 of the 2020 Course Mobile Robot Control. The goal of this course is to design and implement software to the PICO robot which allows it to complete two different challenges, the escape room challenge and the hospital room challenge. Both challenges are in a simulated environment and should be succesfully completed by the PICO robot autonomously. A design document is delivered before participating in these challenges which describes the overal architecture of the software.
Design document
The design document describes the architecture of the software. The document is devided into the requirements, functions, components, interfaces and specifications and is relevant for both the escape room challenge and hospital room challenge. However, the document should be considered a guidance for both challenges, and the initial declared functions are subject to change as the project progresses.
Escape room challenge
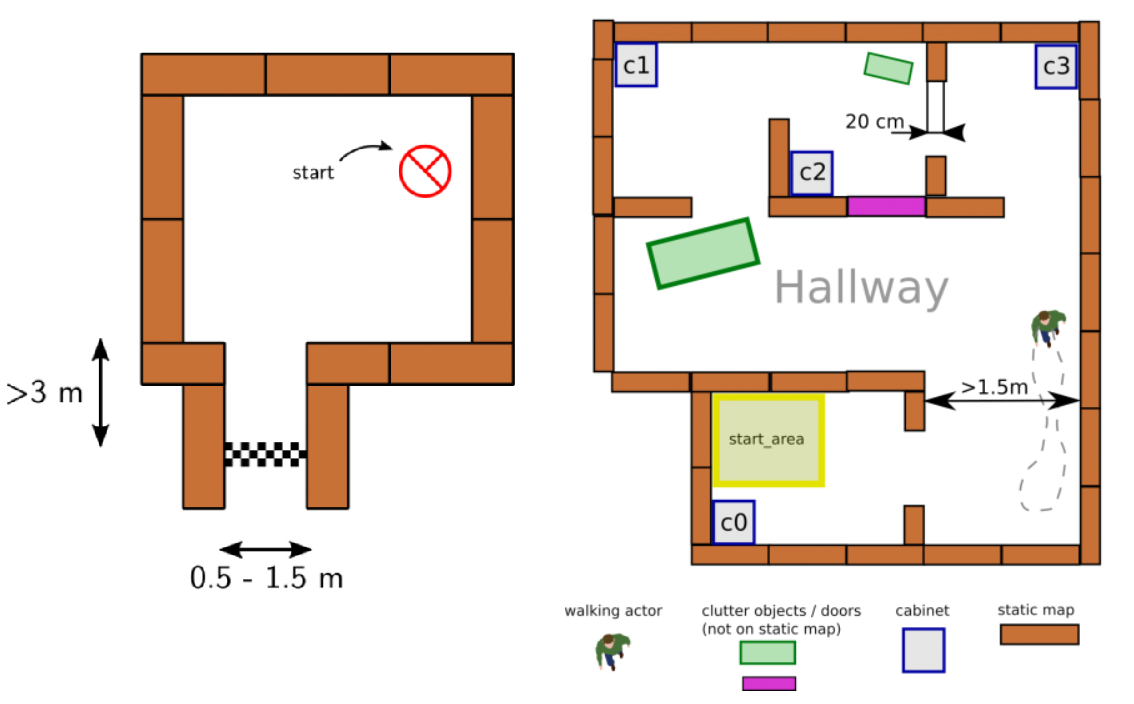
This challenge is designed as an itermediate challenge. The goal of the escape room challenge is to have PICO escape a rectangular room by exiting this said room through a corridoras fast as possible. The dimensions of this room are unknown as well as the initial position and rotation of the PICO robot. The corners of the room are not perpendicular but vary around 90 degrees. A simple example map of the room iss provided before the challenge, which can be seen in figure 1. During the escape of the PICO robot, walls, static and dynamical objects may not be touched, but slightly touching is allowed.
Hospital room challenge
The goal of the hospital room challenge is to have PICO autonomously manoeuvre through a simulated hospital environment. The hospital environment consists of multiple rooms and a hallway. Each room contains cabinets and the objective is for PICO to deliver medicine from one cabine to another, where the order will be defined by the judges. Similar to the escape room challenge, the dimensions of the map and the initial position and rotation of the PICO are unknown. However, the starting room will be provided beforehand. During the delivering of medicine by PICO, a handful of static and dynamical objects will be in PICO's way. It is PICO's job to avoid collision with any objects or walls and deliver the medicine in the correct order as fast as possible. An example map of the hospital environment is provided, which can be seen in figure 1.
Design Document
Requirements
Functions
PICO interfaces
These are all low-level interactions consisting mostly of calls to the IO API (which represents communication with PICO).
- Actuate(v, u, th): Casts a desired velocity profile [ ˙x, y,˙˙ theta] to the robot.
- getLRF(): Pulls LRF data from the robot. Returns a laserdata struct.
- getODO(): Pulls odometry data from the robot. Returns an OdometryData struct.
Mapping
This section describes the outlines of the internal map model and its learning process.
- seeLocal(Laserdata): Interprets laserdata as a local vision envelope, and stores the outcome locally.
- loc2glob(): Transforms local sensor data into a global perspective using calibration elements (e.g. intersections of wall lines).
- tf2map(): Transforms sensor data (in a global coordinate system) to Mapdata, which involves rasterizing the received data.
- integrate(): Compares and contrasts new data with old data, and modifies (and/or expands) the global map model accordingly.
This section covers the system functionalities responsible for (intelligent) navigation. All functions here have read access to the world model’s internal map and LRF envelope.
- localize(): Deducts the PICO’s current location in the map model based on its most recent LRF data.
- pathfind(x, y): Employs a pathfinding algorithm to find a combination of rotations and straight motions (longitudinal or sideways) that will bring the PICO from its current location to the global coordinate (x, y). Returns a PathData struct which describes the intended locations, and necessary rotations and local (x, y) motions to reach them.
- nextTrajectory(): Takes the next first data from PathData, and calculates the necessary velocity profiles and timings to achieve the desired motion smoothly. Returns this as a Trajectory struct.
- compensate(): Checks the PICO’s current location compared to its intended location within the planned path, and determines whether compensation is needed in the sense of adjusting the path, the PICO’s position, or recomputing the path.
Supervisor
This section covers the governing control logic of the proposed system. The idea is that the supervisor makes choices, tunes parameters, and controls flow-of-command within remaining code depending on its mode, and changes modes dynamically. Modes are described here as functions, but may end up in a different form during implementation.
- init(): Initializes the robot, checks (as far as possible) whether safe operation is possible. Sets the mode to scout.
- scout(): PICO is uncertain about its surroundings, and hence scans its surroundings, moving as little as possible in doing so. In this mode, safety parameters are conservative. Once a useful feature (such as a door) is found, or map confidence improves enough for PICO to feel safe, control is yielded to the move mode. If all exploration options are exhausted and PICO is still uncertain, control is instead yielded to wait.
- move(): PICO knows enough, and knows where it wants to go. This mode sets safety margins much more aggressively than scout mode, and looks to move long, efficient motions in pursuit of PICO’s intended destination. During motion, PICO keeps updating its map, and reverts to scout mode if certainty dips to unacceptable levels.
- wait(): PICO decides its goal is currently impossible. Waits, and occasionally returns to scout mode to see if the situation has changed.
- act(): An empty token mode to represent PICO arriving at a destination and doing something there.
Interfaces
Keeping the aforementioned functionalities in mind, and given that the modes of the Supervisor module are represented here as separate locations for clarity’s sake, a rough depiction of the proposed system structure is shown in Figure 3 below.
Components
Specifications
Escape Room Challenge
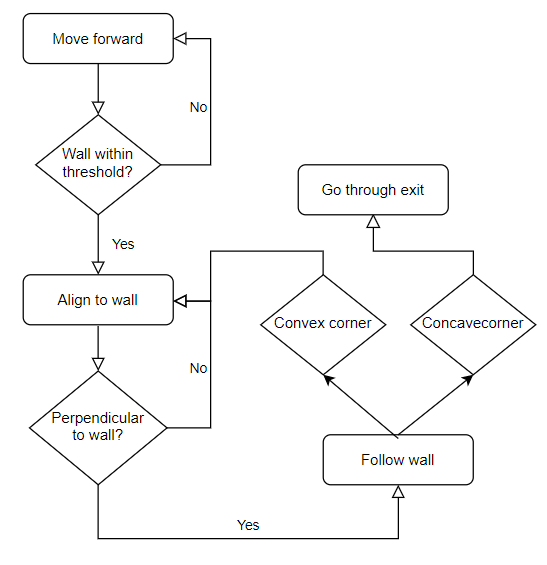
To safely get the PICO robot to the exit of the escape room, the strategy to implement a wall-follow algoritm is chosen. If the Algoritm is implemented succesfully, it should be a safe and quick solution to the problem. The PICO will move to a wall, after which he will align perpendicular to the wall. When aligned to the wall, PICO will move left until it reaches either a wall or a gap. It will choose to rotate or drive into the gap accordingly. This algorithm was chosen because it is a reliable algoritm that, if implemented succesfully, is safe and a relative quick escape.
The wall-follow algorithm is divided into the following subparts:
Step 1: The PICO moves forward
- The PICO moves forward until it reaches a wall. The PICO will start at a random location inside the escame room. This means the robot can be anywhere inside the room. Thus, the first thing PICO does is move forward until it detects a wall getting closer. As the wall gets closer, the velocity of PICO decreases until it reaches a certain threshold from the wall, which means the PICO will stop moving.
Step 2: The PICO aligns to the wall
- When PICO reaches the wall and completely stops moving, PICO starts rotating. It will rotate until it is perpendicular to the wall. This is achieved by having PICO stop rotating once the the middle LFR sensor has the smallest value. Here, the rotational velocity also decreases when the distance to the end point decreases.
Step 3: The PICO follows the wall
- Once the PICO is perpendicular to the wall, it is ready to start following the wall. This is done by moving the PICO to the left until it detects a corner. If the PICO detects a convex corner, this means there is a corner approaching, and if the PICO detects a concave corner, this means there is a corridor approaching. The PICO will take the correct measures in the next step according to what it detects.
Step 4: The PICO makes choices according to what it detects
- If this corner is convex
- The PICO will align to the wall which is close to perpendicular to the previous wall. When aligned correctly it will go back to step 3 and repeat the process.
- The PICO will align to the wall which is close to perpendicular to the previous wall. When aligned correctly it will go back to step 3 and repeat the process.
- If this corner is concave
- The PICO drives a little further until the PICO is aligned to the exit. Once it is aligned to the corridor and feels safe enough to move, the PICO will move forward until the exit is reached.
- The PICO drives a little further until the PICO is aligned to the exit. Once it is aligned to the corridor and feels safe enough to move, the PICO will move forward until the exit is reached.
During the wall-follow algoritm, the PICO checks if it is too close to a wall and if it is well alligned at all times.
Escape room challenge results
With the wall-following algorithm, the PICO achieved second place in the escape room challenge. The exit was reached within 27 seconds. The result of the challenge can be seen in the video. With the created algoritm, it can be seen that PICO firstly moves to the wall in front of him and stops when he is within the threshold range. Afther this, PICO perfectly aligns himself perpendicular to the wall, ready to move to the left. When moving to the left, first it encounters a convex wall, which means he rotates and aligns to the wall left of him. After the PICO is aligned to the new wall, it moves to the left until it encounters the corridor. Here, the PICO positions himself in front of the corridor. Once the PICO is positioned and feels it is safe enough to move, it drive through the corridor to the exit.
Hospital Challenge
[Under construction]
For the Hospital Challenge, the design of the algorithm is divided into four parts: interaction, supervisory, mapping and navigation. Each part has its own functionality and needs to work with the other parts. This functionality is explained below:
Interaction
These are all low-level interactions consisting mostly of calls to the IO API (which represents communication with PICO).
Supervisory
This section covers the governing control logic of the proposed system. The idea is that the supervisor makes choices, tunes parameters, and controls flow-of-command with in remaining code depending on its mode, and changes modes dynamically.
Mapping
Feature Recognition
The Feature Recognition algorithm reads PICO’s laser rangefinder data and recognizes three types of features:
- A corner that is seen in its entirety
- A corner that is seen from one side and inferred
- The end of a wall’s observation caused by occlusion of PICO’s blind spot.
Segmentation
The Feature Recognition algorithm is based on detecting segments of walls. It constructs a line segment and sees if it is a good fit for the data, if not it splits and adapts the segments until everything fits. The end points of the segments are saved as features.
Line Fitting
The segmentation algorithm only finds the first and last point making up a wall, the measurements for these contain noise. To mitigate that noise a line is fitted through all the points making up the wall segment. This is done using a Total Least Squares regression. This looks at deviations in two directions and fits a line that minimizes the orthogonal distance between the points and the line.
Corner Detection
Due to the nature of the segmentation algorithm the segments on opposite sides of a corner do not touch but they are spaced one laserdata point apart. To detect a completely visible corner the list of features is iterated over. If two consecutive features are very close together they make up a corner of type 1. The intersection point of the two regression lines on either side of the corner is then set as the corner’s location.
If there is a jump in the distance between two consecutive features but the angle between them, as seen from PICO, is small the closest of these two features is an inferred corner of type 2. The intersection between the regression line for the visible segment and a line drawn from PICO to the last element of the segment is set as the location of the corner. The other feature is an occluded wall end of type 3.
The first and last features detected sit at the edges of PICO’s field of view, these are always occluded wall ends of type 3. Features of type 3 are not used in the SLAM algorithm.
Corner Identification
In the hospital map that is provided the all corners are labeled. The position and orientation of PICO is provided by SLAM. Using PICO’s localization the coordinates of the map’s coordinates are transformed to PICO’s reference. Then for every detected corner the distance to the map’s corners is computed. If it is smaller than a certain threshold the detected corner gets the label of the map’s corner. If a detected corner can not be matched it gets the label -1. This could occur if there is an object observed that is not in the provided map, like a moving person, or if the localization estimate is incorrect.
SLAM
The chosen algorithm for localizing PICO and updating the map with real-world information is fastSLAM2, with the actual implementation largely supported by online lectures and research by Cyrill Stachniss.
The core idea of fastSLAM (especially in its comparison to normal Extended Kalman Filter (EKF) Particle Filter SLAM approaches) is the concept that the relationship between a robot's motion and sensors, and the outside world, is such that given a perfect model, landmarks will always be in the same position. In a more reduced form, using a particle filter to sample the robot's path, this relationship still holds, allowing one to model the outside world as a list of landmarks with a much more static nature than an ever growing hypothetical map of the outside world (which is what normal EKF filters do). Due to this, the measurement covariance element of a single landmark is nothing more than a 2x2 matrix, which, given that it has to be inverted and the most efficient inversion algorithm is O(n3), is a very big deal.
The core idea of fastSLAM2 is to patch a hole in fastSLAM1 where information is lost. Specifically, in the part of the algorithm that is described as 'sampling the pose' - making a prediction, for a particle, of the robot state in the next measurement iteration - fastSLAM2 does not make use of that iteration's measurements. However, by nature of the above relationship, measurements and odometry data are almost equivalently tied to the robot's behaviour. As such, fastSLAM2 includes measurement data when it predicts a robot's state, which, as the paper linked above explains, dramatically improves performance of the algorithm.
Map Updating
This section covers the system functionalities responsible for (intelligent) navigation. All functions here have read access to the world model’s internal map and LRF envelope. The navigation can be split into two parts: pathfinding and path movement.
Path Finding
For pathfinding, A* is chosen. A* is a pathfinding algorithm based and built on Dijkstra's Algorithm. Dijkstra's Algorithm looks at every available cell all around the start point, until it reaches the goal. A* is smarter, and attaches more value to the cells towards the goal. Because of this, A* needs fewer iterations and is faster.
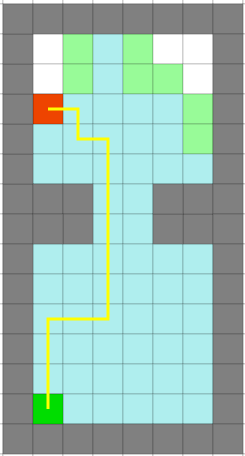
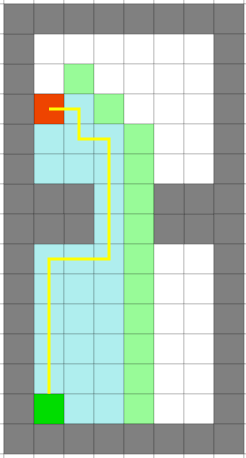
Figure 1: Difference between Dijkstra's algorithm (left figure) and A* (right figure).
Path Movement
Path movement translates the points of the trajectory of the A* algorithm to a vector of necessary x and y speed values for the PICO robot to follow the trajectory.
List of Meetings
| Date/Time | Roles | |
|---|---|---|
| Meeting 1 | 01-05-2020
11:00 |
Chairman: Bas
|
| Meeting 2 | 04-05-2020
11:00 |
- |
| Meeting 3 | 08-05-2020
11:00 |
Chairman: Max
|
| Meeting 4 | 11-05-2020
10:00 |
- |
| Meeting 5 | 12-05-2020
10:00 |
- |
| Meeting 6 | 15-05-2020
11:00 |
Chairman: Dominic
|
| Meeting 7 | 18-05-2020
11:00 |
- |
| Meeting 8 | 22-05-2020
11:00 |
Chairman: Roel
|
| Meeting 9 | 27-05-2020
15:00 |
- |
| Meeting 10 | 29-05-2020
11:00 |
Chairman: Rob
|
| Meeting 11 | 02-06-2020
11:00 |
- |
| Meeting 12 | 04-06-2020
11:00 |
Chairman: Ananth
|
Links
These will probably be invite-based but a backup link could be useful.
Gitlab: https://gitlab.tue.nl/MRC2020/group4
Overleaf design document: https://www.overleaf.com/project/5eabeda72b3e4100010f8b40