Football Table Vision: Difference between revisions
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
<p>This will start the vision GUI, which currently looks like this:</p> | <p>This will start the vision GUI, which currently looks like this:</p> | ||
[[File:Vision_gui1.png|thumb|center|upright= | [[File:Vision_gui1.png|thumb|center|upright=1.0]] | ||
==Basic Settings== | ==Basic Settings== | ||
Revision as of 15:39, 12 September 2013
Building the Vision GUI
In order to build the Vision GUI, you need to install qtcreator and the opencv libraries
sudo apt-get install qtcreator
sudo apt-get install libopencv-dev
This tool runs on both x86 and x86_64 systems, however it is compiled against static libraries from Prosillica. These static libraries have to be specified in the Qtvision.pro file for x86_64:
LIBS = -lopencv_core \
...
../src/pvapi/staticlib/x64/4.4/libPvAPI.a
And for x86
../src/pvapi/staticlib/x86/4.4/libPvAPI.a
To build the GUI press ctrl+B. If it fails to build, install missing libraries using apt-get.
The Vision GUI
To run the vision GUI, you need to have root privileges. After building the vision tool in Qt, the executable should reside in the /Qtvision/bin folder. Start this executable using the provided launcher or using terminal (start using ctrl+alt+T):
sudo su
cd /home/eutaft/foosball/Qtvision/bin
./Qtvision
This will start the vision GUI, which currently looks like this:
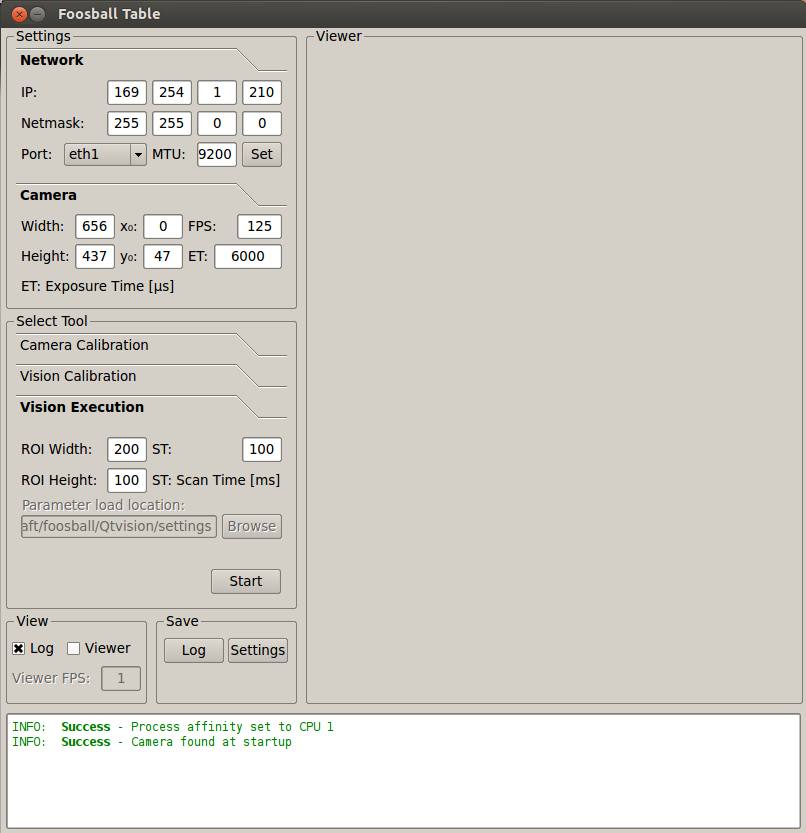
Basic Settings
This GUI allows the user to set-up several basic settings that allow us to connect to the camera.
Setting up the LAN connection
In order to run the vision software, we must first establish a connection with the camera over ethernet. First we need the fix the adress of wired connection we are using the gnome network manager or ifconfig to the following settings:
Address: 169.254.1.210 (manual)
NetMask: 255.255.0.0
MTU : 9200
Setting up basic settings
Network
These settings should be exactly the same as those entered when setting up the LAN connection.
Camera
- Width
- Number of pixels along width of the camera (longitudinal direction of the soccer field)
- Height
- Number of pixels along length of the camera (Lateral direction of the soccer field)
- [math]\displaystyle{ x_0 }[/math]
- Pixel value of the position [math]\displaystyle{ x_0 }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ y_0 }[/math]
- Pixel value of the position [math]\displaystyle{ y_0 }[/math];
- FPS
- FPS stands for Frames Per Second, this is limited by the amount of data that can be sent over ethernet. Higher framerates can be achieved by changing the colormode [insert local link] and the size of the ROI [insert local link]. Setting it too high can cause failure to connect or a crash. More on this can be found in Mark Verrijts report.
- ET
- ET stands for exposure time, this is limited by the FPS.
Camera Calibration
Camera calibration is crucial to achieve good performance.
Vision Settings
Insert Picture here.
Recalibration
Recalibration involves calculating the matrix to undistort the image. To start re-calibration, check the recalibrate box and press start. Now place the checkerboard box, somewhere on the table and wait/re-orient until the checkerboard is properly detected (as shown in the Figure). If it is properly detected click accept and repeat the process. It is good to place the checkerboard in a variety of orientations. The amount of (different) orientations is defined using the Orientations dialog. After finishing
Insert Picture here.
Color Calibration and Mask
Color calibration is done in a seperate, Matlab-based, tool
Insert Picture.