Integration Project Systems and Control 2013 Group 2
Group Members
| Name: | Student id: | Email: |
| Rens Samplonius | 0785119 | r.j.samplonius@student.tue.nl |
| Frank Evers | 0789890 | f.evers@student.tue.nl |
| Juan Guo | 0825223 | j.guo@student.tue.nl |
| Jeroen Lamers | 0771264 | j.w.lamers@student.tue.nl |
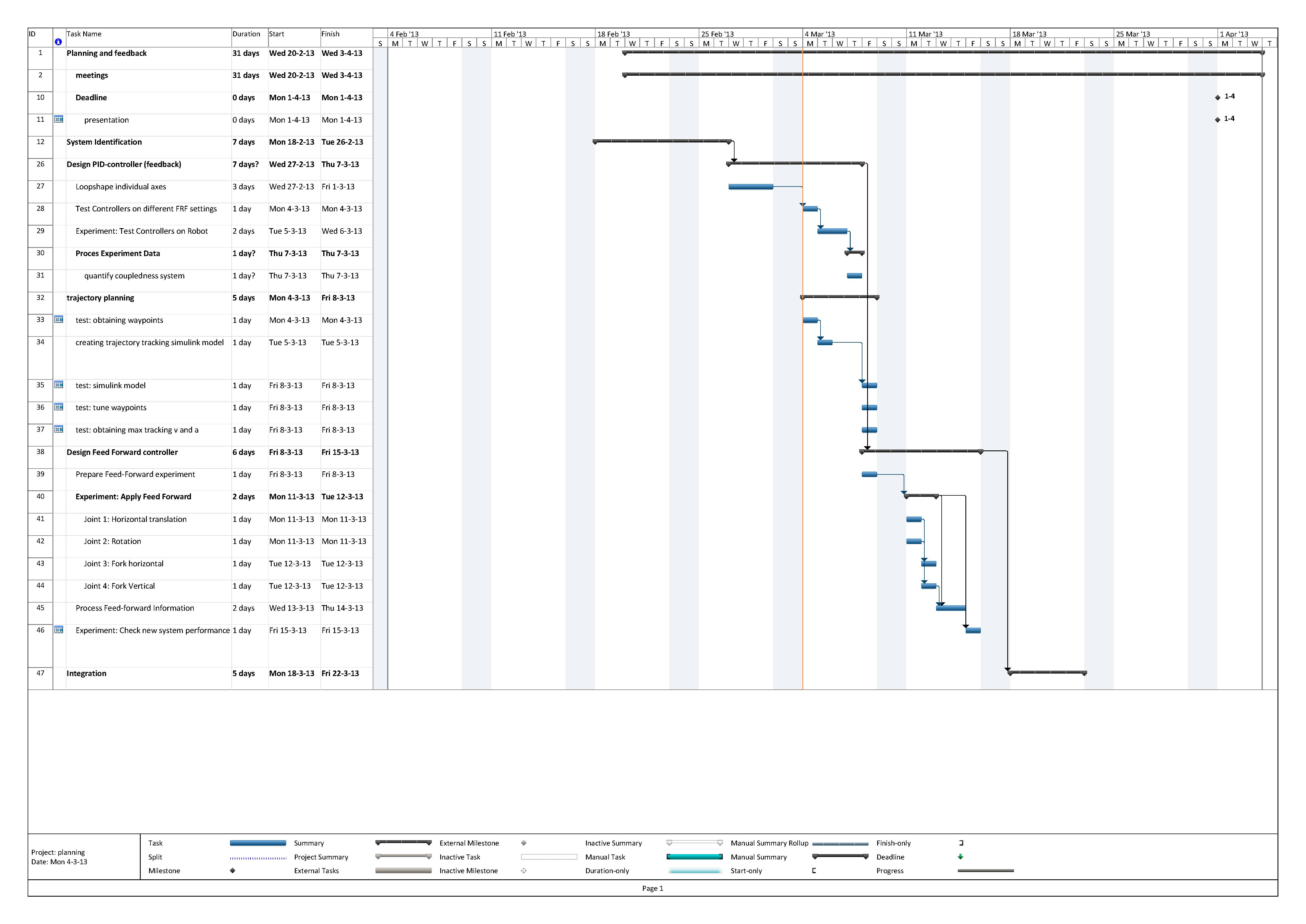
Planning
Progress
Week 1
1) Literature collected and background knowledge reviewed.
2) Control system requirement designed:
<1> All pizzas have to be moved from left to right under 15 seconds.
<2> Reference profile has to optimal in the sense of output [V].
<3> During transport the pizza should remain on the robot.
<4> Controllers design: stability and performance requirement.
<*> Frequency domain
- Bandwidth for complementary sensitivity of individual axis aim for relatively large bandwidth.
- Big cut-off rate the slop of magnitude plot at high frequency of individual axis.
- For open loop, generally we require low frequency high gain and high frequency low gain.
- For sensitivity, we require low frequency low gain.
- Relatively big gain margin and phase margin.
<*> Time domain
- Step or impulse response performance (open loop response), i.e. rise time, overshoot, settling time, steady state error bound.
- Required tracking error individual controller. (Vertical fork x = mm; Horizontal fork y = ..mm; Rotation θ = ..mm; Table translation z = ..mm.)
<5> The complete trajectory has to be splitted in sub trajectories, which have to be executed in the required times. (frank maybe u modify this later.)
<6> Boundary conditions for actuators.
3) Familiarization with the robot.
<1> Initialization of the 4 axis - Vertical displacement of the fork -0.1m; - Horizontal displacement of the fork 0.1m; - Rotation 2.4rad; - Translation 0.2m; <2> Sampling frequency 500Hz <3> Bounds on input range of each motor - Motor 1 -0.625 ~ 6.25V; - Motor 2 -0.625 ~ 6.25V; - Motor 3 -10 ~ 10V; - Motor 4 -10 ~ 10V; <4> Bounds on reference trajectory of the 4 axis - Axis 1 -0.2418 ~ -0.0268m; - Axis 2 0.0231 ~ 0.5301m; - Axis 3 0.0108 ~ 5.5708rad; - Axis 4 0.0694 ~ 0.4494m;
Week 2
1) Obtained FRF measurement on the left pizza robot.
- A closed loop measurement on each axis by applying a sin-wave + white noise to the plant. The sine wave is added to overcome the massive friction. The controller used in the closed loop measurement is tuned very conservative. During the FRF measurement the following data is collected: the input signal (u), the white noise signal (w), and the output voltages (v). With this data we calculated the process sensitivity and the sensitivity and to obtain the plant we divided them (similar as we did during the Motion Control course). We are uncertain if the left and right pizza robots have a similar plant so perhaps we should repeat the FRF measurement on the right robot because that one has the pizza racks on it.
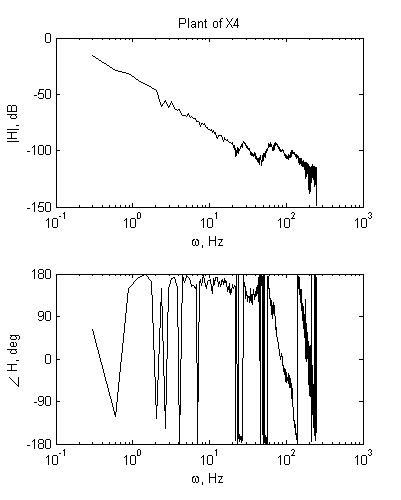
2) Analysis of FRF measurement.
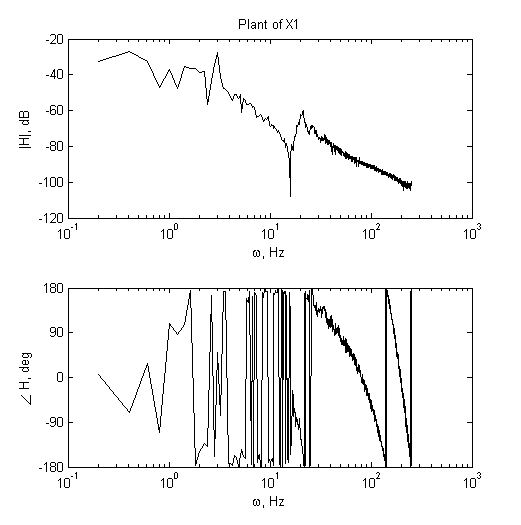
|
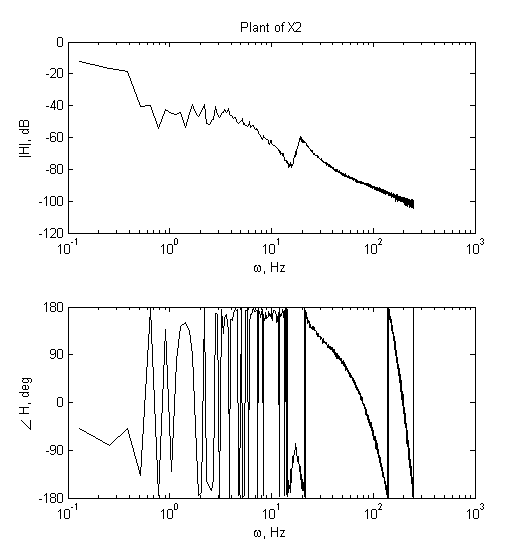
|
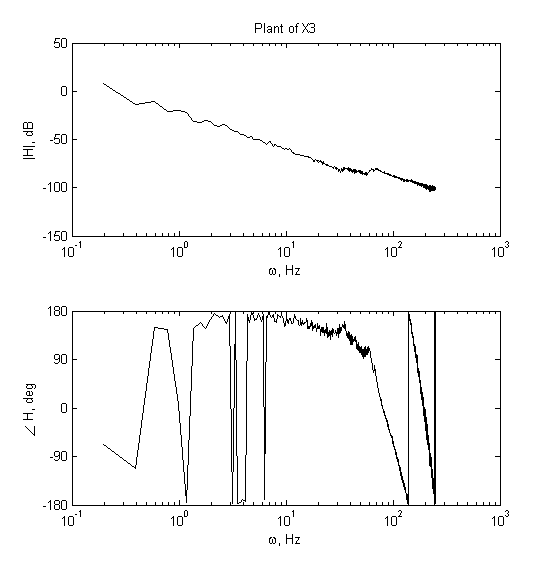
|
|
Week 3
1) Controller chosen.
- We decided to use PID controller to control the pizza robot because we all have the most experience with them. This week we evaluated the FRF measurement data and loaded this in the programme ShapeIt. Because the right pizza robot broke we were not able to do more because we scheduled testing time on that robot.
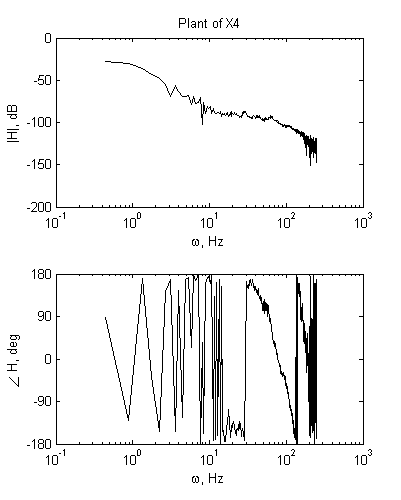
2) Obtained FRF measurements on the right robot.
3) Analysis of FRF measurements.
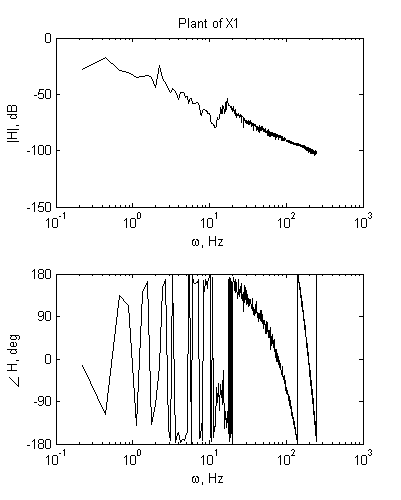
|
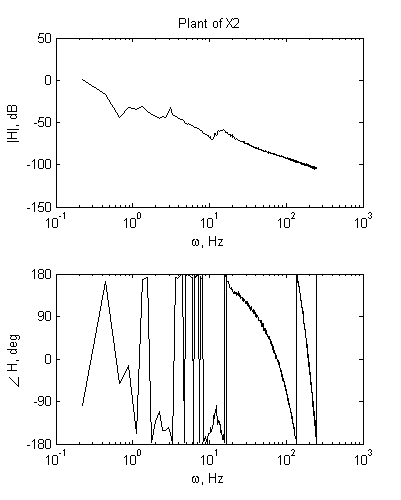
|
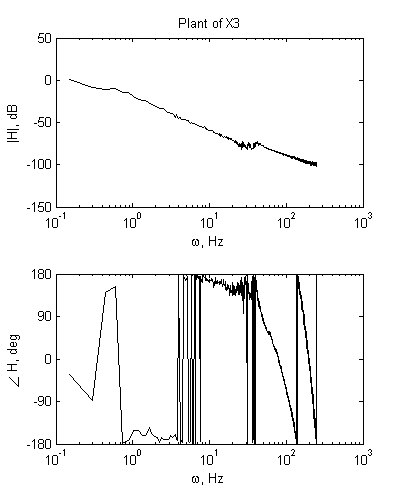
|
|
Week 4
1) PID controller designed using Shapeit.
- We designed four controllers for each axis with a bandwidth of approx. 10Hz.
2) Designed a low frequency PID controller
- We designed four simple controllers without an I-action for the feedforward tuning.
3) Third order "challenging" trajectory designed
- Serveral trajactories are desinged for each axis to do the feedforward tuning.
4) Feedforward controller designed
- In this week we were not able to do the feedforward tuning because of some delay in the design of the "challenging" third order trajectories.
Week 5
1) Obtained locations of pizza shelves
2) Trajectory obtained and controller tested
- We also obtain all the positions to pickup the pizzas. With these positions we start to construct the optimal trajectory.
Week 6
1) Adjust the final trajectory especially the positions from the left shelf to the right one.
- Trivial modifications of the positions on the trajectory. As there aren't so much space for tuning between shelf hands, and the controller designed might have overshoot this tuning part will need to be re-performed after the controller is fixed.
2) Improved trajectory programming
- Combinations of rotation, vertical and horizontal movement of the fork are made.
3) Feedforward controller tuning.