Embedded Motion Control 2017 Group 9
Group Members
| Name: | Student id: |
| Mian Wei | X |
| Zhihao Wu | X |
| Petrus Teguh Handoko | X |
| Bo Deng | X |
| Bo Cong | X |
| Jian Wen Kok | X |
| Nico Huebel | Tutor |
Initial Design
Requirements
➢PICO drives autonomously through maze ➢PICO should find the exit and the whole robot is across the finish line within 5 minutes. ➢PICO is able to deal with approximately axis‐aligned walls, open spaces and loops in the maze. ➢The task has to be finished within 2 attempts in 7 minutes. ➢PICO should not stand still for 30 seconds which counts as an attempt ➢PICO may not touch the wall ➢The whole PICO should stop within 1.3m to a dead end, and detect whether the dead end is a door. ➢PICO should detect every dead it meet ➢At the exit PICO should drive forward for 40 cm ➢The software is easy to set‐up
Functions
The software must have the following functions in order to meet the requirements and fulfill the goal:
| Function: | Description |
|---|---|
| Drive forward | The robot must drive forward unless something, for
example a wall or a corner, is detected |
| Drive backward | The robot must drive a little bit backward if it is unable to rotate |
| Turn left | Make a 90degree left turn |
| Turn right | Make a 90degree right turn |
| Ring bell | The bell must be rang in order to open the door |
| Localize | The robot has to localize itself in the world model, because the
odometry data isn't that accurate |
| Wait | The robot must wait at a dead end in order to check if it is a
door |
Components
The following components will be used to reach the goal:
Sensors
- Laser range finder which uses a laser beam to determine the distance to an object
- Wheel encoders (odometry) to estimate the position of the robot relative to a starting location
Actuators
- Holonomic base with omni-wheels
- Bell to open the door
- Pan-tilt unit for head (which will not be used)
Computer
- Intel I7
- Ubuntu 14.04
Specifications
The goal and the requirements will be achieved with the following specifications:
Robot
- The maximum transnational speed of the robot is 0.5 m/s
- The maximum rotational speed equals 1.2 rad/s
- The corridor challenge has to be solved in 5 minutes
- The maze challenge has to be solved in 7 minutes
- Both challenges have a maximum of two trials
- The laser range finder (LRF) has a range of 270 degrees
- The wheel encoders have an unknown accuracy
- The robot must not be idle for more than 30 seconds
Maze
- The corners will be approximately 90 degrees
- The wall distance is 0.5-1.5 meter
- There is only 1 door in the maze
- The door starts opening in 2 seconds
- The door opens if the robot is within 1.3 meter of the door
- The door is open in 5 seconds
- The number of rings must not be larger than the number of potential doors
- The maze may contain loops
- The maze can contain dead ends
Interfaces
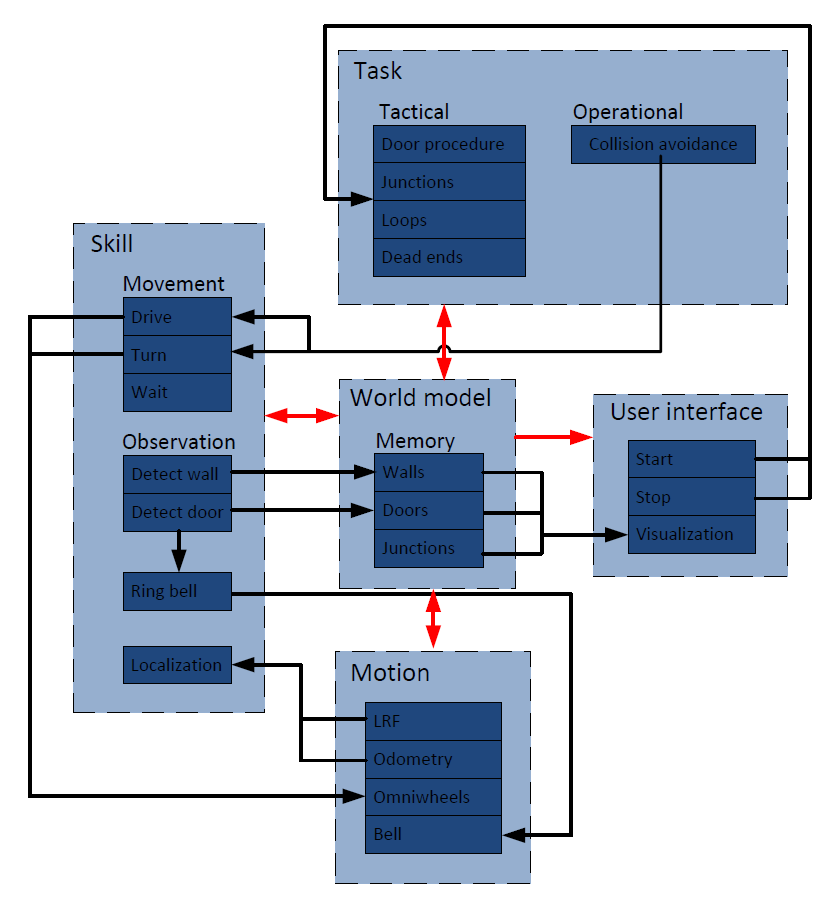
The main relations between the interfaces are colored red and can be described as follows:
World model -> Task:The world model can give information about taken paths to the Task
World model -> Skill:The stored observations in the world model are used for movement skills
World model -> Motion:The world model can give data to the actuators
World model -> User interface: The user interface needs the data from the world model to visualize the world model to the human
Task -> World model:The task needs to store information about paths in world model
Skill -> World model :The world model is build from observations
Motion -> World model :The motion can give sensor data about the position to the world model