PRE2016 3 Groep3
Group 3: Railway Maintenance Robots
- 0902228 | Lindsey van der Aalst
- 0938349 | Thomas Bastiaansen
- 0948949 | Micha van den Herik
- 0939318 | Tim van Leuveren
- 0855969 | Job van der Velde
- 0941574 | Floris van der Velden
Week 1
Introduction
Delays with the trains are a common complaint of most people, and the company Dutch Railways (‘Nederlandse Spoorwegen’) takes a lot of the blame. Some of the delays are caused by small objects positioned on the tracks or the condition of the railway tracks by itself. As a result, the train’s stopping distance increases by big margin. For this problem, a small robot is designed to minimize these problems. It will check the tracks for snow and leaves and use laser technology to free the tracks of these things. Not only that, it also detects the wear and will ultimately also maintain the condition of the tracks.
USE Aspects
User: NS
Could be an expert knowing all the in’s and out’s of the machine. But in general, it is the NS themselves. Efficiency is important for the User. The machine will need to have the ability to move at the same speed as standard NS trains and be able to remove obstacles, leaves and snow when needed, as well as detect any wear on tracks and railway switches. The machine should not conflict to much with the current situation. The Netherlands already has one of the most tight packed schedules in the world, with single delays often causing a chain of delays. The machine should work between (or outside) this schedule, else it will not have any benefit. The main purpose of the machine is to prevent delays and when it is not able to fit in the current schedule, it will only cause more delays. The machine should be easily operable. However, since not everyone has to use this machine, easily operable is not high on the priority list.
Society: Train travelers
Delays can occur due to many reasons, for example tracks that are in need of reparation, or bad weather conditions. Train travelers want to get from point A to B as quickly as possible, delays don't add to the train traveling experience. By the use of an automation machine, which can detect and remove obstacles that cause delays, train travelers can get from A to B more quickly. Time always translates to money, and for all three USE aspects money is on the priority list.
Enterprise: ProRail
As mentioned in User, efficiency is important for both the User and Enterprise. The enterprise is also held partly responsible for the delays and thus they would like to prevent them as much as possible. Also, the Enterprise want the machine to be most profitable as possible. The cost of the machine is then also desired to be as low as possible, while still doing its tasks. It should be reliable because failure can lead to even larger delays or train accidents, which in turn lead to larger costs. It has to be cheaper than the ways used currently or it should weigh up to the costs of the delays, else it is not profitable investing in it. Most of the arguments mentioned in User and Enterprise will overlap. In our case, we will be more focusing on the Entrepreneurial side of ProRail.
Our focus
Our main focus for this project is on the Enterprise, ProRail, and a little bit on the User, NS, since these two have quite some things in common. To us, the most important aspects are efficiency, reliability and costs of the machine and these aspects go best with the Enterprise. We would like the machine to be reliable and efficient, while keeping the costs as low as possible. Our focus lies here because there are already some systems that are able to do (part) of the jobs we want to achieve. But we would like to combine them and make them better. And for our product to be of any interest to the Enterprise, the costs must be low. At least lower than what is currently spent on these activities. But we will not only focus on production costs, also, the maybe a bit more transparent, indirect costs of the machine. Like for example when the machine is broken and thus non-operable, it will cost money. If the machine is slow, it will cost money. These 'costs' are taken into account under the aspects reliability and efficiency respectively.
Objectives
- Functions at the same time as other trains are in use (same speed as the trains)
- Detection wear of tracks
- Rust
- Cracks (ultrasonic?)
- Dimensions & shape
- Maintenance of tracks;
- Removing snow, using a laser
- Removing leaves, using a laser and compressed air/shovel
- Removing rust, using a laser
Side Objectives
- Not have much wear of itself on the tracks
- Charge in front of the trains for optimal use
- Modular ‘carts’ -> different equipment for different tasks
- Additional detection: Condition of welds, fasteners, sleepers and ballast, temperature of railway
- Possible detection of railway track geometry using gyroscope. (heavy maintenance required for readjusting railway track geometry)
Extensions
- Good for the climate and environment.
Approach
- The focus lies on the User and the Enterprise, which are the NS and ProRail, respectively. Especially the Enterprise aspects are important for this system. This means that the system needs to be efficient, sustainable and that the production costs need to be as low as possible while still remaining quality.
- Research has to be carried out about state-of-the-art technology. For example, one of the recent developments in railway technology is a laser which can remove leaves from the railway tracks [1]. We will also implement this technique into our system. Also, currently a monitor has been developed to check the condition of the tracks [2]. This technique is used to measure the cross section without contact. This technique could possibly be used for our system.
- A literature study will make clear if our idea is really innovative and unique. We will also do research about how the system needs to be designed, what the most efficient form is, how it needs to be loaded, etc.
Week 2
https://drive.google.com/open?id=0B8ju55_U5nZ4LWRLalRCbkMxVlU
The above link guides you to our Gantt chart, which has been made with the help of the program "Microsoft Project". We have divided our plan into research, prototype and requirements, and deliverables. First, we’ve described the milestones and the date on which they have to be accomplished. After that, we’ve split up these milestones into different tasks and allocated people to these different tasks, as can be seen in our Gantt chart.
Our planning can also be seen below, where the milestones are boldfaced:
Gantt chart (Job + Lindsey)
Planning & task division 15-02
Explanation focus enterprise (Floris)
Current expenses maintenance & disturbances (Floris)
Define exact problems & suggested solutions (Micha)
USE aspects & problem definition 20-02
Technology competitors in maintenance & problem detection (Tim)
State of the art technology for robot design (Job & Thomas)
Own approach railway switch maintenance (Tim)
State of the art 20-02
Interview NS 22-02 (Floris & Job)
Define prototype & specifications 20-02
Define requirements & specifications 28-02
Propulsion system (Floris & Tim)
Sensors (Job & Micha)
Maintenance equipment (Job & Micha)
Power supply & charging (Floris & Tim)
Link to train (Thomas & Lindsey)
Communication to head station (Thomas & Lindsey)
Interface (Thomas & Lindsey)
3D model (Floris & Job)
Localisation of self and trains and other robots (Micha & Lindsey)
Weather forecast integration (Tim & Thomas)
Sensor feedback integration (Tim & Thomas)
Hardware & software 14-03
Summary of expenses (Floris & Lindsey)
Budget 17-03
Functionality Robot (Job & Tim)
Use of robot (Micha & Thomas)
Future extensions/upgrades (Micha & Thomas)
Functionality, use and future adaptation 27-03
3D Model (Floris & Job)
Reflection USE aspects (Thomas & Lindsey)
Deliverables 30-03
Final presentation/demonstration 03-04
Peer review
Disturbances
There are many different causes for the disturbances in the Dutch railway system. From january 2011 until february 2017, 15110 disturbances were reported. Shown in Graph 1, the most common disturbances are accordingly [3] :
- Faulty train (2279 disturbances, 15,1%)
- Signal interference (1640 disturbances, 10,9%)
- Railway switch failure (1593 disturbances, 10,5%)
- Collision with a person (1498 disturbances, 9,9%)
- Repair work (691 disturbances, 4,6%)
- Previous disturbance (529 disturbances, 3,5%)
- Signal and handle failure (450 disturbances, 3%)
- Signal and railway switch failure (390 disturbances, 2,6%)
- Power outage (388 disturbances, 2,6%)
- Level crossing failure (320 disturbances, 2,1%)
- Miscellaneous (5346 disturbances, 35.3%)
The miscellaneous disturbances consist of both the weather and external factors, which consist of rare disturbances such as theft or vandalism of the copper in the railway tracks, people or animals close to the railway tracks or roadside fires [4] . Concerning the weather, it can have a big impact on the train schedule as the different seasons in the Netherlands all influence the schedule.
On the one hand, there is the turbulent weather in the fall and winter. Leaves are a well-known problem in this time of year. But actually, the main problem is not the leaves, but actually the smoothness of the railway track. The leaves and rain together results in a mush, which makes the tracks more slippery, which on its turn the grip of the train wheels decreases. As a result, the circular shape of the wheels changes and they need to be repaired. In addition, the stopping distance increases exponentially, which has to be accounted for [5] . Snow and ice, next to the slipperiness of the railway track, also cause the railway switches to freeze or get blocked by the snow and ice.
Not only the cold, also hot temperatures can have impact on the railway tracks. Due to the increase in temperature, the steel stretches which causes the tracks to bend. The railways are then unusable to be driven over by a train.
With the railway maintenance robots, the disturbances concerning the railway switches, the weather and a part of the repair work are planned to be solved. These three different disturbances cover a notable part of the total disturbances in the Dutch railway system. Assuming a high efficiency, the railway maintenance robots could potentially prevent a great part of these disturbances, resulting in thousands less disturbances over the researched period.
Detection
Detection is a great part of the railway maintenance robots. Therefore, the railway maintenance robots need to be equipped with numerous sensors in order to determine things of and on the railway tracks. These include the leaves, rust and snow, the profile of the tracks, and the temperature.
Detection and removal of leaves, rust and snow
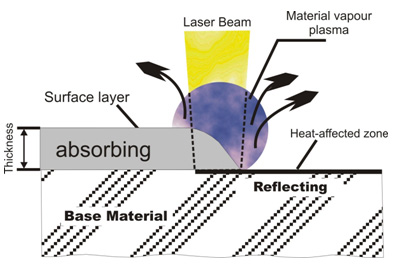
One of the aspects of the railway robot is to perform maintenance on the tracks. The focus herein lies with removing rust, snow and leaves. All of these tasks are possible with state of the art lasers. According to Oliver Smith [6] leaves on railway tracks alone are cause for 5800 hours of delay per year for the British National Rail. A special microwave ray has already been found to be effective in removing wet leaves from the tracks, but further research on using lasers for this purpose is still being conducted and is estimated to be even better.
In the car industry a handheld 1000-watt rust removal laser is already available [7] . This laser is able to remove rust, dirt, coatings and paint in mere seconds. The laser works by adding its energy to the dirt/rust layer, which evaporates, while the base material reflects most of this energy, thus remaining unaffected [8] .
Ice and snow can also be removed by adding laser energy. The patent of Roger and Rose Vega describes an ice removal system for airplanes [9] . The laser vaporizes the ice by moving slowly over the covered surface, thereby re-exposing it.
These three different laser technologies could be combined for all three maintenance purposes since the basic principle for removing the unwanted substance is the same, after which it could be mounted on a railway robot.
Profile detection
A problem with the railway can also be that is shifts in the cobblestones on which the track is placed. The track can be shifted into the cobblestones, resulting in a height difference between the two tracks. Currently, to detect whether or not the railway has shifted, is detected by a railway constructors themselves when checking the normal maintenance planning. This can be done quicker and more efficiently than what the current plan of action. With the use of a gyroscope inside of the monitor machine, the angle of the train can be measured. Also with the help of a device which measures velocity, the position of the vehicle along the track can be determined with an analog to digital converter. Moreover, a whole digital implementation can be made of the track (and if done accordingly, compared to what the original geometry of the tracks has to be. This process can save time, since it is all done digitally instead with the use of humans on only small portions of the track. The vehicle which will detect the geometry can move at higher speeds, and process the data immediately. Comparing the processed date digitally will also make the comparison more accurate than what humans can make of certain parts of railway tracks [10]. An improvement of what the can be digitally implemented of the geometry of the total railway, the same type of measurement can be used to measure the wear and profile of the railway. The old method involved physical contact with the railway and was only able to measure the geometry and undulation of the railway (should a certain threshold be achieved, maintenance workers will have a closer look on the railway). With the new laser method these same parameters, as well as more important ones such as wear and profile of the railway, can be measured. The new innovative approach used, is based on image analysis and processing to reconstruct the whole track profile digitally (just like the geometry measurement). The railways reflects light back into cameras which can detect lasers and can internally process this data. The data will then be converted to a 3D projected image of the track. Using this technique, no extra wear will be made to the railway while measuring the wear. Moreover, the measurements can be done more quickly, since all the data is processed while the vehicle is moving over the track. Using a high-performance architecture, a big amount of information can be processed in a smart and fast method, since it is not possible to constantly store all the images and process them offline (for example with the use of pipelining and parallelism). Also, the use of high-level image analysis avoids the need for continuous and accurate alignment of the monitoring system with the track. The image processing method can be designed in such a way, that it can self-align itself (for example with the combination of the gyroscope as mentioned above) [11].
An example of where profile detection is already used, is the RailMonitor. To detect the wear of the railways the railmonitor will be implemented on the railway maintenance robot. The railmonitor is a mobile measuring system which can measure the cross direction profile of the railway tracks [12]. This system uses a laser for the measurements and stores these measurements internally. Some special software will then compare the measurements with the references for cross direction profile and draw conclusions accordingly. The results are also shown immediately on a screen on the device itself. For the implementation of this system on the railway maintenance robot some features will be improved. Such as the communication of the measurement result immediately to the headquarters instead of storing it in the device itself. Also the screen will be unneeded.
Temperature
This technique is especially useful during wintertime because these switches causes many disturbances during wintertime. The switches can freeze and can become clogged. To prevent the railway switches to freeze and become clogged there is a heating system built into the switches which can heat the switch when the temperatures drop below zero degrees Celsius. However this system does not always work and this problem is hard to detect in time. Therefore the railway maintenance robots need to be equipped with an infrared camera, in order to detect the temperature difference between the switches and the straight parts of the railway tracks.
Drone Tests [13] [14]
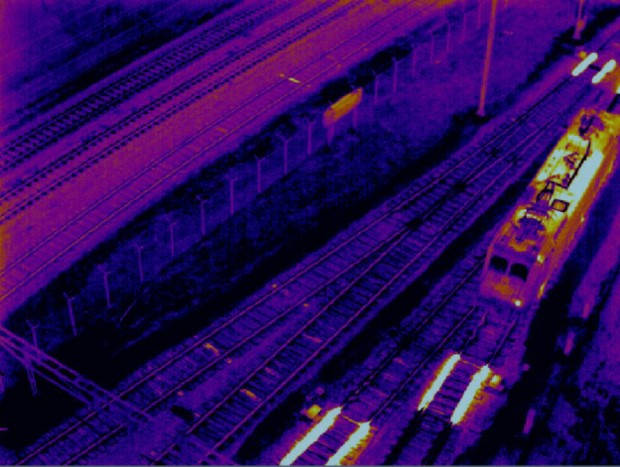

In order to check the heating of the railway switches, ProRail currently uses unmanned helicopters equipped with an infrared camera. This camera can detect whether the heating system is operating or not.
In this picture it is seen that the heating system is working properly. The infrared images provide ProRail with information over the switches and ProRail can act accordingly. The railway maintenance robot will use this technique for which the drones are used now. In order to detect the temperature difference, the infrared camera needs to be placed on a certain height to take proper pictures.
Felix
Felix is the first mobile robot for inspecting railway switches [15]. This robot is equipped with profilometers which create a 3D reconstruction of the inspected switch. This is a useful robot to increase the reliability of the railway switches but can only be used for inspecting these switches. The railway maintenance robot can do this either and can be deployed for other tasks such as cleaning the railway. It can also inspect the railway itself along with the railway switches.
Current Expenses
It is hard to determine the exact cost of the trouble caused by weather conditions, because total amounts spent on maintenance are given but specific amounts, like the ‘cost’ of snow, is not to be found anywhere. Also, these costs are hard to estimate. These costs are not linear compared to the occurrences, meaning each disturbance costs the same amount of money.
The total maintenance costs can be found in the year overview of ProRail, and because ProRail is under partial supervision of the Dutch government, their year overview is public and can be found on their website. The year overview for 2016 has not been published yet, so all data used is from 2015 [16].
In 2015, ProRail received €1.098 million to spend on maintenance and management of tracks, this is a little bit more compared to 2014. They spent €950 million. From this money, ProRail spent €139 million on large-scale maintenance and €269 million on small-scale maintenance. Large-scale maintenance is the maintenance needed to ensure reliability and quality in the medium-long to long term. This includes for example polishing the tracks or preparing the tracks for the winter season. Small-scale maintenance includes all the maintenance needed to ensure availability and safety, as well as incidental maintenance. This is more short-term maintenance. Examples of these are inspections or replacing of (small) components.
ProRail also spent €154 million on managements. Their year overview states this was largely used on ICT services, of which some are used to detect problems in advance. To us, the large-scale maintenance costs are of most use, since they cover the weather conditions. The management costs could be of some use but are not our priority. When our machine can detect problems on rails in advance, some ICT systems will not be needed anymore. This can be a huge cost saver, because in 2015, ProRail invested €60 million these ICT systems to prevent disturbances.
Week 3
Current focus of ProRail
To find out what will be important properties for our robot we have to find out which aspects ProRail prioritizes. Part of this can be found already and for the other part we will try to contact ProRail themselves to hear from them personally what they focus on.
As they mention themselves in their year overview for 2015, they care a lot about efficiency and low costs, both in management and maintenance. For each decision, they take social, environmental, and economical aspects into account. And, as they state themselves, they try to be as transparent as possible and incorporate views from all their stakeholders [16].
Also, because they are under supervision by the Dutch government, the Ministry of Infrastructure and Environment monitors the focus of ProRail, sending them a yearly ‘priority letter’. This letter gives ProRail the main outline the government wants them to pay extra attention to.
Sensors
Localisation & Communication
Localisation
There is already a system that reports the position of the trains to a Radio Block Centre (RBC). This system is the European Train Control System (ETCS), which is part of the European Rail Traffic Management System (ERTMS). Trains in Europe are carried out with GSM-R, which has, amongst other functions, the ability to report the position of the trains, for example after a specific time interval or after passing a specific location, but also on request. On top of reporting the position, it also reports things like the estimated speed, the direction of train movement and train integrity information to the RBC [17].
Thus, our robot can be integrated into this system by implementing GSM-R on it. This systems makes sure that the robot doesn’t collide with other trains or robots and it also keeps track of on which parts of the railways our robot has already been [18] .
Weather
The above specified system could be extended by a weather forecast system. This means that information about the weather will be send to the robot via the GSM-R, in the same way as data about the position of other trains and robots will be send to the robot. By involving a weather forecast system into the ETCS, the robot knows where to scan for leaves and snow and, if present, remove the leaves and the snow.
Week 4
Communication to the head station
Current train network:
The robot must be integrated to the GSM-R (Global System for Mobile communications – Railways) network.
See Localisation (week 3).
GSM-R arranges, amongst other things, data communication between the train and the Radio Block Centre (RBC). When the train or the robot passes a balise (an electronic beacon or transponder placed between the rails of a railway), information about the train or robot will be send to the RBC. This information includes the speed and location of the train or robot. The RBC can also send information to the train or robot, for example permission to enter the next track [19].
Weather forecast integration and sensor feedback integration:
Information about the weather must be sent to the robot through the GSM-R.
See Weather (week 3).
Information about the weather will be sent to the robot via the GSM-R, in the same way as data about the position of other trains and robots will be send to the robot. However, the information about the weather must be taken from the internet, which means that the Internet of Things must be involved in order to gain information about the weather.
The robot must be able to react on the information it acquires through the GSM-R.
The robot receives information about the weather and information about other trains and robots through the GSM-R.
-Weather
See Weather (week 3).
By involving a weather forecast system into the GSM-R, the robot knows where to scan for wet leaves and snow/ice and, if present, remove the wet leaves and the snow/ice with laser technology.
-Information about other trains and robots
Information about other robots can be used to optimize the efficiency of the robot. For example, if a robot receives the information that another robot has just scanned the tracks on which the robot is driving for rust, it would be inefficient to scan these tracks again for rust.
Since the robots will be linked to trains during the day, the robots themselves don’t have to react on delays or malfunctions about other trains in order to prevent collisions. Namely, the trains to which the robots are linked will already receive this information and their schedule will be adjusted to this. It follows then that the schedule of the robots will also be adjusted, since they are linked to the trains.
During the night, the robots will work autonomously and they will not be linked to trains, which means that they have to receive information about the location and speed of other robots to prevent collision and react on this.
The robot must be able to react on the information it acquires through the sensors.
It is already described above how the robot will react on the information about wet leaves and snow/ice. This means there are three types of information left that the robot can receive through sensors, namely information about rust, wear or flaws in geometry. If there is rust detected, laser technology will be activated in order to remove this rust. If wear or flaws in geometry are detected, the robot must report this to the RBC via the GSM-R. The RBC can then decide to take action to solve this.
Week 5
Week 6
Week 7
Week 8
Sources
- ↑ Smith, O. (2016). No more commuter misery? Trains fight leaves with lasers. Retrieved from http://www.thememo.com/2016/09/12/train-leaves-leaf-zapping-trains-rail-safety-and-standards-board-are-arming-up-with-microwaves-and-lasers/
- ↑ ETS SPOOR B.V. (n.d.). Railmonitor. Retrieved from http://www.etsspoor.nl/producten/meetapparatuur/railmonitor/
- ↑ Statistics about railway disturbances in the Netherlands. Retrieved from https://www.rijdendetreinen.nl/statistieken/
- ↑ Different kind of disturbances around railway tracks. Retrieved from https://www.prorail.nl/reizigers/storingen-op-het-spoor/
- ↑ Article about leaves on the railway tracks. Retrieved from http://www.metronieuws.nl/nieuws/binnenland/2016/11/die-rot-blaadjes-op-het-spoor-waarom-doen-ze-niets/
- ↑ Smith, O. (2016). No more commuter misery? Trains fight leaves with lasers. Retrieved from http://www.thememo.com/2016/09/12/train-leaves-leaf-zapping-trains-rail-safety-and-standards-board-are-arming-up-with-microwaves-and-lasers/
- ↑ Sorokanich, B. (2016). This Hand-Held Laser Makes Rust Literally Evaporate. Retrieved from http://www.roadandtrack.com/car-culture/classic-cars/videos/a30597/best-rust-remover-laser/
- ↑ P-Laser (2017). Laser cleaning applications. Retrieved from http://www.p-laser.com/applications_detail.aspx?AGUID=1f846979-8fea-4745-bcea-663800c027e5&LGUID=8565a502-c109-43ef-b1a1-dfba5f3edbf6/
- ↑ Vega, R. et all (1990). Laser ice removal system. Retrieved from https://www.google.com/patents/US4900891/
- ↑ Paper geometry railways. Retrieved from http://crema.di.unimi.it/~fscotti/ita/pdf/Scotti02.pdf/
- ↑ Paper wear railways. Retrieved from https://docs.google.com/viewer?url=patentimages.storage.googleapis.com/pdfs/US6218961.pdf/
- ↑ Railway monitor. Retrieved from http://www.etsspoor.nl/producten/meetapparatuur/railmonitor/
- ↑ Drones with infrared cameras 1. Retrieved from https://www.prorail.nl/nieuws/proef-met-drones-controleren-wisselverwarming-met-infraroodcamera-s/
- ↑ Drones with infrared cameras 2. Retrieved from https://tweakers.net/nieuws/86694/prorail-zet-drones-in-om-verwarming-van-wissels-te-controleren.html/
- ↑ Railway switches inspection robot Felix. Retrieved from http://research.loccioni.com/en/robotics/felix/
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 Jaarverslag 2015, ProRail. Retrieved from http://www.jaarverslagprorail.nl/FbContent.ashx/pub_1000/Downloads/ProRail-jaarverslag-2015.pdf/
- ↑ Europees Spoorwegbureau. System Requirements Specification (SUBSET-026). Paragraaf 3.6.5. Retrieved from http://www.era.europa.eu/Document-Register/Pages/Set-3-System-Requirements-Specification.aspx
- ↑ European Rail Traffic Management System (ERTMS). Retrieved from http://www.railway-technology.com/projects/european-rail-traffic-management-system-ertms/
- ↑ Clear CinCom. GSM-R: What Is It, And Why Does It Matter? Retrieved from http://gsmr-info.com/