PRE2023 3 Group7
Pill dispensing robot
Team and interests
Quinten Liu, 1842471, q.m.liu@student.tue.nl
Fenna Sigmond, 1696947, f.e.sigmond@student.tue.nl
Thijs Frints, 1441523, t.g.g.frints@student.tue.nl
Daniel Joaquim Ho, 1534254, d.joaquim.ho@student.tue.nl
Sven de Gruyter, 1857657, s.d.gruyter@student.tue.nl
Sjoerd van de Goor, 1557815, s.v.d.goor@student.tue.nl
Interests:
- Medical Imaging
- Physical product
- AI
- Tangible / functional product
- Danger detection or prevention
- Healthcare or elderly care
Meetings
Introduction
Problem Statement
Target Audience
We really need a general introduction and problem statement of sorts before this part
Our proposed pill dispensing system should offer help for individuals struggling with the complexities of long-term medication management, which is a wide group. The limitations of our product and the needs of different subsections within this group helps us find a target audience that encompasses a wide range but still limited set of individuals that our product will be able to help.
Problems and potential solutions
Poor medical adherence is a serious and widespread problem, we can find the limitations of our system by looking through the facets of patients’ and caregivers’ problems, proposing how our system might be able to solve them and finding flaws or difficulties.
One of the most common problem patients face is forgetting to take their medication at their prescribed times. Our product will be able to notify users about their medications when they have to take it, thus helping them in this regard. In cases that the user ignores or misses these notifications our system does not have the means to make them do it anyway. Similarly, if the patient has a lack of motivation, as patients with depression or anxiety can cause them to dismiss their medication against their interest, then our product can’t force them.
To partially solve this, our product could be able to detect whether or not the patient has actually taken the pills from the dispenser, to notify them again in case they missed the last notification or to notify a caretaker about the situation, but this still cannot confirm the patient’s cooperation as a very forgetful patient could take the medication, put it somewhere else and forget it again. Additionally, an uncooperative patient could purposefully take the medications only to throw them away as to look like they took it. The features and systems needed to circumvent this issue are currently still conceptually too complex to incentivize delving into them. This is thus our product’s main limitation.
The complexity of medication regimens also plays a role in the medical adherence of a patient. If a patient has trouble with a complicated schedule with multiple medications taken at different times of the day, in different conditions and in different ways, etc., the patient will be more prone to human error. This issue is exacerbated in the case of a caregiver taking care of multiple patients with these kinds of medication regimens. Our product solves this by storing this schedule so that neither the patient nor the caretaker need to rigorously remember it. This ability to store complex schedules however, will be limited, as there will always be medication regimens too specialized and complicated to manage for a simple scheduler.
Another issue regarding medical adherence is the lack of information about the medication, consequences of not taking them and side effects. A patient may not fully understand why they need to take their medications or the potential consequences of not adhering to their prescribed regimen, and some medications can cause (unpleasant) side effects, which may lead patients to skip their medication without consulting their caregiver or healthcare provider. This uneducated group is a subsection of the previously mentioned group of uncooperative patients. Our product aims to solve this issue by being able to inform the user, with the user being able to ask questions about the medicine they are taking and the system looking up answers from a database.
Found target audience
Included target audience
Our product will aim to help people who are experiencing challenges regarding medication adherence, either due to forgetfulness, human error or a tendency to de-prioritize their medication regimen, or due to a lack of understanding or fear of adverse reactions. The product should also help caretakers and healthcare providers involved in the medication management process via notifications and updates about the patients medical adherence.
Excluded target groups
It’s important to keep in mind that our product is not targeted towards people who willingly choose not to adhere to their prescribed medication regimen despite understanding its importance. These patients will not benefit from the reminders or information provided by our system if they are intentionally uncooperative. Additionally, if a patient has a highly specialized and complex medication regimen, where our system cannot adequately address the unique conditions and complexity, the product may not be suitable for them.
Product Overview
A robot which dispenses pills on a specific schedule and can inform about and answer questions about medical usage, which may be interacted with by speech, and buttons, and which talks back and provides subtitles on the spoken texts using a screen.
Preliminary Functional Requirements
Software
- AI integration to understand speech
- AI integration to process natural language inquiries about medicine in the specific context of the patient
- AI integration to process natural language outputs to spoken language
- Software to memorize and on time inform about medicine intake
- Remember which medicine was taken
- Admin-client distinguishment in access to schedule
Hardware
- Easily swappable medicine cartridges for about 4 types of medicine
- Dispensing function
- Speaker, screen, microphone, buttons
- Small and light
- Probably stationary
- Non-intrusive
Informal planning
| Week 1 | Week 2 | Week 3 | Week 4 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Literature review + summaries
Relevant groups’ work |
A
|
Literature discussion
Functional requirements Target audience & problem |
A | Designing
Preliminary software Components + feedback + order needed |
Finalize components
Software prototype 3D modelling of product |
||
| Week 5 | Week 6 | Week 7 | Week 8 | ||||
| Software done
Assembly done 3D Printing done |
Iterate on software or add app
Solve problems |
Solve problems
Prepare presentation Begin cleaning up wiki |
Present
Clean up wiki |
||||
A = All, Q = Quinten, F = Fenna, T = Thijs, D = Daniel, Sv = Sven, Sj = Sjoerd
State of the Art
Available Products on the Market
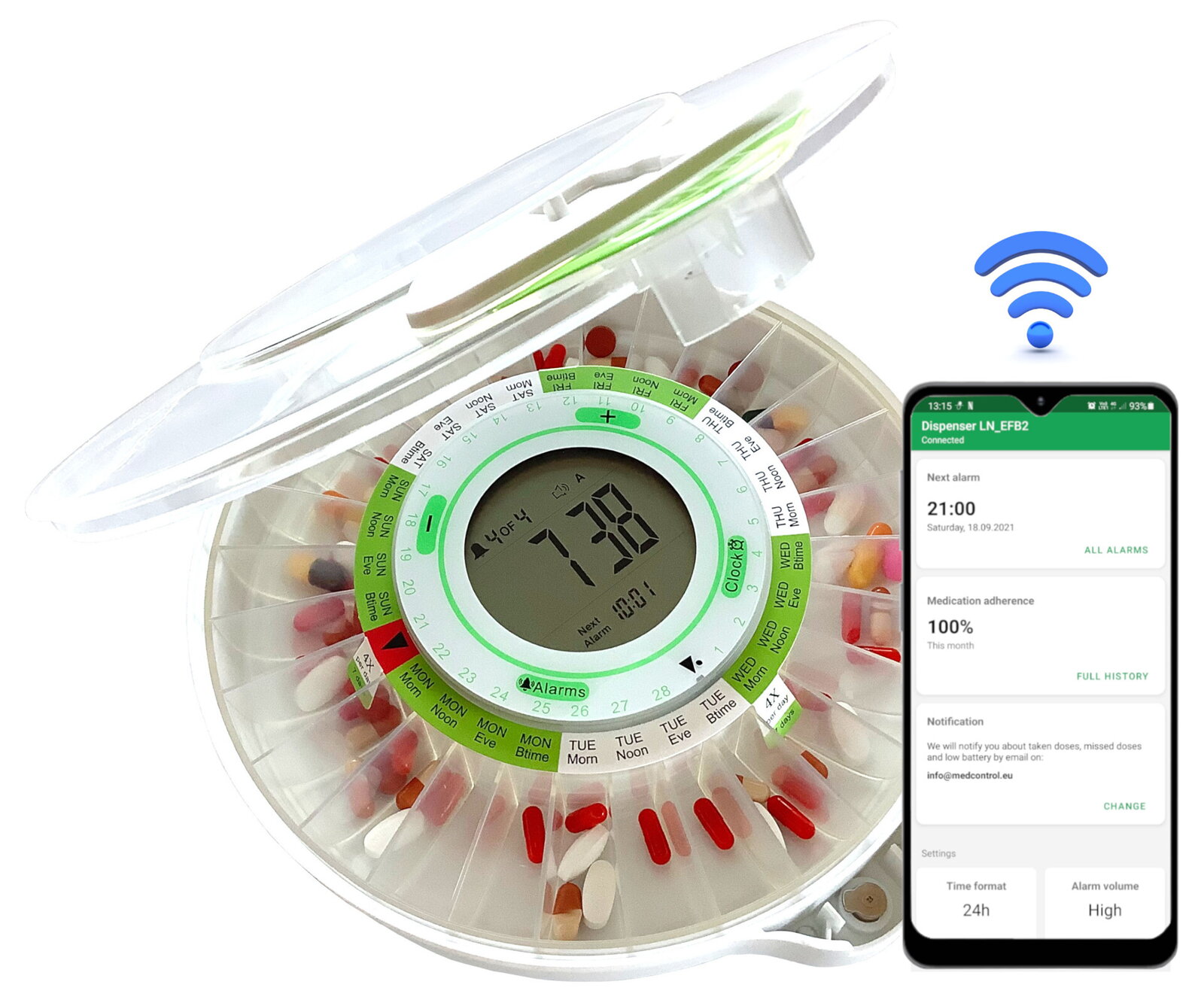

When it comes to the state of the art of medicine dispensing, there are currently two types of solutions: passive and active. The passive solutions are the standard pill boxes that allow the patient to sort the medication into smaller compartments based on which day the medication needs to be taken. Active solutions are the autonomous solutions that dispense medication, notify the patient, and even notify the caregiver when medication should be taken. This project aims to implement an active medication solution.
The passive solution comes in a variety of options, usually being a plastic container with sub-compartments for the storage of medication. These are the more traditional pill boxes, where the user needs to sort the medication beforehand into the correct sub-compartments. This type of solution tends to only hold enough medication for a week, requiring the containers be refilled and medication sorted every week by the user, where human error could play a role. This solution does not include any form or reminders, rather a container of all the medication that should be taken at a specific time. This still requires the user to remember to take the medication.

The alternative is an active device, of which there are two alternatives: DoseControl[1] and the Hero Smart Dispenser[2]. The first device, DoseControl, is a radial pill box that can remind the user to take their medication. The medication still needs to be sorted into their respective compartments, and the time of medication intake set. However, once that is done, the device will rotate the medication compartments such that the next compartment is aligned with the dispensing hole. The device then rings like an alarm clock, and can send a notification via the app if it is set up on the user or care givers phones. This is already an improvement to the pill boxes, but still requires the periodic refilling and organizing of the medication into the compartments. This device also does not have a form of confirmation that the medication has been taken from the device. This is a relatively affordable device, currently available in the EU. Similar devices from other companies are also available.
The Hero Smart Dispenser is a device that has 10 compartments for medication, meaning that it can store up to 90 days worth of 10 different medications. This device is setup to play an alarm noise when it is time to take medication, and dispense the medication according to the prescription. The device is also connected to an app, and both the caregivers and patients can receive notifications when it is time to take medication. The Hero dispenser also has a button on it, which the patient has to press in order for the medication to be dispensed. This also allows for a second notification to the caretaker informing them that the patient has taken the medication from the machine. The app that comes with this device tracks data such as dosages taken, missed, and when medication was taken. This dispenser makes it quite easy for the users to refill the medication, and easy for the caregivers to remotely check on the adherence of the patient. This device is only available in the US, with similar products also being available in the US. There is currently no equivalent in the EU. This device is available on a subscription basis, directly from Hero.
This project aims to create an active solution, similar to that of the Hero dispenser, with an application such that notifications, dosages, intake, and medicinal information can be given. The aim is to have the device be prescribed to patients via hospitals for long-term medicine intake in order to aid the patient and informal care givers.
Medical Adherence
The problem we are trying to address with our product is a lack of medical adherence, predominantly because of forgetfulness. While it’s important to justify the design choices of the product, consulting existing literature and state-of-the-art products in this domain will accelerate the project's development by using existing knowledge.
Effectiveness
One very crucial question to ask is how effective this type of technology has been in addressing medication adherence. In fact, low-cost reminder devices like pillboxes, pill bottle toggles and cap timers do not improve adherence in nonadherent patients, as found in a 50.000 patient data review by Niteesh et al in 2017[3]. Unfortunately, this is the technology most used by people and the easiest to find on the market at the moment. Meanwhile, electrical medical adherence products (MAPs) are not very popular among patients. a review of many peer-reviewed studies testing the effectiveness of electrical MAPs assessed whether MAPs improve adherence and identifies and describes common features of electrical MAP devices. The conclusion was made with the data of 37 qualifying studies with a sample size of 4326 patients. The conclusion is that MAPs have a definite ability to improve adherence by up to 49%. And more specifically, devices that were integrated into the care delivery system and that were designed to record dosing events were most associated with improved adherence.
MAPs also all had 5 common characteristics overall:
- recording dosing events and storing a record of adherence
- audiovisual reminders to cue dosing
- digital displays
- real-time monitoring
- providing patients with adherence performance feedback
Thus it can be concluded that the development and use of MAPs is by all means very relevant as they greatly improve the medication adherence of patients in general, even though they are not commonly used, while low-cost common medication adherence devices seemingly do not improve this statistic at all. Integrated delivery systems and recording dosing events are features that improve adherence the most.
[I'm not done I'm still adding stuff]
Baxter Rolls
The Baxter roll, named after the pioneering company in its production, is one state-of-the-art solution for managing multi-medicine medication schedules in healthcare and private settings. Baxter rolls are comprised of an arrangement of connected transparent plastic pouches, each housing specific medications tailored to the patient's regimen. Printed on each pouch are details including the patient's personal information, medication types and dosages, and scheduled consumption times. Pharmacists, in collaboration with healthcare providers, carefully curate these rolls in accordance with prescriptions, typically spanning one to three weeks, thereby alleviating the burden of daily medication organization for patients.
The utilization of Baxter rolls has multiple advantages. By condensing medication doses into individual pouches, the clarity of medication intake is enhanced, simplifying the administration process and mitigating the risk of dosage errors. Moreover, research[4] suggests a notable improvement in patient adherence to prescribed regimens. However, despite these merits, the Baxter roll is not without its inherent drawbacks.
Foremost among its limitations is the restriction to solid oral dosage forms, such as pills and capsules, excluding injectable or inhalation medications within the roll. Consequently, patients requiring a combination of dosage forms encounter only marginal improvement from Baxter roll usage in managing their medication regimens, due to necessary supplementary dispensing mechanisms. Furthermore, the rigidity of the Baxter roll renders it less adaptable to changes in medication prescriptions, posing logistical challenges and potential disruptions to treatment continuity. Privacy concerns also arise, as the patient's personal details emblazoned on each pouch may be susceptible to inadvertent exposure to third parties, compromising confidentiality and data security. Additionally, the slightly costlier nature of Baxter rolls compared to conventional medication packaging models presents a financial barrier, potentially limiting widespread adoption and accessibility.[5]
In conclusion, while the Baxter roll enables improvements in medication administration, its efficacy is reduced by its limitations. Some of these challenges, including specific details on in what circumstances the medicine must be taken, can be addressed to improve patient trust and adherence.
Promising dispense prototypes
An important part of our design will be the dispense function. Research already lead to promising designs and prototypes that could be an inspiration in this project. For example the autonomous pill dispenser by Chawla[6]. In this project some important requirements are stated and a design is made that showed how these requirements can be met. first the requirements and than the design concept will be given:
- The device should be able to isolate a single pill from a group, regardless of the size and shape of the pills.
- The device should be able to contain multiple types of pills in case the patient takes more than one medication.
To achieve a fulfillment of these requirements a devise with cones were used to isolate the pills and a rotating mechanism, in which a servo motor was used to ‘dispense’ the pill, where it could be obtained by the medicine taker. The results of the prototype are promising, and we could use the cone design to dispense the pills in our prototype, however it should be looked into if the pills can be obtained easily, also for people with motoric problems.
Furthermore, a smart pill dispenser presented by Casciaro et al[7], gives another example of a mechanism, that could be used in our project to dispense the medicines. In this design "a slot is divided in two sections, one containing electrical and mechanical components and one containing a flexible belt with teeth molded onto its internal and external surface. The internal teeth allow the belt to rotate around two pulleys, one of which is driven by the stepper motor. The larger external teeth allow to keep the pills. When the belt rotates, the pills move together with it, and when one of them arrives in the lower part of the belt, it falls off the tooth and simultaneously the servomotor opens the inferior lid and drop out the pill through a special opening located at the bottom of the dispenser, from which the patient can take it"[7]. This design seems to be flawless in dispensing the right medication and the right amount because of the teeth that only let 1 pill go through, but it should be further researched if pills cannot get stuck and if different types of pills can be put into this machine. Also, the systems seems to be more expensive and difficult to realize. Furthermore, in the paper some other possible requirements came forward such as a contact sensor to know whether the medication is taken or not.
AI in customer service
To enable a system to address customer questions, or in the context of the pill dispensing robot, patients' questions, research[8] shows that having AI integrated into chatbots has a positive influence on customer service. Further research[9] into the methods in which companies develop AI chatbots shows the importance of using personalization and intelligent routing for interactions with such systems. Furthermore, the author mentions the importance of suggestions, providing the user insight into which information they can retrieve, as well as personalization, such that the system improves its interactions with the user over time.
Notification ideas
A study about reminders for taking medication at fixed times vs at automatically time-shifted based on sensor data, showed that using the adaptive reminders the medication adherence (how fast people take the medication and user friendliness) is higher[10]. However, this time-based approach is not always the best as “for example, a reminder is triggered when the user is eating, whereas the medication should be taken after meal”[11].
The pillbox system collects real-time sensor data from a smart home environment and analyzes the user's contextual information through a computational abstract argumentation-based activity classifier. Based on user's different contextual states, the smart pillbox will generate reminders at appropriate time and on appropriate devices. This is quite complex and probably not manageable in this project but the idea of the notifications being at certain times to improve the medication adherence might be useful in this project.
Goals of review:
- Find state of the art
- Find what was done; what worked, what did not work. Perhaps reach out to the members of groups of previous years to ask for further details
- Medical technology state
- Pill dispensing specifics
- Elderly technology interaction
- Privacy and ethics of the technology
Literature Review of already existing medicine dispensers
General Literature Review of comparisons, effectiveness, and ethics regarding MAPs
Stakeholders and their interests
Problem statement
The general problem we are trying to solve with our product, and we’ll have to analyse surrounds the subject of medical adherence, the ability for a patient to keep following their medicine regimen. The problem is that medicine adherence is hard to keep high for certain people, be it voluntarily, because they don’t want to, or involuntarily, for example when the patient is forgetful. To identify the full problem statement, the most important stakeholders and their interests in the pill dispensing robot are identified using literature and interviews.
There are many stakeholders that share an interest in our problem, of which a handful are relevant and important to our product. These groups of stakeholders can be divided into three categories: User, Society and Enterprise.
Users
The most important stakeholder to a medical self help device are the patients using it, as they are the ones taking medication. The patients are people that have trouble taking medication on time, or could use help in managing their medication schedule. A device like ours does not address the group of people who do not want to take their medication, only people who are forgetful or find managing their medication hard. The device can assist with medication adherence, which will be done by making a schedule for the medication, alert the patient when to take medication, instructions for taking their medication, and answering questions they might have.
Another group of users of the device is informal caregivers. These users will interact with the machine by setting the device up for the patients in their homes, inputting the medical prescriptions into the device, and refilling the medication. They can also use the device to monitor the medical adherence of the patient. This device aims to help the caregiver provide care for the patient when they are not physically present by automating the task of reminding the patient to take their medication throughout the day. The device can help a general practitioner get a better insight on the medical administration of a patient.
Society
When it comes to the societal aspect of the device, a major stakeholder are governing bodies. The government, specifically the EU parliament is responsible for legislation and regulations regarding medical assistance devices such as this one. National governing bodies would also decide what reimbursement policies there are for this device in the context of healthcare programs and health services, which doesn’t influence the implementation of the product but vastly changes the access and availability of it to the average consumer (Forsberg et al., 2000)[12]. They thus play a key role in deciding how these devices can be implemented and will contribute to society.
Enterprise
The companies that decide to produce such devices need to design the product such that the users are kept in mind. The hospitals and pharmacies that are partnered with these companies can provide the device to the user should a medical professional deem necessary, as well as provide the medication for within the device. Health insurance companies could also incorporate such a device into their insurance plans for people who need it.
Ethical Aspects
Having a robot replacing tasks a human would do comes with its concerns. Patients are still human, and need to be treated ethically. When it comes to a robot to take over tasks a care taker would do, it is important to not take away the human touch of care givers in healthcare and preserve human dignity[13]. This is also to not seem like the care being given is being automated[13]. This device should improve independence for the patient[14], such as assisting a dementia patient in self-management tasks, such as medication intake.
Shift of responsibility
Something to consider when conceptualizing a medication adherence device like ours is what effect it might have on not only the patient, but the caretakers too. Several ethical considerations arise regarding the responsibilities of caretakers. One of which revolves around the responsibilities that are taken away from caretakers due to the use of such products, as well as the new responsibilities that may be imposed on them.
Caregivers play a crucial role in the medication adherence management of patients. Especially in those with poly-medicated regimens and dementia patients. It’s currently important to train caregivers to understand the disease the patient has, as well as the importance of medication adherence in patients as to reinforce it to ensure optimal treatment and is thus recommended. (Segarra et al. 2022)[15] This task can be very hard to perform consistently for some caregivers, especially if they deal with multiple patients. With the use of smart pill dispensers, some of the tedious work can be alleviated. They can automate medication dispensing and reminders, reducing the direct responsibility of caretakers to physically administer medications at specific times, especially helpful when they have to deal with complicated or frequent dosage. Though, this responsibility would not disappear. It would be shifted to the device, and possibly thus to either the programmers or company of said device.
In return, caretakers, or patients self-medicating, would need to bear new responsibilities related to the oversight and maintenance of the smart pill dispenser. Foremost, the caretaker still has to confirm the medication adherence of the patient by interpreting the data they receive from the device, like recognizing patterns in the periods of non-adherence and correlating it to a potential barrier causing it, communicating with the patient or a healthcare provider when needed. The caretaker also needs to maintain the device by refilling, programming the patient’s regimen into it and troubleshooting technical issues, which does ask for a different set of skills from the caretaker. Additionally, caretakers might become responsible for ensuring that sensitive health information is protected from unauthorized access or misuse in accordance with the wishes of the patient, as many devices have configurable privacy settings to consent on the sharing of health information with the device company.
So, with the introduction of a smart pill dispenser like ours, caretakers are relieved from the tedious task of memorizing or planning the medication regiment of one or more patients, and are instead tasked with maintaining the device and interpreting the medication adherence data. In general, caregivers given the option for a device like this will highly prefer to choose it (Forma et al., 2022)[16], so the change of responsibility is generally seen as positive.
Robot Design
Block Diagram
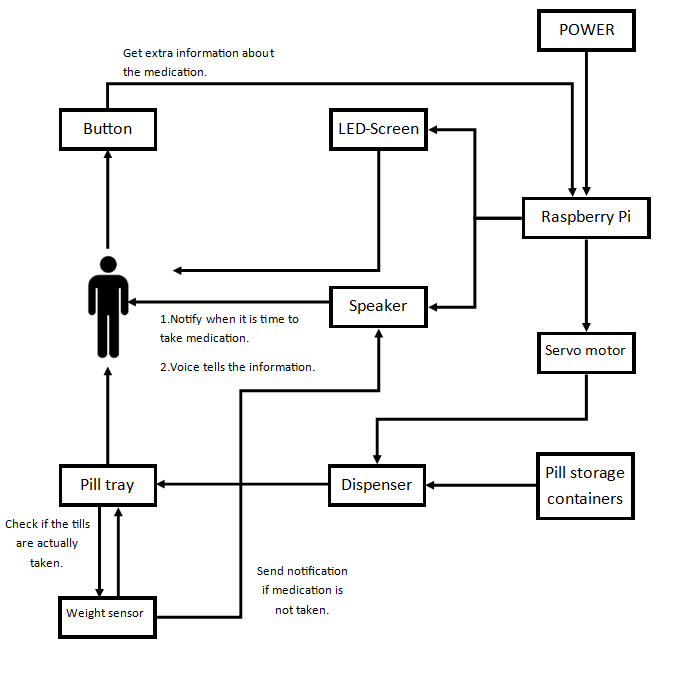
To get an idea of needed components and on the functioning of the robot, a Block diagram was made. This is mainly to get an idea of what is needed to create a prototype. In the block diagram can be seen that the following components are needed in the design:
- Raspberry Pi, this will be the main drive force of the robot. It will control all other components
- Button, the button will be used for multiple things. the user can press it to get medication out of the machine after a notification. It can also be used to get more information about medication.
- LED-Screen, this will be used to display information.
- Speaker, gives the same information as seen on the LED-screen, but then spoken out
- Servo motor, will be used to turn the dispenser and make sure that there is enough rotation to get the correct amount of medication out of the storage container.
- Pill storage, bigger tubes of multiple pills of the same medication.
- Dispenser, used to get all medication needed at a specific time out.
- Pill tray, a weighing plate that knows when medication is on it.
- Weight sensor, a sensor to check if the user really took the medication out of the tray and sends a notification if the medication is not taken out.
Robot Description
We have designed a small (portable?) robot to act as an medication adherence aid for chronic/long-term medication therapy. The robot is to be used as a home product of the patient and can remind the patient to take their medicine (on-time). The robot can contain multiple types of solid medication and is able to release predefined doses per time period as set by the caretaker or patient. When the time comes for a patient to take their medication, the robot will notify the patient via its built-in LED screen and speakers. The combination of audio and visual stimuli is used to ensure that the patient takes notice of the robot and is reminded of their medication. In the case that the patient would like more information about their medication, as they would get in the information leaflet provided in the package commonly bought, the user presses a button and the LED screen and speakers will inform the patient.
Interview preparation
Patient
- Would you prefer to have this device be portable? Why or why not? (Stationary/portable)
- How do you take your medication on holiday or days out?
- Do you want to be able to take medication with you while on holiday? (Ability to take doses away from home)
- Do you prefer physical buttons or touchscreen to interact with the device? (Buttons/touchscreen)
- How many different medications should the machine hold? (Amount of different pills)
- How often do you get more medication from the pharmacy? (Storage capacity)
- How would you like to be notified to take medication? What notification method works best for you? (Notification)
- When the medicine is ready, the machine plays a noise and produce a light signal. It will also send a phone notification after 5 minutes if not taken. Would this be a nice way to be reminded?
- Would you prefer to fill the machine with pre-packaged rolls or pills from a bottle? (refill)
- How do you currently get your information about your medication? How would you like to receive information about your medication? (Information)
- What are suggestions for the device that would make it better to use? (General/ending)
Caregiver
- How does responsibility surrounding medicine intake currently work?
- Do you check that the patient has taken their medication?
- What would you like to be notified about? (Amount of monitoring/ validation)
- How do you want to be notified that the patient has to take/ has taken the medicine? (Notification)
- Would you prefer to fill the machine with pre-packaged rolls or pills from a bottle? (How to refill)
- What is the current protocol for medicine intake? Which aspects should the device do? (Security)
- What are suggestions for the device that would make it better to use? (General/ending)
Old Interview Questions From minutes
- How often do you forget to take your medicine a week?
- How do you currently store your medicine?
- How do you currently get the information about your medication?
- Are you away from home a lot for longer periods and therefore have to take your medication storage with you?
- Do you want to have more information with taking your medication, so for example, let you know that you need water with a specific pill?
- Do you want help with taking your medication?
- What would help you with taking your medication on time?
- Do you currently have problems with taking your medication?
- How do you spend most of your days, are you at home a lot?
- How do you get more medication currently?
- What do you still miss from the description of our proposed design?
Translated old questions for interviews
- Hoe vaak worden medicijnen vergeten door patiënten? En als dat vaak gebeurd, wat is dan de oorzaak?
- Hoe komt de medicatie terecht bij de patiënten? (bijvoorbeeld via mantelzorgers of halen ze die zelf op)
- Hoe komen de patiënten informatie over de medicijnen te weten?
- Komen er problemen voor bij het nemen van medicatie, en wat is hiervan de oorzaak? (bijvoorbeeld bij onduidelijke instructies,( pil nemen met glas water bijvoorbeeld.)
- Hoe en waar wordt de medicatie opgeborgen/bewaard?
- Als patiënten weg zijn van huis, hoe zorgen ze ervoor dat de medicatie op tijd en op een juiste manier wordt genomen? (voor een korte periode, zoals een dagtrip of bezoek, en voor een langere periode van huis)
- Is er behoefte aan een manier om medicatie op een overzichtelijkere/betere manier mee te nemen als patiënten van huis gaan?
(After a brief description of our design idea)
- Zou deze robot patiënten kunnen helpen met het nemen van medicatie op tijd en op de juiste manier?
- Zou deze robot patiënten en mantelzorgers kunnen helpen met de administratie van de medicijnen?
- Zijn er nog andere functies die handig zouden zijn voor een robot als deze?
Privacy Requirements
- A patient can give their permission to use personal data, if they have received all the relevant information about the possible consequences and the reasons for data sharing.
- Assumption of patient’s permission to share information
- In the case that no Personally identifiable information (PII) is used, data can be shared
https://www.knmg.nl/actueel/dossiers/beroepsgeheim/medisch-dossier
- Caregivers that need access to information to care have permission
- Professional secrecy can expire for scientific research purposes
- Caregivers can share information that is directly relevant to their work
https://www.regelhulp.nl/onderwerpen/kwaliteit/beroepsgeheim
- Organizations outside of healthcare can obtain health data but must fulfill the confidentiality obligations
https://www.autoriteitpersoonsgegevens.nl/themas/gezondheid/gezondheidsgegevens-gebruiken-en-delen/gezondheidsgegevens-delen-met-derden#algemene-regels-gegevens-delen
For robot/app:
Compartmentalization of data can be done to avoid the necessary use of private data. The robot would have no access to PII and only to relevant information; the type of medication and doses. The caregiver or doctor connected with the robot would have that information and for example: connect the medical dossier to a number that would be shared with the robot. The only viewer of personal data would be the doctor/caregiver, already having the patients permission.
Norm for data security in healthcare called NEN 7510, publicly available in the Netherlands
- Data can only be given and used when:
o Caregiver needs to carry out an activity for which data is needed
o There exists a healthcare relation between person and patient to which the data is connected to
o Data is needed in support of an activity
https://www.nen.nl/zorg-welzijn/ict-in-de-zorg/informatiebeveiliging-in-de-zorg
For interview/survey:
- Caregivers can give information not pertaining to a specific patient as long as no PII is given
- With permission of the patient, caregivers can give more in-depth information (since our research does not pertain to the patient themselves it is most likely not necessary)
Time spent
Week 1:
| All | 1st meeting (2h) |
| Quinten | Researching SotA (2h); Finding and reading relevant papers regarding medication dispensers (3h); Finding and reading relevant papers regarding ethics and elderly care (2h) |
| Fenna | Research State of the Art (1h); Robot specifications (2h); Research Product Design (1h); Research Use Case (2h) |
| Thijs | Looking at already functioning medicine dispensers (1.5h); Reading papers on dispensing robots and summarizing them (4.5h); look at ethics for medication rules (0.5) |
| Daniel | Research what has been done/state of the art (3.5hr); Dispensing Specifications (1.5hrs); EU regulations, medical technology state, privacy and ethics of the tech (3.5hr); |
| Sven | Research on state of the art/dispenser mechanisms (1,5h); Research AI implementation by notifications (1,5h), naming requirements/specifications (1h) |
| Sjoerd | Setup wiki (2h); process annotations of first meeting (1.5h); Read documentation OpenAI and Google for insight into which we can use (3h) |
Week 2:
| All | Feedback Monday meeting and evaluation (1h), Meeting 23-2-24 (1h) see minutes |
| Quinten | Transfer and ordering of data to wiki (2h) |
| Fenna | Privacy Research (1.5h) |
| Thijs | preliminary design options research (2.5h) |
| Daniel | Identifying Stakeholders (1h), Interview Questions (2h), Data requirements (0.5h) |
| Sven | start identifying stakeholders and specifying the target audience (1,5h), translate and improve interview (1h) |
| Sjoerd | Create prototype AI implementation, with testing and prompt engineering, using API documentation (4h) |
Week 3:
| All | Feedback Monday meeting and evaluation (1h) |
| Quinten | Literature Review incorporation into stakeholders (3h); Responsibility shift (4h) |
| Fenna | Product description (1.5h); Incorporation Literature review (2h) |
| Thijs | Start making a design for the machine and block diagram of systems needed (6h) |
| Daniel | Cleaning up Interview Questions (1h); Incorporating Literature Review into Wiki (4h); |
| Sven | Connecting to informal caregivers to plan an interview/prepare, (3h); incorporating Literature review (2h) |
| Sjoerd | Cleaning up Interview Questions (1h); Incorporating Literature Review into Wiki (2h); |
Week 4:
| All | Feedback Monday meeting and group discussion (2h) |
| Quinten | Analyzing common adherence problems via literature (2h); Finding limitations to solving these problems (3h); Finding a target audience from found limits (2h) |
| Fenna | |
| Thijs | |
| Daniel | Brainstorm (2h); Incorporating Literature (1h); Investigating Hardware (2h); |
| Sven | |
| Sjoerd | Collect functional requirements app (1h); Generate data flow diagram and model modalities (1h); Investigate existing models adjusted for new requirements (3h); Setup software environment for app (3h due to bugs); Find base app to save time (2h); |
References
- ↑ “Pill Dispenser Automatic Model 2021 Connected: DoseControl.” MedControl, www.medcontrol.eu/p/386/smart-automatic-pill-dispenser-with-alarm-dosecontrol-new-model-2021-english-transparent-lid-connected. Accessed 14 Feb. 2024.
- ↑ “Automatic Pill Dispenser - How the Hero Dispenser Works!” Hero, herohealth.com/our-product/. Accessed 14 Feb. 2024.
- ↑ Choudhry NK, Krumme AA, Ercole PM, et al. Effect of Reminder Devices on Medication Adherence: The REMIND Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Intern Med. 2017;177(5):624–631. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2016.9627
- ↑ Connor J, Rafter N, Rodgers A. Do fixed-dose combination pills or unit-of-use packaging improve adherence? A systematic review. Bull World Health Organ. 2004 Dec;82(12):935-9. Epub 2005 Jan 5. PMID: 15654408; PMCID: PMC2623099.
- ↑ De medicijnrol, ofwel de ‘baxterrol’ - verdiepingsartikel - BijnierNET
- ↑ S. Chawla, "The autonomous pill dispenser: Mechanizing the delivery of tablet medication," 2016 IEEE 7th Annual Ubiquitous Computing, Electronics & Mobile Communication Conference (UEMCON), New York, NY, USA, 2016, pp. 1-4, doi: 10.1109/UEMCON.2016.7777886
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 S. Casciaro, L. Massa, I. Sergi and L. Patrono, "A Smart Pill Dispenser to support Elderly People in Medication Adherence," 2020 5th International Conference on Smart and Sustainable Technologies (SpliTech), Split, Croatia, 2020, pp. 1-6, doi: 10.23919/SpliTech49282.2020.9243773
- ↑ Mohanty, Aishwarya & Mohanty, Jitendra & Lingam, Naveen & Mohanty, Sagarika & Acharya, Ajitav. (2023). ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE TRANSFORMING CUSTOMER SERVICE MANAGEMENT: EMBRACING THE FUTURE. The Oriental Studies. 12. 35-47.
- ↑ Best practices for using AI-enabled self-service, R. Gareiss, 19 Feb 2020
- ↑ P. Kaushik, S.S. Intille and K. Larson, "User-adaptive reminders for home-based medical tasks", Methods of Information in Medicine, vol. 47, no. 3, pp. 203-207, 2008.
- ↑ Q. Wu, Z. Zeng, J. Lin and Y. Chen, "AI empowered context-aware smart system for medication adherence," in International Journal of Crowd Science, vol. 1, no. 2, pp. 102-109, June 2017, doi: 10.1108/IJCS-07-2017-0006
- ↑ Forsberg et al.. (2000). Effects of performance-based reimbursement in healthcare. Scandinavian Journal of Public Health, 28(2), 102-110.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 Dolic, Zrinjka, et al. “Robots in Healthcare: A Solution or a Problem?: Workshops: Events: Envi: Committees: European Parliament.” Robots in Healthcare: A Solution or a Problem? | Workshops | Events | ENVI | Committees | European Parliament, Apr. 2019, www.europarl.europa.eu/committees/en/robots-in-healthcare-a-solution-or-a-pro/product-details/20190218WKS02241.
- ↑ Lekadir, Karim, et al. “Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare: Applications, Risks, and Ethical and Societal Impacts: Think Tank: European Parliament.” Think Tank | European Parliament, June 2022, www.europarl.europa.eu/thinktank/en/document/EPRS_STU(2022)729512.
- ↑ Segarra et al. (2022) Role of caregivers on medication adherence management in polymedicated patients with Alzheimer's disease or other types of dementia. Front Public Health. 10
- ↑ Forma et al. (2022) Are caregivers ready for digital? Caregiver preferences for health technology tools to monitor medication adherence among patients with serious mental illness Digital Health, 8, 1-12.