PRE2019 4 Group7
Group members
Student Group
| Name | Student number | Bachelor | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eline Visser | 1375369 | e.a.l.visser@student.tue.nl | Applied Physics |
| Metten de Lange | 1240902 | m.m.d.lange@student.tue.nl | Applied Physics |
| Vera Holtmark van Dijkerhof | 1380893 | v.holtmark.van.dijkerhof@student.tue.nl | Applied Physics |
| Sterre Cuppens | 1387790 | s.cuppens@student.tue.nl | Psychology and Technology |
| Iris de Wit | 1258230 | i.c.d.wit@student.tue.nl | Psychology and Technology |
Problem statement
The current world population keeps expanding. In 1950 there were 2.5 billion people on Earth. In 2020 this number is 7.8 billion. [1] However, this is not the only change. There has also been a shift in the population age distribution. As can be seen in figure 1, there used to be a pyramidal distribution of age, where there are relatively a lot of young people, and fewer elders. But in data of later decades and estimations for the near future, this distribution becomes more and more "block like". This means that at some point, there will be almost the same amount of elders alive as there are young people to care for them. It is estimated that this trend will continue to grow.
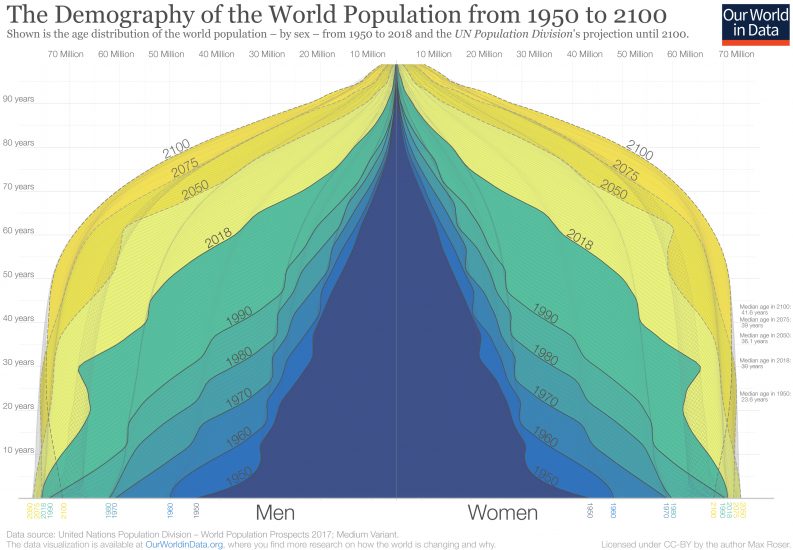
With that, the age-related decease rates will go up as well. Right now 50 million people are living with dementia. It is estimated that the portion of people over age 60 with dementia lies between 5 and 8 percent. The total number of cases is projected to grow to 82 million in 2030 and 152 million in 2050. [2]
This leads to all sorts of detrimental effects for the care industry. Since there will be less and less spots available in nursing homes, elders with dementia will be expected to live at home longer. This demands the invention of new technology to aid them in day to day life.
Not only activities such as eating, taking medicine and staying active require attention, also the social live of elders with dementia is of great importance. As the person grows older, a large part of their social live will cease to exist. This can cause severe loneliness, depression and a variatie of other health problems. [3] Elderly with cognitive impairments are even more likely to experience loneliness. [4]
Objectives
The technology should be able to help older and demented people get through their daily lives. For them, many problems that most people never have to deal with are commonplace and they require lots of attention. However, giving this attention to everyone who needs it takes many people and much time, while it is not always possible to have enough caregivers for this. Technological solutions could provide an outcome.
Most importantly, the technology should be able to alleviate the loneliness of older or demented people. This is a problem that has been getting bigger and bigger, but technological solutions could provide an outcome.
Furthermore, the technology should be able to help demented people get through their daily lives. For them, even the most simple tasks like washing your hands require help from someone else. Robots or similar technology could help these people by guiding them through the process step by step, encouraging and correcting them where necessary.
Approach
This project started with designing an application for elderly people with dementia who experience loneliness. The ideal end product should be an interface of a device such as a tablet designed specifically for elderly with dementia, so that it is easy for them to use. The interface would only have necessary functions/applications. One of the goals of these applications should be decreasing loneliness among elderly with dementia. This could be done by an easy communication function, such as video calling. A cognitive game function that should help remain the cognitive state of the person. The photobook should help with retrieving memories and help the person remembers their memories longer. The navigating function should help elderly with dementia going on their way to their friends, so that it is easy to remember where they are. And the to-do list should help the elderly with dementia in their everyday life with remembering tasks. We think that these functions and the specifically the combinations of them would make up the ideal interface for elderly with dementia. It would be a good addition to their lives. From the beginning of the project, a literature study was performed to investigate the current state of the art of technology for elderly people with dementia. From the literature study, a problem statement has been derived so a solution for this problem can be found and developed. For solving the problem statement, objectives have been determined to set guidelines for the realization of a band. Further research was done to define the users of the application. Then all the team members came up with different possibilities for functions for the application. The functions were an interactive photobook, a cognitive game, a navigation app, a to-do list and task helper and a communication function. The ideal application was designed from all these functions. However, in the scope of this project we decided to focus on a combination between a to-do list and an interactive photobook. For this combination every team member came up with their own design. Eventually, the design of Vera was the most suitable for elderly with dementia. This design was a to-do list with a memory function. Where old photos will be shown of the user. Then different programs were researched to build the application. Eventually, Kivy with a Python was the best option to build the application. To finalize the project, a questionnaire was made for experts in elderly people with dementia. Different care homes were contacted to participate in this questionnaire.
The Users
Primary users
The primary users are the elderly people with dementia. With an elderly population that is set to more than double by 2050 worldwide, there will be an increased demand for elderly care. The shift in societal proportions will place new pressures on all aspects of elderly care. Loneliness, for instance, is a consequence of social, psychological and personal factors. Over half of people over the age of 75 live alone and 17% of older people see family, friends or neighbours less than once a week. A recent meta-analysis showed that the impact of loneliness and isolation carries the same mortality risk as smoking 15 cigarettes a day. This poses several impediments in the delivery of high-quality health and social care.[5] We want to focus especially on elderly with dementia. Because people with dementia experience progressive cognitive impairments that typically commence with short term memory problems but can encompass language deficits, difficulties initiating tasks, planning, monitoring and regulating behaviour, and visuospatial difficulties, agnosia (loss of ability to recognize familiar objects or people and apraxia (loss of ability to carry out complex purposive movements) [6]. For people with dementia it is extra hard to keep social connections with other people. Therefore, we want to make elderly people with dementia less lonely with our device.
Secondary users
Secondary users are the caretakers of the elderly people with dementia. They will have to cooperate with the device for the ultimate care for the elderly. The device should be a supporting tool for the caretakers, which makes the worry and care on daily tasks less. And it should be an addition to the care of the caretakers with the social aspect. It can give the elderly people the extra social interaction what caretakers sometimes can't give.
Tertiary users
Tertiary users of the device are the companies that create the product. Eventually, if there is a high enough demand for the product, companies will be producing the device. New technologies such as the device may create good business opportunities for newer companies and for both well-established companies. The companies will have to take the price of the device in account for the elderly people. They have to find a balance between an affordable device for the elderly people with dementia to reach a high enough demand. And the companies will have to make enough profit of the device to keep the production going.
User requirements
The following points are the user requirements for the application with the to-do list and memories function. These user requirements are conditions or tasks that must be completed to ensure the completion of the project.
The App in General
• The app should only contain the functions that are necessary for the app to reach its goal. More functions than necessary will make the app more complicated to understand. In this project this means that we will have a to-do list and a photo display in order to achieve more independence and less loneliness.
• There should be consistency in the lay-out all throughout the app. One can think of always using the same fonts, colours etc. that make up the overall appearance of the app.
• The app should be able to remind the user of information with help of notifications. The amount of information given and the frequency of the notifications should be customizable.
• The app should have an option that provides help and support for using the app, for instance with a help button where information stands about how to use the application.
• The app should be simple and clear enough to be operated by an elderly with dementia without any help of other people/things outside of the app. There should be a help function at any moment if something isn't clear.
• The app should be able to make elderly with dementia feel at ease by having a relaxing and entertaining appearance. This means that no extra functions/buttons/objects/pop-ups etc. are visible other than the needed function at that moment. The text should be very big and the colors are not bright in order to have no overload of input[7].
• The app should contain colors that can be used for elderly: colors of blue-yellow type are less well perceived by elderly.
To-Do list and task helper
• The app should have a daily to-do list.
• The to do list has customizable items in it. The user or caregiver can make a new item or delete an existing one.
• The app should be able to keep track of what tasks have been done and reset this progress at the end of the day.
• The app should be able to recommend a task to the user they have not done yet or remind them that they should still do it.
• The app should be able to choose its recommendations based on time or other factors that are relevant to the task (i.e. recommend the user to have breakfast when they have just woken up, or wash their hands if they are going to eat) This can be in the form of pup-up notifications.
Interactive Photobook
• The interactive photobook should contain pages with photo's organised in a way similar to a real photobook
• It should be possible to send new pages to the interactive photobook from other devices on distance
• There isn't an option to remove or edit already existing pages from the photobook in the app itself
• The interactive app should be able to show old postcards along side of the pictures
• It is possible to have text along side of the pictures and postcards
• It is possible to let the app read the message of the postcards/text, either with help of spoken audio or a computer generated voice
• The photobook should give notification about "anniversaries" of certain dates and pictures, for example "Last year around this time this happened, look at the pictures"
• The pictures should be in chronological order and the day/month/year should be alongside of the pictures
The following points are the other user requirements that we made for our ideal end product. These will not be used in this project furthermore.
Cognitive game
• The cognitive game should contain a word search puzzle
• The user should be able to play the game against another person online
• There should be a chat option to communicate with the other player
• The word search puzzle should change every new game
• The users should take turns in searching a word
• There should be a pass option when the player can't find a word
• There should be a stop option when the players want to give up the game
This is a feature that should make it possible for elders to use navigation apps.
• The app should show a route from the users location to the final destination.
• The app should be able to walk the route in real time.
• The UI should be clearer than existing apps such as Google Maps. It can be clearer by removing the option to choose a transportation device. (walk/bike/car) The home screen can be a collection of pictures of locations that the uses frequents. When the user clicks on a picture, the route and navigation start automatically.
• The app should have spoken instructions for the route.
Communication
• The interface should have no pop-ups or distractions
• The interface shows the faces with belonging names
• There should be an automatic synchronization between the contact list and the app
• The amount of contacts should be limited to a maximum of 24 persons to keep overview
• The icons of the contacts are placed around the videocalling icon
• When the user clicks on a person, the app should ring the other person
• When the responder responds, the screen displays the other person
• There should be a working microphone and camera connected
• The camera should always be turned to the user's face
• The user can be called as well
• When being called, one big green button appears on the screen with the name and face of the caller and an instruction to pick up
State of the Art
Current technology for elderly people
There already exists a lot of technology in the care for elderly people like electronic sensors and video-monitoring. For example remote health monitoring and equipment such as fall detectors, door monitors, bed alerts, pressure mats and smoke and heat alarms. These all are made to improve a patients’ safety, security and ability to cope at home. [8] In response to ongoing patient safety challenges, health care organizations also have a lot of technology to take care of elderly people. For example they implemented a variety of technological mechanisms to reduce medication errors such as computerized physician order entry, electronic medication administration record, and clinical decision support systems. [9] Another important aspect in technology for elderly are robots. Robots are developing and could be a potential contribution in rationalizing and maintaining, or even improving the quality of elderly care. Robots can contribute to health care support in terms of capacity, quality (performing very accurately and task specific), finance (support or even take over tasks of trained personnel), and experience (e.g., increased feeling of autonomy and self-management). The idea of robotics playing a role in health care was launched some decades ago and has mainly been developed for physical training in rehabilitation as well as personal assistance for tasks of activities of daily living. Robotic applications supporting social behavior are a more recent development. So far, systems have been developed supporting child’s play and care for elderly with dementia. However, the uptake of these systems in care practice has been limited. One of the reasons is that there appears to be a mismatch between what is technically developed and the perceived needs within care environments. [10] Socially assistive robot (SAR) technology could assume new roles in health and social care to meet a higher demand. These are robots adept at completing a complex series of physical tasks with the addition of a social interface capable of convincing a user that the robot is a social interaction partner. Five roles of SAR were identified: affective therapy, cognitive training, social facilitator, companionship and physiological therapy. [5] The use of technology varies considerably among older adults. current models of technology acceptance are missing essential predictors specific to community-dwelling older adults. [11] When designing technology for elderly users it is important to take some changes humans experience in mind. These changes are either sensory and motor changes, cognitive changes or social changes. Sensory and motor changes are the changes that the body experiences, such as decreasing in vision, hearing and motor skills. The cognitive changes cause the rate at which the users can learn and remember the new technology and “computer skill” to decrease. These changes cause elderly people to have difficulty with navigating through out the computer and remembering how to do things they have already done before on the computer. The social environment has a big influence in the technology that elderly people use. The traditional WIMP (Windows, Icons, Menus and Pointers) don’t consider these changes and when designing for elderly it is important to adapt the WIMP’s. [7] For elderly people the barrier to start using technology is rather high, especially compared to younger people who grow up surrounded by technology. The two main factors contributing to the decision for older people to use a given technology are Perceived Usefulness (PU) and Perceived Ease of Use (PEOU). Previous experience with technology makes the barrier to start using it lower. It is important to note that the actual usefulness or ease of use is not that impactful, but rather how the user perceives it to be, even if they haven’t used it yet. [12] The use of technology and its’ providing information allows the elderly to face more easily the difficulties of modern life, trespassing the limits of their social and emotional isolation, thus achieving a more qualitative living. More in detail, this can be accomplished through specifically designed education programs that teach elderly the way new technologies work. Furthermore, these programs should be also addressed to individuals who belong to the supportive environment of the elderly such as the younger members of the family. It would be beneficial if the younger helped them to familiarize with each object, removing fears of using high technology devices. [13]
Dementia and technology
People with dementia experience progressive cognitive impairments that typically commence with short term memory problems but can encompass language deficits, difficulties initiating tasks, planning, monitoring and regulating behaviour, and visuospatial difficulties, agnosia (loss of ability to recognize familiar objects or people and apraxia (loss of ability to carry out complex purposive movements). Whilst drugs have for some time been used and approved by health organizations for the treatment of mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease, these drugs do not cure, reverse or tackle the underlying root problem causing the dementia. Therefore in the absence of a cure, more innovative approaches need to be developed to help promote independence and maximise quality of life. In this context, assistive technologies offer much potential and can make a very significant difference to the lives of people with dementia and to their primary caregivers. Indeed it has been noted that technologies should be part of a home package and should be provided in a thoughtful, sensitive ethical way. Technologies can assist people to maintain their independence and improve quality of life. The overall opportunities technology can create for people with dementia however have to date not been fully maximised. [6] Social activities are most heavily affected by spatial disorientation, which increases the risk of getting lost and exhibiting wandering behavior. Consequently, patients reduce outdoor mobility leading to a more sedentary lifestyle and social isolation, with a primary worsening of the quality of life and with a secondary negative impact on cognitive functions, cardiovascular tone, brain plasticity, and mood. A situation-aware Information and communication technology (ICT) requires a flexible fine-tuning by stakeholders of system usability and complexity of function, and of user safety and autonomy. It should operate by artificial intelligence/machine learning and should reflect harmonized stakeholder values, social context, and user residual cognitive functions. ICT services should be proposed at the prodromal stage of dementia and should be carefully validated within the life space of users in terms of quality of life, social activities, and costs. [14] A range of ICT interventions including, telephone-, video-, and computer-based interventions appear to be successfully targeting caregiver support for a range of affective caregiver outcomes, including burden, depression, and anxiety. Telephone technology can be used effectively as a stand-alone intervention or in tandem with other ICTs. [15] Current technologies for the care of people with dementia are broad in scope and range from sensors to memory aids. The sensors are the most common can be divided into three categories: Physiological, environmental and advanced integrated sensors. [5] There are also Assistive Technology devices, that supports people with memory loss are commercially available. However, there needs to be more research about the effectiveness of the current assistive technology to support people with cognitive impairments with their memory loss. [16] An example of a training program for people with dementia is the Multi-Domain Cognitive Training (MDCT). This is a training programs that may protect people of the loss of grey matter volume in the brain. This could be a non-pharmacological intervention to slow the progress of dementia. The training program has two sessions a week and each session was 1h. Every session the tasks would challenge three out of the following six cognitive domains; reasoning, memory, visuospatial skills, language, calculation and attention. Every week every domain would be tested and trained within the tasks. At the end of two weeks of training, the grey matter volume of the participants was increases by 6.14% on average and a significantly positive correlation between the volume and scores on cognitive function tests was found. [17] Persons with early stage dementia have difficulties with using everyday technology. The barriers to everyday technology use appear in four domains: As interfering conditions related to the person, the context and the design of the artefacts, and as limitations in the participants’ knowledge of the technology and its potential, and as difficulties in direct technology use, characterized by communication problems both in understanding and in the administration of the technology. The participants’ use of instructions for use formed the fourth domain [18].
Loneliness and technology
Large numbers of individuals, many of them senior citizens, live in social isolation. This typically leads to loneliness, depression, and vulnerability, and subsequently to other negative health consequences [3]. Features of a loneliness regulatory loop are employed to explain cognitive, behavioral, and physiological consequences of loneliness and to discuss interventions to reduce loneliness. Loneliness is not simply being alone. Interventions to reduce loneliness and its health consequences may need to take into account its attentional, confirmatory, and memorial biases as well as its social and behavioral effects. [19] Sever cognitively impaired participants experience loneliness more often, while they more frequent visits then less cognitively impaired participants. [4] A construct sensitive to both technological as well as societal change, perceived obsolescence was shown to influence the way personal and telephone contacts were responded to. With low social contacts and high obsolescence being detrimental to feelings of social and societal integration in their own rights, their combination may compound feelings of loneliness far beyond additivity. Going further, feelings of being out of step with modern times were found to mediate the effects impact of low technological competence on loneliness. Given the accelerated obsolescence of both technological devices and user know-how, to keep up with technological progress may become a challenge not only for those persons who never learned how to use a computer. Thoughtful design and implementation of technology is needed to assure access to and orientation within modern society despite varying technological backgrounds and competences. [20]
Design end product
The ideal end product
Having difficulties with technology is very common among elderly users, and especially when the users suffer from cognitive impairments such as dementia. These days we see more elderly people using devices like tablets, but the normal interfaces for these devices are not build with the special needs of cognitive impaired in mind. They often simply do not understand how one device works. They are afraid that they will destroy the software. They do not see the relationship between buttons and their functions and do not know which step to take to achieve a goal. Because spatial awareness and memory deteriorate as people age, older people also have more difficulty navigating through software. And software becomes more complex and gets more possibilities. Current interfaces are often overwhelming for the elderly because there are so many possibilities. Also a lot of the applications and functions of these devices aren't useful for these type of users. Our ideal end product would be an interface that is designed with the special needs of users with dementia in mind that will cover everything that is useful for these users and nothing more.
Examples for the functions the interface/app could have
• Video calling - Technologies like Skype are widely used to keep in contact with family and friends, also by elderly people. But not every elderly person is capable of learning how Skype works. An example for how the layout of this communication function would look like is shown in figure 3. The pictures with the names of the contact would be easier to recognize than only the username of the contact.
• Cognitive game - Studies have shown that cognitive games could be benefitiel for patients with dementia and the concept of a tablet is suitable for games in general.
• Navigation - Some elderly people are still very mobile but they might be in need for a function that guides them on their way. Normal navigation applications have many different settings, like the option if one wants the route for a car or a pedestrian. These functions aren't necessary for elderly users who will walk everywhere. We think that the navigation function would only need preset addresses and routes for pedestrians.
• To do list - Users with dementia sometimes have trouble remembering basic daily activities. A normal agenda application isn't fit for remembering those tasks, a to do list would be more useful. The to do list would contain the normal daily activities like for example the three meals of the day and other, more personal, tasks could be added manually. It would be possible to "cross off" the tasks and at the end of the day the list resets so the tasks can be ready to be crossed off the next day.
• Interactive photobook - Looking at old pictures can be therapeutic and relaxing for people with dementia. Some families make photobooks for their relatives suffering from dementia. It would be a great addition to the app to have an interactive photobook function where families could make pages with photos and subscripts from other devices. An advantage of this interactive photobook would be the ease of use for the family and the additional function such as reading the text out loud.
The user requirements of these functions are all listed at 'User requirements'.



The lay-out of the photobook differentiates a little bit from the other applications in terms of the clock/date. This was chosen to make sure that there is enough space on the screen for the actual pictures. It could also be an option to completely remove the date, but it's important to make sure the users with dementia have an extra reminder of what is 'today' and what is 'the past'. Looking at old pictures might be a little bit confusing for them, so clearly stating the date and how much time has pasted since the picture would be a logical design choice.
Scope of this project
In this project we focus on the to do list and the interactive photobook application. We are programming those two functions in one app, that can be seen as an app all on its own. Therefore the home screen will look different from the home screen that the ideal interface would have. This will be shown by figure 5.

Because we want to make a fully functioning app, containing the to-do list function and the photobook function, it was decided to integrate the two functions in the home screen of the app. The app only has these two function for now and it is possible to display these two function within the same screen, minimizing the amount of menu's the user has to go throw for a specific function. With the five functions the ideal end product would have it is necessary to make an extra menu to organise the functions.
The button 'More functions' would bring forth the interactive photobook page as shown in figure 4.
Building an app
To build the app we looked at a few different options that are described below. Eventually, we decided to build the application with Kivy.
Snappy appypie
Snappy appypie is a free app developer wherefore you don't need to write a code. You can choose from different templates and there can be a lot of editing.[21]
It costs 18 euros per month to use and to develop your app in the App store or Google play. We thought it was a free app developer (apart from the App stores) but it turned out you have to pay 18 euros per month for just developing the app as well.
As stated in one of the articles we found, it is hard for people with dementia to remember how to use the technology. It should be designed as simple as possible. Therefore there should be a "simple" design. People with dementia are really sensitive to stress. The design should be as "calm" as possible with no jumping/moving or pop-up objects in the screen. It should be made as realistic as a physical button for example. So the user should get feedback as it pushes a real button. This could be achieved by changing color or sensation of the screen. It could for example vibrate and change color when the button is pressed. In the article this is stated as 'lack of embodiment of technology'. Older people for example are more used to the movement of writing a letter than typing on a keyboard.
These adjustments might be too hard to achieve in this app developer, because you cannot code it yourself. Therefore it might be more advantageous to work with an app developer that uses simple code.
Adobe Phonegap
Adobe Phonegap is an development framework for building mobile apps. In this video Cite error: Invalid parameter in <ref> tag with explanation, the person uses Adobe Phonegap to make an app that you can instantly see on your device. You can edit multiple things and link it to a phone to download.
We tried downloading it twice and it was not working and the desktop application kept loading forever, so this is not an option in our opinion. We looked at different forums and a lot of people had the same problems so this seems like an unreliable program.
Good Barber
Good barber is a app maker similar to appypie. It seems to have more customizability though. There is a 30 day trail in which you can test the app and develop it. For us those 30 days are enough so we do not have to get the payed version. [22]
Kivy and python code
In our research, we found multiple sources that used Kivy and then used python code to code a mobile app. Kivy is an open source Python library for rapid development of applications that make use of innovative user interfaces, such as multi-touch apps. [23]
The advantages of coding your own app are that it is highly customizable and you do not have to deal with other parties like another app development website when making the app. An advantage of using Kivy is that is allows the app to display well on every screen size. You can alter the dimensions and the widgets will automatically stay centered. A disadvantage is that none of us have worked with this before. However, we took some time and found a couple tutorials that will help a lot.
The first video Cite error: Invalid parameter in <ref> tag is part of a series by Tech with Tim on YouTube which takes you through all the little steps of app making. The second helpful tutorial Cite error: Invalid parameter in <ref> tag helped in setting up the programs that you need and together the two tutorials allowed us to make the first steps of an app.
Details
We needed Python version 3.7.1 for this to work. We also downloaded Pycharm for the code. This is what both videos use. This is a texteditor where you can write the code. You need to know object oriented programming to do this. On the Kivy website there was some info about that and the first video from Tech With Tim mentions that he has some tutorials as well on his page.
Progress
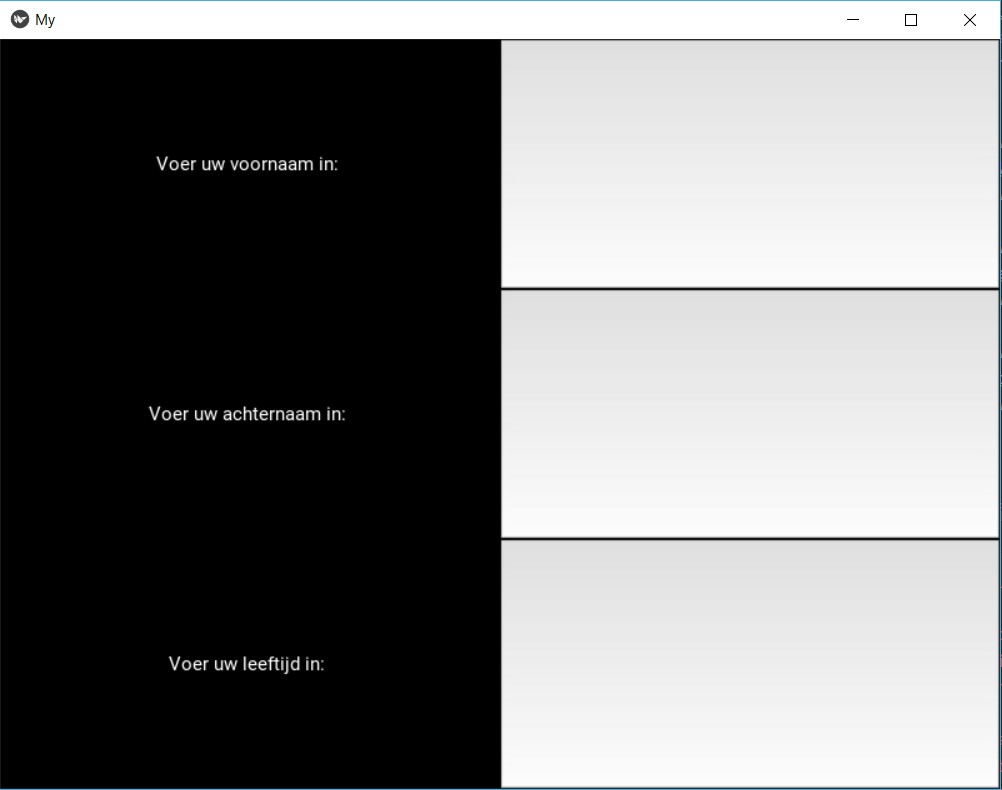
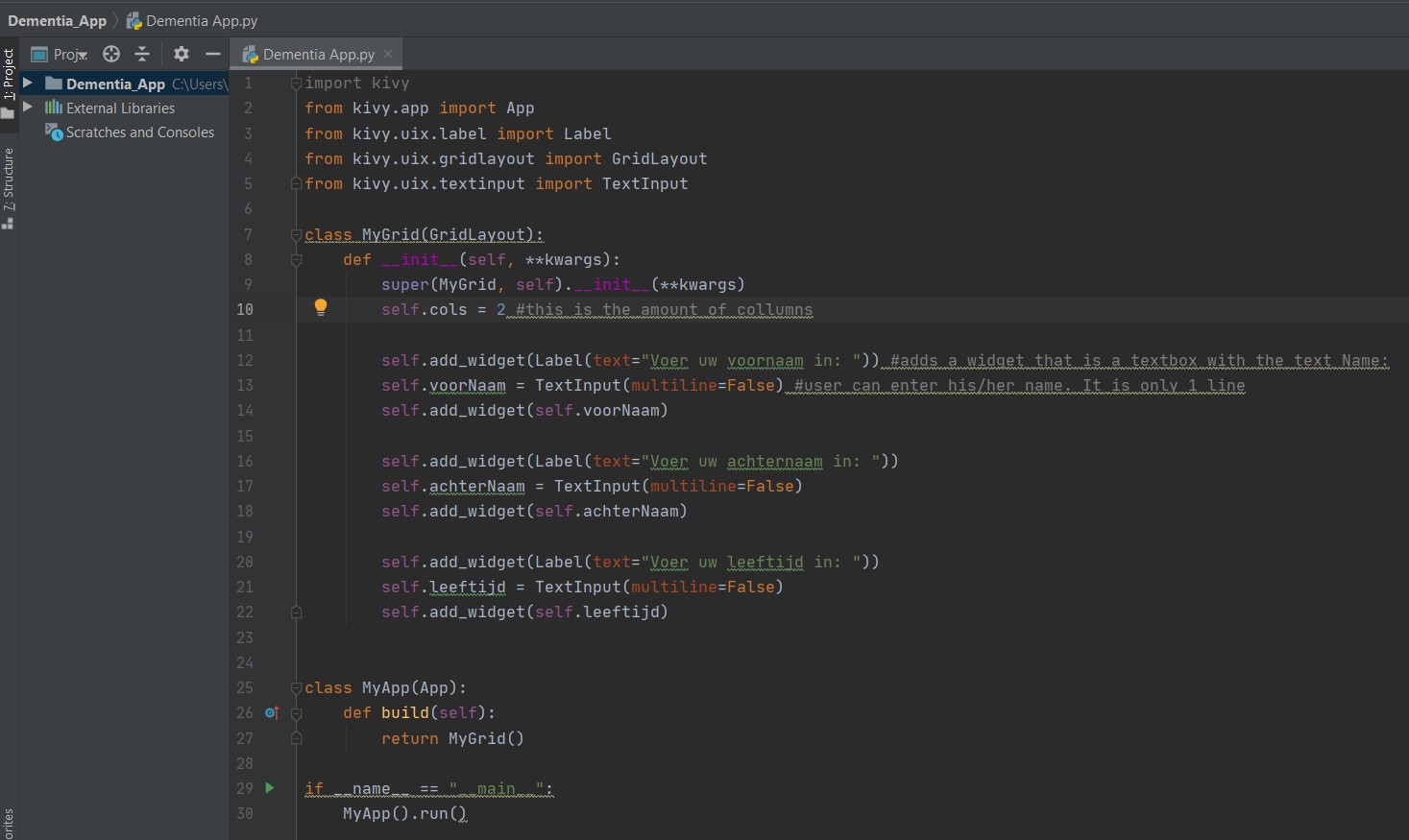
At the end of the second tutorial we were able to make an app that allows the user to put in his or her personal information in text boxes. The following images show the app screen and the code.
Useful tutorials
These are some useful tutorials where someone is building a chat app, not exactly the same as we are trying to do but it explains a lot of codes such as buttons.
1. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FjwD0SOGQ1k&t=655s explains the first steps of making an app
2. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8I2fMqrruwc explains how to make buttons
3. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sJmkhV02lnM explains multiple screens and how to transition between them
4. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hsnch676Lco
5. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=62LSK62Gudc
6. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lmWE2bydekk
7. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CIW0H70wo0M
8. https://likegeeks.com/kivy-tutorial/ offers some help with the different functions of Kivy.
Development in Kivy
We decided to work in Kivy as we want to make the system dynamic. That means it can be used by multiple users and should not only work for one person. How we coded the different functions is shown below:
Displaying pictures
It is important that the pictures are displayed in a specific manner, chronological and with dividing titles.[24] 'Screen Manager' makes it possible to connect multiple screens. This can be helpful with making scrolling through the pictures possible. A down side would be that the user is scrolling through multiple screens which contain pictures and through a list with all the pictures[25].
Import photos
Two ways to display photos in the app. One way is to import photos from the system. { wimg = Image(source='mylogo.png'). The other way is importing from asynchronous loading. This is to load an image asynchronously (for example from an external webserver) {aimg = AsyncImage(source='http://mywebsite.com/logo.png').
In both options, the image title is called. This is not the same for every person. Hence, not dynamic. There is also a video that shows how to do it with one image.[26]
After discussing with some students from Computer Science it turned out that it is really hard to implement this function. First of all we would need a web-server. This is possible, but we also need multiple programs with all sorts of programming languages we haven't worked with yet. We could do research on this and make a list of all necessities, or it might be better for us to work with WordPress and transform it in such a way that it looks like an app. You can make an account, so that caregivers/family can log in to it and add photos. It then is easy to display and import them. However, only a gallery can be displayed, not one picture a day, which makes it less dynamic as well.
OPTION 1: IMPORT PHOTO FROM WEBSITE INCLUDING WEBSERVER
First of all, a website where the photos are uploaded should be used. This is a website called timetomato and it is made to upload photos from your pc.
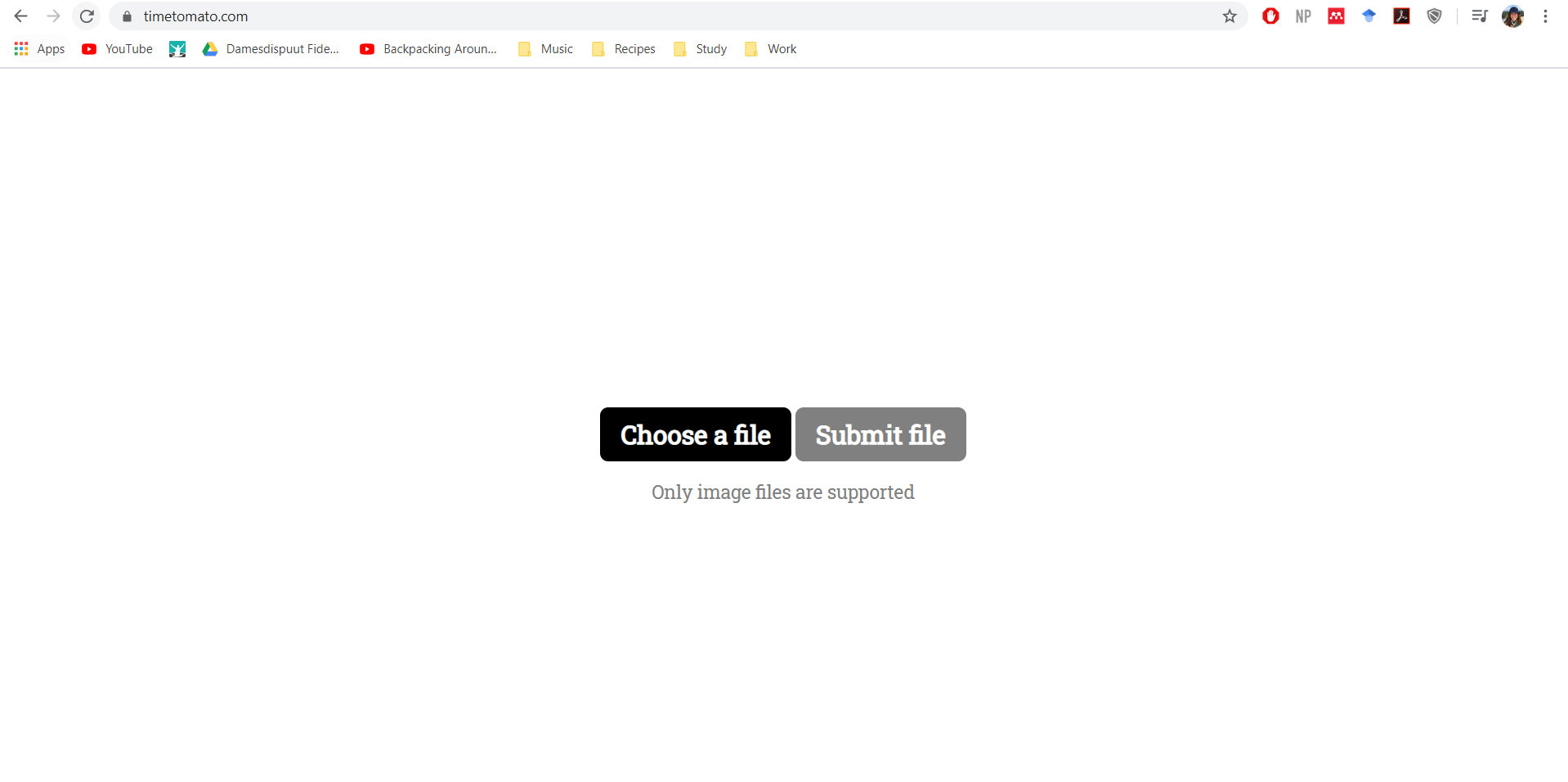
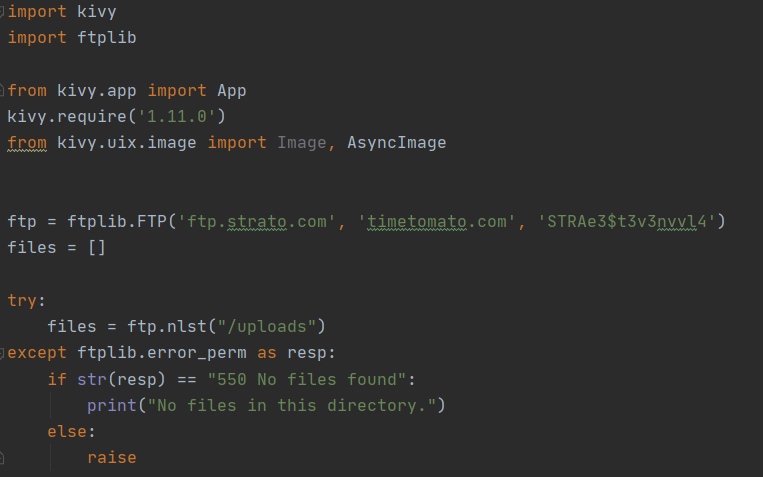
In order to receive this picture from the website into our screen, the next codes are written. This is an easy way to take file 1, file 2 of the website and you don't need the title of the picture so that is easy.
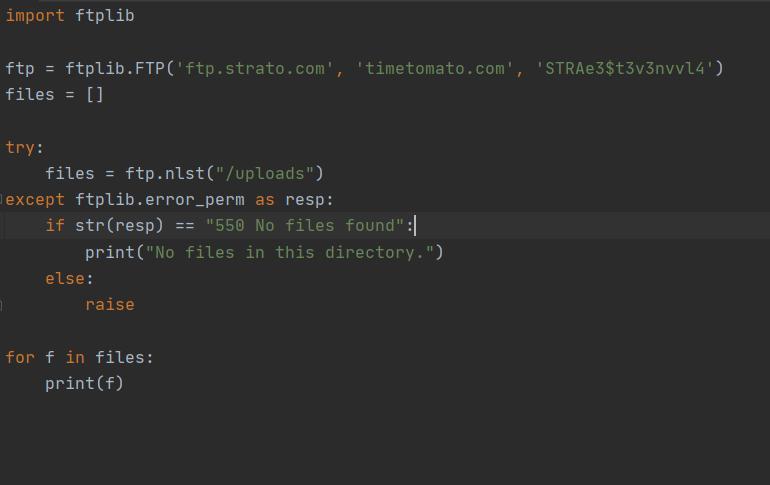
An example of file 1 is shown here. So I uploaded this picture and then ran this code:
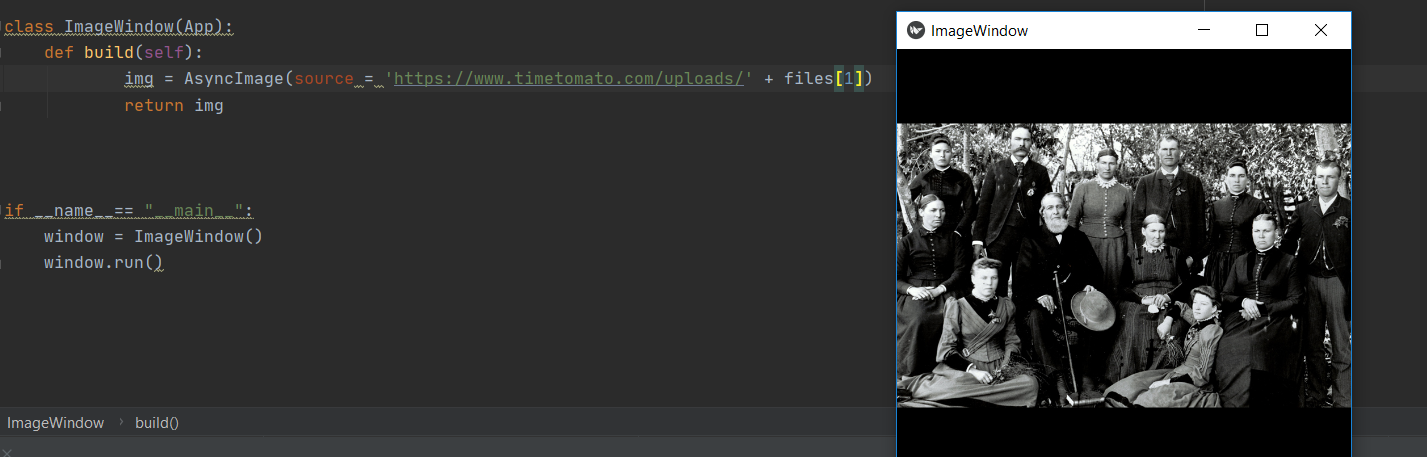
Same for file 2:
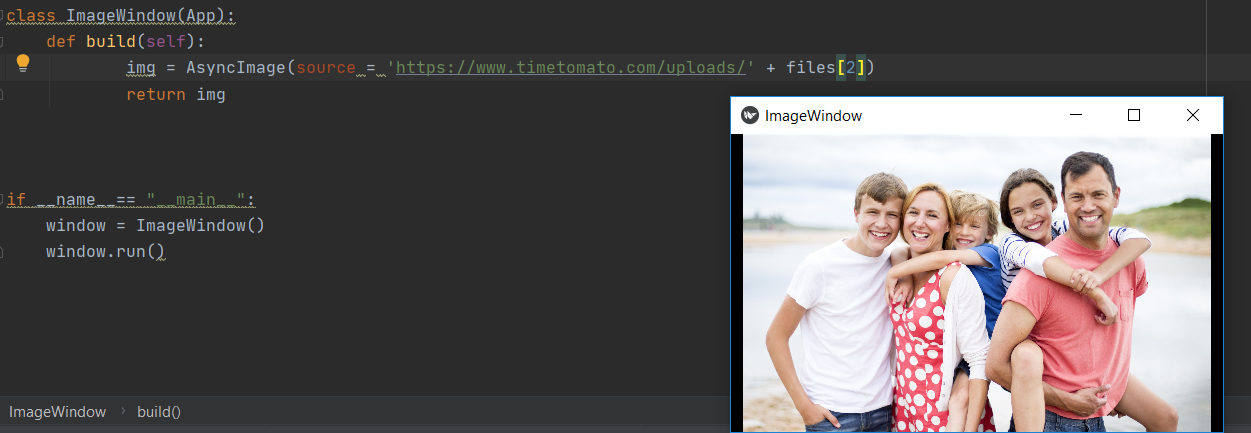
ADVANTGES:
+ Advantages of using this is that the pictures can be uploaded from every laptop from anywhere in the world.
DISADVANTAGES:
- In the Python file, there are not many options to edit the photo.
OPTION 2: IMPORT PHOTO FROM LOCAL PLACE, INCLUDING A KIVY FILE
This is the code and its outcome for the second option. With this option you can upload a photo from your computer, in the same directory as the python file.
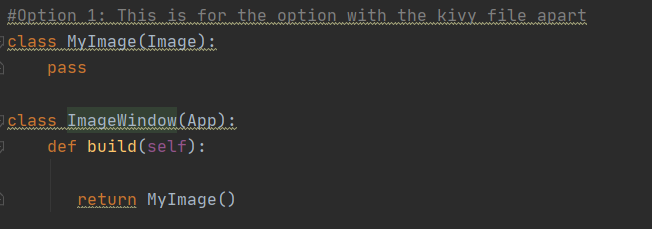
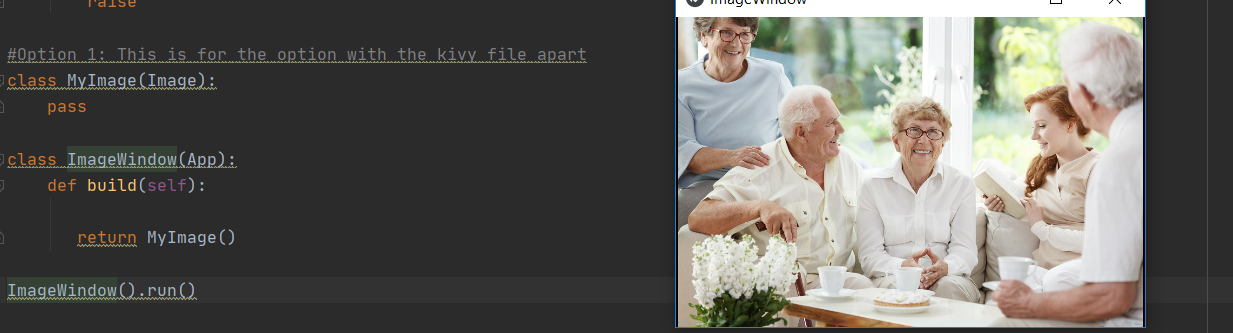
The Kivy file can be read. This one is called by the code in the Python file.
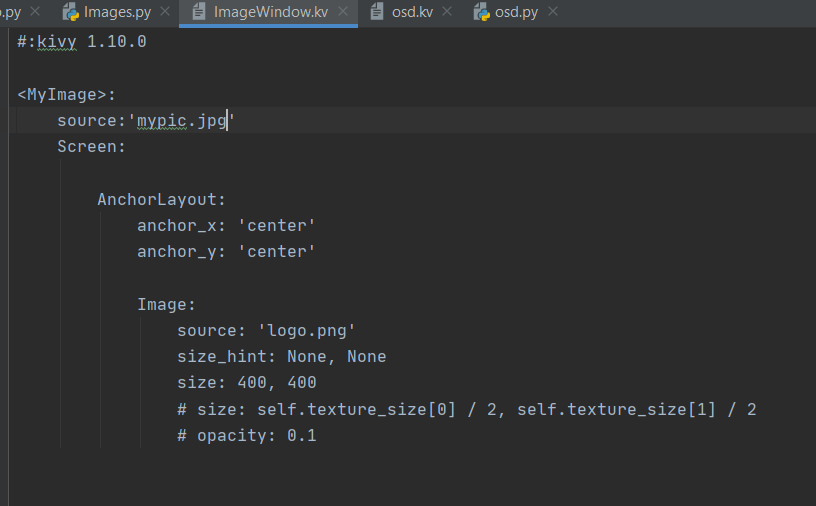
ADVANTAGES:
+ A lot of edits can be done in the kivy file. The code in the Python file is general and the code in the kivy file is very specific; these are all modifications on the picture that is uploaded.
DISADVANTAGES:
- The code is very specific: the name of the picture should be written over precisely. Also, it can be uploaded only from the place where the code is written as well.
To-do list
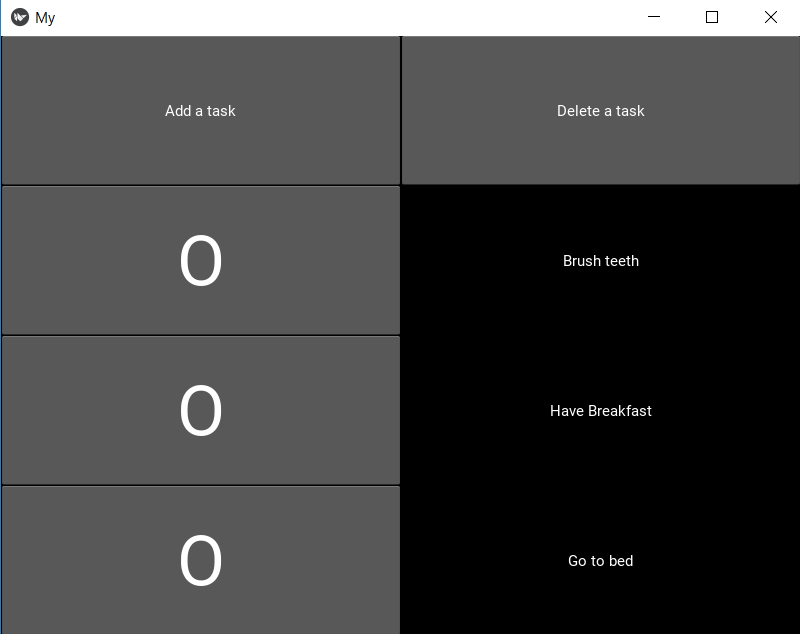
There needs to be a to do list feature in the app. I found a video [27] that explains how to create a program that lets a user enter certain things (to do list items) and then the item is displayed in a list, the user can then also delete items from the list again when they are completed. Later it is found that this tutorial is outdated and uses a function of Kivy that is not available anymore, Listview. This function has been replaced with Recycleview instead. The website Like geeks[28] offered some help with the different functions of Kivy. Right now we are busy combining different functions to make a workable to do list. It has been a lot of trail and error up until this point. Now I have learned how to make buttons, change the colours and font colours, how to disable a button and how to make a scrollable list with the Recycleview.
We made a task list that can be saved between instances. It can be updated using the top buttons and the tasks can be checked off on the left
Template home screen
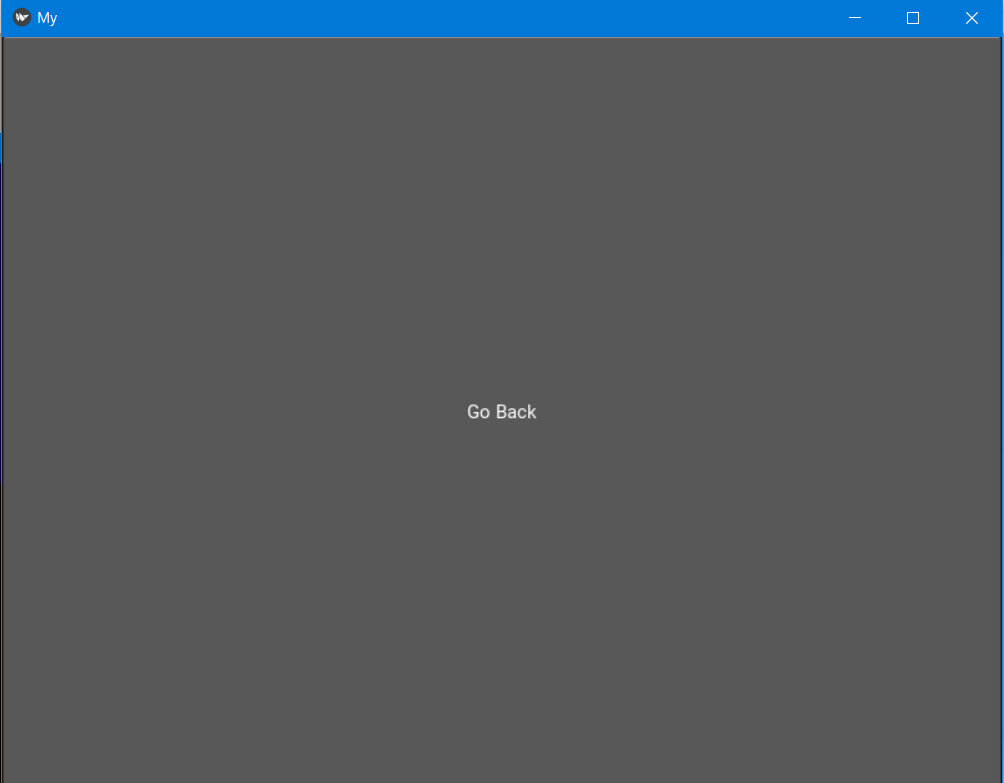
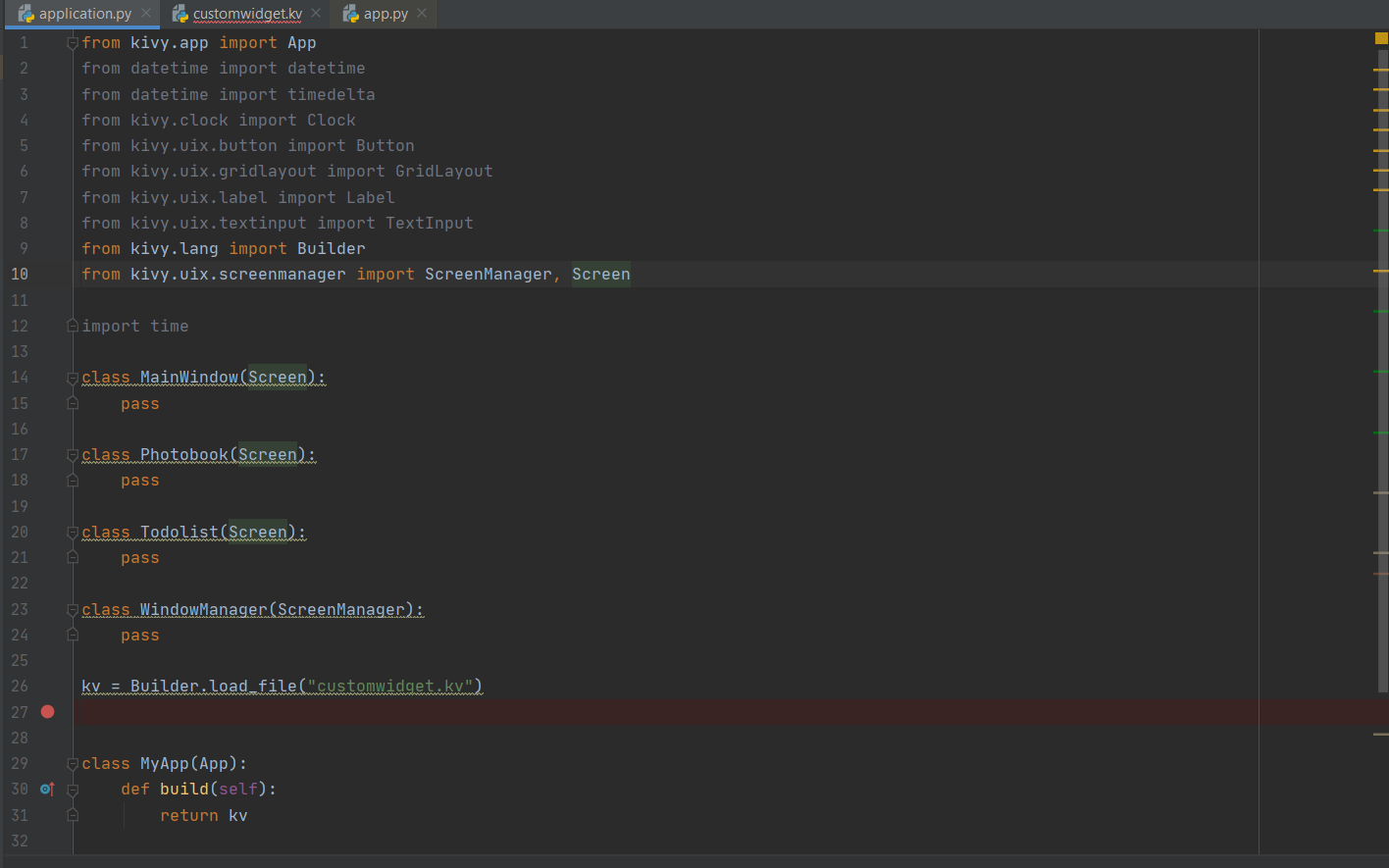
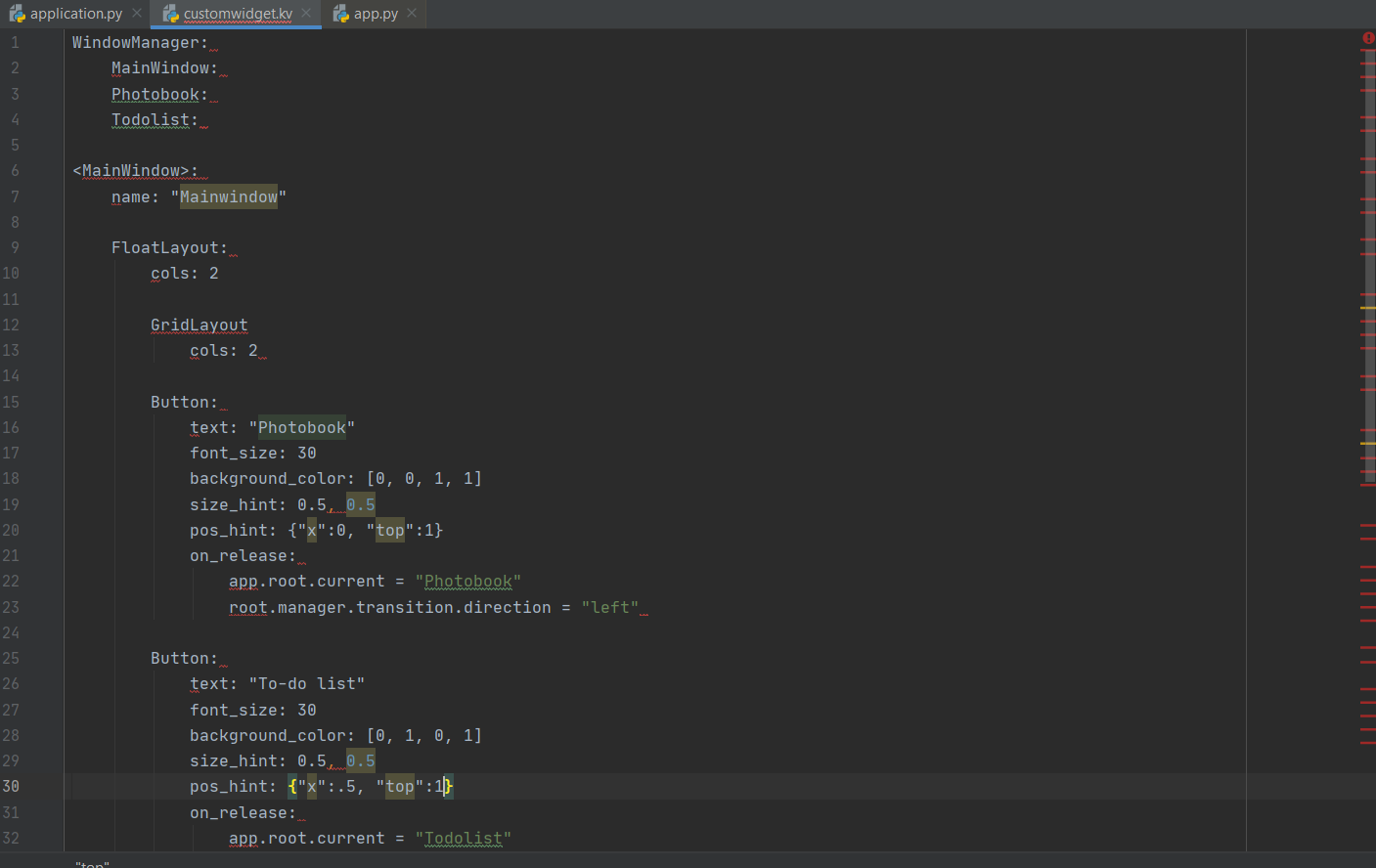
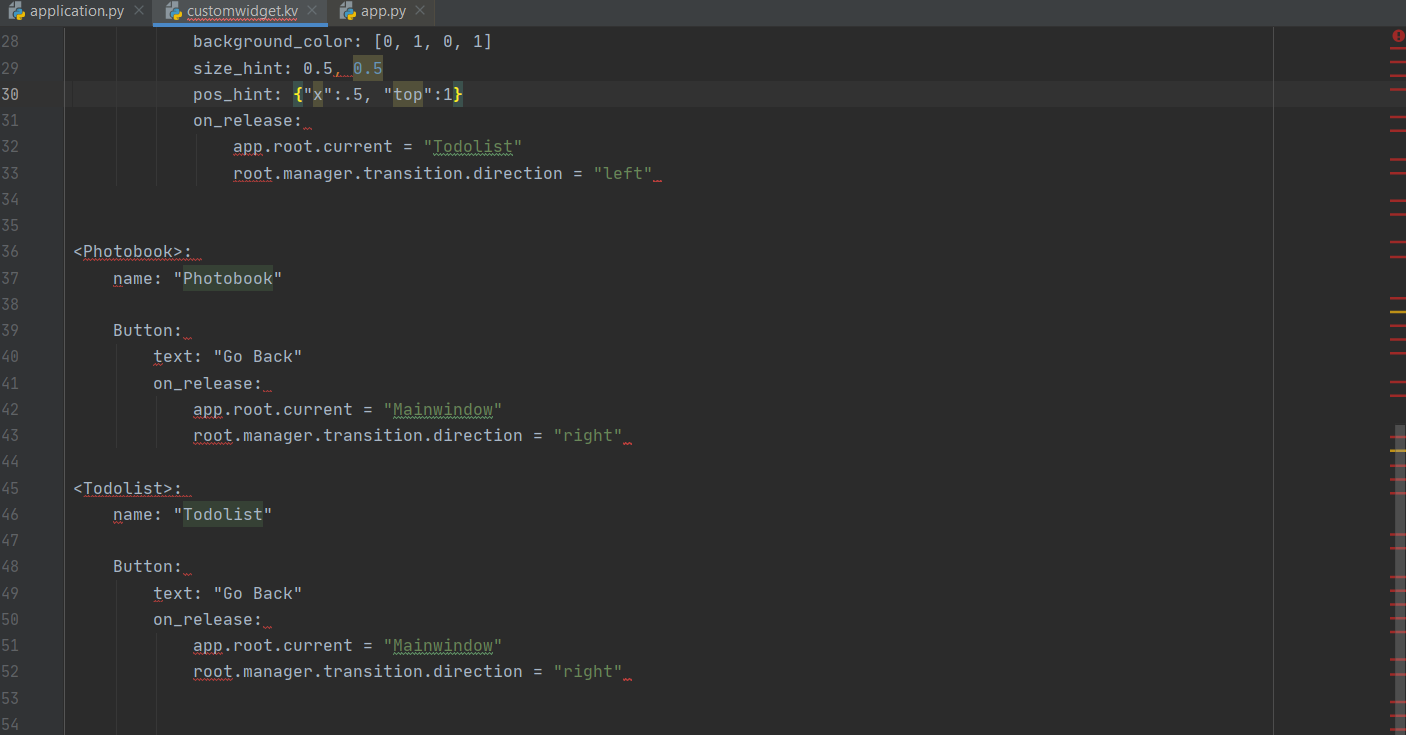
The home screen should have two buttons to go to the photobook and the to-do list. When you click on those buttons you should go the next screen where there will be a template for the function and a button to go back to the home screen. The buttons should be big and have bright colours. First the Pong Game Tutorial was used to make a simple app first[29]. Then the buttons were created to click on. The Button is a Label with associated actions that are triggered when the button is pressed (or released after a click/touch). To configure the button, the same properties (padding, font_size, etc) and sizing system are used as for the Label class[24]. Eventually, the screen manager was used, this is a widget dedicated to managing multiple screens for your application. The default ScreenManager displays only one Screen at a time and uses a TransitionBase to switch from one Screen to another. Multiple transitions are supported based on changing the screen coordinates / scale or even performing fancy animation using custom shaders[25].
The Home screen in kivy:

If you click on the buttons you go to the next screen where you can click on a button to go back:
The code of the Home screen in kivy:
Clock on homescreen
There should be a clock on the homescreen that updates automatically. A code was written that shows a working clock and also includes buttons for the photos and to do list.
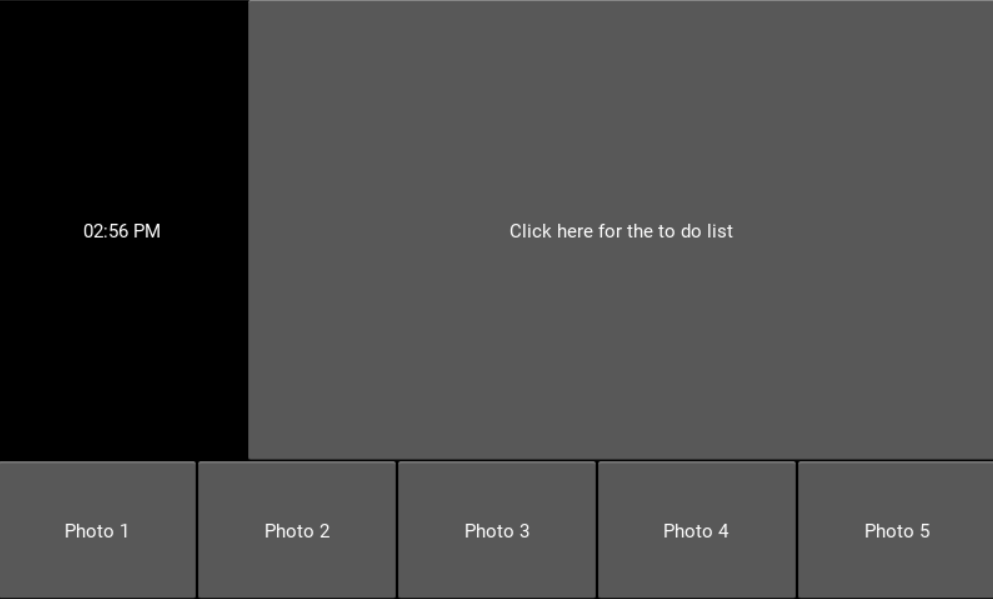
The code is on two parts, one part is a .kv file and the other is the main.py file:
main.py
from kivy.app import App from kivy.config import Config from kivy.clock import Clock from kivy.uix.boxlayout import BoxLayout from kivy.uix.label import Label
import time
Config.set('graphics', 'width', '800') Config.set('graphics', 'height', '480')
class V3Widget(BoxLayout):
pass
class ClockLabel(Label):
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super(ClockLabel, self).__init__(**kwargs)
Clock.schedule_interval(self.update, 1)
def update(self, *args):
self.text = time.strftime('%I:%M %p')
class V3App(App):
def build(self):
return V3Widget()
if __name__ == "__main__":
V3App().run()
v3.kv
<V3Widget>
clock_label: clock_label orientation: 'vertical'
BoxLayout:
orientation: 'horizontal'
size_hint: 1,0.85
ClockLabel:
id: clock_label
size_hint: 0.75,1
Button:
text: 'Click here for the to do list'
size_hint: 0.25,1
BoxLayout:
orientation: 'horizontal'
size_hint: 1,0.15
Button:
text: 'Photo 1'
Button:
text: 'Photo 2'
Button:
text: 'Photo 3'
Button:
text: 'Photo 4'
Button:
text: 'Photo 5'
Designs for a planning app with a social touch
Before we made our final design every team member made design of the app on their own. These designs are shown below. We combined these designs and from these designs we eventually made our final design.
Design Eline
Features that such an app should have
• A home screen with the current day and time and any special events that day: such as national holiday’s, birthdays or other anniversaries or people that the user knows. This way the user has more social contact with those persons. Also events for the next week.
• A daily schedule for that day. With times and activities on there. Things that count for the whole day (birthdays etc.) should also be included here. Furthermore daily routines should be on there, such as 3 meals a day, drinking water, appointments, medicine take-in. The activities on the schedule can be checked of off the list. o Goodbarber feature that might be helpful: You can create a Form where you can use checkboxes. o You can use a chat function, that way when the family has the app as well they can chat in there.
• When the user is late to checking off an item from the task list, they will receive a push notification reminding them of the task.
• When there is an event on the schedule where the user should leave their home, there should be a map function guiding them there. o This is what Goodbarber says about this: Itineraries. Thanks to event geolocalization, your users can create itineraries using external Map services such as Google Maps or Apple Maps.
• If we need any extra functions, we can add our own plugins. “If you are a developer, you may create one or several modules specifically designed for your app. Simply develop your plugin like a mini HTML/JS/CSS app and it will be embedded directly inside your app to function effectively, even without a network connection.” Goodbarder, section Developer/Plugins
Design focus
First, people over the age of 40 are more likely to experience presbyopia, or long-sightedness, which makes reading small text challenging. Second, colour vision, or the ability to distinguish certain colours, fades with age. Colour vision problems in the blue-yellow spectrum(link is external) are often detected among people in their mid-70s. (They struggle to distinguish between blue and yellow colors.) Keeping this in mind we should focus on: [30]
• Increase contrast
• Label Icons with text so they know what they mean
• Large text
• Arial and Verdana as fonts
• All-time visible navigation styles, avoid using slide-out menus
Final design
This is an example of how the app will look for the user. There is the ability to manage the tasks for that day and to look at certain appointments for that day. I made this design in Adobe Illustrator.
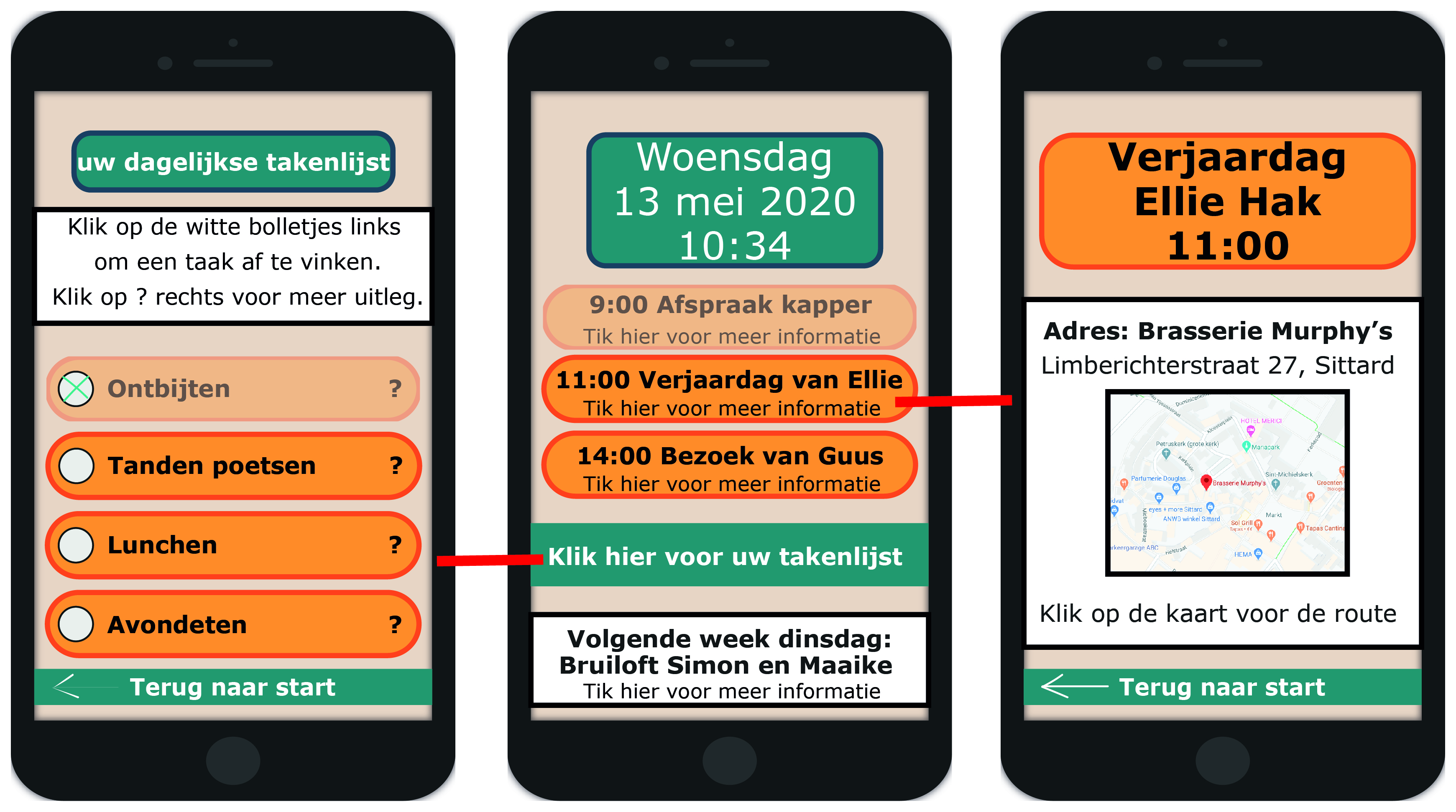
Design Metten
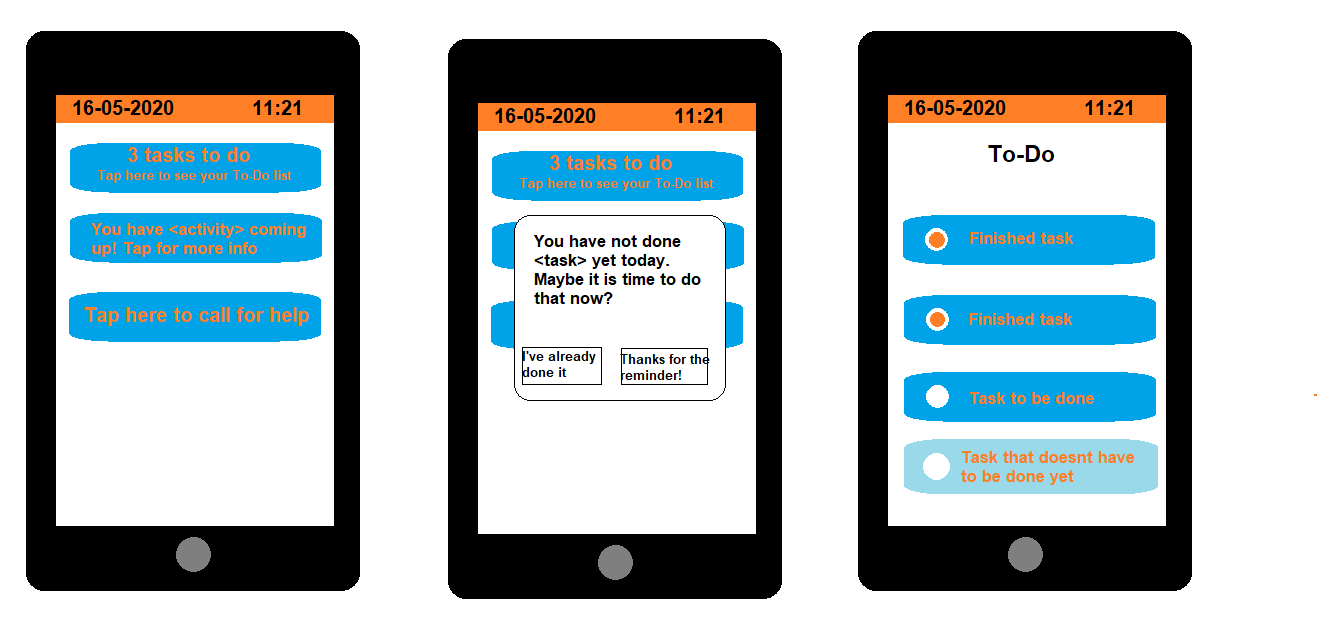
A quick mockup of a possible design for the app. It has a built in to-do list, which can give reminders. The list itself is divided in three categories: Tasks that are already done, tasks that have yet to be done and tasks that do not have to be done yet. The app also has reminders for upcoming activities and a button to call someone in times of emergency.
Design Vera
Features and Functions of the planner app
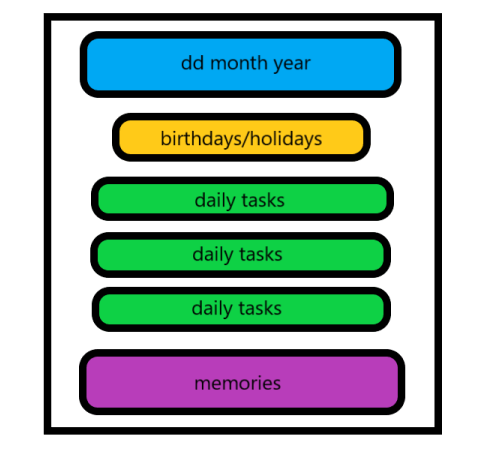
• Overall to do list called 'Daily Tasks', with recognizable icons
• A section with pictures called 'Memories'
• The app gives notifications about 'Memories' of certain dates or 'Daily Tasks' that have been "overdue"
Memory part
• A collection of pictures that can be a subpart of the planner app
In this section it wil be explained how the pictures are organised and what the memory part of the app should do in detail.
• Every picture has a day-month-year attached to it. With this date it should be possible to put pictures in chronological order and to show how long ago the picture was taken.
• Pictures can have a caption that is show below the picture. If a picture has a caption that can be read out loud, a speaker icon is depicted on the picture or at the beginning of the text.
• The photobook is a big list with pictures that can be scrolled through and has big titles that state where a new month begins. The title states "Month - year". Important dates within the months, such as holidays and birthdays, have a smaller title in a different colour. It would be handy to make the background of these pictures a lighter shade of that colour to make clear when the pictures of that event are over and pictures of the normal month resumes. In the under titles is displayed how long ago the month/event happened.
• The Memory part on the home screen of the app depicts a different picture every week (or three to four day maybe) with the title 'Memory of the Week'. When the user clicks on "Show more pictures" the app will lead them to the beginning of the month or event where the picture belongs to.
• If the 'Memory of the Week' has a caption, this caption is also show in the home screen of the app. There will be a limit on the amount of words of the caption that is depicted on the home screen and after this limit … will appear. The spoken audio will be played all the way through and will not end at this limit.
• The 'Memory of the Week' picture is chosen from the pictures in such a way that the 'Memory of the Week' pictures are also in chronological order. Every picture that is 'Memory of the Week' is from a later point that the last. The new picture will also be of another month/event than the earlier one. When all months/events are represented in the 'Memory of the Week' the 'Memory of the Week' will be chosen from the first month/event again.
Example of the Interface
The tasks become green when the user clicks on the square in front of them and will disappear from the list of 'Daily Tasks'.


The 'Memories' section could work according to the user requirements for the "Interactive Photobook' with spoken messages and pictures.

Example of the push notification that the app could give

Design Sterre
Features of the app
• A screen with the current day and the day planning, events, birthdays and holidays for that day.
• An option to go have an overall calendar to see the days per month
• A function called memories, where the memories of that day throughout the years are visualized. This means that photo's of that day that are taken through the years will be visual or stories about that day, that are written or spoken in by family members.
• The letters and functions should be big, so that they are easy to read and find.
• There should be a big contrast between colours
Design Iris
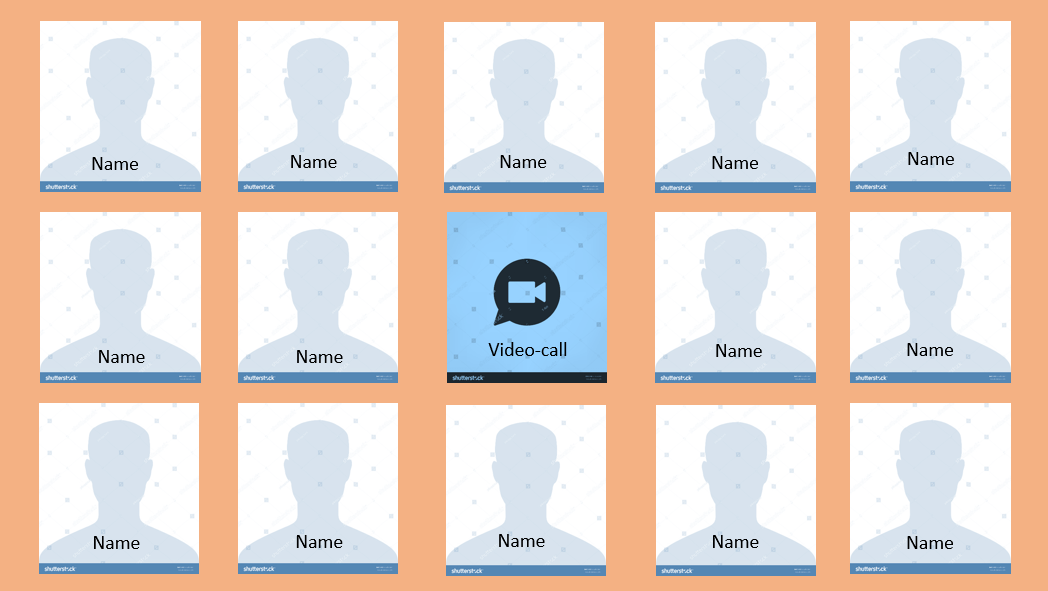

A very simple design is needed in order to not get distracted and keep in mind the function of the app. The most important aspect of this part of the app is that people can call their closest people. It works as follows: the family/caretakers can insert contacts with photos (to a max of 24 because of the design). In order to call the other person, the user has to click on one of the icons with the person's photo and name in it.
User Test
First, we made a test for our application to test the app with elderly people with dementia. This would be a good way to find out if people with dementia understand our application and how they use it. Then we would know how we could improve our application further. However, due to the COVID-19 situation it is not possible to do an user test with elderly people. Therefore, we decided to contact specialists and carers for elderly with dementia. We made a questionnaire to get expertise on our application and how we could improve it.
Test with users
Necessities
- Consent form
- Recording material
- At least one subject (more is better)
- A working app
- Something to make notes in for observations
Process
First the subject has to fill in the consent form and the experimenter has to ask for approval of recording the subject. Name will be anonymous. Then the actions of the subject with the app are recorded (sound and image). Different tasks should be given. The subject reads the exercise and carries it out, following a think-aloud process. Every little thing the subject thinks, should be said out loud. Also when they for example don’t really know what to do. In this way, it can be analyzed easily on what is not clear for the user and how to improve the app. Apart from the recordings, the observer has to write down things that are remarkable . For example, the subject frowns his/her eyebrows which could suggest he/she does not understand what to do. After the tasks, the subject fills in a questionnaire consisting of questions about the app.
Process in steps:
1. Consent form
2. Consent for recording
3. Recording starts
4. Subject does conducts tasks following think-aloud
5. Observer makes notes at the same time
6. Questionnaire for the subject
7. Thank the subject for cooperation
Tasks
1 → Imagine that you would need a guide in order to fulfill your daily tasks. You have brushed your teeth: what do you have to do now in order to show you have done the task?
2 → A photo is shown on the screen. You want to see what the story is behind the picture.
3 → What day is it? Where did you find this?
Consent form
USER-TEST TASK AND MEMORY INTERFACE FOR STARTING DEMENTIA IN ELDERLY
You have been asked to participate in a usability study. This document gives you information about this study and your rights as a participant. Please read it carefully.
About the study
The aim of this study is to discover faults in the app “NAME APP” in order to improve it. The study will last approximately twenty minutes. In this study, you will be asked to conduct a couple of tasks, formulated on the exercise sheet. You will be asked to say your thought process out loud and after the task fill in a questionnaire about the experience. During the study video and audio recordings will be made, as well as notations of other observations during the study. Furthermore the data of the questionnaire will be saved anonymously.
Voluntary
Your participation is completely voluntary. You can refuse to participate without giving any reasons and you can stop your participation at any time during the study. You can also withdraw your permission to use your data up to 24 hours after the study is finished. All this will have no negative consequences whatsoever.
Confidentiality
We will not be sharing personal information about you to anyone outside of the research team. Any audio or video recordings will not be distributed and will not be played back in the presence of persons other than the researchers. The material will be used only for scientific analysis. The information that we collect from this study is used for writing scientific publications and will only be reported at group level. It will be completely anonymous and it cannot be traced back to you.
Further information
If you want more information about this study you can ask Iris de Wit or Sterre Cuppens (contact email: i.c.d.wit@student.tue.nl; s.cuppens@student.tue.nl;) If you have any complaints about this study, please contact the supervisor, ..........
Certificate of Consent
I, (NAME) ………………………. Have read and understood this consent form and have been given the opportunity to ask questions. I agree to voluntarily participate in this study carried out by the research group of Project Robots Everywhere of the Eindhoven University of Technology.
Participant’s Signature Date
_________________________ ______________
Questionnaire for the specialists
1. What kind of technology do the people with dementia use nowadays?
2. How do people with dementia use the current technology?
3. What are the difficulties people with dementia have with using technology?
4. What difficulties do people with dementia have using a daily planning?
5. How do people with dementia experience seeing photos and memories from back in the days?
6. What are your opinions about an app that would have the daily planning with memories from back in the days for someone with dementia?
7. What kind of problems do you think that occur if someone with dementia would use this app?
8. Do you think that this app would help against loneliness among people with dementia?
List of carehomes in Eindhoven
| Carehome | Sent mail | Contact over the phone | Participation |
|---|---|---|---|
| St. Annaklooster | Yes | Yes | We need to send an extra mail in Dutch and then they will talk about it |
| Glorieuxpark | Yes | - | No |
| Neos | Yes | - | - |
| WoonincPlusVitalis | Yes | - | - |
| Archipel Gagelbosch | Yes | Yes | Maybe, they are going to discuss it this week |
| Archipel Passaat | Yes | Yes | Maybe, they are going to discuss it this week |
| Archipel Eerdbrand | Yes | Yes | Maybe, they are going to discuss it this week |
| Archipel Landrijt | Yes | Yes | Maybe, they are going to discuss it this week |
| Vitalis Kronehoef | Yes | - | - |
| Verpleeghuis de Weerde | Yes | - | - |
| Brunswijck | Yes | - | - |
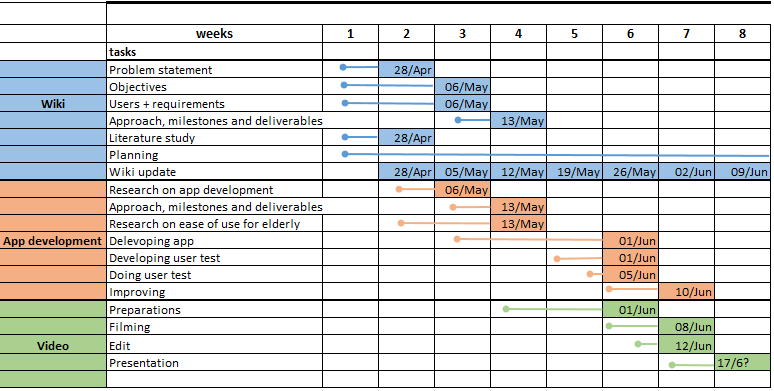
Planning
| Week | Tasks to start | Intermediate Deadlines | All | Eline | Iris | Metten | Sterre | Vera |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (20-4) / 26-4) | Articles - First plan | Articles - First plan | Read and summarize at least 25 papers, set up first plan | Wiki update | ||||
| 2 (27-4 / 3-5) | Research on app development - Research on ease of use for elderly | First plan worked out | Wiki update | Problem statement | Planning | Objectives | Users and requirements | State of the Art update |
| 3 (4-5 / 10-5) | Approach, milestones and deliverables - Developing App | Objectives worked out | Wiki update | Information and plan for building an app | Information and plan for building an app | Improving Objectives | Improving Objectives | Improving Objectives |
| 4 (11-5 / 17-5) | Preparations video | Approach, milestones, deliverables - Research ease of use for elderly | Wiki update | Research in navigation feature and app making with an app maker. | User-test | |||
| 5 (18-5 / 24-5) | Developing user test | Wiki update | Programming the To do list part of the app | Import photos with Kivy, contact with elderly homes | ||||
| 6 (25-5 / 31-5) | Analysis and improve app - Filming and later on edit | App finished - User tests done - Preparations video done | Wiki update | Programming the To do list part of the app | Import photos in Kivy | |||
| 7 (1-6 / 7-6) | Preparing presentation | Improving done, Video finished | Wiki update | |||||
| 8 (8-6 / 14-6) | Presentation | Wiki update |
Time management
Week 1:
| Name | Student number | Time spent | Break-down |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eline Visser | 1375369 | 11 hours | Introductory meeting and study guide + group formation (2h) 2 group meetings (1.5h) Think of ideas and do research + read old wikis (2.5h) Learn how to edit wiki and make start on page (0.5h) 5 articles literary study and summary (4.5h) |
| Metten de Lange | 1240902 | 11 hours | Introductory meeting and study guide + group formation (2h) 2 group meetings (1.5h), Researching ideas for the project (1.5h), Reading and summarizing 5 articles (6h) |
| Vera Holtmark van Dijkerhof | 1380893 | 13 hours | Introductory meeting and study guide + group formation (2h) 2 group meetings (1.5h), reading wiki pages of previous groups (1.5h), reading 5 articles (6h), summarizing articles (2h) |
| Sterre Cuppens | 1387790 | 11 hours | Introductory meeting and study guide + group formation (2h) 2 group meetings (1.5h), Literature research (5 h), Summarize articles, (2 h) Update wiki (0.5 h) |
| Iris de Wit | 1258230 | 11 hours | Introductory meeting and study guide + group formation (2h) 2 group meetings (1.5h), reading wiki pages of previous groups (1.5h), reading 5 articles (6h), summarizing articles (2h) |
Week 2:
| Name | Student number | Time spent | Break-down |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eline Visser | 1375369 | 7 hours | Summaries on articles (1h) Wiki problem statement (3h) Meeting tutor + Group (1h) Watch videos on how to make an app (2h) |
| Metten de Lange | 1240902 | 5 hours | Meeting (1h), reading articles about the subject (2h), describing objectives based on articles (1h), updating wiki (1h) |
| Vera Holtmark van Dijkerhof | 1380893 | 5 hours | Updating summaries and references of articles (2h), meeting with group and tutor (1h), reading article and rewriting requirements with obtained information (2h), |
| Sterre Cuppens | 1387790 | 9 hours | Meeting (1 hrs), Updating references and summaries of articles (1 h), Types of users (3 h), User requirements (3 h), Update wiki (1 h) |
| Iris de Wit | 1258230 | 6 hours | Meeting (1 hrs), Updating references and summaries of articles (1 h), making three different plannings (one over all, one for tasks and one scheme in Wiki) (3 h), Update wiki (1) |
Week 3:
| Name | Student number | Time spent | Break-down |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eline Visser | 1375369 | 9 hours | Research on app making. (2h) Practice with python and Kivy (3h) Documenting the process (1h) Editing the wiki (1h) More research in appypie and app makers after the meeting with tutor. (2h) |
| Metten de Lange | 1240902 | 6 hours | Meeting (1h), reading up on technology that helps demented people with basic tasks (3h), summarizing relevant articles (1h), constructing a set of requirements for to-do list and help app (1h) |
| Vera Holtmark van Dijkerhof | 1380893 | 7 hours | Meeting (1h), reading up about dementia and Alzheimer (1,5), thinking about the concept of an interactive photobook (0,5h), writing requirements for interactive photobook (1h), watching tutorials about animation in preparation for the video presentation (3h) |
| Sterre Cuppens | 1387790 | 8 hours | Meeting (1 h), Read articles again (2 h), Improve user requirements (4 h), Update wiki (1 h) |
| Iris de Wit | 1258230 | 7.5 hours | Research on developing app (2h), Meeting (1h), Editing Wiki (1h), Research on how to use communication function, looking for articles and app-developers about this (3h), making template on communication (0.5), starting user-tests (1.5h) |
Week 4:
| Name | Student number | Time spent | Break-down |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eline Visser | 1375369 | 11 hours | Research for a navigation app and requirements for it. (1h) Meeting with group Monday (1h), Research app makers (2h), Research apps for elders (1h), Designing app (3h), Editing wiki (1h) Goodbarber app making (2h) |
| Metten de Lange | 1240902 | 6 hours | Meeting with group (1h). Study app designs (2h). Making design for app with planner (2h). Updating wiki (1h). |
| Vera Holtmark van Dijkerhof | 1380893 | 7.5 hours | Meeting with group (1h), Looking for animation options for presentation (2h), Making design/concept for social planner app (2h), meeting with group and tutor (1h), working out the details of the memorie part of the app (1.5h) |
| Sterre Cuppens | 1387790 | 9 hours | Research for a cognitive game (3h), Meeting with group (1), Research social planner app (3h), Designing social planner app (1h), Updating Wiki (1h) |
| Iris de Wit | 1258230 | 7,5 hours | Meeting with group Monday (1h), Improving Communication (1h), Updating Wiki (1h), Making Start of User test (1,5), Designing app (1h), Research on communication (2h) |
Week 5:
| Name | Student number | Time spent | Break-down |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eline Visser | 1375369 | 7 hours | Meeting group Monday (1h), Further programming in Kivy (2h), research to do list in kivy (1h), Editing wiki (1h), programming (2h) |
| Metten de Lange | 1240902 | 6 hours | Meeting (1h). Installing Kivy (1h). Learning Kivy and python (4h) |
| Vera Holtmark van Dijkerhof | 1380893 | 10 hours | Meeting with group (1h), installing kivy and start programming (3h), work on Memorie part of app in kivy (4), watching tutorials (2h) |
| Sterre Cuppens | 1387790 | 7 hours | Meeting group Monday (1h), Finishing User Test (2h), Contact with carehomes (2h), Researching Kivy on template home screen (2h) |
| Iris de Wit | 1258230 | 8 hours | Meeting group Monday (1h), Finishing User Test (2h), Contact with carehomes (2h), Researching Kivy on import photos (2h), update wiki (1h) |
Week 6:
| Name | Student number | Time spent | Break-down |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eline Visser | 1375369 | 8 hours | Group meetings (2h), to do list programming (5h), wiki update (1h) |
| Metten de Lange | 1240902 | 9 hours | Learning kivy and python (3h), programming to-do list (4h), updating wiki (1h), group meeting (1h) |
| Vera Holtmark van Dijkerhof | 1380893 | 9 hours | Group meeting (1h), programming photobook (3h), writing for the wiki (1h), making visual content with illustrator (4h) |
| Sterre Cuppens | 1387790 | 9 hours | Group meeting (1h), Updating Wiki (1h), Contact User tests (1h), Homescreen programming (6h) |
| Iris de Wit | 1258230 | 9 hours | Group meeting (1h), Updating wiki (1h), Contact User tests (1h), Import photos in Kivy (6) |
Week 7:
| Name | Student number | Time spent | Break-down |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eline Visser | 1375369 | 8.5 hours | Meeting Metten about to do list (1.5h) programming (3h), Meeting tutor (1h), Coding (3h) |
| Metten de Lange | 1240902 | 11.5 hours | Programming to-do list (8h), updating wiki (2h), Meeting Eline about to do list (1.5h) |
| Vera Holtmark van Dijkerhof | 1380893 | 7.5 hours | Making the powerpoint presentation (3h), meeting with tutor/group (1h), looking for video editing software (2h), updating wiki page (0.5h), writing the script presentation (1h) |
| Sterre Cuppens | 1387790 | 10 hours | Programming Home screen (5h), Updating Wiki (5h) |
| Iris de Wit | 1258230 | hours |
Week 8:
| Name | Student number | Time spent | Break-down |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eline Visser | 1375369 | 4 hours | Coding (2h), Group meeting (1h), Wiki editing (1h) |
| Metten de Lange | 1240902 | hours | |
| Vera Holtmark van Dijkerhof | 1380893 | 2 hours | Group meeting (1h), reading and editing the wiki (1h), making presentation (… h) |
| Sterre Cuppens | 1387790 | hours | |
| Iris de Wit | 1258230 | hours |
References
- ↑ World Population Clock: 7.8 Billion People (2020) - Worldometer. (2020). Retrieved from https://www.worldometers.info/world-population/#:%7E:text=7.8%20Billion%20(2020),currently%20living)%20of%20the%20world.
- ↑ World Health Organization: WHO. (2019, September 19). Dementia. Retrieved from https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/dementia
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Cahilla, S., Macijauskieneb, J., Nygårdc, J., Faulknera, J., & Hagend, I. (2007). Technology in dementia care. Technology and Disability, 19, 55–60. Retrieved from https://content.ios.press.com/download/technology-and-disability/tad00227?id=technology-and-disability%2Ftad00227.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 van de Watering, M. Retrieved from http://marekvandewatering.com/texts/HCI_Essay_Marek_van_de_Watering.pdf.
- ↑ Miskelly, F. (2001). Assistive technology in elderly care. Age and Ageing, (30), 455–458. Retrieved from https://watermark.silverchair.com/300455.pdf.
- ↑ Vogelsmeier, A. A., Halbesleben, J. R. B., & Scott-Cawiezell, J. R. (2008). Technology Implementation and Workarounds in the Nursing Home. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association, 15(1), 114–119. https://doi.org/10.1197/jamia.m2378.
- ↑ Bemelmans, R., Gelderblom, G. J., Jonker, P., & de Witte, L. (2012). Socially Assistive Robots in Elderly Care: A Systematic Review into Effects and Effectiveness. Journal of the American Medical Directors Association, 13(2), 114-120.e1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jamda.2010.10.002.
- ↑ .. Van Der Roest, H. G., Meiland, F. J. M., Comijs, H. C., Derksen, E., Jansen, A. P. D., Van Hout, H. P. J., … Dröes, R. M. (2009). What do community-dwelling people with dementia need? A survey of those who are known to care and welfare services. Retrieved from International Psychogeriatrics. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1041610209990147
- ↑ Dogruel, L., Joeckel, S., & Bowman, N. D. (2015). Retrieved from https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/0144929X.2015.1077890
- ↑ Roupa, Z., Nikas, M., Gerasimou, E., Zafeiri, V., Giasyrani, L., Kazitori, E., & Sotiropoulou, P. (2010). The use of technology by the elderly.Retrieved from Health Science Journal.
- ↑ Lucero, R. J., Fehlberg, E. A., Patel, A., Bjarnardottir, R. I., Williams, R., Lee, K., Ansell, M., Bakken, S., Luchsinger, J. A., & Mittelman, M. (2018). The effects of information and communication technologies on informal caregivers of persons living with dementia: A systematic review. Alzheimer's & dementia (New York, N. Y.), 5, 1–12. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trci.2018.11.003 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6315277/
- ↑ Van der Roest, H.G. Wenborn, J. Pastink, C. Dröes, R. Orrell, M. (2017, June 11). Retrieved from https://www.cochranelibrary.com/cdsr/doi/10.1002/14651858.CD009627.pub2/abstract.
- ↑ Zhang, H., Wang, Z., Wang, J., Lyu, X., Wang, X., Liu, Y., … Yu, X. "Computerized multi-domain cognitive training reduces brain atrophy in patients with amnestic mild cognitive impairment" (2019, January 31). Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6355814/.
- ↑ L. Nygård Ph.D. & S. Starkhammar (2007) The use of everyday technology by people with dementia living alone: Mapping out the difficulties, Aging & Mental Health, 11:2, 144-155, DOI: 10.1080/13607860600844168.
- ↑ Hawkley, L. C., & Cacioppo, J. T. (2010). Loneliness matters: A theoretical and empirical review of consequences and mechanisms. Retrieved from Annals of Behavioral Medicine. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12160-010-9210-8
- ↑ Kaspar, R. (2004). Technology and loneliness in old age. Gerontechnology Journal, Vol 3(No 1), 42–48. Retrieved from https://journal.gerontechnology.org/archives/324-326-1-PB.pdf.
- ↑ Login | App Builder Appy Pie. (n.d.). Retrieved 7 June 2020, from https://snappy.appypie.com/login
- ↑ G. (n.d.). GoodBarber - Create a mobile app: Shopping App and Classic App. Retrieved 7 June 2020, from https://www.goodbarber.com/.+And+a+review+https://apptooltester.com/reviews/goodbarber/
- ↑ kivy. (n.d.). Retrieved 7 June 2020, from https://kivy.org/#home
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 Image — Kivy 1.11.1 documentation. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://kivy.org/doc/stable/api-kivy.uix.image.html Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name "”Kivy" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ 25.0 25.1 Screen Manager — Kivy 1.11.1 documentation. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://kivy.org/doc/stable/api-kivy.uix.screenmanager.html
- ↑ Night king. (2019, October 26). import pictures in kivy app development | python | mobile app developement in simple way. Retrieved from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wXYamQkMyk4
- ↑ Derec Banas (2016). Retrieved from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dxXsZKmD3Kk
- ↑ Kivy Tutorial – Build Desktop GUI Apps Using Python. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://likegeeks.com/kivy-tutorial/
- ↑ A first App — Kivy 1.11.1 documentation. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://kivy.org/doc/stable/gettingstarted/first_app.html
- ↑ Clutch (2017). Retrieved from https://clutch.co/app-development/resources/designing-apps-for-elderly-smartphone-users