Embedded Motion Control 2013 Group 11
Group Members
| Name: | Student id: | Email: |
| Justin Wildschut | 0617495 | j.a.wildschut@student.tue.nl |
| Jeroen Zegers | 0638172 | j.c.zegers@student.tue.nl |
| Alex Andriën | 0652965 | a.r.p.andrien@student.tue.nl |
| Talha Ali Arslan | 0867550 | talhaaliarslan@gmail.com |
| Leroy Hazeleger | 0651762 | l.hazeleger@student.tue.nl |
Discussion and Possible Solutions
Filtering and Processing Laser Data
By applying a set of filters, laser data is processed to give information which are easier to interpret for path planning. By detecting certain features of the environment, we now deal with smaller amount of data which are transferred by custom messages that can be modified.
At first, the filter process was created as a node and it got more complex as new stuff were added. So; for ease of programming,reading and debugging the code, we decided to split up some parts. Then it became much simpler, more fixes were done because it was easier to notice them now and the overall functionality of the processes increased.
After visualizing the environment as we want to; we can now focus on tasks of the robot. Some of the tasks have to be carried out at all times (e.g. obstacle avoidance) and some have to be completed upon requests (e.g. change in trajectory due to decision making).
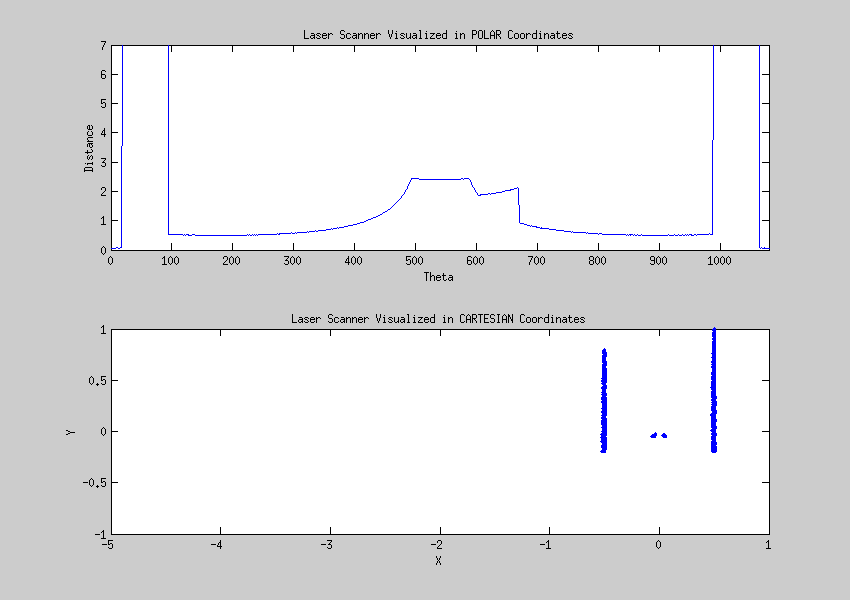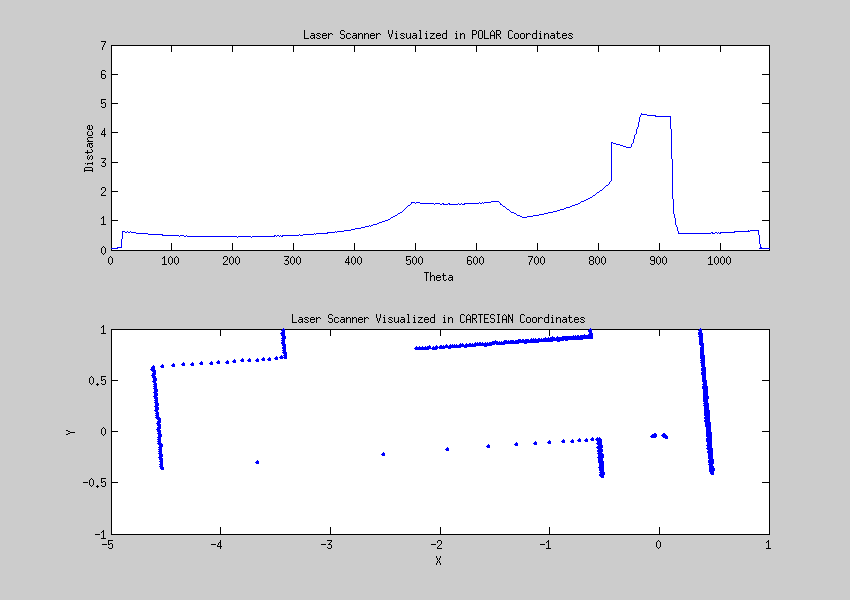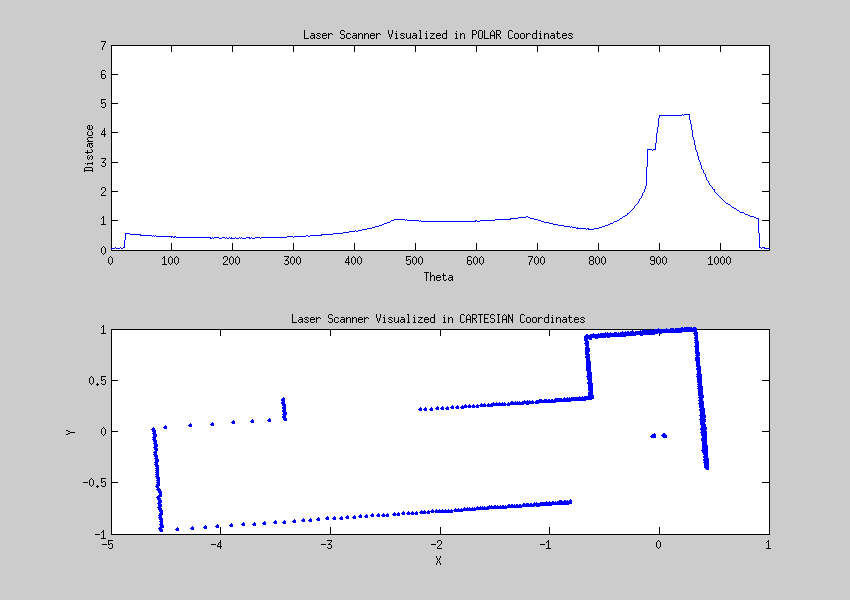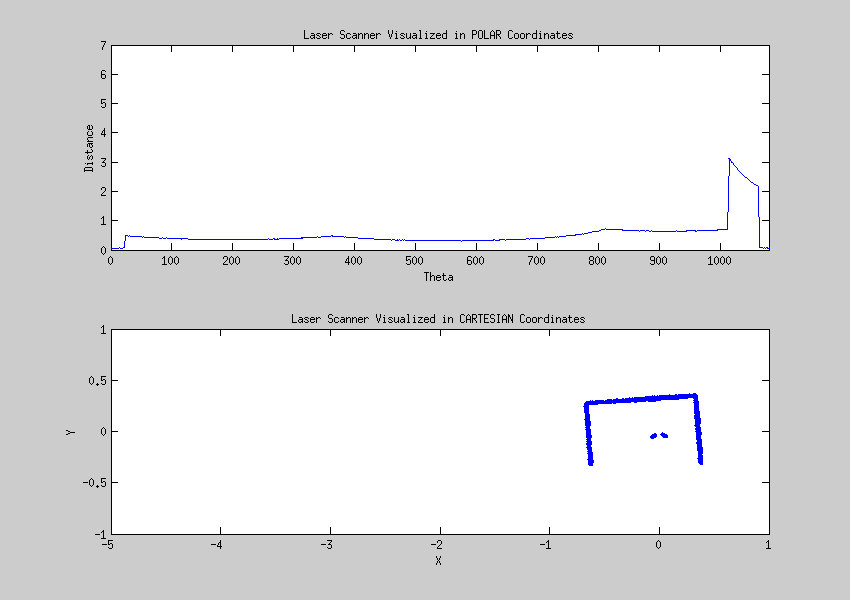
Laser data visualized
The data from the laser can be interpreted as points given in a polar coordinate system, these points can be transformed to a cartesian coordinate system. This visualisation helps to create a strategy for detecting walls and corners.
ROS Nodes and Topics
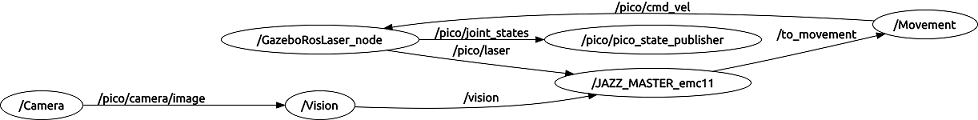
With ROS, one can use nodes and topics to create simpler and easy-to-handle structures. Usage of nodes is very useful when multiple tasks have to be done simultaneously. For this project, a 'Master' node, a 'Movement' node and a 'Vision' node can be created to perform given tasks as solving a maze and recognizing signs, which have to be done simultaneously and which are at times independent of each other. For the corridor competition, the task is simple; so the use of multiple nodes and especially the 'Vision' node will not be necessary. However, for the second competition goal of which will be solving the maze, these nodes can be implemented to perform recognition of signs and to solve the maze. Here is one of the first drafts of the nodal structure of the program:
Useful Things
Hardware info
Technical info about the laserscanner can be found in this document. Mostly to satisfy your curiosity, not specifically needed for programming. Hokuyo Laser Scanner
Creating a different map
Using GIMP Image Editor
1. Download GIMP Image Editor from the Software Center
2. Open the existing map ("maze.pgm") in '/home/s080482/ros/emc/general/gazebo_map_spawner/maps' with GIMP
3. Edit the map how you want it to be. Scroll all the way down in the 'Brushes' box in the bottom right of GIMP. Then there is a square on the second last row on the far right, called ' square (5x5)(5 x 5). (make sure you have this one and not one with 'blur'. Also select the 'Pencil Tool Hard Edge Painting Using a Brush' in the top left box.
4. Now just delete blocks and at add them were you want. Zooming in helps. You can switch color on the top left as well.
5. Also if you look closely, you can see a grey dot in the bottom center. I think this to mark the point where the robot spawns. I suggest we leave it where it is and edit the maze around it.
6. Save the map in the same folder but with a different name.
7. Go to the folder '/home/s080482/ros/emc/general/gazebo_map_spawner/scripts' and open spawn_maze in a text editor.
8. Change the name of the map in needs to load, i.e. change the OWN_MAP in the text below to your own map name.
rosrun gazebo_map_spawner map_spawner `rospack find gazebo_map_spawner`/maps/OWN_MAP.pgm
9. Now simply spawn the maze in exactly the same way as you did before, so with exactly the same commands!
Using Gazebo Model Builder
1. Open Gazebo
2. Go to 'Edit', 'Model Builder'.
3. You will see a 2-D image and 3-D world under it. Choose 'Add Wall' and start drawing walls on the 2-D image.
4. Check the locations and distances from the 3-D world.
5. Hit 'Done', save it to a file 'example.sdf'. Close 'Model Builder'. The model should spawn in the world.
6. Go to 'File', 'Save As'; again save as 'example.sdf'.
7. To load, go to the save folder and hit command:
gazebo example.sdf
Teleop Controller for Pico
To be able to move the robot around manually and easily is very useful when testing simple things in the algorithm. Here you can find the teleop controller for PR2:
And here is the revised version of the teleop controller for our robot pico:
/*
This code lets you move the jazz robot using your keyboard.
This is obtained from a sample code for pr2 from this link:
http://wiki.ros.org/pr2_simulator/Tutorials/Teleop%20PR2%20arm%20in%20simulation
It basically goes into a loop, where the terminal is set for user-input kind of operation
and everytime a button is pressed, velocities are published as the cmd_vel topic for pico.
--emc11
*/
#include <termios.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "ros/ros.h"
#include "geometry_msgs/Twist.h"
#define KEYCODE_A 0x61
#define KEYCODE_D 0x64
#define KEYCODE_S 0x73
#define KEYCODE_W 0x77
#define KEYCODE_Q 0x71
#define KEYCODE_E 0x65
class teleop_pico_keyboard
{
private:
geometry_msgs::Twist cmd_msg;
ros::NodeHandle n;
ros::Publisher cmd_pub;
public:
void init(){
cmd_pub = n.advertise<geometry_msgs::Twist>("/pico/cmd_vel", 1000);
cmd_msg.linear.x=0.0;
cmd_msg.linear.y=0.0;
cmd_msg.linear.z=0.0;
cmd_msg.angular.x=0.0;
cmd_msg.angular.y=0.0;
cmd_msg.angular.z=0.0;
cmd_pub.publish(cmd_msg);
};
~teleop_pico_keyboard() { };
void kloop();
};
int kfd = 0;
struct termios cooked, raw;
void quit(int sig)
{
tcsetattr(kfd, TCSANOW, &cooked);
exit(0);
}
int main(int argc, char **argv){
ros::init(argc, argv, "jazz_teleop_t");
teleop_pico_keyboard tpk;
tpk.init();
signal(SIGINT,quit);
tpk.kloop();
return 0;
}
void teleop_pico_keyboard::kloop()
{
char c;
bool dirty=false;
ros::Rate loop_rate(5);
// get the console in raw mode
tcgetattr(kfd, &cooked);
memcpy(&raw, &cooked, sizeof(struct termios));
raw.c_lflag &=~ (ICANON | ECHO);
// Setting a new line, then end of file
raw.c_cc[VEOL] = 1;
raw.c_cc[VEOF] = 2;
tcsetattr(kfd, TCSANOW, &raw);
puts("Reading from keyboard");
puts("---------------------------");
puts("Use 'WS' to forward/back");
puts("Use 'AD' to rotate left/right");
//puts("Use 'QE' to ...");
while(ros::ok())
{
// get the next event from the keyboard
if(read(kfd, &c, 1) < 0)
{
perror("read():");
exit(-1);
}
switch(c)
{
case KEYCODE_W:
cmd_msg.linear.x = 1.0;
cmd_msg.angular.z = 0.0;
dirty = true;
break;
case KEYCODE_S:
cmd_msg.linear.x = -0.5;
cmd_msg.angular.z = 0.0;
dirty = true;
break;
case KEYCODE_A:
cmd_msg.angular.z = 0.5;
cmd_msg.linear.x = 0.0;
dirty = true;
break;
case KEYCODE_D:
cmd_msg.angular.z = -0.5;
cmd_msg.linear.x = 0.0;
dirty = true;
break;
// You can use these for different tasks
// case KEYCODE_Q:
// dirty = true;
// break;
// case KEYCODE_E:
// dirty = true;
// break;
}
if (dirty == true)
{
cmd_pub.publish(cmd_msg);
}
}
}
Just create a ros package dependent on roscpp and geometry_msgs, compile and run it in a seperate terminal. As an example; by pressing 'W' in the terminal, you will move the robot forward in the simulator.