PRE2023 1 Group3
| Name | Student Number | Study | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wilbur van Lierop | 1703870 | Applied Mathematics | w.p.v.lierop@student.tue.nl | |
| Quincy Salden | 1749900 | Applied Mathematics | q.salden@student.tue.nl | |
| Jerome Bleyendaal | 1483870 | Electrical Engineering | j.bleyendaal@student.tue.nl | |
| Jack Grunfeld | 2064677 | Exchange (software and Robotics engineering) | j.w.v.grunfeld@student.tue.nl |
GitLab link: https://gitlab.tue.nl/20233137/projectrobotsg3/-/tree/main (please note git is not currently working for me (Jack) so I have uploaded the import code files for viewing, and the .zip file of the actual program.
Introduction
The TU/e, University of Technology Eindhoven, is a large university where over 10.000 students and 2.000 staff members come together to educate, research, and learn about technological sciences. TU/e shares its location with Fontys, an university with a few thousands students as well. In total, the schools have around 20 buildings that are home to lecture rooms, meeting rooms, study spots, cafeteria’s, and a variety of other facilities.
For newcomers to Eindhoven it will initially feel overwhelming navigating the campus grounds. Buildings of course follow a certain structure when it comes to labelling their rooms, using signs to sent you in the right direction. However, despite this organization it can still feel like walking around in a maze, especially when a certain route is blocked off, or when your destination is not indicated by signs, such as printers and water fountains. Not being able to find your destination is never appreciated, especially if it means arriving late for classes, meetings or exams.
It is for this reason that we wish to find out which problems newcomers to the campus experience, and hopefully provide a way to navigate around campus more efficiently, and additionally, we shall not restrict our focus to just sending newcomers from A to B as quickly as possible, but we will also take into account students and staff that are already a little familiar with the TU/e and are interested to learn alternative routes that would also guide them from A to B.
Objective | Problem Statement
The aim of this project is to create an interactive mapping solution tailored to the needs of TU/e students, which entails providing the user with essential information about campus facilities, including building locations, lecture rooms, study spots, bicycle parking, and more. The project focusses primarily on guiding around first-year students and newcomers to the Eindhoven campus, and secondly focusses on providing a way for students already a little familiar to the campus alternative routes for navigating themselves around, or providing them information about events and out-of-order amenities.
%The aim of this project is to create an interactive mapping solution tailored to the needs of TU/e (Eindhoven University of Technology) students, with a specific focus on first-year students and newcomers to %the Eindhoven campus. The project aims to develop a user-friendly platform that provides essential information about campus facilities, including building locations, lecture rooms, study spots, bicycle %parking, and more. This platform will also offer real-time updates and recommendations to enhance the overall campus experience.
Target user
1. First-year students and newcomers to Eindhoven:
- Orientation: First-year students and newcomers are often completely new to both the university campus with its corresponding structure. They may not be familiar with the layout of the campus, the locations of key facilities, or the services available to them.
- Needs: They require guidance and support to navigate the campus efficiently. They may also seek information about academic resources, extracurricular activities, and student services.
- Challenges: Finding lecture rooms, study spots, and other essential places can be challenging during the initial days. They may also face difficulties in understanding the campus culture and community.
2. TU/e students and staff that are somewhat acquainted with the campus:
- Orientation: Typically they are already familiar to the structure whithin the buildings of the TU/e campus, though they might for example be unaware of all facilities and study spots available to them. Also, they might often take a longer route to get from A to B as a consequence of not knowing alternatives.
- Needs: They require to be time-efficient most of the times, though sometimes they might wish to deviate from their usual options and try-out new ones, such as finding a study spot in a different building opposed to the building they would usually settle for, or they might wish to take more outside walks when going from one building to another, but only know the indoor route.
- Challenges: Finding rooms in case their ''usual'' option is blocked off by constructions, or facilities when the known options are out of order. Further, they require to be time efficient and therefore need up-to-date information about events.
- %Orientation: new students are often new to both the university and the city. They may not be familiar with the layout of the campus, the locations of key facilities, or the services available to them.
- %Integration: They are in the process of adapting to a new environment, which includes adjusting to the campus, city life, and local culture, seeking information around groups, extracurricular activities or student services, very required for student who have not been at TUe from first year which TUe puts on integration and orientation programs.
3. %Diverse Backgrounds:
- %International Students: TUe attracts a diverse student body, including international students. This diversity adds to the complexity of the target audience, as language and cultural differences may %influence their needs and preferences.
- %Varied Academic Disciplines: TUe offers a range of academic programs, each with its unique requirements and facilities. Understanding these variations is important when tailoring the solution.
User portfolio
Based on our own visions of the needs target users have, we came up with a user portfolio. This portfolio strictly covers common problems first-year students, newcomers, and the other people to which TU/e is their working place, experience at the TU/e. This is useful to us, as this provides a general direction for the project, and helps us establish a user-survey which either hopefully confirms our thoughts on what the user needs and requires, or it will otherwise hopefully give us new insights which will be beneficial for the product design.
Here is the list of problems and difficulties we thought of, with a brief explanation if applicable:
- Underestimating walking times from one building to another -> In general it is very stressful being late for your lectures due to not being able to find the right room or underestimating the time required to get from one place to the room. Especially at time of exams, being late can have negative consequences.
- Bicycle parking in front of Atlas is always full, making it difficult to get your bike out of the racks. Many students do not know where to find alternative parking’s.
- Finding the stairs and elevators in particular buildings.
- Parking your car at TU/e, finding a spot at around 11:00 can sometimes take over fifteen minutes.
- Finding a good study spot without reservation can be a pain, especially finding a spot where you can sit with a couple of friends.
- Irregular building opening hours.
- Long lines at cafeteria's like Subway during lunch break and coffee machines in brakes of lectures.
- Events taking place, e.g. career expo in Auditorium -> Subway is closed, not really pleasant to study there.
- Presence of AED machines, first-aid kits, fire extinguishers in case of emergency.
- Gender-neutral restrooms.
- Ping-pong equipment for the ping pong tables.
- Parking for people with a disability.
Survey
Survey methodology
We conducted a survey to gather insights from TU/e students, with a focus on first-year students and newcomers to Eindhoven. The survey was distributed to various participants via social media. Participants were informed that their responses would be kept anonymous. The survey was open for a week and
Survey results
A total of 40 participants contributed to the survey, providing valuable feedback on various aspects of campus navigation.
First-Year Status:
When asked if this was their first year at TU/e, 15 respondents (37.5%) indicated that they were first-year students, while 25 respondents (62.5%) reported that they were not.
Campus Navigation Challenges:
A significant number of participants acknowledged facing challenges in finding various campus facilities. Specific issues included locating specific rooms, such as those in Metaforum zaal 11-15 and OGO rooms in Atlas. Participants also mentioned difficulties in navigating between buildings, especially those less commonly visited, such as Fenix. Additionally, finding study spots, rooms, and parking spaces posed challenges for some participants.
Usefulness of App Features:
Participants were asked to rate the usefulness of potential features for the campus navigation app. The highest-rated features included room finder (average score: 4.18 out of 5), study place finder (average score: 4.1 out of 5), and printer finder (average score: 4.08 out of 5). These results highlight the importance of features that aid in locating specific facilities within the campus.
Events Information:
A majority of respondents (average score: 4.35 out of 5) expressed interest in a feature that would display information about social and academic events happening on campus, such as open days for sports associations and lunch lectures.
Location Tracking:
In response to the question of whether they would allow the app to track their location for navigation purposes, 23 participants (62.2%) indicated their willingness, while 14 participants (37.8%) preferred not to. This would allow for the possibility of dynamic features which uses location tracking.
Reporting Broken Amenities:
A significant portion of participants (75%) expressed their willingness to actively participate in keeping the interactive map up to date by reporting broken amenities through the app.
Additional Ideas:
Some participants shared additional ideas for the app, including providing information on building opening and closing times, walkways, food and drinks spots with their menus and operating hours, and the possibility of including humorous comments from teachers and students.
User Scenarios
Based on the survey responses, and our own mindmap, four user scenarios have been established to provide a better vision for the scope of our project.
Scenario 1:
Dylan is a 19 year old boy from the Netherlands, right on the voyage of starting his bachelor time at TU/e. In high school he was pretty chaotic, never able to put structure in his daily routines, causing him to often be late for class, and sometimes even for exams. At university he hopes to make a fresh start and try to get into a daily rhythm that is not as chaotic as in high school.
In order for him to fix his bad habit, he wants to start showing up on time. He would like an interactive map that shows him the fastest route that guides him to the right lecture room. He also likes to have up-to-date information about opening hours of cafeteria’s, and how busy they are, as he often forgets to bring his own lunch. Lastly, he requires some assistance with finding good places to study, as he is pretty chaotic and easily distracted when working in crowded area with much distraction.
Scenario 2:
Emmi is a 28 year old high school teacher who occasionally tutors at university for specific courses related to teaching. She has been in a wheelchair since the age of ten, and she has just gotten a request to tutor a group of students following a course that prepares them for educating high schoolers in a particular subject.
Her disability is something that costs her a lot of time and effort, since a lot of buildings, especially older ones, tend to be very unclear with showing where wheelchair entries are. Apart from that, it is often a struggle to navigate across the hallways of buildings, since she often encounters obstacles that prevent her from following the shortest route available. She also feels bothered when other people have to make space for her so that she can pass through, so she often goes to her lecturing rooms well before the start of her lecture. Therefore, she likes to have some assistance for navigating across buildings on campus, with in particular information about where she can enter buildings and which hallways are wheelchair-friendly. Additionally, some facilities like coffee machines are not particularly well designed for people in wheelchairs, and because of Emmi’s willingness to be independent, she would really appreciate it if she had a good overview of all coffee machines that allow her to get coffee herself.
Scenario 3:
Max is a 18 year old boy from England, born as a female kid, but Max did not feel at the right place of the spectrum, and underwent a program that altered his gender, making him a transgender. Max had a difficult time at high school due to him not feeling comfortable going to the toilets, as there were no gender-neutral ones, and similarly for locker rooms. Another characteristic of Max is his poor sense for orientation and navigation, and difficulties adapting to new environments. Max also tends to sleep very little usually, so he requires 2-3 coffees per day to keep active. Lastly, he is very smart, and just started with an exchange program at TU/e for software engineering.
Max would really appreciate an app that can help him get to his right location on campus, since he considers the campus really big, and poorly structured. Buildings, lecture rooms, meeting rooms, elevators, and water taps are all considered to be hard to find. In specific, he really struggles with finding gender-neutral restrooms, as this relatively new concept is not yet adapted in most buildings. Besides that, he would find it helpful to always know the closest coffee machines a his disposal. This is because he has to walk pretty far when going to the toilet, so he does not want to spend as much time searching for coffee.
Scenario 4:
Tris is both sporty and very clever when it comes to studying. She likes going for outdoor runs as often as she can, preferably through nature. She is 22 and is enrolled for a masters program at TU/e, after easily completing her bachelor elsewhere. She is a bit of an environmentalist, an art-lover, and likes to explore new places.
Tris would like an app with a map that can help her navigate around her new university, but also makes adaptations to the route when she wants to explore where an interesting path might lead her. She also hates using the elevators, so she prefers to strictly take the stairs if able. And in case the weather is really nice, she would love to take an outdoor walk if she has to go from one building to another, but if it is raining, she rather limits this to just staying indoors.
Project Requirements, Preferences and constraints
In this chapter, we outline the components that will shape the development of the interactive campus map for the TU/e. The RPC-list (Requirements, Preferences and Constraints) serves as a guide for our project, to ensure we work towards an end project which aligns with not only our own vision and goals, but also those of our users. We recognize that our user's input is very important, if not the most important, and have therefore taken their opinions into account when making this RPC-list.
RPC-List
Requirements
Map accuracy and completeness:
- The interactive map should accurately represent the TU/e campus layout. (prototype will only include a detailed layout of the inside for atlas floor 8)
- It should include information on important facilities, such as buildings, room numbers, study spots, etc.
- It should have a navigation system allowing users to find rooms or buildings.
- The navigation should be able to determine the fastest route from the entrance of atlas to any room on the 8th floor. (prototype might be limited to only a few rooms)
- Navigation system should be able to determine how long a route takes.
- It should be able to find the nearest toilet and determine the fastest route, given a certain starting position
User-friendliness:
- The app should be easily accessible and free to all TU/e students and staff.
- It should have a user friendly interface.
- It should have a search function to be able to find specific buildings, rooms or amenities.
Feedback system:
- The app should have a feature allowing users to report broken amenities.
Preferences
Integration with campus system:
- The mapping system should be integrated within the TU/e app to make it easier for the user.
- This integration should allow users to be able to reserve rooms and study spots through the app.
Multilingual support:
- The app should have support for multiple languages, as there are many users with various backgrounds.
Real-time data:
- The map should provide real-time information on disruptions and availability of buildings, rooms or bridges between buildings.
- It should also provide information on how busy certain area's are or if certain study spots are available.
Campus social hub:
- The app should have a social hub showing events and social activities in the near future.
Constraints
Time constraints:
- The project should be finished within the span of this course.
Data constraints:
- Users might not agree to share their location, rendering any dynamic map features less effective.
Vision
- to develop a dynamic Application, which allows students to have clear and useful hub for information around campus, this includes:
- easy and accessible navigation
- frequent and reliable updates about on-campus amenities.
- information about Cafes/food/drink locations around campus.
- vital knowledge such as bathroom locations, tire pumps, water dispensers.
- access to social hub networks such as events, clubs and gatherings.
- information about study zones and busy timeframes.
-
Key Features
- Real-Time Updates: Implement a dynamic system for real-time updates, including alerts for occupied bicycle parking areas, out-of-order coffee machines, and suggestions for available study spots.
- User Engagement: Encourage user engagement through features like reviews, ratings, and reporting mechanisms, fostering a sense of community among TUe students.
- Mobile Accessibility: Ensure that the interactive map is accessible via mobile devices, allowing students to use it conveniently on the go.
- Path finding: to have the ability to show the best route to locations around TUe. (Using A* search or Dijkstra's algorithm) .
Milestones | Time Frames
10/09/2023 | Tutorial
- Update wiki with basic info about project
12/09/2023 | group meeting
- Understanding Scope of Project, focus on First year students
- TODO:
- Make scope smaller, do research on USER based survey and questions
- Pick a building/ Area to focus on.
- Each member come up with 10 questions before 13th.
18/09/2023 | Tutorial
- Gage how to start without having the user feedback
-get advice from professionals and other lecture figures
- technical issues see first slide.
- email the BIMS lady
- start building a app to find current location and other basic services etc,
-start mapping out the building
weekly roles:
Jack - initial app set-up and dev.
Wilbur - BIMS research
Quincy - BIMS use and dev
Jerome - Survey release
25/09/2023 | Tutorial
- extrapolate survey result, find scope.
- meeting/understanding BIMS.
- continue App dev, for other services on map
- research indoor map methods and techniques.
- figure out what our functional scope is?
weekly roles:
Jack - continue app dev, focus on other features of the app.
- focus of part of app which users identified from survey.
Wilbur - State of the art research
Quincy - RPC-list
Jerome- gage survey data / Look into the BIMs
02/10/2023 | Tutorial
- Define concrete goals; what do we hope our indoor navigation is capable of? -> Find-nearest function.
- Wilbur shall figure out the way to determine expected times of taking stairs and elevators
- Write out answer to question how we envision the user to define the location where he/she is, when using the indoor navigation. -> Use GPS location, small error indoors, which we don't cosider a problem as it will be small compared to the distance between two different facilities.
- Maybe find 2D maps of Atlas, cause we only require coordinates of the facilities in a building.
- explain why BIMs are better for our project than just 2D maps -> BIMs can have inherited information, and information can easiliy be updated once set-up. Also if BIM works at floor 6, it can work for entire building.
- Write down what we achieved with the navigation part (A* algorithm)
- Wilbur try to figure out how the matrixmap is generated from the CSV file, and what is in the CSV file, using the BIM of Atlas.
09/10/2023 | Tutorial
- continue to create smaller scope
- figure out how precise the location services are.
- develop floors and stairs in map finding.
- lack of infrastructure around UNI to completer all areas of project (keep in mind for later wiki writing)
- make plan for testing and release.
- look a B.I.Ms for a more extensive understanding of locations, perhaps for views, scenic routes, fitness routes, etc
- look a chatting to another body of knowledge around using and understanding B.I.Ms
Research/findings/IDEAS
USEFUL Application:
- https://www.mazemap.com/ Mazemap introduces themselves as follows: "MazeMap is an innovative digital wayfinding platform, offering solutions for large campuses such as universities, hospitals, offices, hotels, and event venues. In addition to wayfinding, we also offer space booking & visualization tools, indoor positioning, IoT integrations and more." One nice feature of Mazemap is the ''Find Closest Available'' feature, which performs the action described by its name for a few types of facilities. Another particularly unique feature is their heatmap function, which can provide information about places of a building experiencing high traffic. This feature would be helpful in preventing areas on campus becoming way too crowded, which we consider to be a problem worthy of implementing in our campus map. One example where Mazemap is being used is the NTNU (Norwegian University of Science and Technology), where Mazemap became very popular with as two main use-cases the planning of meetings, events, conferences and visits, and navigation around campus by users of the app. It helped students save a lot of time, and optimize their schedules. Mazemap also receives praise for allowing it to implement other services, such as space booking tools, allowing the users to just look in the app where there are unoccupied study spots, and which spots are readily being used.
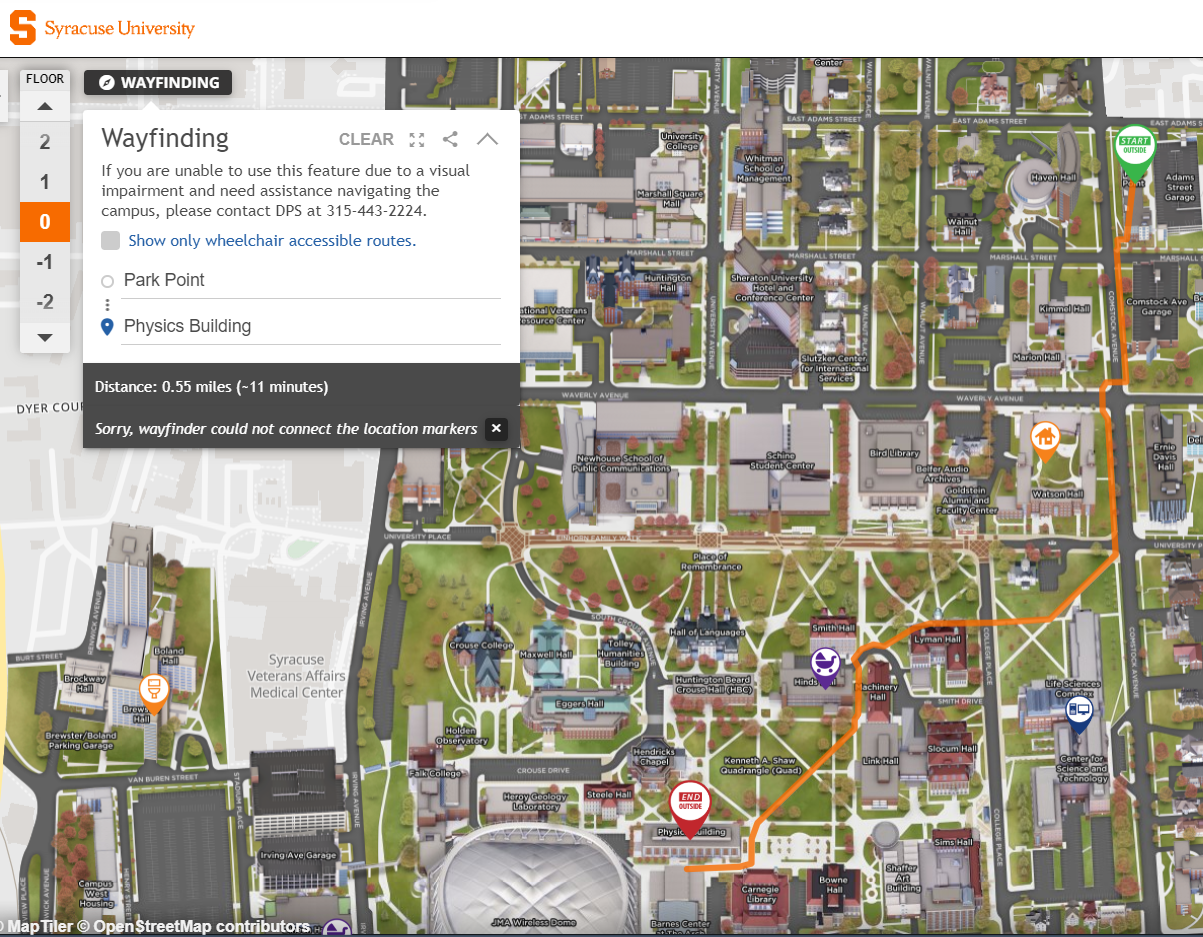
- https://maps.syracuse.edu/?id=1275#!ct/48860,43018,42873,34415,34413,34416,38441,38498,38500,38611,38612,38613,38617,53074,53075,57269?s/ Syracuse University has their own interactive campus map. One nice feature of this map is 3D-renderings of the exterior of buildings. Furthermore, it has as sidebar with grouped facilities like parking and dining options. It also provides an outdoor-navigation system, though on the webbrowser it does not really function very user-friendly. The wayfinding feature also works between two places in the same building, though the route is not displayed clearly, as it maintains the outdoor-navigation view. Interesting to note is that this map is only accesible as a website, and therefore not as an app. With well over 100 buildings and 20.000 students enrolled, one might suspect to prefer an app over a website, as apps tend to be easier to access on mobile phones.
- Işıkdağ, Ü., Zlatanova, S., & Underwood, J. (2013). A BIM-Oriented model for supporting indoor navigation requirements. Computers, Environment and Urban Systems, 41, 112–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compenvurbsys.2013.05.001 - ''A BIM is a digital representation of all the physical and functional characteristics of a building through its entire life cycle.'' - ''Semantic information is a clear definition (and naming) of building storeys, elements, spaces, as their usage would support better orientation and guidance.'' - ''Primal models include a geometric representation in 3D Euclidean Space and a topology representation for expressing the relationships between building elements. Dual(s) of these models are a network (metric graph) for representing the physical connectivity and a graph (logical graph) for denoting abstract connectivity in a building.'' - ''The representations in the primal layer are mainly utilized for information provision, retrieval and visualization purposes. The geometric networks and graphs in the dual layer are usually derived from the primal representations and used to compute the required (i.e. shortest, fastest) navigation path.'' - ''BIMs contain advanced geometric and semantic representation of the building elements and they are considered as the most valuable source for representing and managing building information through the lifecycle of a building.'' - ''In the development of the new model, IFC was selected a source BIM standard, as it is the mainstream schema standard of Building Information Modeling.''
- Schuldt, C.; Shoushtari, H.; Hellweg, N.; Sternberg, H. L5IN: Overview of an Indoor Navigation Pilot Project. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13040624 This article poses the project Level 5 Indoor Navigation, which has the aim to show how 5G signals can be used for indoor positioning in ''navigation systems, which have thus far only been available in the outdoor segment, can now be integrated into existing smartphone systems for indoor navigation.'' Here are some key findings of this paper that are in correspondence with our project:
- When it comes to indoor positioning for navigation, the most-used techniques today are Bluetooth and WLAN, but these methods have the downside that a client server has to be held up in order to work.
- This project also uses a university as demonstration location, where building information modelling was used for positioning.
- The paper explains that in theory it should be possible to create a map data set quickly and easily by just using escape and rescue plans, which exist for a lot of universitial buildings.
- The underlying motivation for using BIMs for the L5IN project: ''The advantage of working with BIMs is that different information about a building can be collected centrally within a data set. Information that otherwise comes from different sources (such as drawings, tables, presentations, and charts) can be bundled within a BIM. The fact that working with BIMs allows the use of a combination of semantic, geometric, and topological attributes is one reason for their growing usage in different cases.''
- In regard with the aim to create a digital map, the following quote seems worth mentioning here: ''Due to the already mentioned role of the model as a single source of information for relevant building information, it makes sense to generate the required maps directly from the model. A distinction must be made whether the modeled 3D geometries of the BIM should be used directly for a navigation application or if they should be abstracted from the 3D geometries and used as a 2D map.''
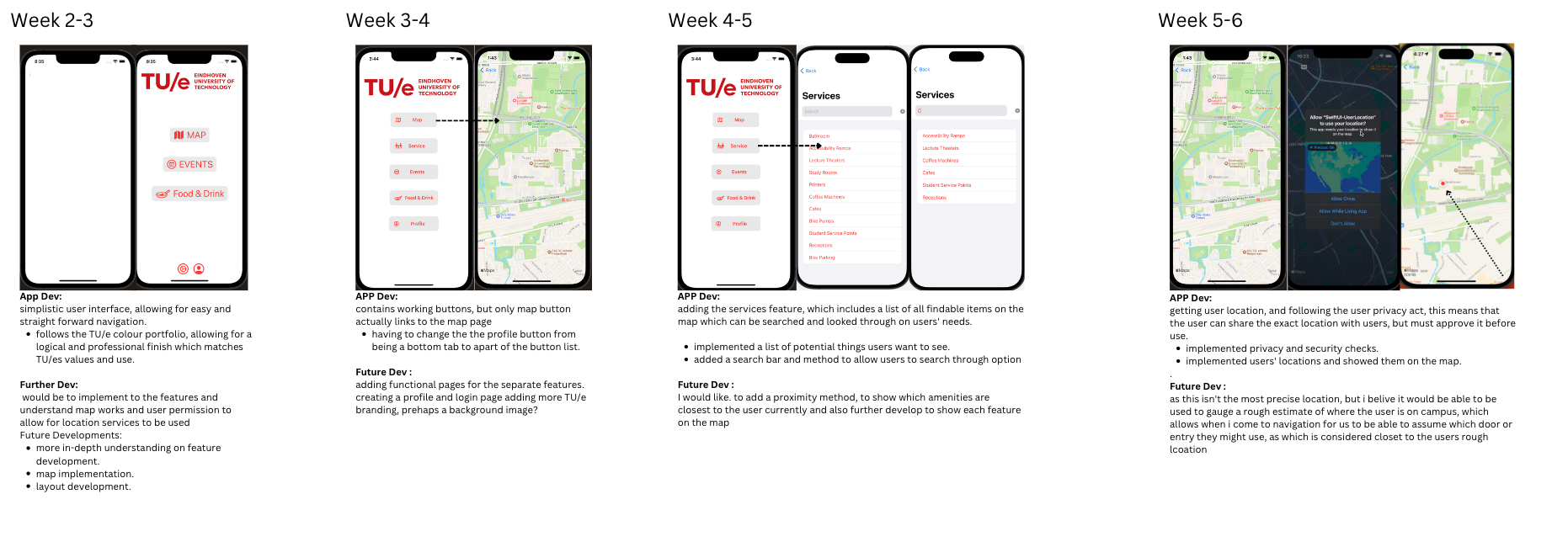
APP DEV
developing app using SWIFT and Xcode, for seamless easy app development, see gitlab for code Updates.
Indoor positioning
Before talking about navigation, we would first have to tackle the problem of getting the user's location on the map, as we of course require a starting point to guide the user to his or her destination.
GPS
GPS (Global Positioning System) is one of the, if not the, most dominant methods for outdoor navigation worldwide (1). GPS makes use of satellites that send out signals to earth. The signals are then detected by the ground device. If the ground device, such as a smartphone or laptop, receives three or more signals from distinct satellites, it can use this information to triangulate the device's position. As long as the signals are strong enough, the accuracy of the device's location can be very precise. For outdoor position, the accuracy of a standard smartphone is around 5 to 10 meters (2). Also, GPS can follow a device's location while it is in motion, making it a perfect method for navigation. Hence its popularity.
Whithin the scope of this project, GPS positioning for outdoor routes seems very reasonable. Though we have to make a small note here. Despite having an accuracy of only a few meters, for some outdoor routes this may still be too much. In traffic, crossroads and buildings are often far enough apart from eachother for the positiong to be sufficient enough. Additionally, the device can take the direction of the vehicle and its velocity into account, allowing for good adaptation of its position. But GPS positioning might be problematic when walking on a narrow path between buildings, since the accuracy might be large enough to ''think'' the user is located inside one of the buildings. Therefore we must explore other forms of indoor positioning:
Alternate indoor localization methods:
- Wi-Fi-Based Indoor Positioning:
- Description: This method leverages the existing Wi-Fi network infrastructure within a building. There’s multiple methods which use Wi-Fi to determine one’s position. The first one being a signal strength based method, in which the user scans for nearby Wi-Fi access points and measures signal strength. Using a database of known access point locations, the device can estimate its position based on the signal strengths and triangulation. A method to do this is called ‘trilateration’. Since this method is not quite as accurate as one might want it to be, there’s ways to improve the accuracy, namely fingerprinting. This is a similar method to the previous one, except instead of determining location based on signal strength, it uses a database to determine it’s location. This database needs to be created first and will contain Wi-Fi fingerprints of all areas you want to track. Creating this database involves walking around the area and relating the recorded signal strengths to the known locations. Once this database is made, it can then be used to determine one’s location. It does this by comparing the perceived signal strengths with the signal strengths in the database and finding the best match, which then results in a location.
- Pros: Utilizes existing infrastructure, namely the existing TU/e Wi-Fi network, provides reasonably accurate positioning, i.e. within 5-8 meters accuracy. [1] Or in the case of fingerprinting: <3m [2] accuracy, for which room-level accuracy is usually enough. (Note that these accuracies vary based on various factors, such as the variation in signal strength, density of Wi-Fi points, quality of the fingerprint database and the dynamic environment. This means that we cannot confidently give a prediction of the accuracy of this method if it were to be used on the TU/e.)
- Cons: Can be affected by changes in Wi-Fi network configurations and may not provide highly precise results.
- Bluetooth-Based Indoor Positioning:
- Description: Bluetooth-based indoor positioning is similar to the previous method, but instead of Wi-Fi it relies on Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) beacons. Mobile devices detect and communicate with these beacons, enabling them to determine their location. This is, once again similar to before, done by measuring the strength of the Bluetooth signals received and then using triangulation to determine position. Fingerprinting is also possible for Bluetooth-Based indoor positioning and increases it’s accuracy.
- Pros: Precise location information <3m when calibrated correctly, (Once again this varies depending on many factors and it is not possible to say how accurate it would be if it would be implemented in our app), low power consumption.
- Cons: Requires beacon installation and maintenance, making it costlier to implement, signal interference and variations.
- Inertial Navigation Systems (INS):
- Description: INS uses the sensors within a mobile device, like accelerometers and gyroscopes, to measure changes in velocity and direction. By tracking these changes over time, the system estimates the user's position. However, it needs some initial known position. From which it can then determine the positions the user is in after that by keeping track of the changes in acceleration and angular velocity. This way of determining the position is prone to cumulative errors, since any error made is kept for all positions determined later on. Thus using this as a sole system seems like a bad idea. However, using this in combination with other methods would be possible. INS could recognize if an elevator is going up or the precise direction the user is looking at or going to.
- Pros: Provides real-time information and is suitable for short-term navigation.
- Cons: Accumulates errors over time, leading to inaccuracies in long-distance navigation.
- Ultra-Wideband (UWB) Positioning:
- Description: UWB is similar to Bluetooth-based indoor position finding, but instead of using BLE’s, it uses UWB beacons which make use of very short-duration radio pulses to communicate with the user. The beacon sends a signal, which is then bounced back by the user. This time is measured and since the radio pulse is of a very short duration, a fairly accurate estimation of the location of the user can be made. When expanding this to a multilateral system, using multiple strategically placed beacons, this system becomes very accurate. This method, using duration of radio pulses, is called Time-of-flight measurement.
- Pros: Exceptional precision, low interference.
- Cons: Initial setup and infrastructure costs can be high, especially on a big campus like TU/e.
- Visual-Based Positioning:
- Description: Visual-based systems use the cameras on smartphones to analyse visual cues in the environment, such as QR codes or landmarks. In our case it could recognize room numbers or direction signs, since they are very common on TU/e and would give an accurate location. However, to be able to recognize these room numbers or direction signs, a system would need to be in place to be able to do so. Furthermore the user would have to ‘look around’ with their camera to recognize these ‘landmarks’, which is not as user-friendly as we would like it to be.
- Pros: Provides an accurate location.
- Cons: Relies on visual markers and may not work well in environments with limited visual cues, Not User-friendly, If the user wants an updated location it needs to ‘look around’ continuously.
- Magnetic Field-Based Navigation:
- Description: Magnetic field-based navigation uses the Earth's magnetic field to estimate position. Devices detect changes in magnetic fields within a building to determine location. However, since this technique is somewhat new and, on top of that, very difficult to implement, it may be out of our reach currently.
- Pros: Can work in environments where other technologies might not function well, accurate localization.
- Cons: Sensitive to metal objects and magnetic interference, difficult to implement.
- Acoustic-Based Indoor Positioning:
- Description: Acoustic-based systems use sound waves or ultrasound for positioning. Mobile devices detect and analyse acoustic signals to estimate their position.
- Pros: Can provide accurate results and is suitable for specific applications.
- Cons: Sensitive to ambient noise and may not be suitable for all environments, since there is a lot of ambient noise on the TU/e, this makes for a not very efficient method.
- Radio Frequency Identification (RFID):
- Description: RFID systems use RFID tags to identify and track objects or people within a building. RFID readers and tags communicate via radio waves to determine location.
- Pros: Effective for asset tracking and inventory management.
- Cons: Limited to tagged objects and requires RFID infrastructure.
- Dead Reckoning:
- Description: Dead reckoning estimates a user's position based on a known starting point and information about their movement, such as step count, direction, and speed. It continuously updates the estimated position based on user movement data.
- Pros: Suitable for short-term navigation without the need for additional infrastructure.
- Cons: Prone to accumulating errors over time and requires recalibration.
- Infrared Positioning:
- Description: Infrared positioning uses infrared sensors or transmitters to detect and locate objects or people within a building. Devices communicate with infrared sources to determine their position.
- Pros: Suitable for applications like indoor gaming and virtual reality.
- Cons: Requires specific infrared infrastructure.
- Indoor GPS:
- Description: Indoor GPS is a concept that combines various positioning methods like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, UWB, and sensor data to mimic outdoor GPS indoors. These systems use hybrid approaches to improve accuracy. This method, since it combines multiple other methods, would arguably be the best. But since it requires multiple methods to have the corresponding infrastructure and proper software to be able to work together, it is probably too difficult to implement.
- Pros: Can provide more accurate results by combining multiple data sources.
- Cons: Requires integration of multiple technologies and may be complex to implement.
Determining the best option
- Bluetooth-based positioning, UWB positioning, RFID positioning and infrared positioning all seem like good options, which would give accurate results. However, they all come with one major flaw, namely that they all require specific infrastructure. This is of course not realistic within the scope of our project. But even for a project with more time and resources, this still does not seem like a good option, since creating and upkeeping this infrastructure is simply too much work for what you get back from it. (Note that in the case of a project with a lot of resources, these options could be considered.)
- Magnetic field based Navigation and Acoustic based indoor positioning both do not seem like they would be accurate enough for room-level accuracy. On top of this these are both very difficult localization methods to implement.
- Visual based positioning would, in theory, work. However, it would require the user to constantly ‘look around’ with their phone, which is not the user-friendly app we want to create.
- Inertial Navigation system and Dead-reckoning both have their use, but when used on their own are simply too prone to cumulative errors. They could be used in combination with other systems. They could assist in localization whenever the other method isn’t able to or they could determine the direction of the user.
- Which leads us to Indoor GPS, combining multiple methods. It would make sense to have INS or Dead-reckoning to determine the direction the user is going, but other than that there isn’t much benefit to it. This is assuming you have a well-functioning, consistent localization method.
- Finally we have Wi-Fi-Based localization, which we believe to be the best option for indoor positioning. Not only does the Wi-Fi infrastructure already exist on the entire campus, it can also, assuming limited interference or errors, reach room-level accuracy.
Implementation of Wi-Fi-Based localization
As mentioned before, there is two ways to implement this, namely the signal strength based approach and the fingerprinting approach. Firstly we will take a look at a signal strength based approach.
Signal strength based approach
- Relation between signal strength and distance:
The most common relation used in indoor navigation is the following path loss model[3]: equation Where represents the received signal strength in dBm at distance d (in meters) from the user, represents the received signal strength at d_0 (which is usually 1m), gamma is the path loss exponent and G_x is a gaussian random variable, which is often ignored when dealing with large quantities of data.
- Determining location[4]:
Once the n signal strengths have been converted to distances, you end up with a system of equations which looks like this:
d_1 = (x-x_1)^2 + (y-y_1)^2
…
d_n = (x-x_n)^2 + (y-y_n)^2
where d_n represents the estimated distance to an AP (Access point, i.e. Wi-Fi router) with coordinates (x_n,x_y). finally (x,y) represents the coordinates of the user. In a world with no object interference or other kind of errors, this system of equations would give a single solution for (x,y).(figure 1) Of course, the environment won’t be so ideal, and thus we can’t get a single point out of these equations. However, the solutions to these equations give us intersection points, which consequently give us a localization area, rather than a point. (figure 2) The precise location would then be estimated by taking the center or average of this localization area.
- Object interference:
The issue of object interference can be solved in the following way according to T. Nakatani et al:[5] There is a difference in which object interference affects signal strength in 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. More specifically, 5 GHz signals weaken much faster than 2.4 GHz signals when dealing with object interference. This can be used to our advantage by devising a neural network which takes both these signals as inputs and estimates the probability of the presence of walls or some other object interference. However, not all walls are equally thick and will of course cause different amounts of interference. This is why the probability found by the neural network is then used as an estimate for the condition of the object interference. i.e. a high probability suggests a lot of object interference, while a low probability suggests little interference. Finally an estimation is made for both the situation of no object interference and the situation where there is object interference. These two results are then fused together, depending on the probability found earlier. Using this method would result in a MAE (mean absolute error) of about 3-4m, which is room-level accurate.
fingerprinting
Since the previous signal strength based method is not a guarantee for an accurate result and could prove difficult to implement in the correct manner, we will take a look at another way to approach this problem, namely fingerprinting. This method, as described before, requires a database of location fingerprints to be created first. Once this is done this database can then be accessed to determine a user’s current location. We’ll explore this in more detail in this section.
- Database creation:
The first step is to create a database with location fingerprints. During this phase, often referred to as the ‘offline’ phase, fingerprints of RSS (received signal strengths) are collected from multiple known locations. These fingerprints are then stored in a local or cloud based database which has the following structure for n measurements where each fingerprint has m received signal strengths:
(x_1 , y_1): (RSS_11 : (x_AP_1 , y_AP_1)) … (RSS_1m : (x_AP_1m , y_AP_1m)
…
(x_n , y_n): (RSS_n1 : (x_AP_1 , y_AP_1)) … (RSS_nm : (x_AP_nm,y_AP_nm)
Where (x_n , y_n) represent the actual coordinates, either in longitude/latitude or in a relative coordinate system, depending on which other methods are chosen. RSS_m represents measured signal strength from AP_m with coordinates (x_AP_nm , y_AP_nm).
- Determining location:
After this first phase is completed, one can now begin with phase two, most commonly referred to as the ‘online’ phase. Firstly the user will need to receive input signals from the AP’s. We define these perceived signal strengths as PSS_m. it then compares these perceived signals to the database and chooses the fingerprint with the smallest Euclidian distance. In a more rigorous way this would look like the following:
Argmin_n {(RSS_n1 – PSS_m)^2 + … + (RSS_nm-PSS_m)^2 | n in |N|}
Where |N| describes the number of fingerprints
References:
(1) Kunhoth, J., Karkar, A., Al-Maadeed, S. et al. Indoor positioning and wayfinding systems: a survey. Hum. Cent. Comput. Inf. Sci. 10, 18 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13673-020-00222-0
(2) Menard T, Miller J, Mowak M, Norris D. Comparing the GPS capabilities of the Samsung Galaxy S, Motorola Droid X, and the Apple iPhone for vehicle tracking using FreeSim_Mobile. 14th International IEEE Conference of Intelligent Transportation Systems. 2011, Oct. Washington, DC.
For the 7th OR 8th floor of atlas we have the data of the walls/pillars that is needed for navigation. With this a 2d matrix is created with 255 (white) indicating a movable space and 0 (black) indicating an obstacle. Currently A* is being used for the navigation part, where the path and path length is returned and. This path is plotted in gray (120). The optimal path is often navigates very close to the walls, which makes the path more difficult to see and it is not natural for people to navigate so close to an obstacle. Erosion was used on the white area with a diamond shaped footprint, which results in that A* does not use those areas for navigation. The pathfinding is also able to navigate to the closest of multiple coordinates, which can be used when for example the coordinates of the toilets are known. The starting location of the pathfinding can also be set by longitude and latitude values.
To Do list navigation: - Ground floor + elevator/stair added the ability to navigate from the north/west/south entrance to a room on the 8th floor. - Navigate to somewhere passing something(toilet, coffee) able to choose the shortest path from starting point to end point(s) passing something (if multiple avaible, only passes the one with the shortest distance) - Path length --> meters --> duration computed the path length in meters using the path length from A*. Duration is added using elevator time + length [m] / walking_speed [m/s] (walking speed currently equal to 1.5m/s) - Certain information from the Bims (toilets, stairs, etc (coordinates and navigation array)) - red color path?
Taking the stairs in Atlas
Atlas has staircases right behind each set of elevators, so on opposing sides of the building, and additionally, there is also a staircase in the center, but this staircase is more difficult to model, since the staircase upwards on some floors is not directly next to the staircase downwards. Since we cannot model the floors two up until six within the timespan of this course, we shall therefore not model the central staircase, and only model the staircases directly behind the elevators.
The following assumptions were made with regard to modelling these staircases:
- The time it takes to take each staircase is the same for all staircases. The reason for this is that all staircases are all of (nearly) equal steps, and there are two staircases opposing each other at each side of the building so that even if it is a little crowded, this will not significantly increase the time to take a staircase.
- Going up the stairs takes more time than going down the stairs.
- We assume the user to maintain the same walking speed while walking the stairs, regardless of the number of stairs they have already taken.
- The stairs at each side of the building are identical.
We have taken the stairs ten times, two times per day on five different days. Each trial we used a stopwatch to time the time it takes to go from the first to the second floor, which takes two staircases. This resulted in a mean time of 20.2 seconds to go up from the first to the second floor, and a mean time of 13.8 seconds to get down from the second to the first floor. Hence we shall use these numbers for the estimated walking times of the navigation function.
Taking the elevators in Atlas
Atlas has two sets of elevators at opposing sides of the building, with each set consisting of three elevators. The three elevators of one set operate together in the sense that, upon pressing the button, one of the three elevators will make its way to the corresponding floor. The elevators traverse between the floors -1 to 12. We are interested in the expected time T it takes between pressing the elevator button and arriving at the requested story. We will make an estimation of T based on the following assumptions and estimates:
- It will take at most three minutes for an elevator to arrive at the requested story.
- The elevator will take approximately six seconds to go up or down precisely one story.
- The elevator takes five seconds to get up or down one floor
- When people want to get in get out of the elevator, the elevator will take longer to get to the desired floor.
We let c be a variable with range [0,1], which denotes how crowded it is at the elevator. When c is close or equal to zero, there are assumed to be very few to none other people. When c is close to or equal to one, there are assumed to be a lot of other people that want to make use of the elevator. We let D denote the floor difference between ones current floor and the floor they wishes to go to.
For the sake of simplicity we assume that it will take 180*C seconds for an elevator to arrive at the requested floor. Also, with regard to assumption 4, we shall assume it will take the elevator 10*C*D additional seconds to bring one from its current floor to their requested floor.
Hence we arrive at the following formula to estimate T, with T given in seconds:
T := 180*C + 6*D + 10*C*D.
In order to determine whether or not our estimating formula is reasonable, a few trials were done. For these trials we required to make an estimation for C based on the time of the day and how crowded the elevators are. T.B.C.
BIMS
For this project we experimented with the use of BIMs. BIM stands for Building Information Modeling and is defined as “a digital representation of the physical and functional characteristics of a facility. A BIM is a shared knowledge resource for information about a facility forming a reliable basis for decisions during its life-cycle; defined as existing from earliest conception to demolition.'' The use of BIMs has been on the rise for the past decade, due to the fact that the traditional way of denoting building information comes with a variety of problems.
The use of BIMs facilitates one central information point, which leads to clear, efficient and transparent communication among all parties which are involved in the project. It is the process where 3D-models are created and used to design, plan, construct, and maintain build- and infrastructureprojects. These models are more than regular 2D-drawings.
This means all relevant information usually is gathered in just one single 3D-model. To be more precise, a lot of detailed information could be stored, which is useful to make renovations easier, and the end-of-lifecycle more efficient. Examples of information that can be stored in the semantics of a BIM project are room specifications, dimensions, materials, color, and more. This makes BIMs much more convenient in terms of involving all stakeholders. Usually, when one stakeholder needs information from another stakeholder, this requires a lot of time and effort, since the stakeholders have different standards and ways of denoting their information. Therefore the stakeholders have difficulties with proper communication. BIMs in some sense erase these barriers, by sharing the same standards across all stakeholders, and make retrieving information quick and efficient.
Other postive points about making use if building infromation modelling include the following:
- BIMs already provide a good visual representation in the early stages of development.
- Using BIMs heavily reduces the amount of time required for the building process, as relevant information is easier accesible to all stakeholders.
- Besides time reduction, BIMs also tend to lead to a decrease in costs. This is due to a lower risk of misinterpretation of drawings, as well as a lower chance of making errors in the construction phase.
For our project we would use BIMs that are stored on a server, which could be queried to retrieve the data the user requires, and then the server sends this data to the app.
TIME FRAMES
| Week | Scope | description | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | gauge Idea | group brainstorming, find project scope and idea | - idea found, student helper app for navigation |
| 2 | -scope of Proeject
|
-Understand how and where to start with Project, what is required and how to approach idea
|
- we each found roles within the group which could work on
|
| 3 | - release Survey
|
- releasing the survey to the users, aiming for mostly first years and Exchange students
|
- waiting for survey results, to compute
|
| 4 | - continue app dev
|
- see app dev page
|
- looking into pathing algorithims using python
- waiting longer to receive more responses for survey |
| 5 | |||
| 6 | - wilbur: find accuracy gps mapkit library in swift x-code phone gps | ||
| 7 | - start preparing final presentation | - find expected walking times
- (mathematical) time it takes to take the elevator from floor i to floor j |
|
| 8 | - add code to Wiki |
HOURS
When you want to edit something in the table, double click on a entry to start editing....
| WEEK | Jack - hours | Jack - breakdown | Wilbur - hours | Wilbur - breakdown | Jerome - hours | Jerome - breakdown | Quincy - hours | Quincy - breakdown | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0hr | N/A | 13hrs | Introductory presentation; formation of group; brainstorming ideas for possible projects; researching feasibility and state-of-the-art of two prominent project ideas; extra brainstorming meeting | 10 hrs | Introduction, group formation, idea brainstorming, state of the art research | |||||
| 2 | 10hrs | had the first meeting where we discussed approaches and where to start development processes. Started research into to the Idea and steps needed for app dev, see APP dev section now. | 8 hrs | Assist with making a survey, work on pathfinding | |||||||
| 3 | 12hrs | started app dev, please description above in APP dev. | 12 hrs | Reading about BIMS and how to extract required information, survey release | |||||||
| 4 | 10hrs | continue app development, implement new features, please see above in APP dev. | 15 hrs | Working on pathfinding on a certain floor using a matrix | |||||||
| 5 | GraphDB tutorials; loading and querying of BIM data in GraphDB; looking into the data of the CSV-file which generates the Matrixmap in the Python notebook; partly wrote some short scenario's | 14 hrs | Expanding on the pathfinding: coordinates to array index, navigate via, added some known (toilets, elevators, room) | ||||||||
| 6 | Rewritten introduction and target-user; described what BIMs are and which applications they have + why we can implement it in our project | 13 hrs | Work on pathfinding: added time estimate with elevator estimate, allow to navigate from entrance to floor 8 using shortest time route | ||||||||
| 7 |
Bibliography
- ↑ Are Wi-Fi Positioning Systems Still Worth Implementing in 2023?https://mapsted.com/blog/wifi-positioning-system-explained
- ↑ Kotaru, Manikanta; Joshi, Kiran; Bharadia, Dinesh; Katti, Sachin (2015-01-01). "SpotFi". Proceedings of the 2015 ACM Conference on Special Interest Group on Data Communication. SIGCOMM '15. New York, NY, USA: ACM. pp. 269–282.
- ↑ Localization Algorithm of Indoor Wi-Fi Access Points Based on Signal Strength Relative Relationship and Region Division Wenyan Liu1 , Xiangyang Luo1, *, Yimin Liu1 , Jianqiang Liu2 , Minghao Liu1 and Yun Q. Shi
- ↑ MOBILE INDOOR POSITIONING USING WI-FI LOCALIZATION Bianca BOBESCU, Marian ALEXANDRU Transilvania University, Brasov, Romania
- ↑ Estimatingthe Physical Distance between Two Locations with Wi-FiReceived Signal Strength Information Using Obstacle-awareApproachTOMOYA NAKATANI, TAKUYA MAEKAWA∗, MASUMI SHIRAKAWA, and TAKAHIRO HARA,Os-aka University, Japan