PRE2016 3 Groep1
Group members
- Guus van Dongen 0960106
- Johan Somers 0876720
- Teun de Groot 0951139
- Jur Bartels 0885497
- Laurence Keijzer 0900387
- Bastiaan Wuisman 0884362
Project Description
The world population is growing very fast [1]. It is expected that the world population reaches 11.2 billion people by the year 2100. Nowadays, around 800 million people will go to bed without a proper meal [2]. This problem will only grow when the world population increases. To tackle this problem, precision agriculuture and robotics can be a solution. Precision agriculture is way to reduce the the amount of fertilizer, water, seeds and fuel used and increase the overall yield of the fields.
Besides the global impact which precision agriculture and robotics can have on the ecology and the food production, it may of course also be a very interesting investment for farmers to decrease the costs and increase the production on the same field.
So what will the deliverables of this project be?
A user-friendly interface will be presented in which the economical and ecological impact of robotics in agriculture and precision agriculture is showed. This model will apply on a company scale and on a global scale. The interface will be made with Java. The initial focus will be on the impact of the use of drones in agriculture. More specific: the impact which image processing and analyzing of the pictures drones take of fields can have. All the parameters which can be obtained from these pictures will be elaborated later, but some examples are the nutrition of plants and the growth of crops.
To create the user-friendly interface, a mathematical model will be implemented. As can be seen in the planning underneath, first a model which is suitable for The Netherlands will be made. This model will have inputs (parameters the farmer or other users have to submit), process constants (constants which are inside the model, submitted by the programmers), process variables (variables used to get to the final output) and outputs (information which is the result of the model and showed to the user). A table of these variables can be seen in the 'Models' section.
The inputs of the model can be submitted with different means, for example sliders, drop-down menu's and input fields.
Use Aspects
It is important to check what the USE aspects are when we want to locate the problem and try to invent something for it. The use of drones can have impact in the following USE related topics:
USE aspects
- Societal problem of hunger
- Cheaper food for user
- Cheaper than workers in the long run
The following USE-agents are chosen for this project:
- Primary Users: The primary users for the drones are the farmers. They are going to work with the technology as a tool to optimize the food production.
- Society: This benefits everyone, since everyone needs food.
- Enterprise: The companies who produce the drones and software.
Project Planning
Week Planning
The general approach to create a succesful project is:
- Research state of the art
- Abstract from state of the art
- Contact with user
- Create model
- Analyze impact
Week 1
- Create presentation
- Determine concept idea of drones helping for agriculture
- Research about state of the art
Week 2
- Finish the state of the art [milestone]
- Weeding
- Seeding
- Fertilize
- Harvesting
- Irrigation
- Crop protection
- Contact with User
- Definition of the problem
- Visiting van den Borne [milestone]
- Create presentation
- Create planning
- Evaluate scenario
Week 3
- Contact with User
- Contact with 'Jan Staal adviesbureau' made (Has contact with many farmers)
- Contact with 'Johannes Strever' (Uses GPS a lot)
- Contact with University Team (Are developing a drone for van den Borne)
- Formulate concept [Milestone]
- Start of the model [Milestone]
- Search for essential information (data)
- Economical
- Ecological
- Company scale
- Global scale
- Software: what software are we going to use
- Update wiki
Week 4
- Implementing the model in software [Milestone]
- Update wiki
Week 5
- Finished model of application in the Netherlands [Milestone]
- Update wiki
Week 6
- Finished model global scale [Milestone]
- Update wiki
Week 7
- Testing the models [Milestone]
- Changing the models
- Update wiki
Week 8
- Finished Wiki [Milestone]
- Formulated advise [Milestone]
- Prepare Presentation
- Giving Presentation
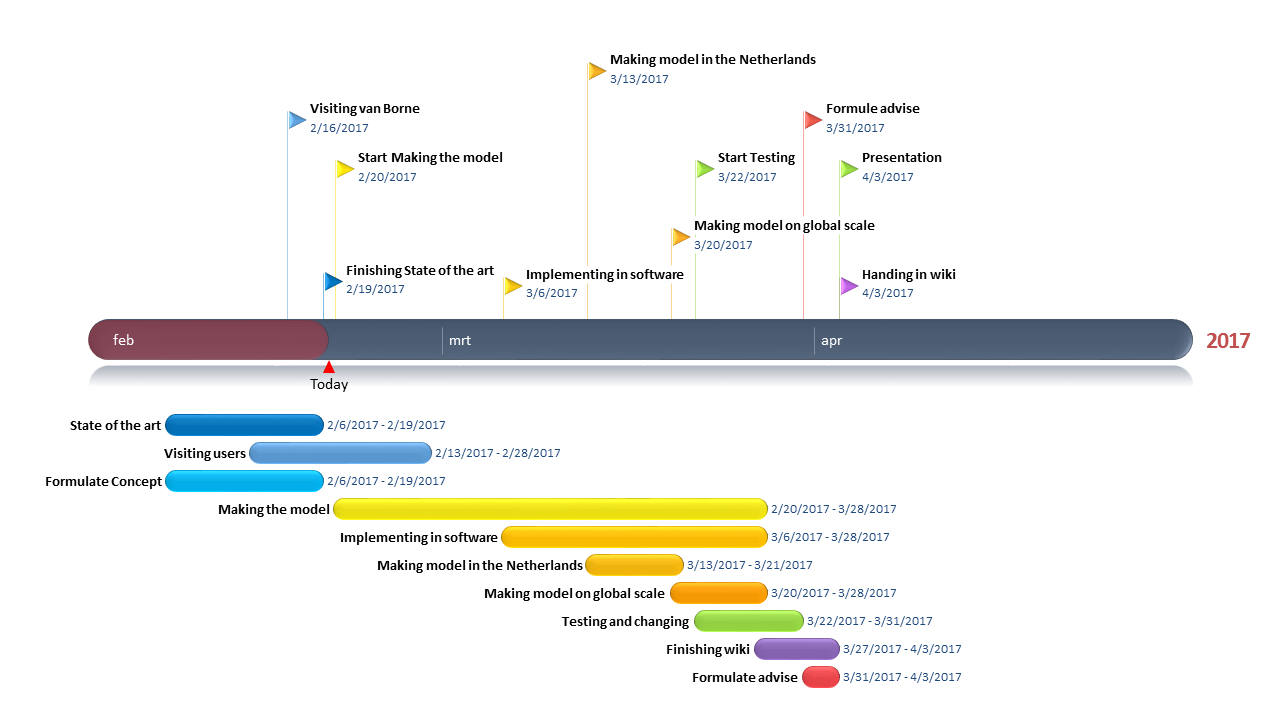
Gantt chart
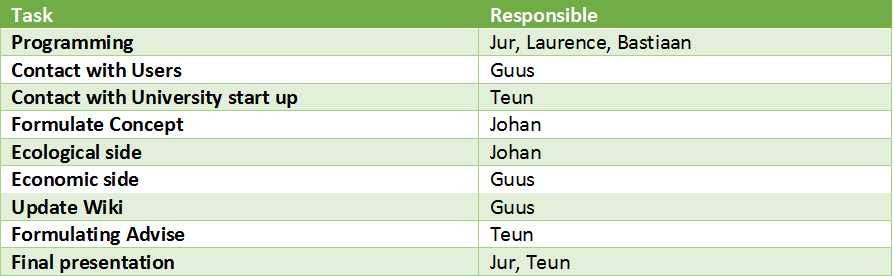
Responsibilities
Tasks
| Task divison week 3 | |
|---|---|
| Crops research | Bastiaan + Laurence |
| Edit wiki | Jur |
| Contacting users | Guus |
| Consultancies | Johan |
| Model specifications | Johan |
| Problem description | Johan |
| Overlap and drones research | Teun |
| Impact model study | Jur |
| Planning on wiki | Guus |
| Visio model | Teun |
| Create Logbook wiki | Jur |
| Farm data | Guus |
| Task divison week 4 | |
|---|---|
| Summary group work | Johan |
| Adding sources and text about the source | Laurence |
| Searching for grow model for water | Bastiaan |
| Start making the interface for the model | Bastiaan |
| Defining the concept for our model | Guus |
| Ideal values for the nutrition | Guus |
| Cleaning up the Wiki | Teun |
| Task divison week 5 | |
|---|---|
| Formula relation pH for potatoes | Laurence |
| Formula relation Water for potatoes | Bastiaan |
| Contact Wouter Kuijpers | Johan, Guus, Teun |
| Contact Eline van der Haak | Johan, Guus, Teun |
| Task divison week 6 | |
|---|---|
| Building the model, Javascript. | Laurence |
| Building the model, HTML, CSS. | Bastiaan |
| Building the model, Javascript. | Jur |
| Relation between nitrogen/yield | Johan, Teun, Guus |
| Defining a new concept | Guus, Teun, Johan |
Summary group work week 4
Our group had 2 group meetings in week 4. The first meeting was right after the feedback session. One thing that came forward in the feedback session is that we had to specify the model more thoroughly. A thing we agreed on was that we will use an 'average' drone to calculate the profits of using a drone. This drone has a multi-spectral camera to identify the nutrition in the crops and to measure the growth. We also concluded that we have to narrow down the parameters of which the growth process of crops is dependent. The growth of crops is of course dependent of a lot of parameters, but we narrowed it down to water, fertilizer and pesticides. Drones can measure parameters to determine how much of these sources need to used. The model would take the starting level of the water and nutrients in the soil and compare them to the ideal level to grow a certain crop. The possible gain in yield (and therefore profit) can be determined based on the difference in the starting and ideal value of the parameters. The differences are evaluated based on growth models to get an insight in how 'severe' the deviations of the ideal value are. We agreed to look up parameters which are key for the growth of crops, and try to find good models which describe the relation between the key parameters and the growth of the crops.
The second group meeting was Thursday. We elaborated the model even more. This is described in the 'Concept of the model'. After a long discussion we think we had a much better view of what the model would look like. But we also encountered a big problem. The model needs relations between key parameters and the growth. We first looked into the growth relations of fertilizers / nutrients. There are a lot of different nutrients, for example nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. Every nutrient has its own relation to the growth of different crops. We found a lot of information about relations between nutrients and growth of different crops, but they only give general tendencies and no hard formulas. The formulas which were found were too specified for one certain environment that we could not use it. So we closed the meeting with the idea to focus on pH-values and water usages. So, some of our group members will look in those growth relations. The rest of the tasks are stated in 'Task division week 4'.
Previous work
Here we will discuss some of the previous work done in modelling the impact of the use of robotics in agriculture. We start with a study by George Graetz and Guy Micheals called Robots at Work[3], which discusses the economical impact of industrial robots, used in fields such as mining and agriculture. They define a mathematical model which they use to predict the following:
1 A fall in robot prices leads to an increase in robot density. 2 An increase in robot density leads to an increase in average labor productivity in the robot-using sector.
They follow up by providing an empirical analysis and comparing the results to the predictions from the model. They conclude that the predictions hold in light of the analysis.
Another interesting work is Agricultural robots-System analysis and economic feasibility[4]. This paper provides feasibility studies for three different applications: Robotic weeding, crop scouting and grass cutting. Case 1 and 2 are of particular interest for our study. for each case they show us how conventional systems compare to autonomous alternatives in cost, maintenance and productivity.
A third study has a focus on the robotics themselves. In their paper Robotics for Sustainable Broad-Acre Agriculture[5] the researchers argue how the use of smaller cheap machines to produce lightweight robots could be used instead of larger machines. The study compares the results of one existing autonomous weeding machine to a simulation of 12 smaller robots, and finds that the smaller robots would do the job faster and with more precision.
What happens if robots take the jobs? The impact of emerging technologies on employment and public policy[6] explores the relation between the emergence of robots in the workplace and the loss of jobs this causes. They conclude that the rise of robots in the workplace is inevitable and that we should not strive to fight it in the first place. Robots are our chance at an age of abundance due to the increase in productivity and efficiency they can deliver. Instead of fighting this phenomenon they argue a change in public policy is required and give a few suggestions as to how we could prevent mass unemployment and use the generated income from robots for the good of a country or people.
Contact
Eline van den Haak
We had a conversation with Eline about our project. We asked her about the procedure to do soil research and how the results are presented. She showed us an example of an soil analysis. Eline advised us to find contact with an employee of Van den Borne named Marnix. We had contact with Marnix about the data analysis of Van den Borne. Marnix gave us data files from the potatoes of 2016, so we are able to check the data en try to find some relations between the nitrogen and the yield. Futher we talked about the work she did. She explained us the difficulties. She told us where we could start with finding information for our model.
Wouter Kuijpers
We also had contact with Wouter. He is PHD student and is doing research about grow models of tomatoes. Tomatoes behave like potatoes, but he could not really help us with finding information for the relation between nitrogen and yield.
Marnix van den Brande
We had contact with Marnix. He was a coworker of Van den Borne. New he switched jobs, but is still the contact person for students. Eline van der Haak advised us to contact him. We did a lot of research for Van den Borne, to find relations between the measurements and the yield. He wrote a MSc-thesis. The thesis estimated the amount of nitrogen in the plant via sensor measurement. Furthermore Marnix helped us with some questions about the drones, the camera’s and the analyzing process. Last he advised us to go to the slot presentation from Puck Mulders. Puck is master student Data-Science and did investigation to find relations between the different measurable parameters. Last Marnix gave us some datasheets from Van den Borne, so we are able to find relations out of the data ourselves.
Puck Mulders
After the contact with Marnix, Teun and Johan went to the presentation of Puck Mulders. She is a data science student who is searching for correlations between growing days and key potato plant parameters. The presentation was very interesting and she was very keen to help us. Unfortunatly she had a meeting right aftwerwards so she couldn't help us face to face. But, there is an e-mailconfersation going on.
State of the art automated agriculture
Weeding
There are some quite exciting technological developments going on in the area of automated weeding. The most important technologies will be discussed below.
Deepfield Weeding Robot
The first far-developed technology is the Deepfield Weeding robot of Bosch, see below.
This robot has GPS navigation to move through the fields with a 90% electrical efficiency. A row of linear actuators is attached to the bottom of the robot. When the robot detects weed, it punches one of the actuators in the ground the destroy the little plant. The company claims that the positions accuracy is 2 mm and that it can remove 20 weeds per second. Given 40 weeds per square meter, the robot can process a hectare in three hours. The machine will cost about the same as a mid-sized tractor [7].
Advantages of this design:
- Herbicide-free farming
- Relative fast operation
Disadvantages of this design:
- Only suitable for small weeds
- Only suitable for field with small crops
There is also an other variant of this machine under development. This machine looks almost the same, but it does use herbicides. A greater working with of six to seven meters is possible with foldable booms. This machine will still lead to massive herbicide savings, but with a much bigger capacity potential.
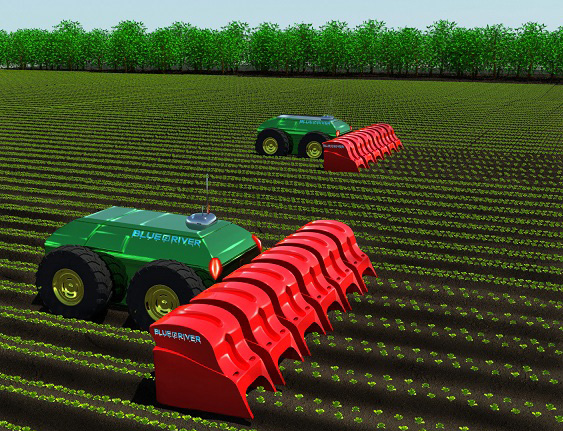
LettuceBot
A company called Blue River created a robot which can identify weed and excess planted lettuce plants with the use of image recognition. When it is determined which plants need to be removed, the robot sprays a little amount of herbicide on it. This can result in a 90% reduction of use of pesticides. Currently the robot is towed behind a conventional tractor, but Blue River is working on an fully automated version of the LettuceBot.
While driving four miles per hour the precision is a quarter of an inch. The machine can process 40 acres per day and can cared for up to 5000 plants per minute. The machine also collects data about the plants when driving through the field to keep track of the growth and health of the plants.
Advantages of this design:
- It is already a fully functioning machine
- It is really fast
Disadvantages of this design:
- It can only be used on lettuce
- It isn't fully autonomous yet
Naïo Technologies
Naïo Technologies is a company that produces different types of weeding robots. They are suitable for different kinds of users and crops. The one thing that the different robots have in common is that they remove weeds by hoeing. This lets the robots stand out to the opposing companies and robots. The most important robots of Naïo technologies can be seen below.
The first robot is called 'Oz' and is suitable for smaller fields. The small battery driven robot has a maximum moving speed of 1.3 kilometers per hour. It follows the mounds via different optical sensors and RTK GPS. The robot can turn itself around to start independently with a new mound. It only uses about one euro worth of electricity to weed one hectare.
The second robot is created for bigger farms and uses the same techniques as the Oz robot.
The third robot is called 'Ted' and is used to weed vineyard. The maximum speed is four kilometer per hour and it can maintain a surface of about 25 hectares. This robot also shares the most techniques used in the other robots. The company is working on extending the capabilities of the robot with adding functionalities as mowing, leaf thinning and trimming.
Seeding Machine
There are two kinds of seeding machines, the normal one and the precision machine.
Normal seeding machine
A seeding machine is a device that is able to sow the seeds by metering out the individual ones. The machine positions the seeds in a soil and covers them to a certain average depth. The machines makes sure that the seeds are placed at equal distances and depths. Eventually the machine covers the seeds with soil so they can’t be eaten by birds.
Precision Agriculture
For the precision agriculture there is a new design for seeding machines. This model makes use of GPS. This makes it possible that the machine exactly knows where to drop the seeds.
Automated Seeding machines
In 2006 an Australian company designed a machine that is able to plant 6 rows at a time. Eventually the machines have been sold to English and Dutch farmers as well.

Field robot event
In 2016 there was a robot event in Hassfurt, Germany. One of the games they played there was a seeding game on the field. The robots have to operate on an area of 10 x 1 meters. The robot should take wheat seeds from a station and has to sow them on the area. There were no specific rules how the machines should complete the task. The robots had to distributes the seeds as even as possible and cover them with soil.
Other kinds of mini robot seeders:
Harvesting
There already are a few robots designed for the harvesting of crops. Due to the difference in the way certain crops should be picked, robots that harvest crops are often designed for one specific crop, such as bell pepper, cucumber or any other crop.
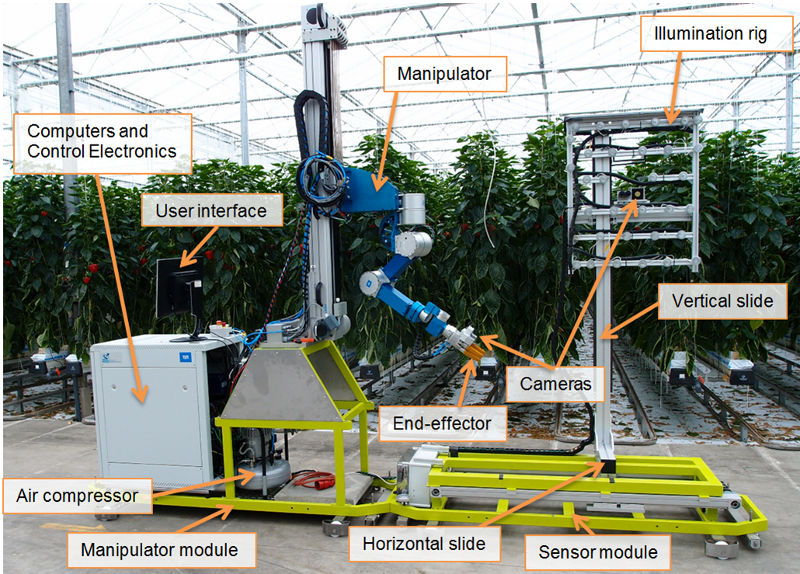
Sweeper[8]
The Wageningen University and Research center developed a robot for picking bell peppers in collaboration with a group of bell pepper growers. The robot is displayed below.
The robot picks the crops using a mechanical arm (The manipulator) and then places the crops into a container. To locate the peppers it uses multiple cameras to build a 3D picture, while trying to eliminate potential obstructions such as leaves. It has a special lighting rig to prevent bad light from being an issue. This robot was tested successfully in 2014, but was limited to slower speeds at that time due to fear that higher speeds may damage the crops.
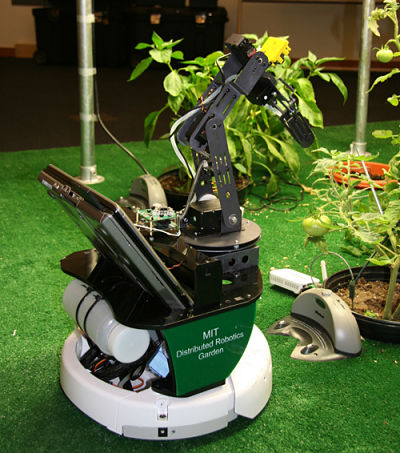
MIT Robot Gardener
MIT developed its own gardening robot in 2009. The robot has a mechanical arm for picking the crops and a watering pump to water them. A difference with the usual approach here is that the robot does not contain any sensors to analyze the plants, the sensors are placed on the plants themselves. Using sensors that can detect soil humidity and other techniques borrowed from botanical science, the sensors broadcast the need per plant, giving this technique a high precision in picking and watering the plants.
Agrobot SW6010
The Agrobot SW6010 is a commercial berry picking robot. It features a rather large truck-like design, but is fully capable of autonomous harvesting of berries such as strawberries. To pick crops it utilizes a set of precision arms, with five arms on each side. Using the multiple arms, the robot can reach multiple plants and pick crops more efficiently. There is space for two passengers to check and sort berries that the machine collects. To identify the berries, the system uses the companies patented AGvision system, which supposedly determines the ripeness of the fruit by analyzing the color and form.
Cucumber harvester
Another project of the Wageningen University and Research center is a robot for cucumber harvesting, which utilized a double camera system and a mechanical manipulator arm to detect and harvest ripe cucumbers. They built and tested a prototype in 2001 and were able to detect 95% of the ripe cucumbers, and successfully picked 75% of those. The vision techniques developed by this robot can be found in multiple modern harvesting robots.
Flyer[9]
Berry Nice
This machine is a berry picking machine developed by the Japanese Shibuya corporation. It features robots that move on rails in contrast to most autonomous robots which use wheels. Using rails increases stability and speed, but makes adapting the system more difficult as the robot can only move to where the rails are. It also uses 3D stereo cameras to determine ripeness.
CROPS solution[10]
The CROPS solution is a modular adaptable robot to harvest ripe fruits, the project is sponsored by the European Union. The goal of the project is to develop a robot that can not only harvest one, but multiple types of crops easily. It uses FinRay fingers, which are adaptable grippers to hold a fruit, and a knife to cut the fruit off the plant. To detect ripeness, cameras and color and humidity sensors are used.
Fertilization
There are some different aspects in the fertilization process that are currently improved by the use of robots. Four of the main aspects are soil Electrical Conductivity mapping systems, GIS services, precision sampling and precision fertilization. Those four aspects will be discussed below.
soil Electrical Conductivity mapping systems
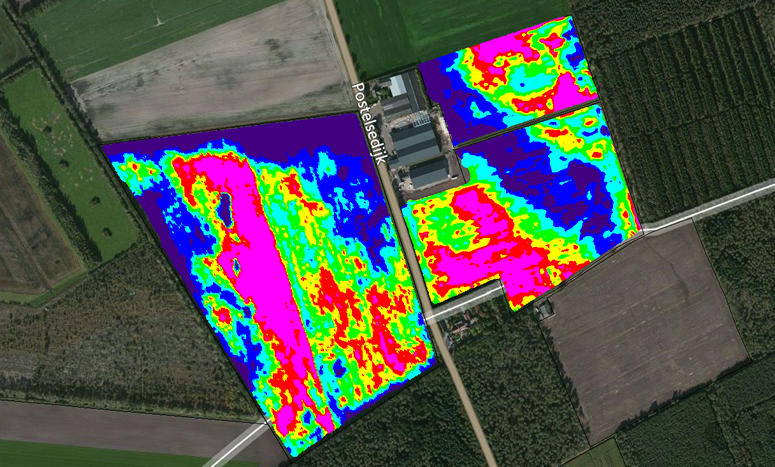
Soil Electrical Conductivity (EC) is a measurement that correlates to soil properties affecting crop productivity including soil texture, cation exchange capacity, drainage conditions, organic matter level, salinity (salt level) and subsoil characteristics. This information is used to make a fertilization plan. Soil EC is one of the simplest and least expensive ways of soil mapping for precision fertilization. Some examples of soil EC mapping systems are the EM38-MK2 sensor (left) and the Dualem 21s sensor (right).
Below, the result of a Soil EC measurement is given, this map is made by dragging the sensor across the field. The sensor measures how good the different patches of soil conduct electricity and the needed data can then be determined from this information.
GIS services
GIS is short for Geological Information System. GIS services use satellites to analyze all sorts of geological information. With the aid of GIS, maps of fields or farms are created with different layers (yield map, EC map, soil sampling, remote sensing, etc.), allowing the precise application of fertilizer (and other inputs) according to the variability of the field. Some examples of GIS services are Google Earth and esri.
Precision sampling=
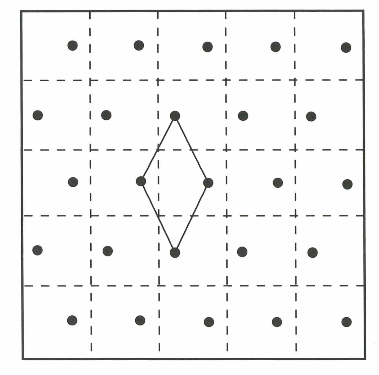
Precision sampling is soil sampling with the use of global positioning system (GPS), which allows to precisely locate position in the field. First the field is mapped, after which a grid is placed over the field, dividing the field in smaller sections. In those grids sample sections are chosen, more sample sections means more accurate sampling, but also higher costs. GPS is then used to accurately take the samples, the accuracy of the GPS can be increased by using a correction signals. The accuracy can range from 500-1500cm to 1-2cm. Finally the soil is analyzed in a lab and the outcomes are displayed on a map.
Above is an example of a sampling grid. With this particular way of sampling the distribution of the sampling sections gives the most accurate outcome. It is called a diamond sampling pattern, since the sampling sections are in a diamond shape, as can be seen above.
Precision fertilization
There are a lot of machines for precise row fertilization. These machines inject the fertilizer into the ground in very precise quantities so that every spot gets the exact amount of fertilizer it needs. An example on the market is for instance the “precisiebemester”, this machine promises a simple and cheap way for precision fertilization. The amount of fertilizer given is regulated by the use of different gear combinations, for every situation a combination can be calculated. There are also some devices[11] for regulation available.
Another example is the machine of ‘Schoonen precisie bemesting’. For this machine special injection wheels are developed, that make tiny holes in which a little bit of fertilizer is injected. A big benefit of this technique is that the ground gets aerated as well. This also leads to an improved root system[12] for the plants.
Irrigation
Irrigation is a big part of agriculture, without enough water the plants cannot grow and the harvest is lost. It is easy to spray water everywhere, but if we know exactly where the water needs to be and how much, we can save a lot of water that is otherwise lost in the soil and doesn't go into the plants.
Drip Irrigation
When it comes to row crops, it is possible to install a system that is called drip irrigation. As the name already implies with such a system you can control how much water every row of plants get. Besides controlling the amount of water, it is also a more efficient way of watering plants because you only use water where it is needed, not on places where there are no plants. These drip strips can be applied at the surface of a row of plants or buried under ground down to about 0.45m[13]., depending on what is best for the crops it is used on. There are many different drip strips each with different properties and suitable for different crops and environments. They vary in diameter, wall thickness, emitter spacing and emitter flow rates[13]
Soil Moisture Monitoring
There currently exist equipment that can be used to measure the moisture levels of the soil. This is especially useful in combination with watering systems that can moisturize different parts of the field with different amounts of water. This equipment enables the farmer to exactly see how much water there still is and to determine if the crops need water or if they can wait for the next rainfall[15]. This has the advantage that the crops don’t get too much water if there is rain coming and also not too little if the time of the year is dryer than normal.
Automated Bay Outlets
If there is a source of water nearby a big section of land it can be an option to use bay outlets. These can control the flow of water and in turn be used to decide how much water a section of land needs to get. With automated bay outlets this can happen automatically, saving the farmer time[22]. Not only can it save time, it can also reduce the water usage with about 5% to 9%, depending on the soil type[15] . Because these systems use telemetry, they can also be used to share their data with a central system and/or receive data from a central system. This way working as a group instead of separate entities.
Center Pivot Irrigation
The idea behind center pivot irrigation is that there is a large machine that rotates around a center point (the pivot point) and sprinkles water on top of the crops it rotates above. The advantage of a center pivot irrigation system over classical irrigation systems is that it uses less water to moisturize the same amount of crops[18]. It also consumes less electricity than ordinary systems when water needs to be pumped up to the farm.
Pest control
Applying pesticide to the crops is an integral part to agriculture. It is a subject with a lot of public attention, mainly concerning drift. This ‘drift’ is when some of the pesticide gets carried by the wind, or the ground to a lesser extent, possibly spreading it to nearby houses. Pesticide is harmful to humans, thus it is reasonable for the public to be concerned. Another group of people that has high stakes in this subject are the workers that apply the pesticide. It can be dangerous to them because they are in direct contact with the pesticide. Lastly it obviously impacts the costs of agriculture as well. The more pesticide is needed, the more it will cost. A possible way of reducing all of the above problems is the spray more precisely by using robots. Preferably even on a plant specific level. There are currently robots being developed to handle pesticide spraying.
Pesticide Spraying Robot
An example is a robot created by an Australian team. This robot is meant for indoor usage only, but it does show a proof of concept that robots can eventually take this dangerous job on them and be more efficient with the pesticide. The latter being useful for all of the USE aspects.
Steps for Pest Control
Pesticide use relies on 2 aspects in order to make it automatic. We already have the above information about the spraying part, but that only gets us half way. That way we can remove the dangerous task of spraying from the workers, but it doesn’t do any of the other promised benefits. For these to work we need detection of insects, again preferably on plant level, so we can spray more precisely.
Pest Detection Technologies
To get this working there are multiple technologies in the works. There are 3 main options at the moment. These being: computer vision, (near) infrared and scanning a sample size of plants using destructive methods. This last one not really being applicable to the situation, but is more aimed towards testing the harvested crops before selling them. The first 2 are more useful to growing plants. Computer vision more up close on a plant-by-plant basis while (near) infrared could be used with a drone on a slightly bigger scale (but possibly plant-by-plant if the resolution is high enough and you don’t fly the drone too high)
Visiting van den Borne
We visited one of the most advanced precision farms in the Netherlands, where a lot of new techniques for precision agriculture are being used. The name of the farm is Van Den Borne Potatoes. The biggest difference on this farm is that almost everything they do with the potatoes is done by precise machines. They are able to work with a precision of 6x6 meters.
We had a conversation with Jacob in which we talked about the pros and cons of precision farming and the usage of new technologies.
He explained to us that by using new technologies you will get more work, but it is worth it because of the higher yield gained. The investment in technologies costs a lot of money. But because of the precise measurement and management of the plant, you are able to reduce the overlap, meaning that there are less resources used. This saves a lot of money if you are a big farmer. The biggest problems he struggles with are the legal restrictions. There are many rules for flying with drones which makes it hard to work with this technology.
The cameras they are using are able to collect a lot of data. One of the cameras measures 5 different spectra, the standard RGB and the extra close-infrared and normal infrared. The pictures made with this camera are stitched together, so one big picture is gained. This picture is then analyzed. With the pictures of another drone with a normal camera, they are also able to make a 3d model of the farmland.
Jacob explained that the precision farming is mostly used with corn, wheat and grass. Van den Borne grows potatoes, because potatoes have a high efficiency. He also explained to us that if the bottom of your farming land exists of sand, you have to add liquid manure. When working with the precision agriculture concepts on sand the results are much better.
All machines that are required for executing the process of growing potatoes are designed for operating with GPS. Everything that happens on the land of van den Borne will be actuated by a computer.
The only part that is difficult with the technology is that it is simple to measure all kinds of things, but it is difficult to process the 'raw data' to data you can work with. It will always stay hard to exactly tell, out of a picture, where you should change something for optimizing the grow process.
The current project he is working with right now, is that of a building team that tries to build a new drone. And because of the legal restrictions he is observing the possibilities for using drones that fly with a fixed power cable.
Models
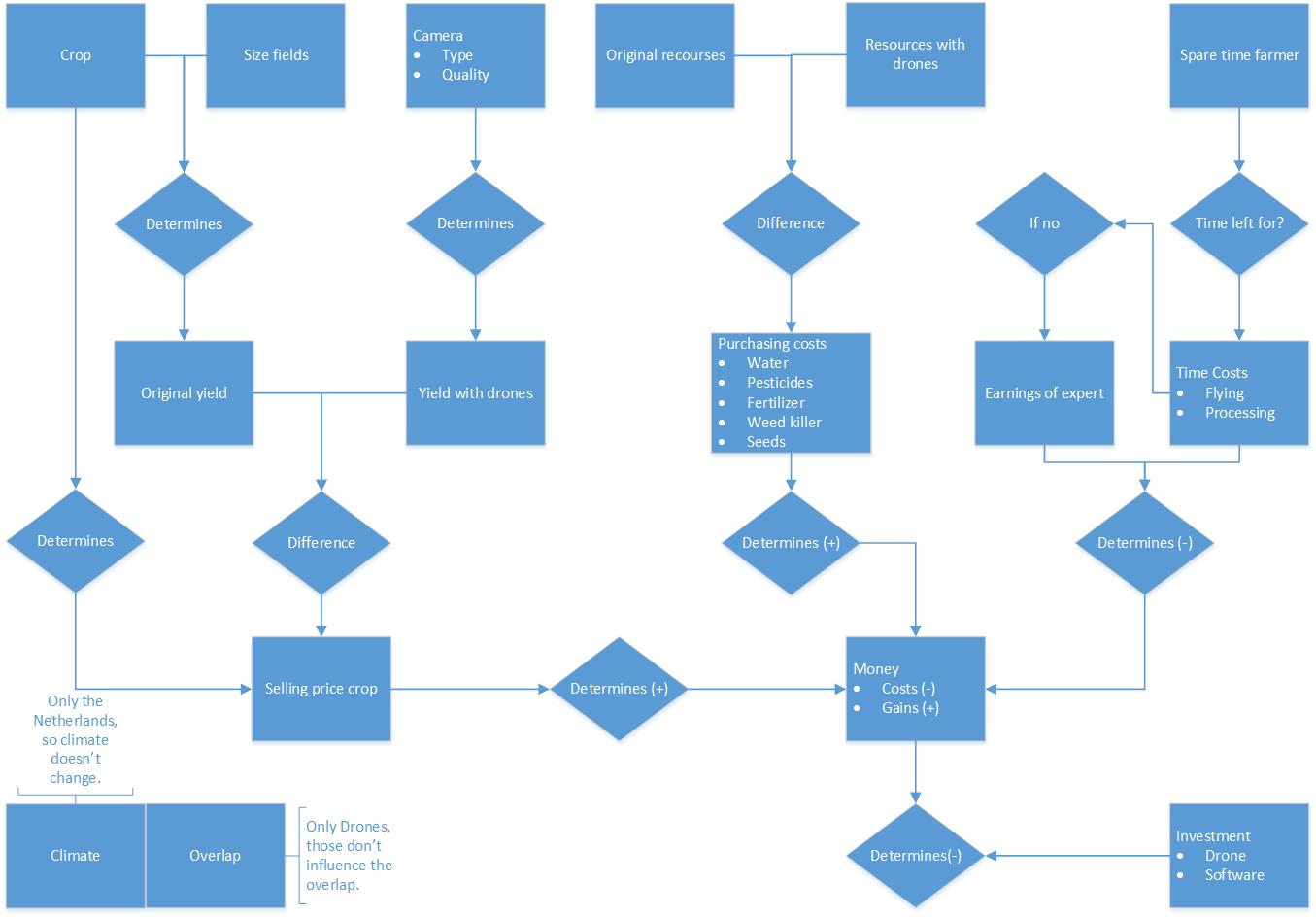
To create a solid mathematical model a list of all the important variables need to be made. Then the relations between those variables can be describes to create the model.
The first model which is made is the economical model for The Netherlands. A list of relevant variables can be found underneath. This list is not complete yet!
| Inputs | Process constants | Process variables | Outputs | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Abbreviation | Description | Name | Abbreviation | Description | Name | Abbreviation | Description | Name | Abbreviation | Description | |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | |
| Climate | Yield | Time flying | Money | |||||||||
| Soil | Overlap | Time image processing | ||||||||||
| Crop | Investment drone | |||||||||||
| Size fields | Investment software | |||||||||||
| Spare time farmer | Type camera | |||||||||||
| Purchasing cost water | Quality camera | |||||||||||
| Purchasing cost pesticides | Earnings expert | |||||||||||
| Purchasing cost fertilizer | ||||||||||||
| Purchasing cost weed killer | ||||||||||||
| Purchasing cost seeds | ||||||||||||
Below, the first draft of the Visio model can be seen, in this graph the variables are displayed by a rectangle and the relations with diamonds. Towards the costs the relations are either determines(+) of determines (-), the determines(+) relations are the gains and the determines(-) relations are the costs. Furthermore, in the bottom left corner the variables overlap and climate can be seen, those won't be taken into account in the model due to the reasons stated beside them.
Consultancies / outsourcing companies
To be able to generate an advise for farmers whether to invest in drone technology or not, it is important to know what it would cost them to outsource the task. And what general consultancy costs are.
The following outsourcing companies were found:
Loonbedrijf Thijssen Nieuwehorne
This company uses soil sensors and an EBee drone to preform precision agriculture. They claim to that their services can reduce use of water, fertilizer and pesticides by 70%. The pixel size of the EBee drone is 10 cm, which creates detailed crop information maps.
De Samenwerking BV Elsloo
This company uses a lot of GPS to decrease overlap and increase efficiency, but they don't use drone image processing. They mainly equip their machines with GPS to be able to adjust the amount of different inputs depending on the location. However it might be very useful to contact to company to ask what their opinion is about the use of drones.
PrecisionHawk
PrecisionHawk is a company that offers drone solutions for all kinds of applications. One of these applications is agriculture. The company offers total packages which consist of the drone, service, apps and software. The user has to buy a license for the software annually. The cheapest and simplest packages which is offered is the 'Crop Scouting Package', which start from +- 1200 US dollar. The most complete package is the 'Lancaster Standard Kit'. This package start from 13000 US dollar.
The software offers a wide variety of diagnostic tools to evaluate the soil and the crops.
Company Thijssen, based in Nieuwehorne, is the only drone outsourcing company found in The Netherlands. Contact with this company will ensure that some key parameters for the model are obtained.
Crops
Potato
Production
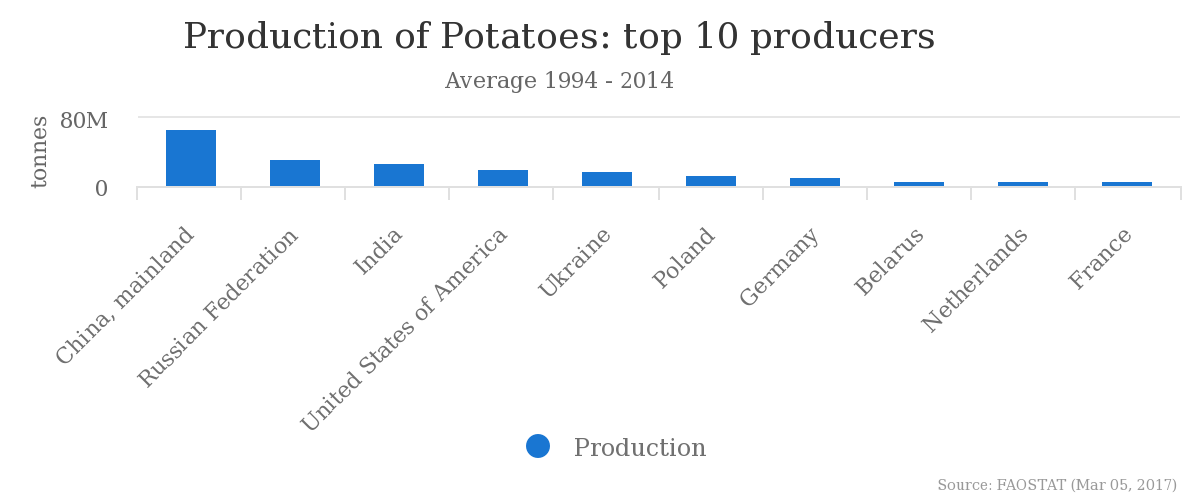
In 2014 the countries with the highest potato production were China and Russia (69 and 33 million tonnes relatively).[19]. The Netherlands ranks 9th, however considering the population of said countries this is quite impressive. With the highest production per head being in Europe. The list is as follows according to “Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations”[20]:
| Country | Production (tonnes) |
|---|---|
| China | 39.0 |
| Russia | 33.5 |
| India | 28.9 |
| USA | 20.4 |
| Ukraine | 18.8 |
| Poland | 15.2 |
| Germany | 11.4 |
| Belarus | 8.0 |
| Netherlands | 7.1 |
| France | 6.6 |
The Plant
The potato plant reaches a length of about 60 cm [21] and can produce up to 300 seeds. There are over 4000 varieties of potatoes [22], but the most cultivated species is Solanum tuberosum. Each potato holds about 322 kJ per 100g[23]
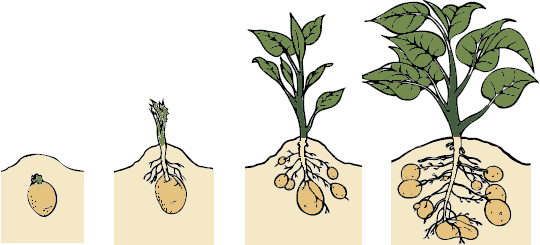
Growth Process
Growth takes place in five stages:
| 1. Sprout and root growth |
| 2. Photosynthesis |
| 3. Stolons grow (runners, new plants can emerge from these) (stops above 27C) |
| 4. Tuber bulking (at this moment these factors are critical: optimal soil moisture and temperature, soil nutrient availability and balance, and resistance to pest attacks) |
| 5. Maturation (sugars convert to starches) |
Potatoes are very sensitive to frost and can grow on any type of soil except saline and alkaline and preferably loose (pH 5.2 to 6.4). The average world farm yield for potatoes was 17.4 tonnes per hectare, in 2010. (America 44.3 tonnes per hectare and some new zealand farmers 60 to 80 tonnes per hectare) [24]
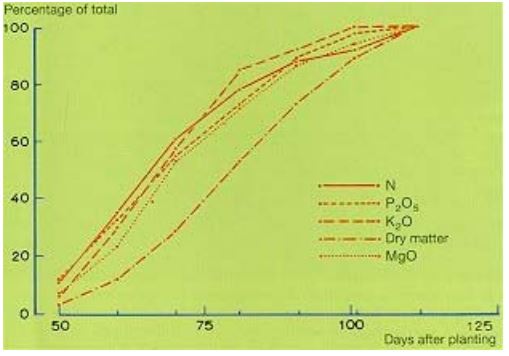
Important growth factors
The most important minirals for potato plants are Nitrogen, Phosphate, Potassium and Magnesium [25].
Nitrogen is absorbed by the potato plant. The amount which is absorbed depends on the stage of the growth. The begin stage absorbs more nitrogen, so this is where nitrogen is the most important. The total amount of nitrogen in the plant when it's fully grown is around 1.5% to 2% of the total weight. This means that an amount of 1.5 to 2% of the weight of the potato plants should be in the soil as nitrogen (about 150-200 kg/ha). Nitrogen is an important element in protein synthesis. Nitrogen deficiency produces light greet plants with stiff leaves and a low yield.
Phosphate is used in the entire growing proces, but like nitrogen, it is absorbed the most in the beginning of the growth proces. About 60 kg/ha of Phosphate is absorbed. About 0.7% of the total mass of a potato plant consists of Phosphate, so this amount has to be present in the soil. About 80% of the phosphate is concentrated in the stem of the plant. This amount is removed when the plants are harvested. The soil depends in which amount phosphate is absorbed, because phosphate is not absorbed very readily by the potato plant itself. More acid soils help to absord the phosphate. A low phosphate deficiency results in dirty green coloured leaves and unsatisfactory growth.
Potassium is especially absorbed in the period when the plant emerges to the point were the stem reaches it's maximum length. This is a fairly short period, as can be seen in the above graph. Low level of potassium in the leave hasn't got as much negetive influence as a low level of nitrogen. About 350 kg/ha of potassium is absorbed, which is a lot more than for instance Phosphate. Potassium deficiency in the leaves results in drak green and bronze discolorations. A long term effect masy become necrotic, which is a form of cell death. Potassium deficiency in the tubes results in easy bruising.
Magnesium is not absorbed much, but is has a big influence in the growth. About 30 kg Mg/ha is absorbed, all before the main stem has reacted it's total length. Thus the magnesium must be present before this length is obtained. Potassium impedes magnesium absorption. So, excessive use of potassium often results in magnesium deficiency. Magnesium deficiency results in more necrotic veins at the olderst leaves.
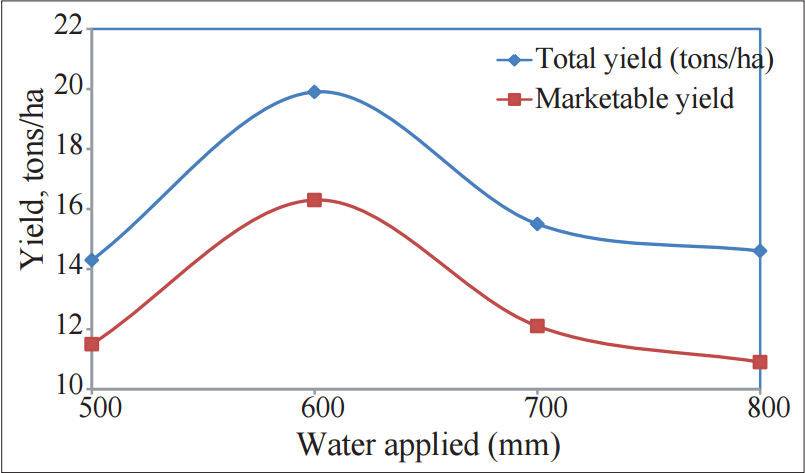
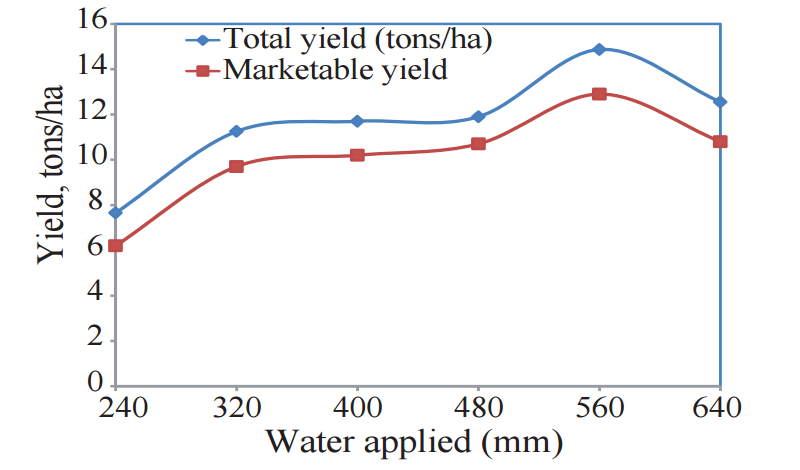
Water deficiency reduces the foliage growth and the efficiency of the photosynthesis. Furthermore, water deficiency stimulates maturity, which results in smaller tubes. Below are two graphs of the influence of water on the yield of potatoes in the season 2008/2009 (left) and 2009/2010 (right).
Soil Ph is something that influences the yield of potatoes. To show the effect below is a table with results from a study that influenced the Ph level of the soil to see the resulting yields, done over multiple years:
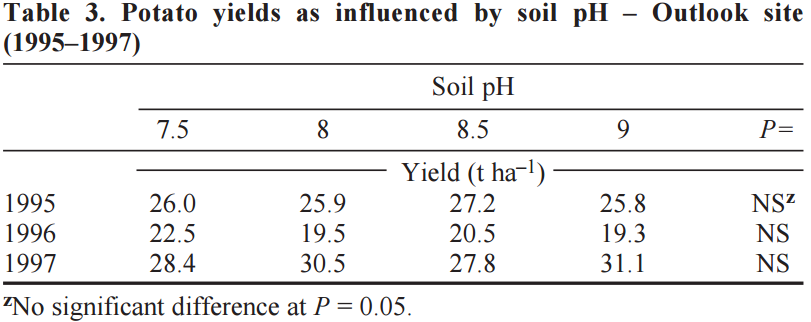 Cite error: Invalid parameter in
Cite error: Invalid parameter in <ref> tag
There are a lot more parameters which influence the growth of potatoes. Think about temperature, light intensity and air quality. The paramters can be measured with drones. But these parameters can't be adjusted by the farmer. So it is not usefull, in the scope of this project, to look at the impact of those values
Maize
Production
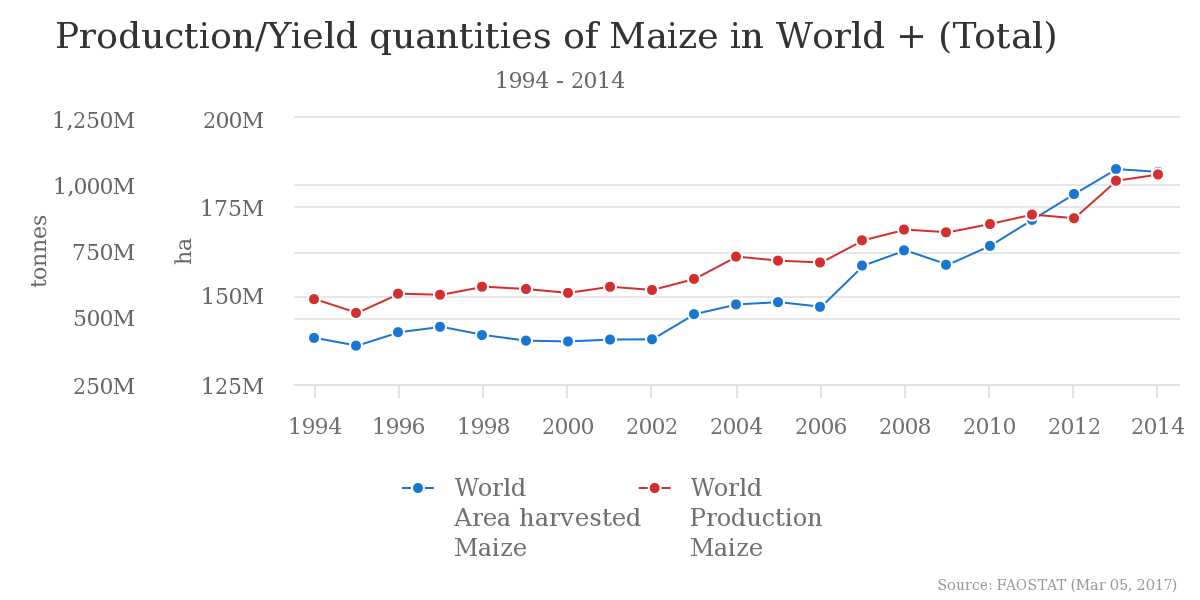
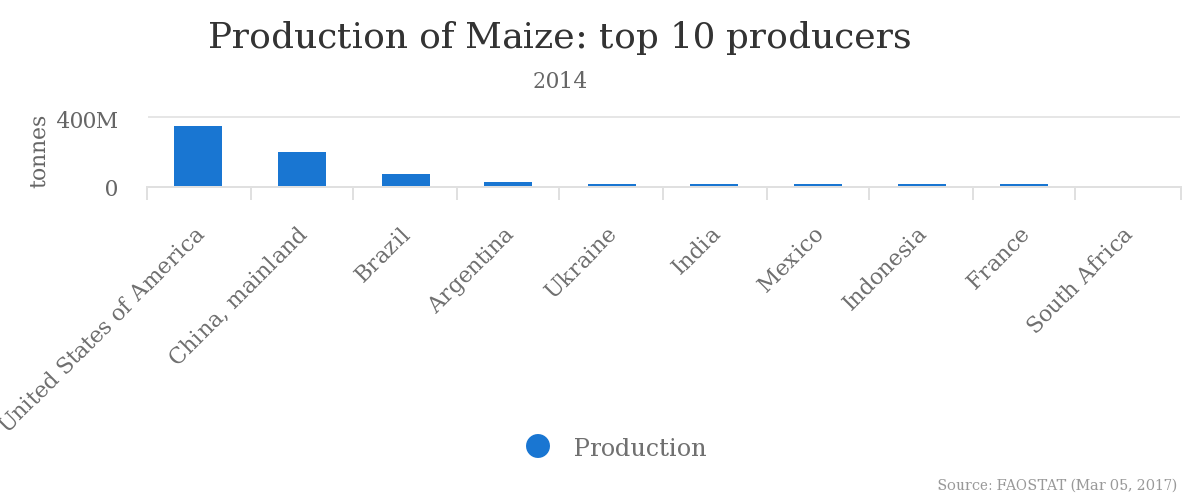
The production of maize is the highest in the USA and China (361 and 216 million tonnes respectively)[19] with the land efficiency being around 5.6 tonnes/ha in 2014[19]. The list is as follows according to “Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations”[19]:
| Country | Production (tonnes) |
|---|---|
| USA | 361.1 |
| China | 215.6 |
| Brazil | 79.9 |
| Argentina | 33.1 |
| Ukraine | 28.5 |
| India | 23.7 |
| Mexico | 23.3 |
| Indonesia | 19.0 |
| France | 18.3 |
| South Africa | 14.3 |
The Plant
Maize (meant for harvest) grows about 3m in height[27], however some natural varieties are able to grow to lengths of 12m[28].
Growth Process
In the milk stage pollination has taken place but starch hasn’t formed yet, this is when corn can be harvested to get sweet corn. Sufficient soil moisture is critical to the growth of corn. Further it is a very versatile crop when it comes to climate[29].
Drone Usability
Drones seem quite useful when it comes to maize. Most symptoms of problems seem to be related to color, uneven growth or geometric changes in the leafs[30]. These symptoms then often lead to the problem being something to do with the soil (dry, wet, cold, crusted), which is partially possible to solve (more/less water). Mainly the color symptoms can be related to diseases or insects, this last one solvable using pesticide.
As to using drones to detect these symptoms, color changes are easily detect from pretty high (thus allowing to scan more crops in less time). However uneven growth might need to be scanned for at a lesser height, and especially geometric changes in the leafs. This geometry needs some relatively close scans (with the current resolution cameras), this is not suited for entire scans. Checking the geometry should be done on a reasonable sample size of plants distributed over the entire plot.
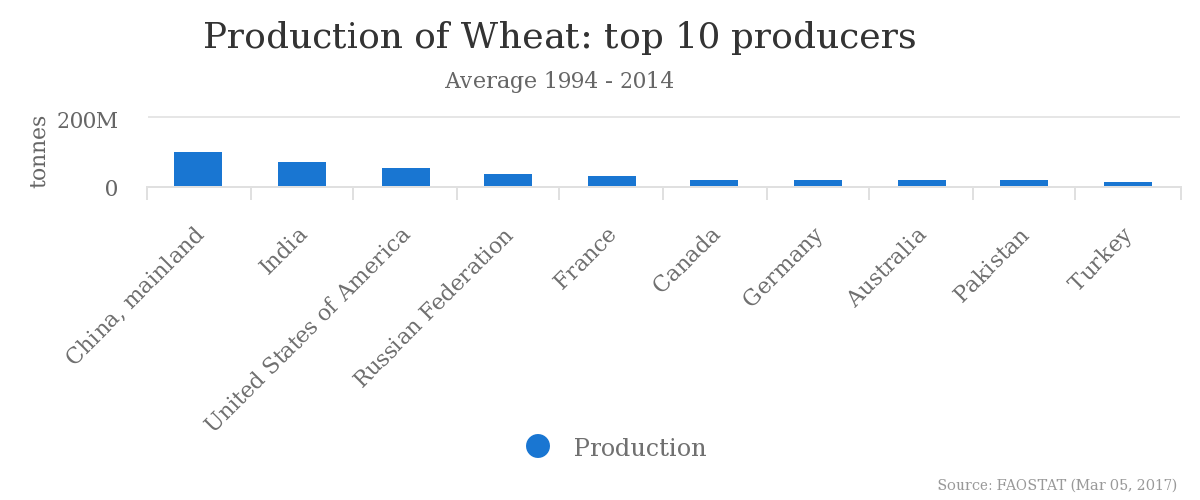
Wheat
Production
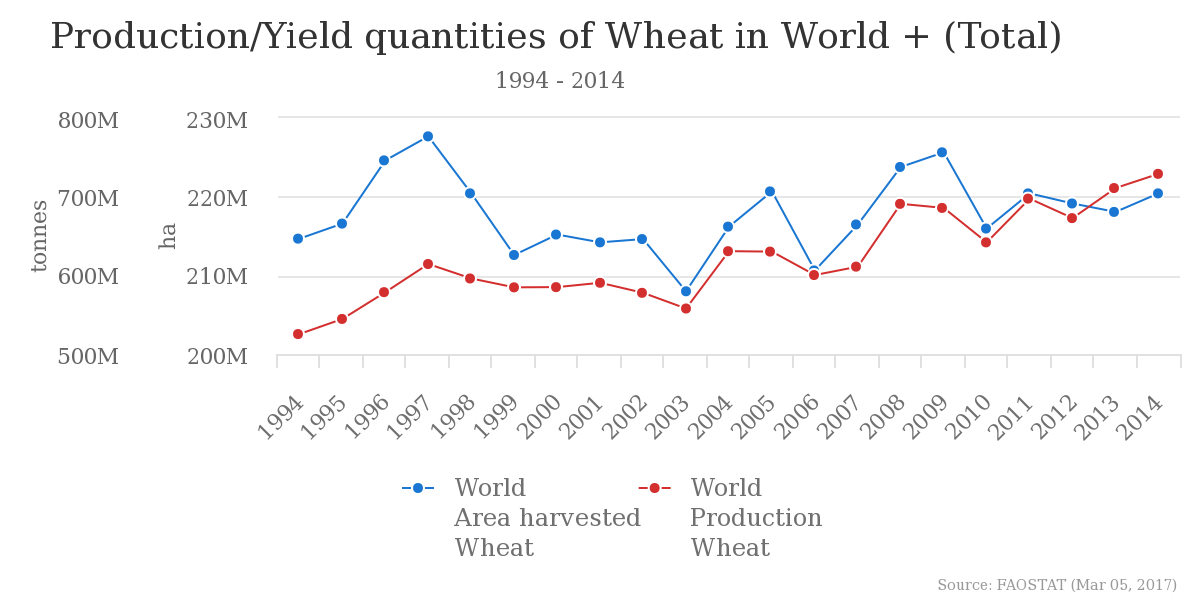
The production of wheat is the highest in the China and India (108 and 75 million tonnes respectively)[19] with the land efficiency being around 3.3 ton/ha in 2014 and a maximum of 10 ton/ha.[20] The list is as follows according to “Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations”[19]:
| Country | Production (tonnes) |
|---|---|
| China | 107.9 |
| India | 75.1 |
| USA | 59.2 |
| Russia | 44.1 |
| France | 36.1 |
| Canada | 25.4 |
| Germany | 22.0 |
| Australia | 21.0 |
| Pakistan | 20.6 |
| Turkey | 19.6 |
Growth Process
Here we will explain a bit about the different growth stages (GS) of wheat. We later refer to some growth stages when discussing the influence of water and fertilizer on the growth of wheat. Wheat is a C3 plant[31].
Germination to Emergence (E)
During this stage, the plant grows from a seed[32]. In order for germination to start, the seeds need a water content of 35 to 45 percent by weight[31]. Besides the water content the temperature also needs to be within the maximum range of 4 to 37 degrees C and optimally within 12 to 25 degrees C[31].
Emergence to double ridge (GS1)
The is the stage where the plant goes from just after emergence to when floral differentiation occurs[31]. The flowering of wheat occurs after vernalization, and the double ridge stage is only reached after the chilling requirements are met[31]. There are two main types of wheat, spring and winter type. While spring type has a mild response to no response to vernalization, winter type needs a cold period because has a strong response to vernalization[31]. This winter type starts out with high resistance to frost, but loses this resistance during this growth stage.
Double ridge to anthesis (GS2)
During this growth stage a plant will go from having only four to eight leaves to a plant that has developed flowers. At the beginning the apex is only approximately 0.5mm[31]. But during the terminal spikelet stage, the amount of leaves has gone up to 7 to 12 and the apex has grown to 4mm[31]. After this a spike growth occurs, of which the intensity and the duration are dependent on the amount of radiation the plant receives and the temperature. The more radiation the more intense the growth spike and lower temperatures, not lower than 4.5C, the longer this growth spike lasts[31].
Anthesis to physiological maturity (GS3)
During this stage the plant goes from having some flowers to a fully developed plant. The central part of the plant is where the anthesis begins and continues towards the basal and apical parts during a three- to five-day period[31]. After this the endosperm cells and amyloplasts are formed[31].
Influence of Water
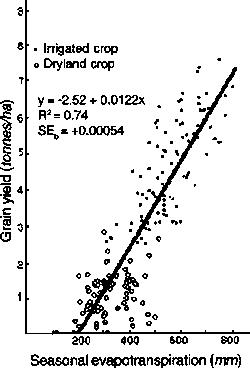
There are two major processes that are involved with the usage of water: the first is the water absorption by the plant itself. The second is the crop evapotranspiration. This depends on net radiation, vapor pressure deficit, the crop ground cover and stomatal conductance[31]. Plant evapotranspiration (ET) is positively and linearly related to grain yield in C3 plants[31]. Because of this reason water shortage will decrease grain yield. See figure below:
Relationship of grain yield to seasonal evapotranspiration for irrigated and dry-land wheat crops
Next is the influence of water shortage on the different growth stages explained earlier.
Germination to emergence
The negative impact on seed growth in this stage can be reduced if the seeds are bigger[31]. Bigger seeds have a larger root mass and may help the plant of getting to the deeper water if there is less water available[31].
Emergence to double ridge
Drought during GS1 may result in an increase of the phyllochron of bread and durum wheat, but on the other hand leaf growth will suffer from a lack of water, especially if the water potentials are between -0.7 and -1.2 MPa[31]. The following table shows how less water influences the different stages of GS1:
| Stress Period | Stress Period | Stress Period | Stress Period | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Control | Pre-anthesis | Anthesis | Grainfilling |
| Leaf area index at booting | 5.00 | 3.30 | 5.00 | 5.00 |
| Fertile tillers/m2 | 513.00 | 658.00 | 434.00 | 485.00 |
| Grains/spike | 32.70 | 13.00 | 27.10 | 31.40 |
| 1 000 grain weight (g) | 56.30 | 55.20 | 53.70 | 49.20 |
| Grain yield (g/m2) | 779.00 | 559.00 | 498.00 | 658.00 |
| Harvest index | 0.52 | 0.50 | 0.53 | 0.53 |
| Sugar (g) | 0.64 | 0.41 | 0.78 | |
| WUE (kg grain/ha mm ET)a | 16.80 | 14.60 | 12.40 | 15.20 |
aWUE = water-use efficiency; ET = evapotranspiration.
Double ridge to anthesis
Because GS2 is a period of active growth, a mild to moderate water deficit will decrease cell growth and leaf area with a consequent decrease of photosynthesis per unit area[31]. If water deficiency occurs during the spike growth period, the grain number will decrease sharply[31]. The lowest yield will happen if the water deficiency starts from 10 days before spike emergence.
Anthesis to maturity
Water deficiency close to anthesis will accelerate the development, but the eventual grain weight will decrease due to a shorter grain filling period[31].
It is clear by now that a water deficiency leads to a lower grain yield, but how exactly is shown with the following formula: GY = T * TE * HI, where GY is grain yield, T is the product of transpiration, TE is the transpiration efficiency and HI is the harvest index[31].
The reason that fertilizer is used to grow crops is because it adds nitrogen to the soil, which wheat needs to grow[33]. After water, nitrogen is the biggest constraint to crop growth, it is especially needed for leaf growth[31]. The biggest yield gain to be gotten if the nitrogen is added right before the initiation of stem extension. The nitrogen concentration in the spike during the anthesis stage correlates closely with the grain yield of crop[31]. Around 25 kg of nitrogen is required in the fertilizer to produce 1 tonne of wheat[31]. The nitrogen can be added in two stages to increase the efficiency[31].
Some more formulas we found that might be useful
- GDD = (Tmax + Tmin)/2 - Tb
- This shows the cereal development that is normally expressed in degree-days(GDD). With Tmax and Tmin being the maximum and minimum daily temperatures and Tb being the base temperature[31].
- PARA = RS * 0.5 * 0.9 * (1 - I/I0)
- PARa is the photosynthetically active absorbed radiation, Rs is the total solar radiation (MJ/m2), the factor of 0.5 refers to the fraction of total solar energy, 0.9 refers to the fraction of radiation absorbed by the crop and (1 - I/I0) is the fraction of total solar radiation flux, which is intercepted by the crop[31].
- I/I0 = e-K * LAI
- I/I0 is the same as before, e is the natural logarithm, K is the canopy extinction coefficient and LAI is the crop leaf area index.
- CGR = RUE * PARA
- CGR is the crop growth rate, RUE is the radiation use efficiency (g/m2 d)[31].
- GY = KNO * KW
- With GY as the grain yield (g/m2), KNOW is the kernel number (m-2) and KW is the kernel weight 9g)[31].
- PTQ = Rs/(T - 4.5)
- With 4.5 degrees C as the best temperature for wheat growth, PTQ the photothermal quotient (MJ/m2 d C), Rs being the solar radiation and T the temperature[31].
Nutrients
| Nutrient component: | Maize / Corn | Wheat | Potato | RDA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water (g) | 10 | 13 | 79 | 3000 |
| Energy (kJ) | 1528 | 1369 | 322 | 2000–2500 |
| Protein (g) | 9.4 | 12.6 | 2.0 | 50 |
| Fat (g) | 4.74 | 1.54 | 0.09 | |
| Carbohydrates (g) | 74 | 71 | 17 | 130 |
| Fiber (g) | 7.3 | 12.2 | 2.2 | 30 |
| Sugar (g) | 0.64 | 0.41 | 0.78 | |
| Calcium (mg) | 7 | 29 | 12 | 1000 |
| Iron (mg) | 2.71 | 3.19 | 0.78 | 8 |
| Magnesium (mg) | 127 | 126 | 23 | 400 |
| Phosphorus (mg) | 210 | 288 | 57 | 700 |
| Potassium (mg) | 287 | 363 | 421 | 4700 |
| Sodium (mg) | 35 | 2 | 6 | 1500 |
| Zinc (mg) | 2.21 | 2.65 | 0.29 | 11 |
| Vitamin C (mg) | 0 | 0 | 19.7 | 90 |
| Vitamin B6 (mg) | 0.62 | 0.3 | 0.30 | 1.3 |
| Vitamin A (IU) | 214 | 9 | 2 | 5000 |
| Vitamin E (mg) | 0.49 | 1.01 | 0.01 | 15 |
| Vitamin K1 (μg) | 0.3 | 1.9 | 1.9 | 120 |
Concept of the model
Goal
The goal of the model will be to give an advice. The model has to be able to determine, for a given input, if it will be a good investment for farmers to extend their business by investing in drones.
Users
The model will be designed for farmers in agriculture, who want to explore the possibilities in starting to use drones for precision farming.
Working principle of the model
There are three main parts of the model.
Input
The input of the model will consist of some old data from the farmer and new data received from soil measurements. The data the farmer has to give to the model are the old yield of the land, the nitrogen levels belonging to this old yield and the current nitrogen level for every subsection, received from soil measurements. Finally the most important input given by the farmer, this is the shape of the land that has to be analyzed, this can be done by dragging the subsections (squares) in the model to form the (roughly) correct shape.
Processing the data
For the processing the data some formulas are used, the main one being the one described in subsection "Nitrogen/growth-function", which is y = -0,0005x2 + 0,1976x + 28,414. This formula won't of course hold for every field and every situation, that is why the first step of the model is to correct the formula according to the old yield and nitrogen levels the farmer set as an input. The formula will be made to return the old yields the farmer gave in when the old nitrogen levels are used as the x-value. Furthermore the top of the graph will be put on the optimal nitrogen level, which is calculated by the formulas seen in the table displayed below.
| Destination | Guideline (kg N/ha) |
|---|---|
| Consumption potatoes, clay ground | 285 - 1,1 * (N-mineral 0-60 cm) |
| Consumption potatoes, sand ground | 300 - 1,8 * (N-mineral 0-60 cm) |
In these formulas the input is the current nitrogen level in the first 60 centimeters of the soil. When the formula is set correctly the fertilization level in the case without precision agriculture will be calculated from the average nitrogen level of the field. This fertilization level is obtained from the equation in the table shown above again. The fertilization in this case is the same over all subsections, this leads to a difference in yield per subsection. All these yields will be calculated and the average of all those subsections will be taken as the yield in kg/ha. After this, the case in which precision agriculture would be used will be reviewed. Firstly the nitrogen level per subsection will be used to calculate the fertilization per subsection, again using the equations in the table above. This means that the nitrogen level at every place in the field will be the same, so the yield is the same for every subsection. The average yield of the case in which precision agriculture would be used is then the yield of one subsection in kg/ha.
Output
The outputs of the model will be the average yields in the two cases, with and without precision agriculture. Another output of the model will be the amount of fertilizer used for each of the two cases. With this information a conclusion can be made about the use of precision agriculture on the field of this farmer.
Assumptions
For the model we have to make a few assumptions to be able to calculate the extra yield. The first one is that the production only depends on the nutrition’s in a specific area. We don’t take the influence of insects, mold, etc. Last assumption is that the farmer already has machines with GPS for precision farming.
Nitrogen / growth - function
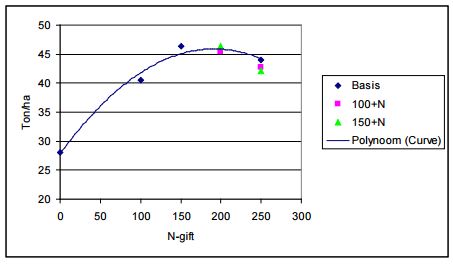
It is very complex to predict the growth of a potato plant. A lot of veriables influence the quantity and the quality of the yield. To make the problem workable we will only look at the relation between nitrogen and the yield. A lot of research is done on this topic, but every research has other boundry conditions, such as species, soil, weather, etc. These conditions deviate a lot between different tests. To create a basis for the model we tried to choose an average research. The research "Geleide N-bemesting voor aardappelen op basis van gewasreflectie-metingen" of F. van Evert showed relation between the amount of nitrogen and the yield. The research consisted of multiple different subtests with other boundry conditions. After a thorough comparison we thought that the subtest 'Rusthoeve 2010 Consumptieaardappel' was the best test to use.
This subtest consisted of multiple testfields near eachother on which different amounts of nitrogen were applied. The species 'Victoria' was grown which is suitable for direct consumption or french fries. The test was conducted at farm 'Rusthoeve' in Colijnsplaat in Noord-beveland. The soil consisted of 1.7% organic material and the phosphorus conditions were good (PW 37; P-AL 51).
At the end of the growing period the yield per subfield was inspected. The result can be seen in the following plot.
The function which is fitted through the results can be described with:
y = -0,0005x2 + 0,1976x + 28,414
In which y is the yield [ton/ha] and x the amount of applied nitrogen [kg/ha]. This fitted function has a R² of 0,9717, which is an indication that the result is a good fit ( R² = 1 is a perfect fit).
Software implementation of the model
In order to get a working software implementation of the model we first needed a platform. We choose to use html, css and javascript to create a platform for the model to be implemented in. This also means the model can be viewed as a regular webpage meaning there is no need for the user to download extra software to use it. Such a model requires input and output. Thus we divided the site in 2 blocks, the left being input and the right being output. The input being the more complicated one. The thing that drones are useful for is treating the land in small pieces. So instead of bringing, for example, the average water level to the desired values drones can help to bring every sub-plot to the desired values. Therefor there is the need for a method to input values per sub-plot. We designed a grid which allows each field to be turned on/off and for a value to be selected. The site also allows for an image to be uploaded and rescaled so it is easier for the farmer to select the fields which best define his/her land.
Drone
Camera
There are a few different camera's which can be used for drones in agriculture:
- The RedEdge MicaSens: which is able to make pictures in five bands: Blue, green, red, red edge, near IR. it is very useful to do a health analysis of plants. This camera is able for about USD $4900.
- Canon S110NIR: It can make pictures in the near infrared band. It is able to give information about biomass indication, growth monitoring, crop discrimination, leaf area indexing. This camera is specially used for the eBee-Ag.
- Canon S110RE: It can make pictures in the red egde band. It is able to give information about plant stress assessment, chlorophyll indication, senescence analysis, drought assessment. This camera is specially used for the eBee-Ag.
- Canon S110RGB: It can make pictures in the visible spectrum. It is able to give information about real colour 2D and 3D visual rendering, chlorophyll indication, drainage evaluation. This camera is specially used for the eBee-Ag.
- Airinov multispec 4C: It is a sensor specially customized for the eBee-Ag. It contains four separate sensors that are controled by the autopilot. These acquire data across four highly precise bands, plus each sensor features a global shutter for sharp, undistorted images. The camera is able to give inforamtion about biomass, leaf area indexing, nitrogen recommandation and phenology. This camera is specially used for the eBee-Ag.
Measurable values
With the camera's discriped before you are able to monitore the following things:
- Health analysis: Because the frequent meassurements with the drone, you are able to controlle the growth and health of the plants
- Biomass: the camera's are able to look through the plant and meassure the collor. Therefore they are able to give a estimation about the biomass of the crop. The biomass is the total mass of the plant. This gives an estimation about the yield.
- The camera's are able to give information about the drainage evaluation.
- The camera's could give recommandations of the nitrogen
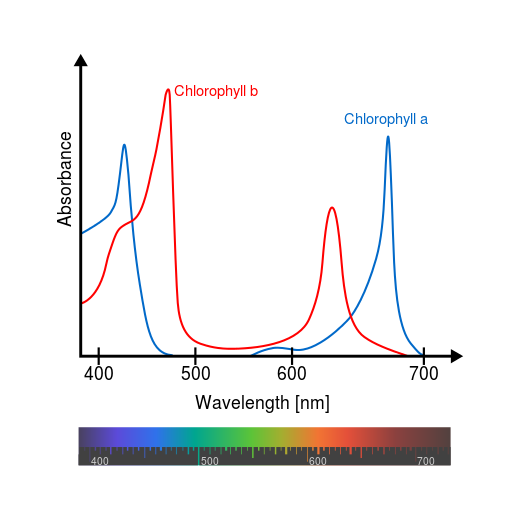
- The camera's can meassure the Chlorophyll, this tells something about the amount of green pigments in the plant. Chlorofyll makes it possible for the plant to use the energy from the sun for the photosynthesis.
Logbook
| Week | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guus van Dongen | Brainstormed about the subject. Research on the topic of robotics for seeding. | Visited van den Borne. Prepared an interview and processed the results. Made a presentation, planning and gannt chart. | Had contact with Straver and Jan Staal but they had no time last week. Prepared Interviews. Collecting valuable information from 'Boerderij' and CBR. | Made a start on the complex model. Defined the concept of the model. Defined the input, | Have conversations with Eline and Wouter, contact with Marnix. | Defining new concept, find relations for the nitrogen, Analyse data from Van den Borne | ||
| Johan Somers | Brainstormed about the subject to research and did a general information search on the topic of robotics in agriculture. | Also went to Van den Borne, and prepared and gave the presentation. Also did a state of the art research to weeding robots. | Update the wiki and add parts of the model variables and the project description (2.5 hours), had a useful brainstorm with the group to make a start with the model, searched for consultancies and drone outsourcing companies. | |||||
| Teun de Groot | Brainstorming and finding useful sources about our topic, robotics in agriculture. | Went to Van den Borne for an interview. Did a state of the art research about use of robots in the fertilization process. Correcting wiki in grammar and syntax. | Made a first draft for the Visio chart for the economical model. | Cleaned up the wiki and checked everything on grammar and syntax. | ||||
| Jur Bartels | Brainstorming about the topic, finding resources and making a start with the wiki | Did state of the art research for robots in harvesting, updated wiki | Researched previous work done in modelling impact of robotics in agriculture, created logbook and task list in the wiki | |||||
| Laurence Keijzer | Brainstorming about robotics in agriculture + research. | Went to Van den Borne for the interview + state of the art research about use of robots in irrigation. | Done research about different crops we want to use in our model | Gathering more information about wheat and what water and fertilizer have on the growth rate of wheat | ||||
| Bastiaan Wuisman | Research about our topic and thinking about a topic. | Visited Van den Borne for an interview about his farm. Did a state of the art research about use of robots in pest control. | Researched potato growth | Researched the effect of water on crop growth. Also started the creation of the platform for the model |
References
- ↑ https://ourworldindata.org/world-population-growth/
- ↑ http://www1.wfp.org/zero-hunger
- ↑ http://eprints.lse.ac.uk/61155/1/__lse.ac.uk_storage_LIBRARY_Secondary_libfile_shared_repository_Content_Centre_for_Economic_Performance_Discussion_papers_dp1335.pdf
- ↑ https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Spyros_Fountas/publication/225527407_Agricultural_robots-System_analysis_and_economic_feasibility/links/00b49528e6ebce9eda000000/Agricultural-robots-System-analysis-and-economic-feasibility.pdf
- ↑ https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/851d/0d9f6bc13986012beea5d5e88b543699d3f3.pdf
- ↑ http://www.insidepolitics.org/brookingsreports/robots.pdf
- ↑ http://www.dairyherd.com/news/german-company-demonstrates-automated-weeding-machine
- ↑ http://www.crops-robots.eu/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=22&Itemid=22
- ↑ http://www.wur.nl/upload_mm/5/5/7/c221711e-98da-4865-805a-8fc8531aa624_flyer_cucumber%20harvesting_robot_uk.pdf
- ↑ https://www.festo.com/cms/en_corp/14014.htm
- ↑ http://www.precisiebemester.nl/precisiebemester/index.html
- ↑ http://www.precisiebemesting.nl/techniek.html
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 https://www.ksre.k-state.edu/sdi/abstracts/drip-irrigation-of-row-crops.pdf
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Drip_irrigation
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 http://vro.agriculture.vic.gov.au/dpi/vro/vrosite.nsf/pages/lwm_state_art_irrigation_docs/$FILE/Stateoftheart_edition1_web_tagged_final.pdf
- ↑ http://vro.agriculture.vic.gov.au/dpi/vro/vrosite.nsf/pages/lwm_state_art_irrigation_ed1
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 http://vro.agriculture.vic.gov.au/dpi/vro/vrosite.nsf/pages/lwm_state_art_irrigation_ed2
- ↑ http://vro.agriculture.vic.gov.au/dpi/vro/vrosite.nsf/pages/lwm_state_art_irrigation_docs/$FILE/Stateoftheart_edition2_web_tagged_final.pdf
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 19.2 19.3 19.4 19.5 19.6 19.7 19.8 http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QC/visualize
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 http://www.fao.org/home/en/
- ↑ https://books.google.nl/books?id=QDrqL2J-AiYC&pg=PA209&dq=potato+plants+60+cm&redir_esc=y&hl=nl#v=onepage&q&f=false
- ↑ http://news.nationalgeographic.com/news/2002/06/0610_020610_potato.html
- ↑ https://ndb.nal.usda.gov/ndb/search/list
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 http://www.fao.org/potato-2008/en/potato/cultivation.html
- ↑ 25.0 25.1 http://www.aardappelpagina.nl/doc/potatoes_cultivation_netherlands.pdf
- ↑ 26.0 26.1 http://www.agrojournal.org/20/02-11.pdf
- ↑ https://books.google.nl/books/about/Races_of_Maize_in_Mexico.html?id=tXxQAAAAMAAJ&redir_esc=y
- ↑ http://www.agron.missouri.edu/mnl/86/MNL86.pdf
- ↑ Fernandez-Armesto, Felipe (2011). "The World: A History", p. 470
- ↑ https://www.aganytime.com/dekalb/tools/Documents/CornDiagnosticGuide.pdf
- ↑ 31.00 31.01 31.02 31.03 31.04 31.05 31.06 31.07 31.08 31.09 31.10 31.11 31.12 31.13 31.14 31.15 31.16 31.17 31.18 31.19 31.20 31.21 31.22 31.23 31.24 31.25 31.26 31.27 31.28 31.29 31.30 http://www.fao.org/docrep/006/Y4011E/y4011e06.htm
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Germination
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fertilizer
- ↑ https://nl.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bladgroen
Sources
1.Company that makes ground scans and 3D scans with drones: https://3dr.com/ 2.Drones made for agriculture: https://www.sensefly.com/applications/agriculture.html 3. Drones that also map the ground: http://www.precisionhawk.com/ 4. Examples of agriculture robots: https://www.intorobotics.com/35-robots-in-agriculture/ 5. Some facts and companies analyzed: https://www.therobotreport.com/news/ag-in-transition-from-precision-ag-to-full-autonomy 6. Benefits analyzed: https://www.geospatialworld.net/article/drones-and-robots-future-agriculture/ 7. Professors etc. giving their views: http://fruitworldmedia.com/index.php/featured/robots-huge-potential-robotics-agriculture-industry/ 8. Japanse company that founded a fully autonomous indoor farm: http://spread.co.jp/en/sustainable-farming/ 9. Project of the EU for percision lifestock farming: http://www.eu-plf.eu/index.php/publications/ 10. eLeaf technology: http://www.eleaf.com/products-showcase-fruitlook#technology-pimapping 11. Automated precision weeding: http://www.bluerivert.com/ 12. Case study of drones in argiculture https://blog.dronedeploy.com/case-study-ce39c9f44e48#.tsnfhikpp 13. Mechanical weeding robot http://link.springer.com/article/10.1023%2FA%3A1015674004201?LI=true 14. Seeding and fertilazation robot goo.gl/s2ehLC 15. Machine-to-machine communication goo.gl/UVJDFS 16. Framework for argicultural systems goo.gl/RGzsuo 17. Farmer in the Netherlands which uses the drone: http://www.loonbedrijfthijssen.nl/contact/ 18. An other farmer in that uses drones: http://www.vandenborneaardappelen.com/ 19. Bosch Weeding Robot: https://www.deepfield-robotics.com/en/Weeding.html 20. Drip Irrigation Of Row Crops: What Is The State Of The art? https://www.ksre.k-state.edu/sdi/abstracts/drip-irrigation-of-row-crops.pdf 21. State of the art - on irrigation farms. Edition 1 http://vro.agriculture.vic.gov.au/dpi/vro/vrosite.nsf/pages/lwm_state_art_irrigation_docs/$FILE/Stateoftheart_edition1_web_tagged_final.pdf 22. State of the art - on irrigation farms. Edition 2 http://vro.agriculture.vic.gov.au/dpi/vro/vrosite.nsf/pages/lwm_state_art_irrigation_docs/$FILE/Stateoftheart_edition2_web_tagged_final.pdf 23. Pesticide spraying robot: http://www.araa.asn.au/acra/acra2005/papers/sammons.pdf
24. Soil Ph influence on the yield of ceirtain crops https://www.nrcs.usda.gov/Internet/FSE_DOCUMENTS/nrcs142p2_053293.pdf 25. Extremely in-depth doc on how to control the Ph value of soil. Even the effects of a single type of nutrition in the soil on the Ph level http://extension.cropsciences.illinois.edu/handbook/pdfs/chapter08.pdf 26. Contains data about what crop type needs what Ph level http://www.cropnutrition.com/efu-soil-ph 27. Influence of nutrition supply on the crop yield http://www.eolss.net/Sample-Chapters/C10/E5-21-03.pdf 28. Influence of Ph value on the yield and marketable yield of potatoes. With concreet data which we can use http://www.usask.ca/agriculture/plantsci/vegetable/resources/journal/Impact_pH_scab.pdf 29. Influence of water on the yield of potatoes, inc data and graph representation http://www.agrojournal.org/20/02-11.pdf