Embedded Motion Control 2015 Group 11
Group Members
| Name | Student number | |
|---|---|---|
| Changjie Guan | 0927222 | c.guan@student.tue.nl |
| Yang Xu | 0918430 | y.xu.1@student.tue.nl |
| Bolin Zhao | 0925735 | b.zhao@student.tue.nl |
| Zhe Zhao | 0815651 | z.zhao@student.tue.nl |
| Fei Chen | 0923761 | f.chen@student.tue.nl |
| Yizhou Ye | 0925611 | y.ye@student.tue.nl |
| Yiran Liu | 0843177 | y.liu.1@student.tue.nl |
Introduction
Task and goal: Find way out of maze as fast as possible.
Requirement
The requirement analysis base on the problem statement and divide in different level of important as ‘must’,’should’,’could’ and ‘wont'
- the robot must can get out of the maze
- the robot must take action by itself
- the robot should get out of the maze as soon as possible
- the robot won’t hint the wall
Functions
Ensure all the requirements can be meeted.
- Move forward and backward, turn around
- Detect the doors
- Detec the distance between the front wall and the robot
- Remember the path and and the door, grid the path and store it with 0 or 1, representing the pass available or not respectively.
- Each step, select a direction where is available. If the current grid has not been recorded, record it and move on. If the current gird has been recorded as well as its surrounding grids, randomly choose a grid from recorded and move on. If all the maze has been searched, the robot must go out the maze.
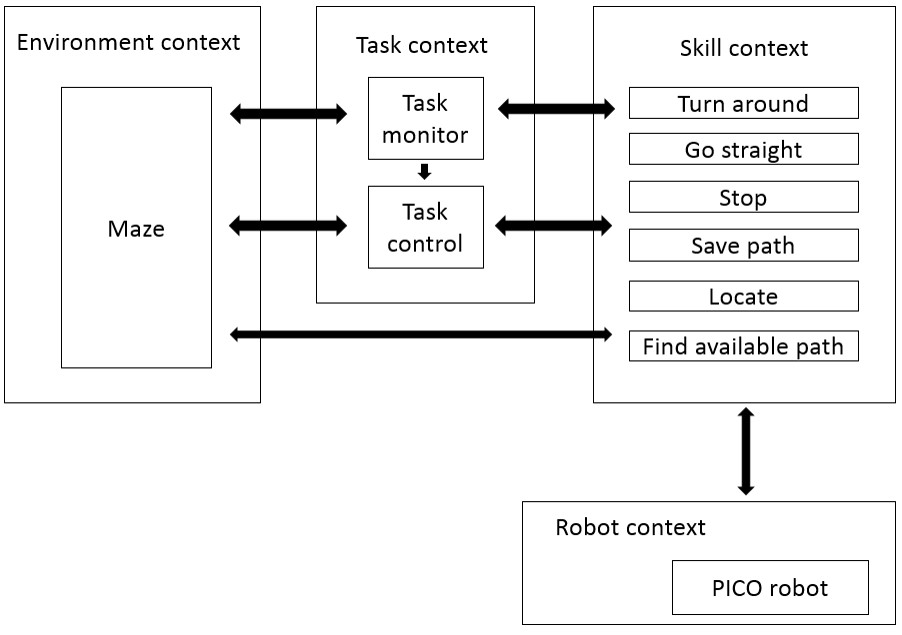
Activity model
Behavioural model
Behavioural model:
- Environment context
- Task context
- Task monitor
- Task control
- Skill context (updated to latest version)
- Find minimum value of sensor (“index”)
- Save data (including map, robot situation, etc.)
- Calculate the location and situation of robot (“update”)
- Align the robot coordinate system (Feedback angle)
- Turn around & J-turn
- Judge the robot is in the center of the road
- Check and judge cross
- Check exit (Leave the maze)
- Check dead end (J-turn)
- Make the robot back to the center of the road (Feedback location)
- Robot context
Structure model
Function block – Behaviour and Structure
Ten functions:
- Find minimum value of sensor (“index”)
- Judge the robot is in the center of the road
- Save data (including map, robot situation, etc.)
- Check and judge cross
- Calculate the location and situation of robot (“update”)
- Make the robot back to the center of the road (Feedback location)
- Align the robot coordinate system (Feedback angle)
- Turn around & J-turn
- Check exit (Leave the maze)
- Check dead end (J-turn)
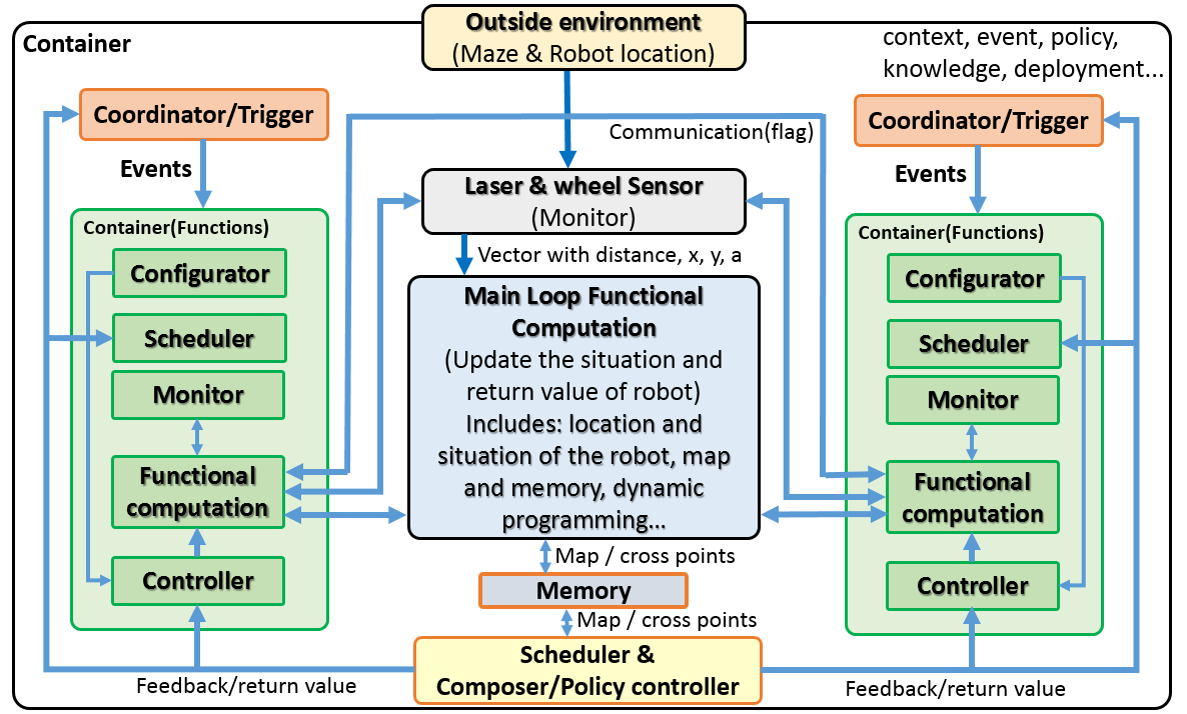
In the following, the structure model will be decoupled into Composition Pattern (5Cs)
The system level
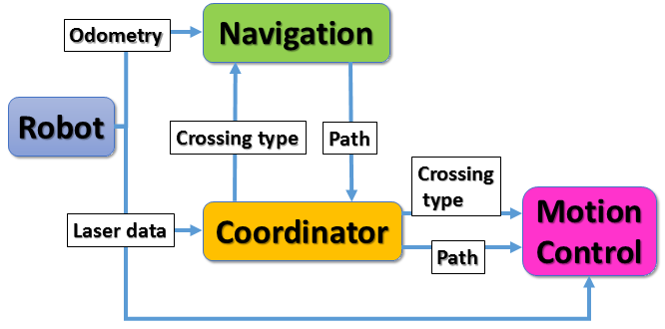 The Coordinate and Navigation
The Coordinate and Navigation
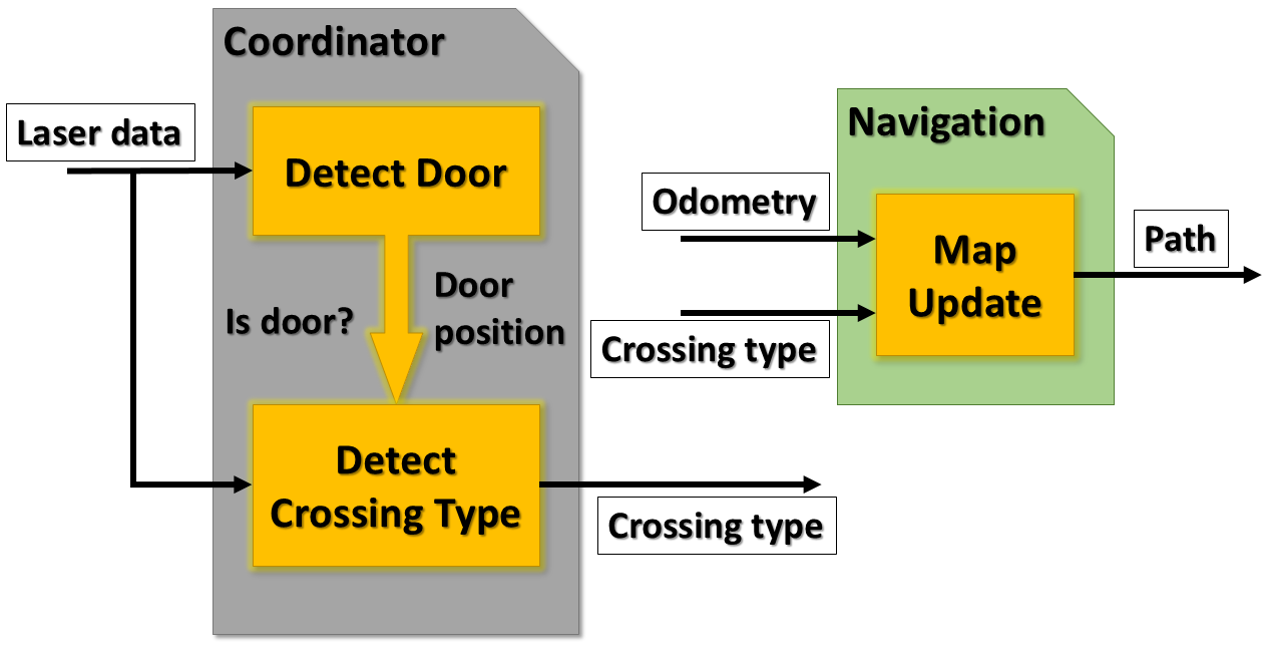 The Motion control
The Motion control
Schedule
May. 13: Corridor competition.
June. 10: Final presentation.
June. 17: Maze competition.
Corridor Competition
Our PICO failed at the corridor competiton. Fortunately, we get some feedback from it:
- The “move ahead” function was executed in open loop, with too accurate drift control.
- The robot crashed into the wall.
- The robot slide was not controlled, the judgement condition code needs to be rebuilt.
After some effort in improving code, during the second time test, our program finally works.
 |
Algorithms
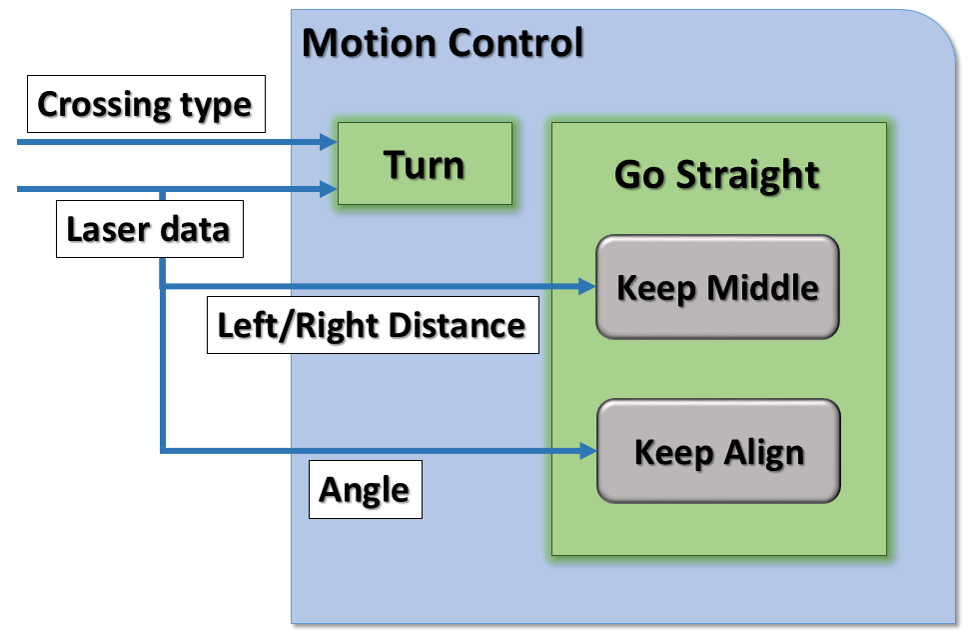
Moving forward or backward
Compare left and right distance, combined with P controller to make the PICO in the middle of corridor; Check the angle of the PICO.
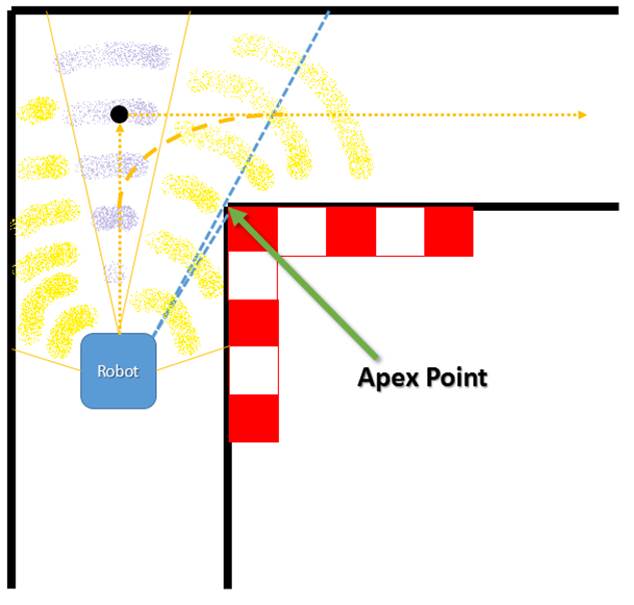
Turning
- Detect range:-20°-80°,20°-80°
- Check the differences between the sensor return values
- Oval trace
- Memory the corner for DP
Map Saving
Door Detection
Presentations
- First presentation (week 3): File:First presentation.pdf
First presentation is about: Task-skill-motion system architecture and the composition pattern.
- Second presentation (week 6): File:Second presentation.pdf
Second presentation is more about: Coding and Composition Pattern.
- Final presentation