Embedded Motion Control 2015 Group 6
Group Members
| Name: | Student id: | E-mail: |
| Akash Agarwal | 0923269 | a.agarwal@student.tue.nl |
| Angus Pere | 0926353 | a.f.pere@student.tue.nl |
| Ashish Yadav | 0925559 | a.yadav@student.tue.nl |
| Floris Remmen | 0920072 | f.remmen@student.tue.nl |
| S. Cagil Mayda | 0926975 | s.c.mayda@student.tue.nl |
| Ugonna Mbaekube | 0927006 | u.o.mbaekube@student.tue.nl |
| René van de Molengraft | Tutor | m.j.g.v.d.molengraft@tue.nl |
Planning
Week 1: 22 April - 29 April
- Introduction lecture
- Meeting 1: Initial design document & C++ tutorials
- Ubuntu and other required softwares Installation
Week 2: 29 April - 6 May
- 27-04 12:00: Deadline initial design
- Finishing C++ tutorials
- Start studyin maze algorithms
- Meeting 2: Division of team roles in the project
- Reading tutorials
- Prepare presentation
Week 3: 4 May - 10 May
- 6 May: First presentation of the design
Week 4: 11 May - 17 May
- 13 May: Corridor competition
Week 5: 18 May - 24 May
- Lecture 3: Composition Pattern part II by Herman Bruyninckx
Week 6: 25 May - 31 May
- 27 May: Second presentation of the design
Week 7: 1 June - 7 June
- Lecture 4: Communication patterns
Week 8: 8 June - 14 June
- 10 June: Presentation of final design
Week 9: 15 June - 21 June
- 17 June: Final competition
Initial Deisgn
Goal
The goal of the “A-Maze-ing challenge” is to design and implement a software for the PICO robot to navigate through a maze autonomously while optimizing time.
Requirements
- To program a PICO robot to participate in the “A-Maze-ing challenge”.
- The PICO robot should be able to navigate through the maze autonomously.
- The PICO robot should be able to navigate through any maze regardless of its configuration.
- The PICO robot should be able to avoid all obstacles during its navigation through the maze including contact with the walls of the maze.
- The PICO robot should never get “stuck” at any position in the maze.
- The PICO robot should be able to make use of its sensors to navigate the maze.
- The PICO robot should have some sort of “memory” that prevents it from moving back towards paths already navigated through.
- The PICO robot should be able to find the optimal path through the maze while optimizing time.
- After navigating through the maze, the PICO robot should be able to autonomously terminate its movement.
Functions
The basic functionality of the robot are as follows:
1) Motion
- Move Forward
- Move Backwards (Reverse)
- Turn Left/Turn Right
2) Environmental Awareness
- Obstacle Detection using sensors
- Decision making during navigation
- Termination of movement on completion of the maze
- “Memory” storage
- Optimal Path calculation
- Localisation
Components and Specificications
Schematic overview of the components to be used in the software design
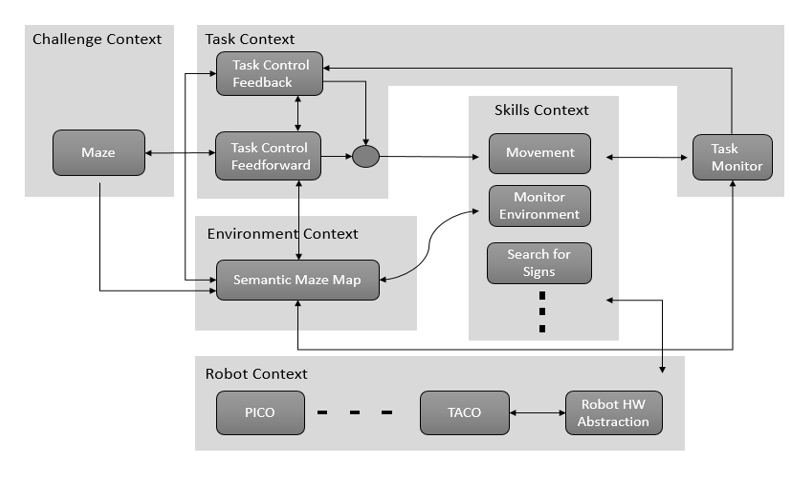
Task Context: Controls the implementation of the robots functions depending on the challenge and environmental context. Task Monitor: Monitors the implementation of the robots functions and sends the information to the task control feedback. Task Control Feedback: Implements control action on the robot based on information received from the task monitor. Task Control Feedforward: Contributes in the implementation of control actions on the robot depending on the state and the goal of the challenge.
Interfaces
- 1st
- 2nd
- 3rd
- 4th