Mobile Robot Control 2023 Group 8
Welcome to our group page.
Group members
| Name | student ID |
|---|---|
| Eline Wisse | 1335162 |
| Lotte Rassaerts | 1330004 |
| Marijn Minkenberg | 1357751 |
Exercise 1 : The art of not crashing
Instead of just stopping, we made the robot turn around whenever it came close to a wall in front of it. The video of the bobo robot running our dont_crash script can be found here: https://drive.google.com/file/d/109fDDzf6ou2HHuSZgOicY27pRdOpJs0s/view?usp=sharing.
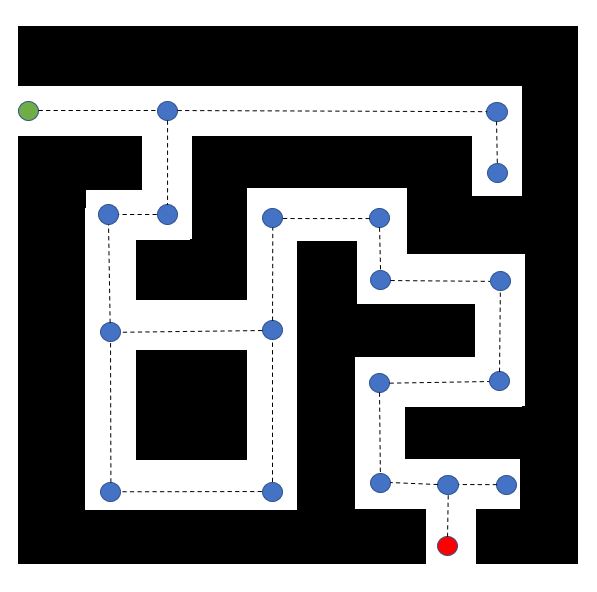
It is more efficient to only place nodes at turning points of the robot (so it can drive straight from node to node), or at a decision point (where the robot can take either of two routes). In between the nodes, the robot will have to drive straight anyway, so it is not necessary to use extra nodes in between. This way the number of nodes is decreased from 41 to 20. Hence, the algorithm will have to explore fewer nodes on the way. This will save unnecessary computations, making the algorithm more efficient.
See main branch in repository.
The used approach for this assignment is open space detection. First, it is determined whether the range of the laser data points is within the set horizon. This is evaluated for the laser data over the whole range. If the range of the laser point is larger than the horizon, this laser point is added to the open space. Laser points of the open space that are next to each other, belang to the same open space. Hence, it can occur that the robot observes multiple open spaces. In this case, the robot chooses the widest open space, and drives to the middle of it. The robot will only correct its direction if the new open space deviates more than 5 laser points from the midpoint of the robot. This, to make sure the movement is smooth and no unnessecary corrections are made. On top of that, if right in front of the robot no object is present within the horizon, it will drive straight forward for 0.5 seconds, or until it encounters an object. After this 0.5 seconds or when an object is detected, the open spaces will be determined again. If the robot detects no open space, or is very close to an object it will rotate, in an attempt to find a new open space.
Screen recording of simulation: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1EcfIyBl419EeOkya5rmSvxfzes4J4Fpt/view?usp=share_link
Recording of experiment: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1usk2VdcQFwjlW3zfe1Fuc-l8EOWuFPkF/view
Possible improvements we worked on/are working on:
- The implementation of multiple horizons: In this version, when no open space is found at the maximum horizon, the horizon is reduced in an attempt to find an open space with a smaller horizon. The horizon will be reduced until 0.5m, since from then onwards objects will be very close and it is better for the robot to first rotate and then re-check for open spaces. This should make the algorithm more robust against different sizes of hallways and object distances. This implementation has been succesfully tested in simulation, but could not be tested on the real robot due to time constraints.
- Dead-reckoning and global localization: In this version, the final goal (being the end of the hallway) is taken into account. This to try to make sure the robot always reaches the end of the hallway, also when it encounters a dead end somewhere in the hallway. To this extent, the position of the robot is tracked and compared to the final position, to make a better choice about which open space to drive to. The code needs a bit more time to finalize, so it is not tested yet.