PRE2020 3 Group7
Time-Machine
When you are studying you sometimes forget an important meeting, because you are deeply focused on your materials. Also, sometimes you need a little motivation to start studying. To solve that problem we are going to develop a clock that displays your agenda. This allows for users to get a clearer overview of their daily planning. The clock will also take your study/work time into its planning, and, of course, your spare time. It also gives you a push notification when you need to start studying in the form of a motivational message. So far, we have brainstormed about multiple extra fucntions that could be added in the future. Firstly, there is evidence that environmental lighting conditions influence concentration **ADD SOURCES**. Secondly, it could check the activity of the user's phone during work hours and shut down certain distractors if it is used too much. It is also possible to use a webcam to check whether the user is working with the necessary focus and send a notification if this is not sufficient (should be looked at with privacy regulations).
Group Members
| Name | Study | Student ID | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wouter de Vries | Computer Science | 1463748 | w.p.h.d.vries@student.tue.nl |
| Ilana van den Akkerveken | Psychology & Technology | 1224158 | i.a.f.v.d.akkerveken@student.tue.nl |
| Joep Obers | Mechanical Engineering | 1455117 | j.g.p.m.obers@student.tue.nl |
| Jens Reijnen | Psychology & Technology | 1378074 | j.m.t.reijnen@student.tue.nl |
| Erick Hoogstrate | Mechanical Engineering | 1455176 | e.hoogstrate@student.tue.nl |
Planning
| Week | Activity | Name |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Choose a subject | All |
| Literature research for the problem statement and SotA | All | |
| 2 | What should the robot look like | All |
| What should the robot be able to do | All | |
| 3 | Order Parts | Wouter |
| Make a survey | Jens & Ilana | |
| Make a first sketch of the idea | Joep | |
| 4 | Gather survey responses | All |
| Analyse survey responses | Jens & Ilana | |
| Put the raspberry together and install the basics | Wouter & Joep | |
| Look at how to plot a clock in python | Erick | |
| Look at how to extract an agenda in python | Joep | |
| 5 | Transfer data from agenda to clock | Erick & Joep & Wouter |
| Make small slices from the clock | Erick & Joep & Wouter | |
| Implement code on raspbery pi | Erick & Joep & Wouter | |
| Implement research from the survey | Jens & Ilana | |
| 6 | Make a code that combines the clock and agenda | All |
| Complete the liturature on the wiki | All | |
| Make code that can make apointments for studying | All | |
| Look on how to connect philips hue to rpi | All | |
| 7 | x | x |
| x | x | |
| x | x | |
| x | x | |
| 8 | Finish the interface | All |
| Finish the program | All | |
| Do a user test | All | |
| x | x | |
| 9 | x | x |
| x | x | |
| x | x | |
| x | x |
Problem statement
As students, we have been working from home due to Covid-19 for over a year, which has been causing drastic changes in our freedom for months. The consequences are noticeable in many areas but primarily in the psychological well-being of the public**ADD SOURCES**. Since working and studying from home has become the norm, students report feelings of loneliness, less (study) motivation and less concentration. When no fun distractions can take place anymore and everyday seems a repetition of the day before, it is hard to stay productive, or happy in general. Therefore, it is important that we come up with a device that will keep people motivated to study and work from home, but due to time limitations we will focus on students. It has been said that sticking to a set schedule is helpful when working from home, but in practice this is not that easy. It could be beneficial for students to have some help with this. Help in making an executable and achievable week schedule with clear distinctions between work/study and relaxation. Additionally, the students should be made aware of their social media/phone use in order to keep them focused and not distracted.
Approach
Objectives
In order to fulfill this projects multiple objectives have to be reached in the upcoming 8 weeks.
- Literature research has to be done in order to get an idea about what products there already are on the market and to see where there is room for improvement. This literature search will additionally focus on finding multiple points that can influence or enhance concentration while studying and what prod. This might also help increase the understanding of which distractions are most common while studying. After this literature search it will be possible to create a research question and an application.
- Secondly, a survey will be held. This survey is used to confirm the findings from the literature and ask for advice concerning our product. Furthermore, if the data is gathered from all respondents, it will contain practical problems that might not emerge from literature alone.
- After data collection, the first bit of code could be written and we can start ordering parts after which prototyping can start. During this stage it will be important to keep the data of the survey in mind to make sure the product will fulfill the needs of the end-users.
- When the prototype is done, a user-study/usability test will be conducted to investigate how helpful and functional the product truly is. As a finishing touch, the prototype or code may need to be adapted, depending on the user tests.
Requirements
Students want to achieve their degree. In order to achieve it they need to study a lot, which can be very hard in the wrong environment. Therefore they require a stimulating study environment, but also after studying a place to relax and let go of all the stress.
| Id | Requirement | Priority |
|---|---|---|
| 01 | The product displays an analog clock on the screen. | high |
| 02 | The clock reads the agenda items of the user. | high |
| 03 | The agenda items of the user are displayed on the clock in colors on the time when they are set. | high |
| 04 | The user can connect their agenda to the clock by entering their agenda URL. | high |
| 05 | The clock will automatically show the correct time and agenda items after being turned off and on again. | high |
| 06 | The product has a digital clock below the analog clock. | medium |
| 07 | The screen displays the agenda items next to clock | medium |
| 08 | The user can give their desired color to agenda items in which they will be displayed on the clock. | low |
| 09 | The clock changes the room's lighting according to preset keywords. | low |
| 10 | The speakers of the clock can set off an alarm sound for certain agenda items. | low |
| 11 | The clock plans breaks in study/work time. | low |
Milestones
1) Literature study
2) Survey results
3) Sketch of the idea
4) Picking up all the parts for the project
5) Setting up the Raspberry Pi so that it can be operated through wifi
6) Creating code for a simple clock
7) Creating code to extract an agenda and import it to our clock
8) A functional prototype
9) Creating a presentation of our prototype
10) Creating the actual presentation
10.5) (optional) Do some user tests
11) Finishing the wiki
Deliverables
- survey-study
- prototype
- user-study
- complete wiki page
USE analysis
User
The main users of this device will be students. In times of the Covid-19 pandemic lots of students are forced to study from home. For some, this has caused motivation and concentration problems and struggles with maintaining/creating a good planning. The goal of our project is to make a device that helps students in maintaining a clear overview of their tasks and help them in study planning. To gather information about the problems students are facing while working/studying from home, a survey study has been done among 85 students in the age of 17-27 years.
Society
A device such as our study clock will benefit society in terms of education. The more and the better students stick to their study tasks the less guidance has to be given by professors and teachers and the less study delay will have to be covered.
Enterprise
Effects of lighting
There has been done a lot of research on the influence of lighting on humans.
Medical and biological research has shown that light entering the human eye has both visual as non-visual biological effects on the human body. Good lighting can have a positive effect on health, well-being, alertness and sleep quality. For many years, scientists considered cones and rods to be the only photoreceptors in the eye, until Berson et al. (2002) discovered a third type of photoreceptor in the retina of mammals. This photoreceptor regulates non-visual biological effects, such as body temperature, circadian rhythm (sleep-wake cycle), heart rate, cortisol production (stress), melatonin production and alertness. The sensitivity of this specific photoreceptor also varies for different wavelengths of light. The curve of both the cones and the biological action curve can be seen in the figure below. When comparing these two curves it is clear that the biological sensitivity is different from the visual sensitivity.
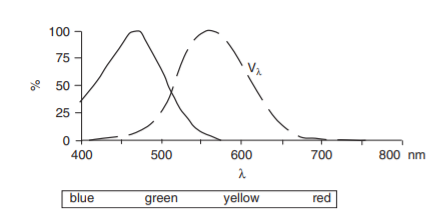
Now, what are the non-visual biological effects that are regulated by the third photoreceptor?
First of all, it sends signals to our biological clock. When the light comes up in the morning, cortisol levels increase and the body gets ready for the day. Gradually the cortisol levels decrease during the day, getting to a minimum at midnight. The sleep hormone melatonin decreases in the morning and increases the moment it gets dark, causing sleepiness. It is important that these rhythms are not disrupted. Therefore, it is important to maintain the right light levels during the day.
One of them is a research paper by Hoffman et al. (2008) which looks into the qualitative and quantitative aspects of workplace illumination. The study investigated the impact of different lighting conditions on sulphatoxymelatonin and subjective mood in an experimental office accommodation. Results of this study show an increase in alertness and speed of information processing when working under more blue light as compared to yellow light.
Previous Projects
Time Tracker
Time tracker is a software that is used to keep track of the way people spent their day. The user turns on the clock, gives the activity a name and at the end of the day both the user themself and their employer have a clear overview of what has been done. This program also has Google Calendar integration, which means that the names of their activities are taken from the Calendar, while the employee still has to time everything with the time tracker add-on.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Clear interface | Does not help the user manage their appointments |
| User can name activities themself | Cannot extract nature of activity (paid or unpaid) from Calendar |
| Employer gets an overview of what all of their employees do during their day | Timer must always be started manually |
Alarm Clock for Google Calendar
This Play store app is used to keep up with planning. It has Google Calendar integration, which it uses to determine when to give notifications. Specifically, it will alert the user of every item in their Google Calendar by giving an alarm similar to the alarm clock function of a smartphone. Most settings are customisable within the app.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Alarms are very difficult to miss because you have to manually turn them off | Only works with Google Calendar |
| Works with all calendars that are linked to your Google Calendar | Does not use a widget to get an overview of the day |
| Multiple settings increase quality of life for the user | Automatically turns on alarms for every agenda item (which is redundant and obnoxious) |
Pomofocus.io
Pomofocus is an app that works on desktop and mobile browser and helps you focus on any tasks you have to work on. This could for example be, studying, writing or coding. This app is inspired by the a time management method developed by Francesco Cirillo, called the Pomodoro Technique. This technique uses a timer to break down work in intervals of, traditionally 25 minutes, separated by short breaks. The app lets you add tasks to work on that day and asks for an estimation of pomodoros (1 pomodoro = 25 minutes of work), after which you can start the timer and get to focus on the task for 25 minutes. After these 25 minutes an alarm clock will ring and you get to take a small break for 5 minutes. This will then be repeated for the set amount of pomodoros.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Customizable timer with intervals that suit your preference | Having to add all tasks yourself |
| Audio notifications at the end of set timer period | Having to start each timer manually |
Amazon Echo Show
This is the first ever ‘smart alarm clock.’ The Amazon Echo functions as any regular alarm clock would, it shows the time, the date, it rings an alarm when you need to get up, and more. This alarm clock has an interface that is equal to that of a smartphone and it has Amazon’s Alexa installed. This means that it can keep your agenda/calendar, look up recipes, make a video call with your friends or family and many more.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Alexa voice assistant installed | Microphone is always on |
| Much more functionality than you average alarm clock (e.g. Netflix, video calls, smart home controls) | Emits a lot of blue light, which is not good for sleep |
| Customisable 'home screen' | Small |
Survey study
An online survey is made using google forms. After some demographical questions, students are asked about their experiences and preferences concerning working/studying from home, using Likert-scale, to get a general idea about their needs. Afterwards they are asked about their opinion on our general idea, to see whether their needs and our expectations are in line. These questions will help us making choices for the design in order to fulfill the needs of the end users.
The full survey can be found here: https://forms.gle/vjDVp6oWTFR5Vjkt6
Results
This survey was distributed among friends and acquaintances of the researchers. In total there were 85 respondents, of which 56 male and 29 female, with an age between 17 and 27 years. In the responses on participant's experiences and preferences concerning working/studying from home we found some important problems. On the question 'When I'm studying, I get easily distracted' 52.9% of the respondents agreed and 27.1% even strongly agreed. Additionally, almost 65% struggles staying motivated while studying and more than half of the participants struggle to make and keep up with a clear planning. However, 76.4% answered they like to set goals for themselves while studying. These answers show that the majority of the respondents have problems with studying/working from home and could use some help for these problems. In the following pie-charts the responses on the project-related design questions are displayed.
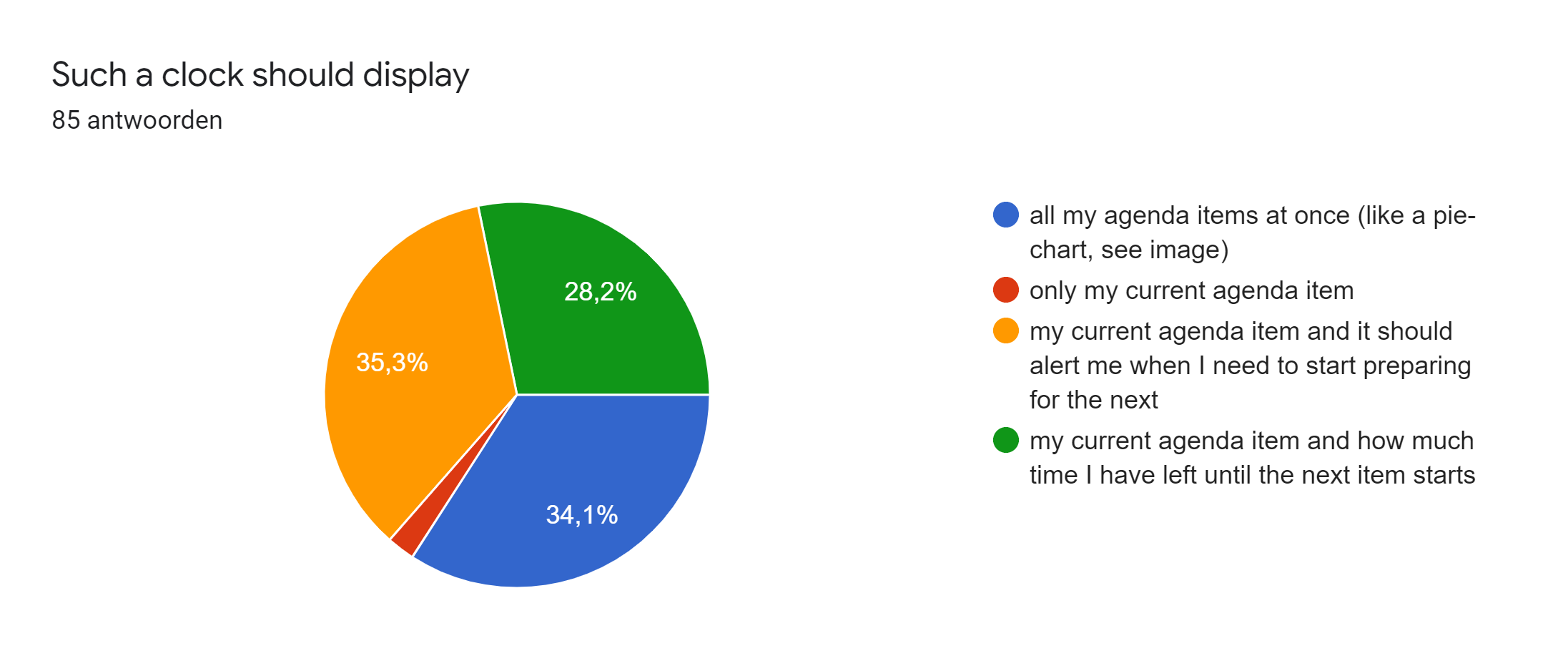
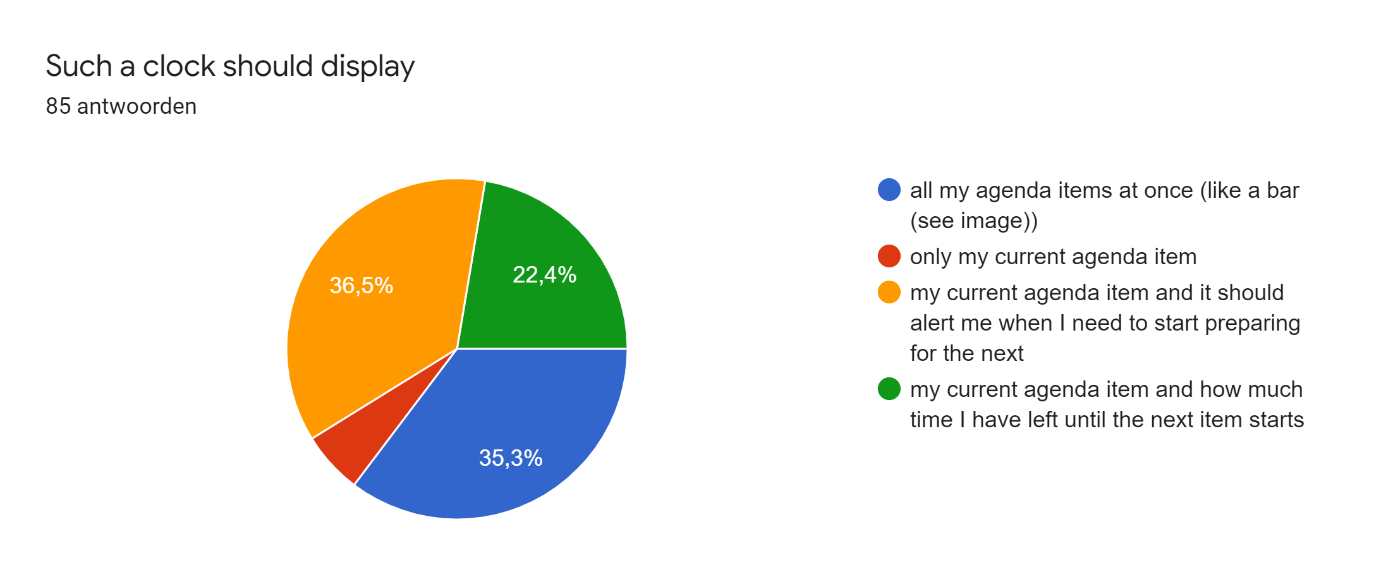
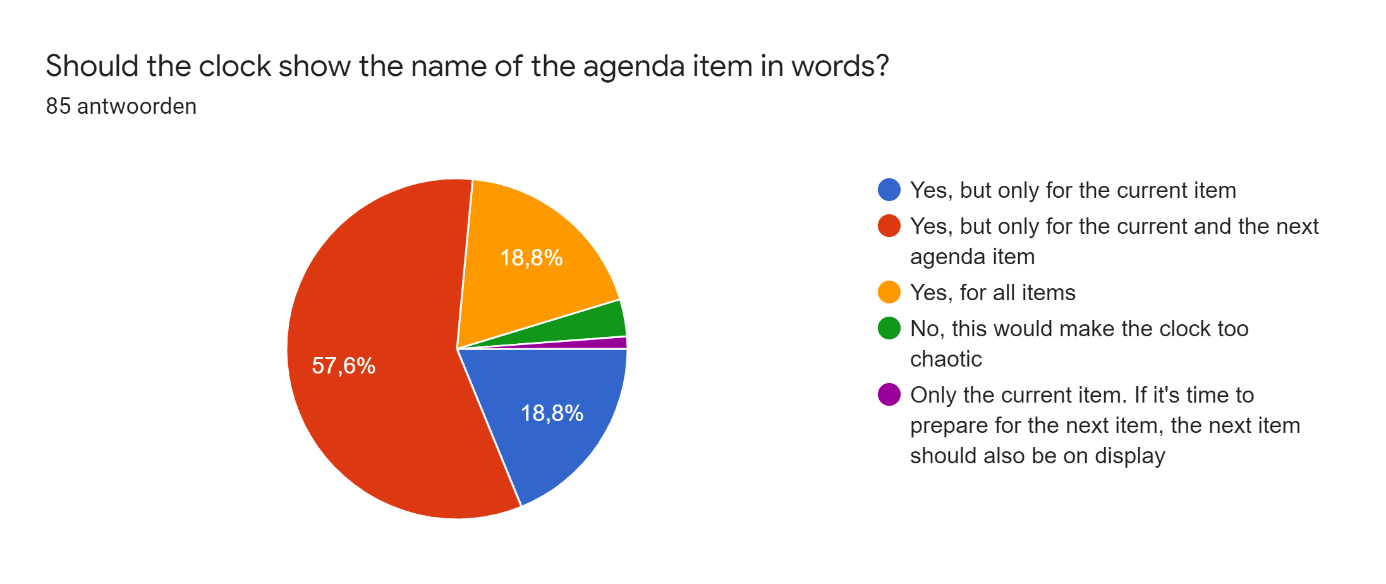
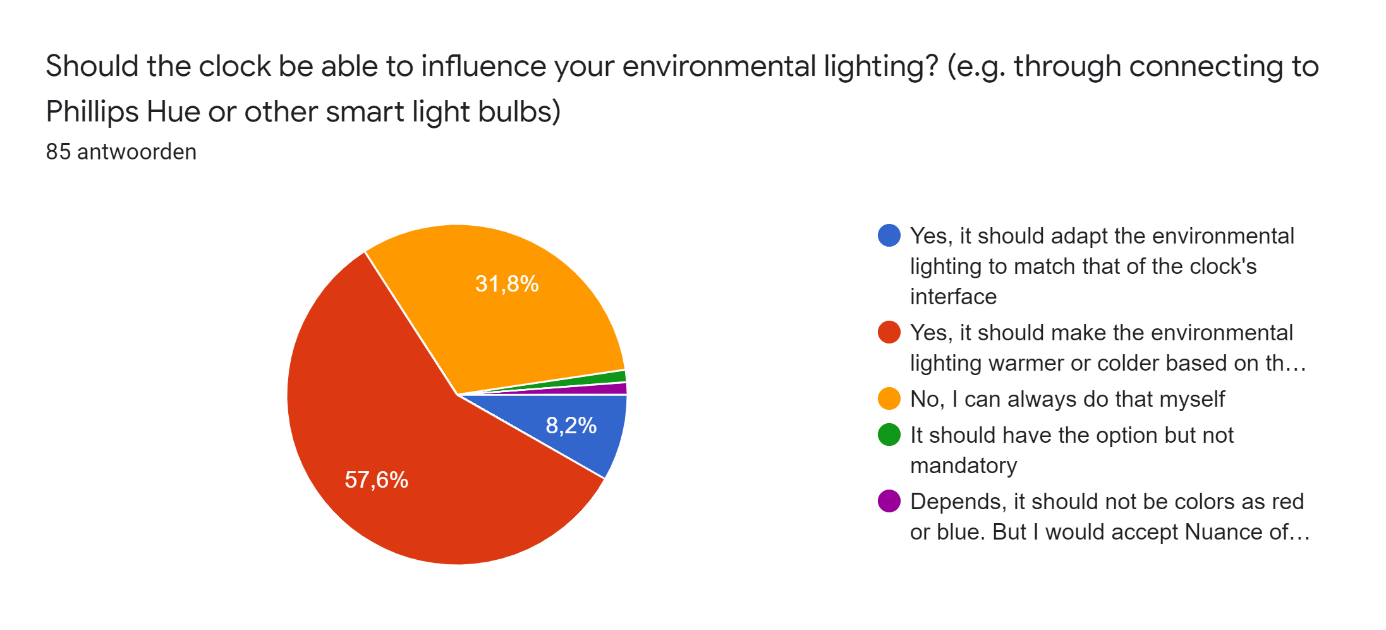
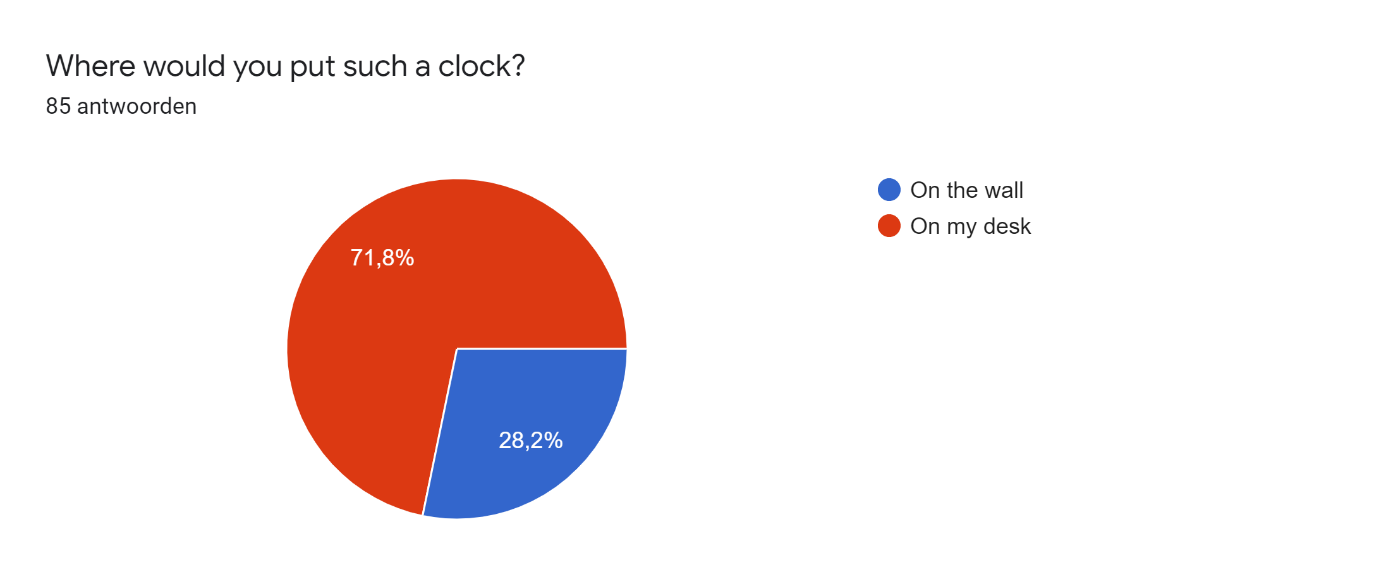
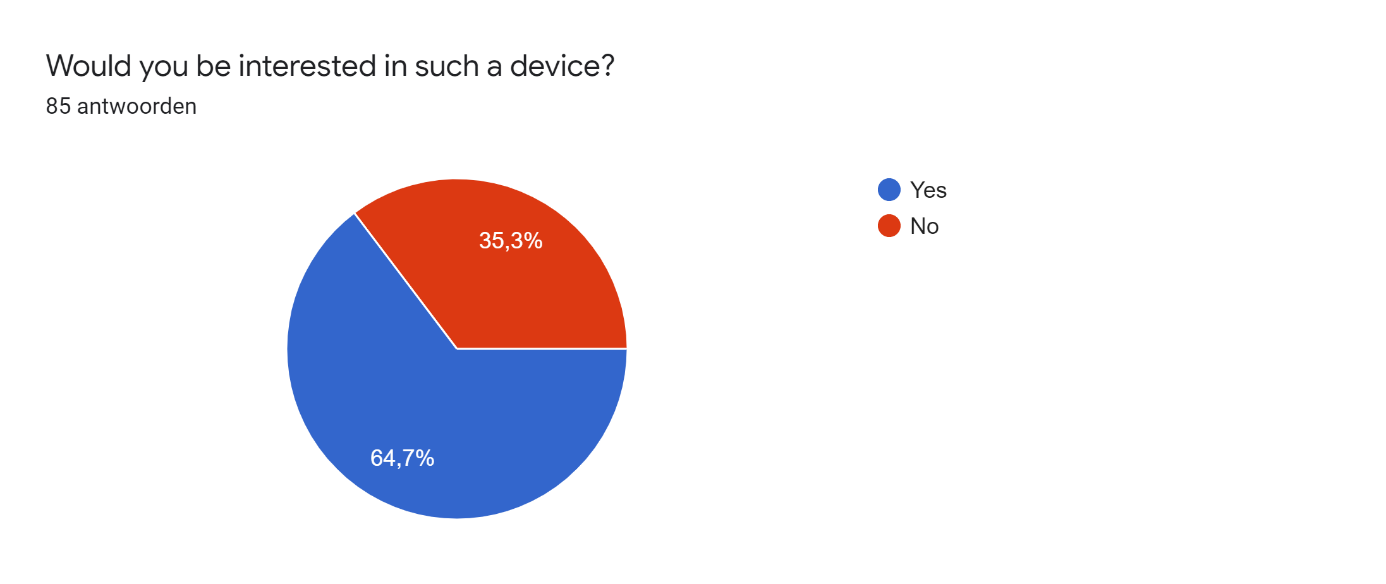
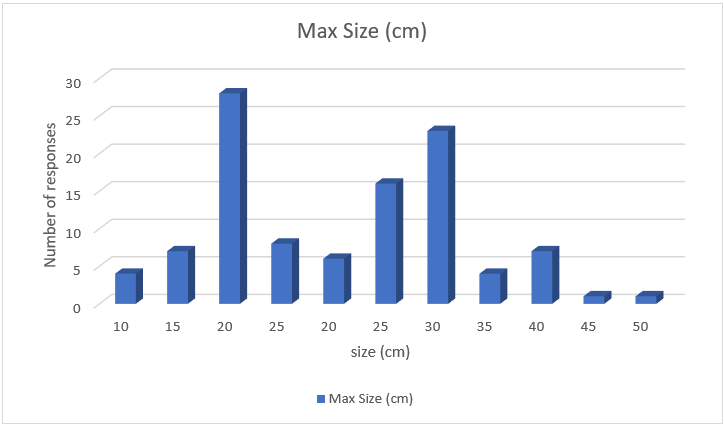
After answering the question on interest in the invention the people where asked to explain why or why not they would be willing to buy such a device in an open question. The responses of all people who answered they were interested in the device can be seen below.
| Responses of people willing to buy a study-clock |
|---|
| * I think it could really help me study better and more active |
| * It could help me with my studying and concentration levels. |
| * Als het me helpt om te plannen en zorgt voor motivatie en structuur |
| * Because I am currently unable to keep track of everything that is due, a clock like this would help. However, it could also cause a lot of stress and should maybe have a setting where you can turn off the agenda setting. |
| * It might be motivating to know for how long i’m supposed to be studying, and help to prevent procrastinating |
| * I think it can help me to keep up with my schedule |
| * Because I'm looking for tools to improve my productivity. Id give it a try |
| * Because in my house it is almost always too dark and maybe such a device can help me to be more concentrated during studying |
| * I think it would be of great use |
| * It seems handy to just have an ‘agenda’ like that on the wall so you can see what you have to do at any time. An agenda inside a phone or physical agenda requires more time and effort, and doesnt help saying when you got to shift to a next part of your planning. A countdown timer seems like a great feature. |
| * Could help me stay focused an plan better |
| * It seems a cool idea and it might help me stick to a planning |
| * It might give some overview i am currently lacking. I also tend to forget what I wanted to do. |
| * It seems beneficial and inventive. |
| * Because it helps me with studying |
| - It would be usefull to have an item which can help you keep up with your agenda without having to grab you phone and seeing all sorts of distractions |
| - Nice thing to have if cheap |
| - Helps me stay motivated |
| - It takes out some stress, I think, because it could alarm me when I should prepare for something I forgot |
| - To keep track of my plans for the day and to help me motivate myself to continue working |
| - Because it helps with your daily things |
| - It seems useful enough in a time where almost everyone struggles to find much motivation or structure in their life |
| - Simply for convenience, and short time interval planning enforces concentration since you'll feel like there is no time for procrastination. |
| - To help me manage my time |
| - It helps me motivate to study and reduces stress when it is a planning |
| - Could give me a clear view of what I should be doing at that time without always checking my agenda and helps stay focussed more easily. |
| - Improve planning |
| - Cause I struggle with planning and motivation, it is hard to keep in your study rhythm. |
| - Could be pretty handy |
| - It would help me to keep a nice overview of my tasks without being overwhelming and help me to remain focused on my tasks |
| - Maybe it would motivate me to keep up with my planning |
| - Its a clock and agenda in one device, and regulates your meetings/planning |
| - It seems like an easy way to keep a clear overview of your day, without having to constantly grab your agenda. I also think this device could help me with a planning if it tells my how much study time I have left |
| - Handy way to see calendar |
| - I like the idea and since the influences of light on concentration and vitality are promising it seems like a useful tool. |
| - I really struggle with the studying in current conditions and would welcome the opportunity of improvement. |
| - Since I am a student that needs a useful and handy way to look at my agenda without having to pull it up on my phone or computer. |
| - It can help me schedule my tasks |
| - Because I have some struggle with time management, sometimes |
| - It reminds the agenda better than a human brain |
| - It allows me to get an overview of my daily task in one glance |
| - It might help in terms of organizing and staying on track with your schedule |
| - As it is Innovative |
| - I want to try everything that possible helps my study |

Prototype
First sketch
For a first design idea, we came up with a 7-inch display that can be fitted on your desk. What the specifications are for this particular design will be determined in a later stadium. For now, we want to show what the design will look like.
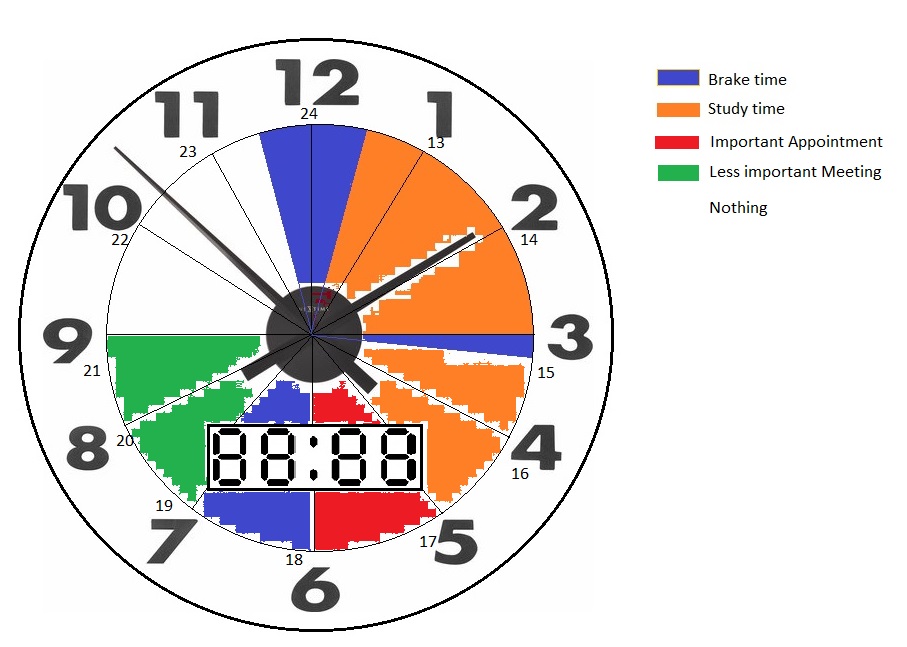
In this figure, you see the first design we had in mind. When you have sufficient free time at a specific moment the clock will schedule study time for you. It will also display your appointments so you have a quick overview of your day. When the clock passes the hour it will automatically update to 12 hours later, for instance from 01:00 to 13:00. This could be altered in the future and depends on what the user prefers. Since some users prefer a digital over an analog clock, the design will include both. This function can be switched on or off in the settings.
First Interface
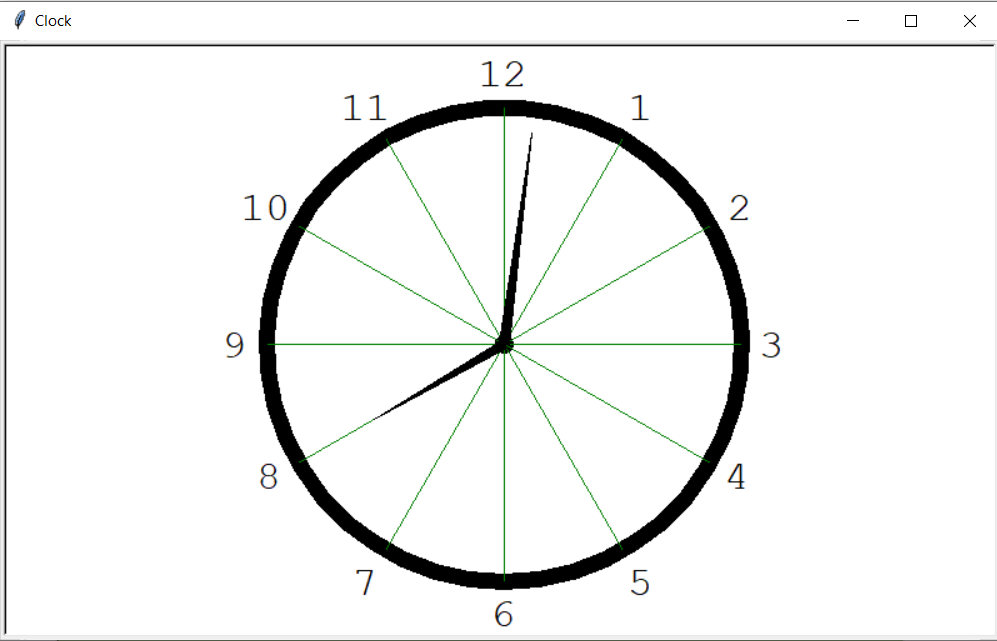
For the first prototype, we looked at different designs for clocks. Eventually, we landed upon the design which can be seen in Figure 2. This design has numbers that indicate the time and has clear clock hands.


For the adapted design we made all the background colors white, to give it a more professional appearance. Removed the second hand and moved the numbers outside the clock. The numbers have been moved outside the clock to make it easier to color in the pie slices on the clock without the numbers disappearing.
However, there have been some problems with getting it to work on the raspberry pi. At this moment it is unclear what the problem exactly is.
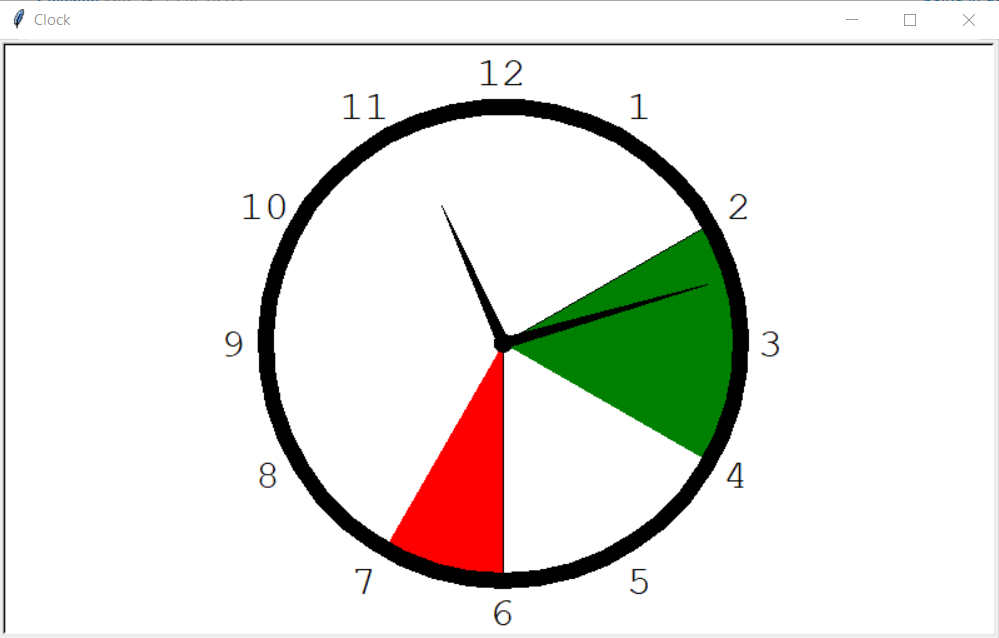
The most recent version of the clock can be seen in figure 4. This design has been updated to fit correctly on the raspberry pi's screen. For this, every aspect had to be moved by hand since all the components were positioned based on the pixels. In addition to this, I made a function that divides the clock into slices based on the input (time division) that you give. For now, it can only divide the slices into equal parts and it will start with dividing from the top(12).
The code has been completed that divides the clock into different slices. It has been done slightly differently compared to the method used in figure 3 because that method would not allow the slices to be colored in. The function that I wrote gives you the option to set the duration, an integer, the start time, a number on the clock, 1,2,3,4, etc. (btw. you can either fill in 12 or 0 if you want to start from the top both should work) and lastly, you can choose the color you want the slice to be. Finally, the border is updated again to hide any overlap of the colored slices with the border itself.

To add the title of each activity on the clock we decided to move the clock to the left of the screen and add the legenda to the right of it.
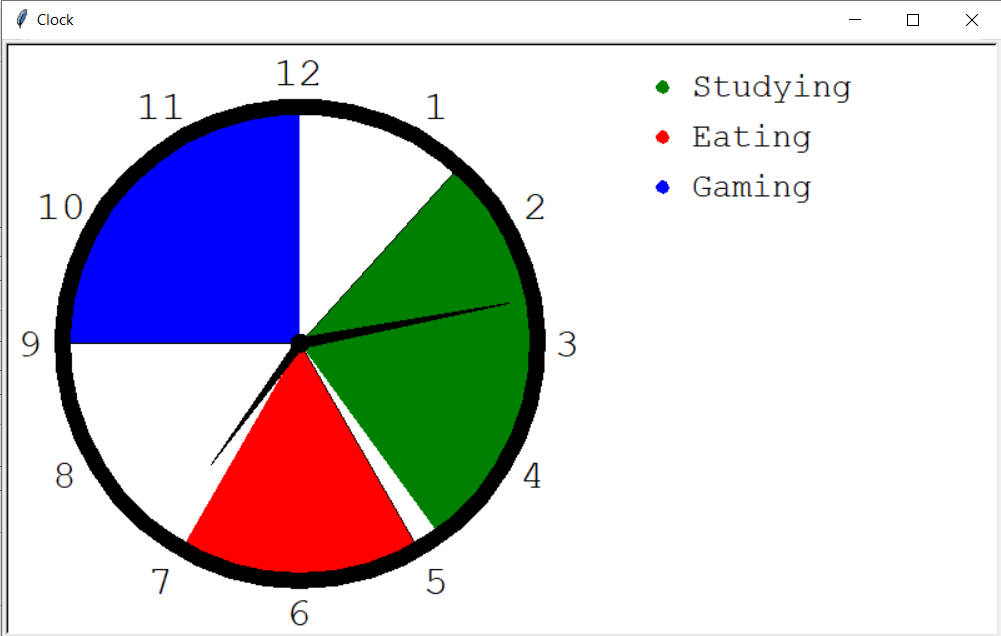
As can be seen in figure 7, the legenda has been added. If you add a new activity it will automatically add it to the clock and to the legenda. It is also possible to start activities at any time instead of only the numbers on the clock (1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12).
Retrieve agenda from Google Calendar
For the clock to work we needed to retrieve the Google Calendar from the internet. In order to do this, we found a program that is able to so, with a bit of finetuning. In order to run the code, a few packages needed to be installed. One of them is the api google client. This is done using pip install, but the code still did not work afterward. We tried for a few hours and different solutions, but nothing worked. We ultimately found one solution that worked, which was to install the modules in the same folder as the .py file. This made that one working file quite large and the correct file could not be found anymore. We then tried running the code on a laptop instead of on the pi. On the laptop it did work. After a while, we found out that the pip install function installed the module for Python 2.7 and we used Python 3.8. This was fixed by using pip3 install function which installs the modules for Python 3. Even though this looked promising, it still did not work. The modules were apparently installed for python 3.5 and not for 3.8, so that still gave errors. This last part was fixed easily by using the pip3.8 install function, which installed the modules for python 3.8. These modules worked and thus the code finally worked. Now we could configure a Google account to retrieve the agenda from. We created a test account, thetimemachine5000@gmail.com. Now we have a nice array of appointments in Python, which we can continue our work with.
Status of the prototype
We only needed to order two parts for this project, which are a Raspberry pi (3B+) and a (7-inch touch) screen to display the clock. First, we put the different parts together, then installed Raspbian on the pi so we could use it. The pi was running in no time and the screen worked perfectly. We thought that the touchscreen would require special drivers or programs but this was not the case. Now the base setup was done.
After this, we set up a remote connection with the use of VNC Viewer. This is done so every team member can work on the pi from home without having the pi at home. When the remote connection was set up. A virtual keyboard should be installed. This is needed for later use if you want to type anything using the touch screen.
The only problem now is that the screen does not stand on itself therefore brackets were made so the screen can actually stand on your desk. The angle on which it stands is not definite and could be changed in the future since the most convenient angle should be determined.
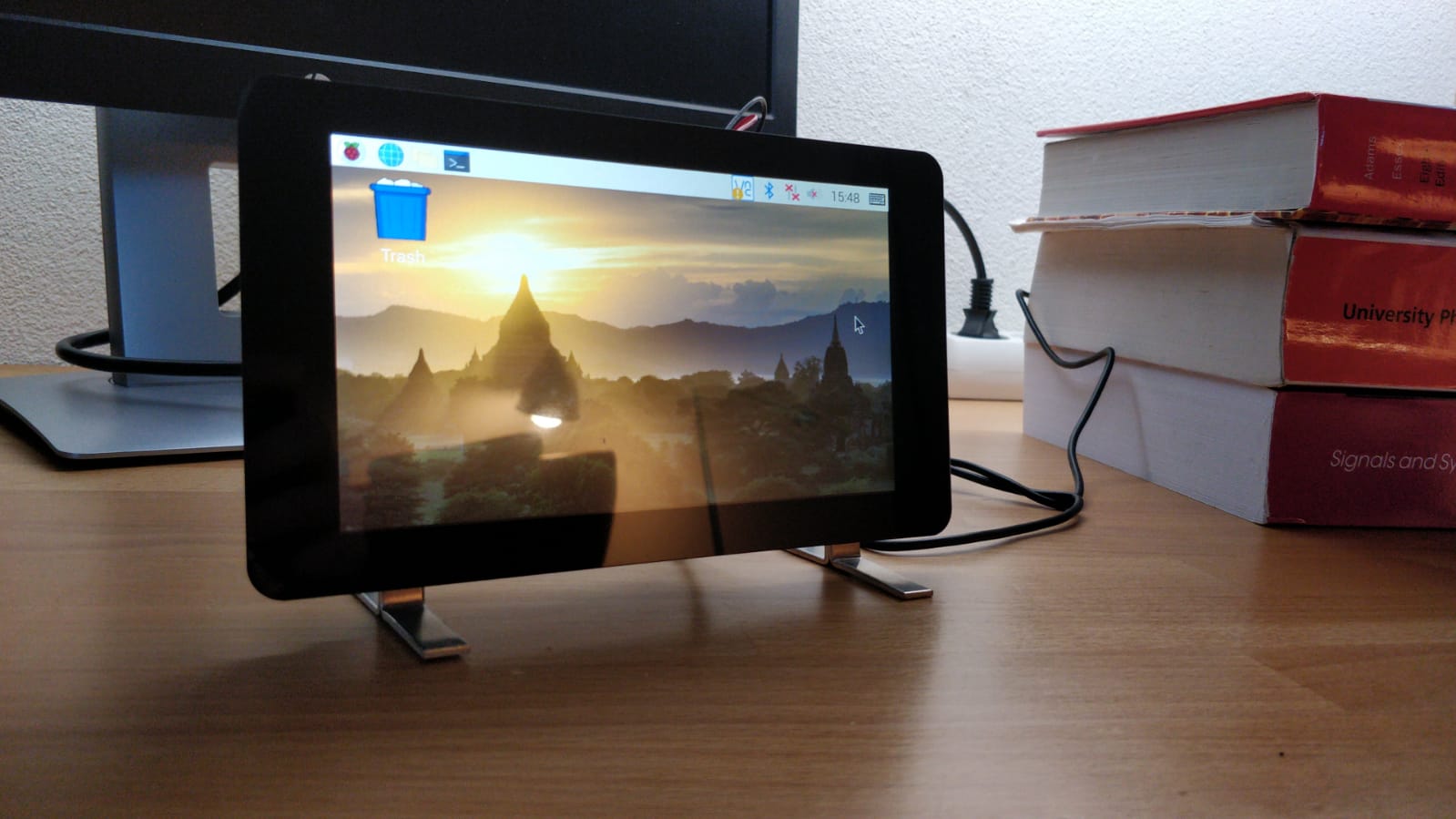
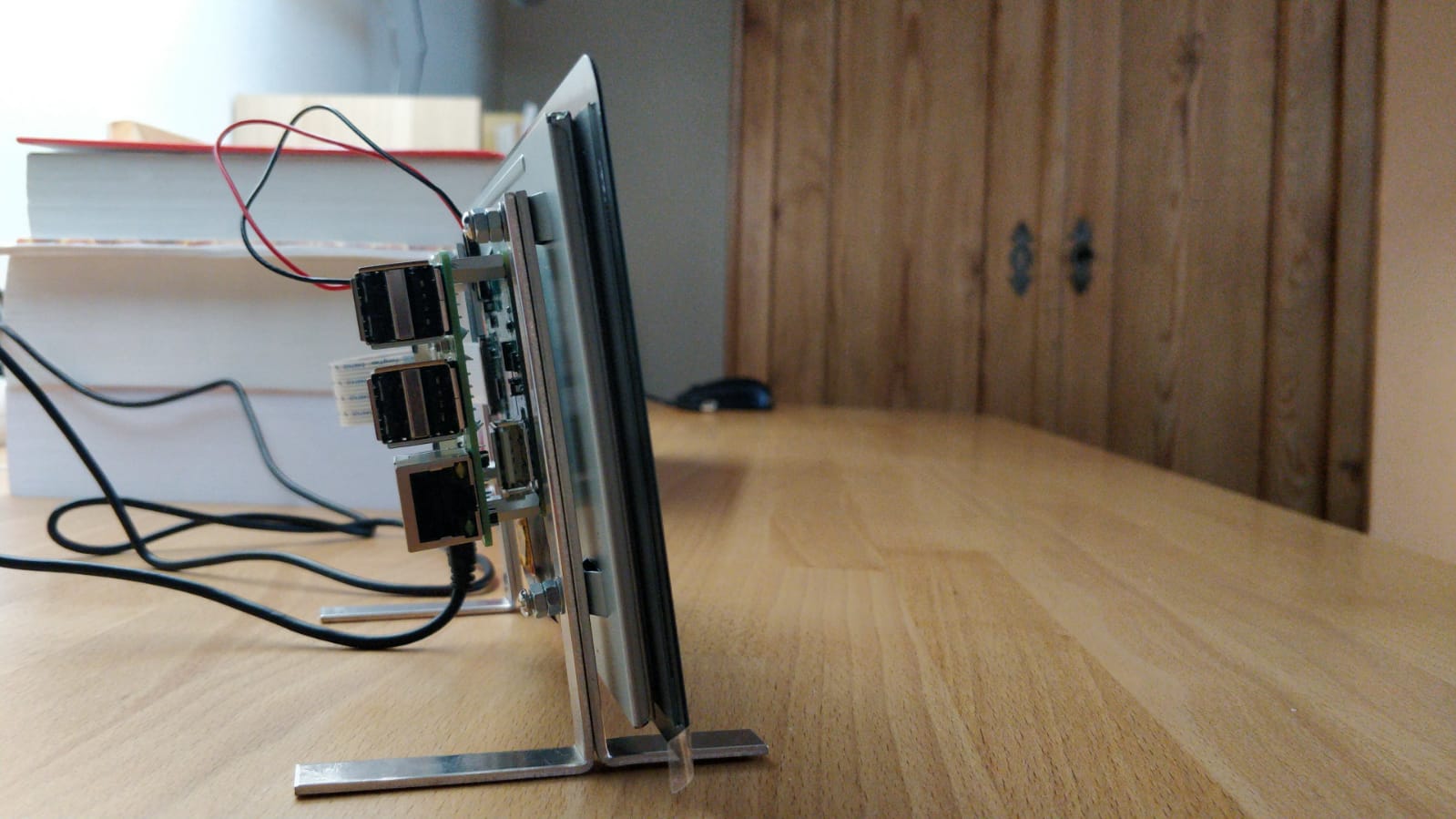
State of the Art
1. Bahsi et al
- This article reports a survey study that was held at the medical faculty of the Gaziantep University school of Medics. The survey considered 11 open-ended demographical questions and 29 Likert-scaled questions about the study environment, attention spans and motivation levels during study and study methods. The researchers used this data to find out how to increase the Grade Point Average (GPA). They concluded that is good to inform students about factors that can influence attention spans and motivation, identifying good learning strategies is beneficial for students and a good place to study is essential.[1]
2. Bunce et al
- In this study, the researchers investigated how much attention students of chemistry classes could maintain during their lectures. They noted at the start that there were two types of interactivity in a lecture. The first type were quizzes that involved the use of a clicker. This allowed students to answer multiple choice questions on the smartboard and the teacher could show how the students did on these questions immediately. A second way was by doing demonstrations of the phenomena they explained. The study, however, only focused on the first part.
This study asked students to report lapses of attention through their clickers. Before this study, the researchers expected that students would be able to stay focused for 10 – 20 minutes at a time, disregarding the first and last 5 minutes of lecture, where no student would be active. However, they found that students continuously alternate between being engaged or disengaged during a lecture for periods as short as 1-2 minutes. The suspicion that students are more engaged during interactive parts of the lecture was still confirmed. The researchers advise teachers to use interactive ways of teaching and include multiple student-centered pedagogies in their lessons.[2]
3. Saalmann et al
- In this article, attention is defined as a mechanism that is used to select relevant information from the environment. The authors state that this is a top-down process. There is evidence that the posterior parietal cortex (PPC) is a brain area that is heavily involved in attention. This area is part of a dorsal stream and thus mainly considers spatial information. These two statements are backed by studies with monkeys. In an experiment where monkeys had to respond to certain stimuli, the response times of the monkeys who had to respond to ‘spatial’ or ‘spatial and featural’ stimuli responded significantly faster compared to monkeys in a ‘neutral’ condition. These experiments tested the response of the medial temporal (MT response) lobes, but found that the MT response got feedback from the lateral intraparietal area (LIP). This was evidence for the top-down feedback.
From these experiments, they concluded that attention is gained quicker if stimuli were within the visual field and if a preceding stimulus was presented within the visual field as well.[3]
4. Buckley et al
- The gamification of the learning process shows to have a positive effect on the learning experience. While playing people will be more engaged with the material and be more productive. This helps the student to be more motivated to study. However, this effect is mainly visible in students that are naturally keen on learning / are willing to learn. Students who do not like to learn will have different results. However, the method looks promising.[4]
5. Seifert et al
- A student's motivation can be based on multiple variables, for instance: religion, parents, self-efficacy, self-worth and willingness to achieve certain goals among other things. A student’s motivation will have an influence on the way he or she will learn. It will have an effect on the behavior of things like the pursuit of mastery, failure avoidance, learned helplessness, and passive aggression. Students prefer their work to be meaningful and they like to have control and autonomy during their study. However in the end it all comes down to the personal emotions and beliefs of each student to really get a feel for their individual motivation.[5]
6. Ames et al
- This article shows the importance of a good working environment and what kind of effects this can have on the learning behavior and motivation of the students.[6]
7. Zheng et al
- Summary[7]
8. Iriarte et al
- This paper shows the benefit of using a VR “game” to perform tests on students with a disorder, like ADHD. Since it helps them to focus better on the different tasks than if they would have done them with paper and pencil. While the test in the paper is focused on a younger audience, 6 to 16 years, it could give an indication for (young) adults as well. There also seems to be a difference in performance when looking at the different genders. The main takeaway message is that VR can be used to help students with a (learning) disorder to focus better by removing distractors for instance.[8]
9. van Gog et al
- Eye tracking can be used as an input but also to measure the effect of various learning processes which make use of visual attention cues. Eye-tracking can provide more information on the split-attention effect, modality effect, redundancy effect, goal-specificity effect. The information gathered can be used to optimize learning strategies or layouts.[9]
10. Vandewalle et al
- According to this article wavelength, duration, and intensity of light exposure modulates brain responses. Immediately after light exposure, you can observe physiology, for example, heart rate, sleep propensity, alertness, and body temperature. The non-visual responses are maximally for blue light (480nm) while the spectral sensitivity of classical photoreceptors is maximal for green light (550nm).
- Also, cognition is affected by light in which we are interested the most. Because this includes attention, executive functions, and memory. These cognitive performances decline during the biological night and progressively improve during the biological day. The light could affect cognitive performance through its synchronizing/phase-shifting effects on the circadian clock. Also with light exposure, cognitive performance can be increased acutely.
- From the article, we can conclude that exposure to blue light gives the highest brain-responses ranging from a few seconds to about 20 minutes.[10]
11. Selvaraj et al
- According to this article students are very fond of using social media such as Facebook, Twitter, YouTube (based on the social media form 2013). The colleges are now pushing the classroom through social networks. Also, most of the information on social networks is fake or half-truth which could be a problem for students. Also, the students become addicted to social networks, which also means that their real-life friends become less in numbers while the digital friends become more and more. Too much of anything is good for nothing.[11]
12. Perrin et al
- From this article, we can conclude that social media usage has increased very much between 2005 and 2015. From which we can only imagine that the trend continued to 2021. So the usage of social media is enormous. Young adults between 18 and 29 years are most likely to use social media 90% of this group uses social media.[12]
13. Küller et al
- Humans have a circadian rhythm from approximately 24 hours, including being awake and asleep. This process is regulated by neural and hormonal processes. This process is being synchronized by the solar night and day. When far from the equator this internal clock can be disrupted by the short days and long nights (for half a year) which results in fatigue, sadness, and sleep problems. When you are indoors for a long time indoors during the day, windows are very important. Dark environments can have a negative effect on well-being and work capacity.
- All types of light within the visual range can have an influence on the biological clock. Bright is more effective than dim light and white or daylight more effective than colored light(possible with some exceptions).[13]
14. Ogbodo et al
- In this paper, good study habits are discussed. The most important conclusion from this paper is that to form effective study habits you should have good counseling. They help you with a proper study schedule. They also note that a study should be divided into three periods where the subjects should be divided into relative importance. Also, a good schedule is very important in maintaining a good study schedule. And one point they note is: Do you have enough light in your study place?[14]
15. Ezemenaka et al
- The author states that students have been more and more distracted since the introduction of the smartphone and that academic performance has become lower. They state, however, that there is no evidence linking the one to the other yet. The goal of their research is to find this link, if it exists. A survey-study was used to find out how many students used smartphones, what they used them for and whether they thought that it had an influence on their academic performance. The outcome of this study was that there was no significant relation detected between the use of a smartphone and academic performance.[15]
16. Raviv et al
- It has been speculated a lot of times that students’ concentration decreases by a lot after physical exercise. They should be highly aroused, which leads a decrease in their concentration. This study found three things. Firstly, there does not seem to be a difference in concentration between physical or science classes. Secondly, concentration levels are very low at the beginning of a (science) class and higher near the end, but not so much to say that there is a significant effect. Thirdly, the concentration levels of all students are generally higher in the morning than they are in the afternoon. This means that the study found that concentration levels depend more on time than on the nature of the class.[16]
References
Ames, C. (1992). Classrooms: Goals, structures, and student motivation. Journal of Educational Psychology, 84(3),
Bahsi, I., Çetkin, M., Orhan, M., Kervancioglu, P., Sayin, S., & Ayan, H. (2017). Evaluation of Attention - motivation level,
- studying environment and methods of medical faculty students. European Journal of Therapeutics, 1-7.
Buckley, P., & Doyle, E. (2014). Gamification and student motivation. Interactive Learning Environments, 24(6),
- 1162–1175. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2014.964263
Bunce, D. M., Flens, E. A., & Neiles, K. Y. (2010). How Long Can Students Pay Attention in Class? A Study of Student
- Attention Decline Using Clickers. Journal of Chemical Education, 1438-1443.
Ezemenaka, E. (2013). The usage and impact of Internet enabled phones on academic concentration among students of
- tertiary institutions: A study at the University of Ibadan, Nigeria. International Journal of Education and
- Development using Information and Communication Technology (IJEDICT), 162-173.
Gog, T. van, & Scheiter, K. (2010). Eye tracking as a tool to study and enhance multimedia learning. Learning and
- Instruction, 20(2), 95–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.learninstruc.2009.02.009
Iriarte, Y., Diaz-Orueta, U., Cueto, E., Irazustabarrena, P., Banterla, F., & Climent, G. (2012). AULA—Advanced Virtual
- Reality Tool for the Assessment of Attention. Journal of Attention Disorders, 20(6), 542–568.
- https://doi.org/10.1177/1087054712465335
Küller, R. (2002). The influence of light on circarhythms in humans. Journal of PHYSIOLOGICAL ANTHROPOLOGY and
- Applied Human Science, 21(2), 87-91. doi:10.2114/jpa.21.87
Ogbodo, R. (2010). Effective study habits in educational sector: Counselling implications. Edo Journal of Counselling,
- 3(2), 229-239. doi: https://doi.org/10.4314/ejc.v3i2.63610
Perrin, A. (2020, May 30). Social media usage: 2005-2015. Retrieved February 06, 2021,
Raviv, S., & Low, M. (1990). Influence of Physical Activity on Concentration among Junior High-School Students.
- Perceptual and Motor Skills, 67-74.
Saalmann, Y. B., Pigarev, I. N., & Vidyasagar, T. R. (2007). Neural Mechanisms of Visual Attention: How Top-Down
- Feedback Highlights Relevant Locations. Science, 1612-1615.
Seifert, T. (2004). Understanding student motivation. Educational Research, 46(2), 137–149.
Selvaraj, S. (2013, October). (Pdf) impact of social media on student's academic performance.
- Retrieved February 06, 2021, from https://www.researchgate.net/publication/288516435_IMPACT_OF_SOCIAL_MEDIA_ON_STUDENT%27S_ACADEMIC_PERFORMANCE
Vandewalle, G., Maquet, P., & Dijk, D. (2009). Light as a modulator of cognitive brain function. Trends in Cognitive
- Sciences, 13(10), 429-438. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2009.07.004
Zheng, S., Han, K., Rosson, M. B., & Carroll, J. M. (2016). The Role of Social Media in MOOCs. Proceedings of the Third
- (2016) ACM Conference on Learning @ Scale, Association for Computing Machinery. https://doi.org/10.1145/2876034.2876047
Automatic references test
- ↑ Bahsi, I., Çetkin, M., Orhan, M., Kervancioglu, P., Sayin, S., & Ayan, H. (2017). Evaluation of Attention - motivation level, studying environment and methods of medical faculty students. European Journal of Therapeutics, 1-7.
- ↑ Bunce, D. M., Flens, E. A., & Neiles, K. Y. (2010). How Long Can Students Pay Attention in Class? A Study of Student Attention Decline Using Clickers. Journal of Chemical Education, 1438-1443.
- ↑ Saalmann, Y. B., Pigarev, I. N., & Vidyasagar, T. R. (2007). Neural Mechanisms of Visual Attention: How Top-Down Feedback Highlights Relevant Locations. Science, 1612-1615.
- ↑ Buckley, P., & Doyle, E. (2014). Gamification and student motivation. Interactive Learning Environments, 24(6), 1162–1175. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2014.964263
- ↑ Seifert, T. (2004). Understanding student motivation. Educational Research, 46(2), 137–149. https://doi.org/10.1080/0013188042000222421
- ↑ Ames, C. (1992). Classrooms: Goals, structures, and student motivation. Journal of Educational Psychology, 84(3), 261–271. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.84.3.261
- ↑ Zheng, S., Han, K., Rosson, M. B., & Carroll, J. M. (2016). The Role of Social Media in MOOCs. Proceedings of the Third (2016) ACM Conference on Learning @ Scale, Association for Computing Machinery. https://doi.org/10.1145/2876034.2876047
- ↑ Iriarte, Y., Diaz-Orueta, U., Cueto, E., Irazustabarrena, P., Banterla, F., & Climent, G. (2012). AULA—Advanced Virtual Reality Tool for the Assessment of Attention. Journal of Attention Disorders, 20(6), 542–568. https://doi.org/10.1177/1087054712465335
- ↑ Gog, T. van, & Scheiter, K. (2010). Eye tracking as a tool to study and enhance multimedia learning. Learning and Instruction, 20(2), 95–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.learninstruc.2009.02.009
- ↑ Vandewalle, G., Maquet, P., & Dijk, D. (2009). Light as a modulator of cognitive brain function. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 13(10), 429-438. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2009.07.004
- ↑ Selvaraj, S. (2013, October). (Pdf) impact of social media on student's academic performance. Retrieved February 06, 2021, from https://www.researchgate.net/publication/288516435_IMPACT_OF_SOCIAL_MEDIA_ON_STUDENT%27S_ACADEMIC_PERFORMANCE
- ↑ Perrin, A. (2020, May 30). Social media usage: 2005-2015. Retrieved February 06, 2021, from https://www.pewresearch.org/internet/2015/10/08/social-networking-usage-2005-2015/
- ↑ Küller, R. (2002). The influence of light on circarhythms in humans. Journal of PHYSIOLOGICAL ANTHROPOLOGY and Applied Human Science, 21(2), 87-91. doi:10.2114/jpa.21.87
- ↑ Ogbodo, R. (2010). Effective study habits in educational sector: Counselling implications. Edo Journal of Counselling, 3(2), 229-239. doi: https://doi.org/10.4314/ejc.v3i2.63610
- ↑ Ezemenaka, E. (2013). The usage and impact of Internet enabled phones on academic concentration among students of tertiary institutions: A study at the University of Ibadan, Nigeria. International Journal of Education and Development using Information and Communication Technology (IJEDICT), 162-173.
- ↑ Raviv, S., & Low, M. (1990). Influence of Physical Activity on Concentration among Junior High-School Students. Perceptual and Motor Skills, 67-74.
Logbook
| Date | Name | Activity | Time spent (HH:MM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 01/02/21 | All | Whatsapp Discussion | 1:00 |
| 01/02/21 | All | Group Meeting | 1:30 |
| 01/02/21 | Jens | Approach, milestones and deliverables | 0:15 |
| 01/02/21 | Joep | Literature study for SotA | 2:30 |
| 03/02/21 | Jens | Literature study for SotA | 3:30 |
| 03/02/21 | Erick | Literature study for SotA | 2:30 |
| 03/02/21 | Ilana | Literature study for SotA | 2:00 |
| 03/02/21 | Wouter | Literature study for SotA | 1:00 |
| 03/02/21 | Wouter | Programming research | 2:00 |
| 04/02/21 | Erick | Updating wiki page | 0:30 |
| 04/02/21 | All | Group Meeting | 1:30 |
| 04/02/21 | Erick | Updating wiki page | 0:35 |
| 04/02/21 | Ilana | Problem statement | 0:45 |
| 04/02/21 | Ilana | Literature study for SotA | 2:00 |
| 04/02/21 | Joep | Literature study for SotA | 1:00 |
| 05/02/21 | Jens | Literature study for SotA | 1:30 |
| 05/02/21 | Joep | Literature study for SotA | 2:00 |
| 06/02/21 | Erick | Literature study for SotA | 2:00 |
| 06/02/21 | Ilana | Literature study for SotA | 2:00 |
| 06/02/21 | Joep | Literature study for SotA | 2:00 |
| 06/02/21 | Wouter | Literature study for SotA | 2:30 |
| 08/02/21 | Erick | Coming up with ideas | 0:30 |
| 17/02/21 | Erick | List of materials | 2:00 |
| 20/02/21 | Joep | Description | 1:00 |
| 23/02/21 | Wouter | Research materials | 1:00 |
| 24/02/21 | Erick,Joep,Wouter | Meeting for list of materials | 1:00 |
| 24/02/21 | Jens, Ilana | creating online survey | 2:30 |
| 24/02/21 | Wouter | Emailing for picking up parts over multiple days | 1:00 |
| 25/02/21 | All | Group Meeting | 1:00 |
| 25/02/21 | Joep | Sketching | 1:00 |
| 01/03/21 | All | Group Meeting | 1:00 |
| 01/02/21 | Joep | udating the wiki and write first sketch | 1:30 |
| 26/02/21 | Jens, Ilana | Finishing the survey | 1:00 |
| 01/03/20 - 04/03/21 | Jens | Quickly overlooking survey results and responses | 0:30 |
| 04/03/21 | Jens, Ilana | Converting and analysing survey data | 2:00 |
| 04/03/21 | Wouter,Joep | Setting up the raspberry pi | 4:00 |
| 04/03/21 | All | Group meeting | 0:45 |
| 04/03/21 | Joep | Updating the wiki | 1:00 |
| 05/03/21 | Jens, Ilana | Analyse survey and create graphs. Update wiki. | 3:00 |
| 05/03/21 | Joep | Setting up the virtual keyboard | 1:30 |
| 05/03/21 | Erick | Research into plotting different clocks with python | 1:30 |
| 06/03/21 | Erick | Adapting the clock and implementation | 1:00 |
| 06/03/21 | Joep | Making a holder for the screen of the rpi | 1:00 |
| 07/03/21 | Ilana | Updating the wiki | 1:00 |
| 07/03/21 | Joep | Writing Status of prototype and updating the planning | 1:00 |
| 07/03/21 | Wouter | Working on google calendar API | 2:00 |
| 08/03/21 | All | Group meeting | 1:15 |
| 08/03/21 | Jens | Update Milestones in wiki | 0:30 |
| 08/03/21 | Erick, Joep | Setting up updated version of python and changing settings on raspberry pi | 1:00 |
| 08/03/21 | Erick | Updated the clock to look good on the raspberry pi and functional | 2:30 |
| 09/03/21 | Wouter | Working on google calendar API | 1:00 |
| 10/03/21 | Joep | work on the agenda retrieval code | 2:30 |
| 10/03/21 | Jens | Update references section of wiki | 0:30 |
| 10/03/21 | Jens | Research other similar projects | 3:00 |
| 10/03/21 | Wouter | Begin of redoing technical requirements | 0:30 |
| 10/30/21 | Ilana | Research on similar projects | 2:00 |
| 11/03/21 | Wouter, Joep | working on agenda retrieval code | 2:00 |
| 11/03/21 | All | Group Meeting | 1:00 |
| 11/03/21 | Erick | Move clock and add legenda | 1:30 |
| 11/03/21 | Jens | Research on references and citations on wiki | 0:45 |
| 11/03/21 | Wouter | Research agenda retrieval code | 0:30 |
| 12/03/21 | Wouter, Joep | finish agenda retrieval code | 1:30 |
| 14/03/21 | Ilana | USE analysis + effect of lighting research + wiki update | 2:30 |
| 14/03/21 | Jens | Rewrite wiki, update figure captions, references, etc. | 2:00 |
| 14/03/21 | Wouter | Redone technical requirements and work on wiki | 1:30 |