Embedded Motion Control 2019 Group 2: Difference between revisions
| Line 387: | Line 387: | ||
To avoid obstacles a potential field algorithm is implemented in the drive controller. This algorithm uses two types of forces which are added and used to find a free direction. The first force is an attractive force towards the desired location. Secondly all the objects (walls, static and dynamic objects) that are close to the robot have a repellent force away from them. The closer the object, the larger the repellent force. All the forces are added together and the resulting direction vector is determined. This new direction is used as a desired direction at that time instance. In the gif shown here the repellent forces are visualised and it can be seen that Pico uses this to drive around an object in its path. | To avoid obstacles a potential field algorithm is implemented in the drive controller. This algorithm uses two types of forces which are added and used to find a free direction. The first force is an attractive force towards the desired location. Secondly all the objects (walls, static and dynamic objects) that are close to the robot have a repellent force away from them. The closer the object, the larger the repellent force. All the forces are added together and the resulting direction vector is determined. This new direction is used as a desired direction at that time instance. In the gif shown here the repellent forces are visualised and it can be seen that Pico uses this to drive around an object in its path. | ||
[[File:Close_prx.gif|thumb|upright=4|center| | [[File:Close_prx.gif|thumb|upright=4|center|800px|Visualisation of the Pico driving around an object with the potential field algorithm.]] | ||
Revision as of 22:44, 17 June 2019
Group members
- 1. Bob Clephas | 1271431
- 2. Tom van de laar | 1265938
- 3. Job Meijer | 1268155
- 4. Marcel van Wensveen | 1253085
- 5. Anish Kumar Govada | 1348701
Intro
This project is a part of the Embedded Motion Control course in which a particular software architecture and behaviour is designed for the PICO robot to execute tasks autonomously keeping in mind the various constraints. It is comprised of the escape room challenge and the hospital challenge. The goal of the escape room challenge is to exit the room from any given initial position of the PICO inside the room in minimum time. The goal of the hospital challenge is to visit an unknown number of cabinets in a specified order placed in different rooms in minimum time. A very generic software structure was implemented so as to tackle both the challenges. The design requirements, specifications, software architecture, program flow and the results of the two challenges are shown in the following sections.
Design document
To complete the two assignments for the course “Embedded motion control” specific software must be written. In this design document the global architecture of the software is explained, and the given constraints and hardware is listed. This document is a first draft and will be updated during the project. The first version can be found here.
Requirements and specifications
The requirements and related specifications are listed in the following table. The listed specifications are required for the final assignment and the escape room challenge.
Components and functions
The components and their functions are split in software components and hardware components.
Software components
Hardware components and their general functionalities
Environment
The environments for both assignments will meet the following specifications:
Escape room challenge
- Rectangular room, unknown dimensions. One opening with a corridor.
- Starting point and orientation is random, but equal for all groups.
- Opening will be perpendicular to the room.
- Far end of the corridor will be open.
- Wall will not be perfectly straight, walls of the corridor will not be perfectly parallel.
- Finish line is at least 3 meters in the corridor, walls of the corridor will be a little bit longer.
Final challenge
- Walls will be perpendicular to each other
- Global map is provided before competition
- Location of cabinets is provided in global map
- Static elements, not showed in global map, will be in the area
- Dynamic (moving) elements will be in the area
- Objects can have a random orientation
- Multiple rooms with doors
- Doors are time-varying opening an closing
- list of "To-be-visited" cabinets is provided just before competition
General software architecture and interface
TODO: Anish
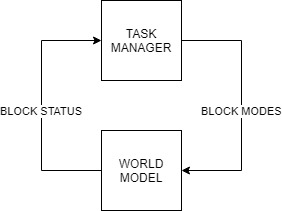
The overall software is split in several building blocks such as the Task manager, World model, Perceptor, Path planner and Drive controller as shown in the figure below :
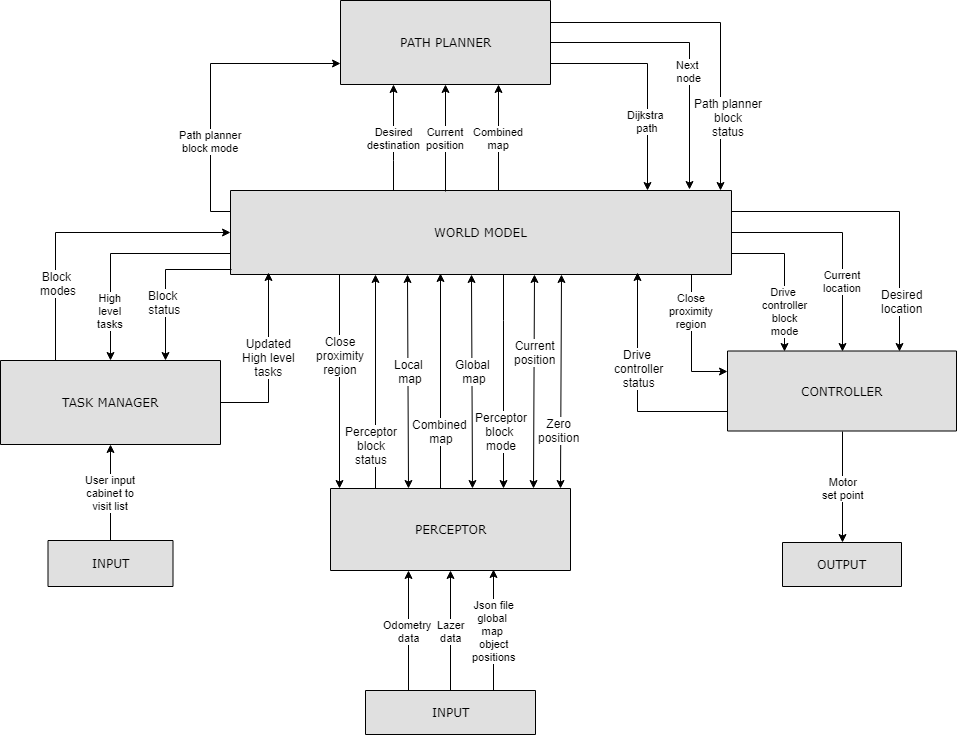
Data flow
| Block | Data | Transition from | Transition to | Block | Data | Transition from | Transition to |
| Perceptor | Lazer range finder data | LRF Sensor input | Perceptor | Path planner | Desired destination | World model | Path planner |
| Odometry data | ODO Sensor input | Perceptor | Current position | World model | Path planner | ||
| Json file - Global Map and location of cabinets | File read | Perceptor | Combined map | World model | Path planner | ||
| Perceptor block modes | World model | Perceptor | Path planner block mode | World model | Path planner | ||
| Local map | World model | Perceptor | Path planner block status | Path planner | World model | ||
| Global map | World model | Perceptor | Next node | Path planner | World model | ||
| Current position | World model | Perceptor | Path from Dijkstra algorithm | Path planner | World model | ||
| Zero position | World model | Perceptor | Drive controller | Desired location/Next node | World model | Drive controller | |
| Global map | Perceptor | World model | Current location | World model | Drive controller | ||
| Perceptor block status | Perceptor | World model | Close proximity region | World model | Drive controller | ||
| Local map | Perceptor | World model | Drive controller block mode | World model | Drive controller | ||
| Combined map | Perceptor | World model | Drive controller block status | Drive controller | World model | ||
| Zero position | Perceptor | World model | Motor set point | Drive controller | Output | ||
| Current position | Perceptor | World model | |||||
| Close proximity region | Perceptor | World model | |||||
| Task manager | User input cabinet list | User | Task manager | ||||
| Block status | World model | Task manager | |||||
| High level tasks | World model | Task manager | |||||
| Block modes | Task manager | World model | |||||
| Updated high level tasks | Task manager | World model |
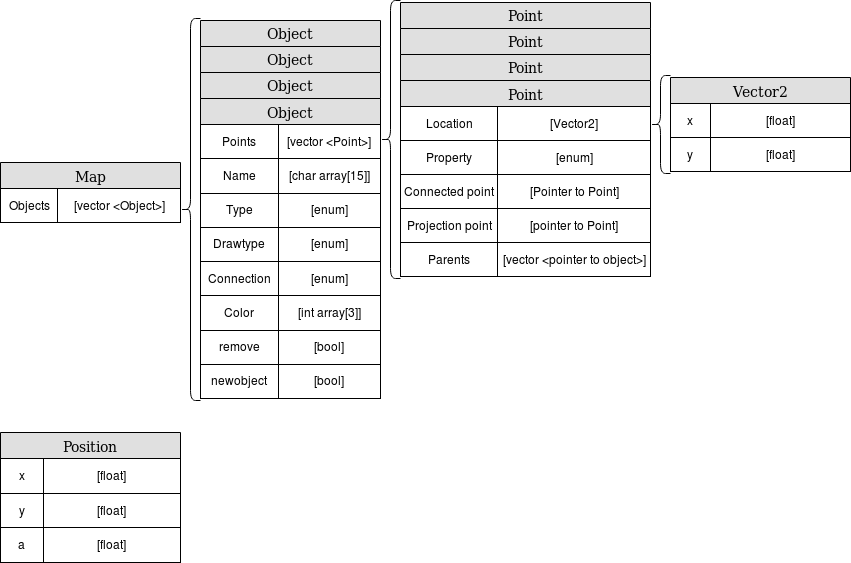
World model
The world model is the block which stores all the data that needs to be transferred between the different blocks. It acts as a medium of communication between the various blocks such as perception, task manager, path planner and drive controller. It contains all the get and set functions of the various blocks to perform respective tasks.
As seen in the data flow table, the various input data and output data that are sent in and out of the world model are accessed using get and set functions.
Input
- Updated high level tasks - Task manager
- Block modes - Task manager
- Block statuses - All blocks
- Close proximity region - Perceptor
- Current position - Perceptor
- Zero position - Perceptor
- Global map - Perceptor
- Local map - Perceptor
- Combined map - Perceptor
- Next node - Path planner
- Path from Dijkstra algorithm - Path planner
Output
- High level tasks - Task manager
- Block statuses - Task manager
- Block modes - Drive controller, Perceptor and Path planner
- Close proximity region - Drive controller
- Current location - Drive controller, Path planner
- Desired location/ next node - Drive controller
- Current position - Perceptor
- Zero position - Perceptor
- Global map - Perceptor
- Local map - Perceptor
- Combined map - Path Planner
- Desired destination/ next cabinet node - Path planner
Overall program flow
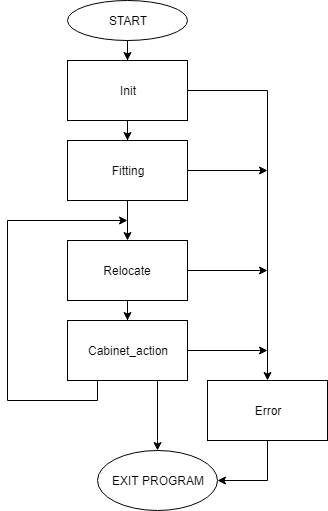
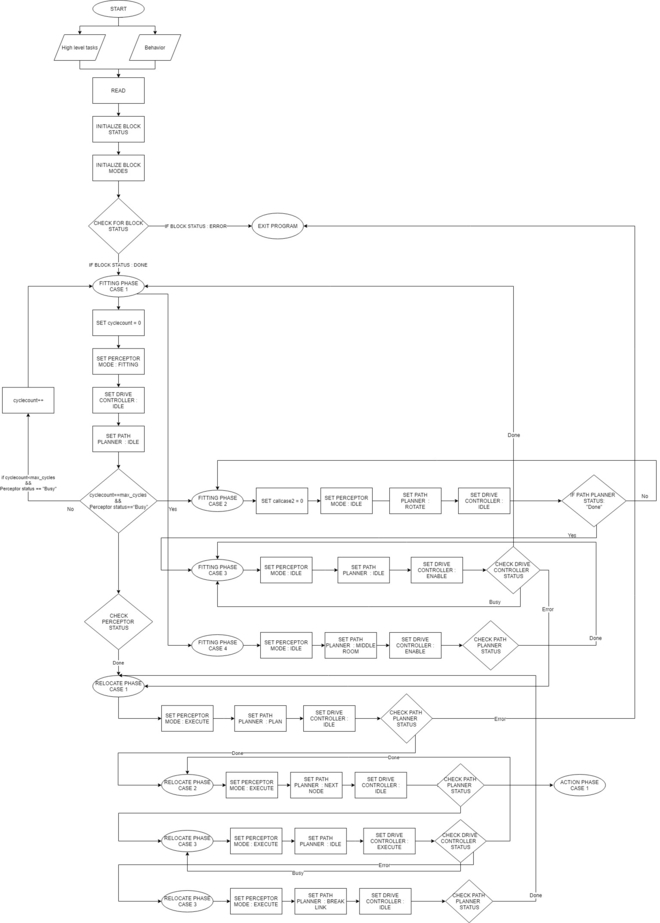
The overall program is divided in 5 phases. During a phase all actions lead to one specific goal. When the goal is reached, a transition is made towards a new phase. Within a phase it is possible to have multiple cases. Each iteration of the program it is evaluated to what phase and case the program should move. It is also possible to stay in a specific phase and case for longer than one program iteration, however, in most situations this is not needed. Every case has a specific block mode for each software block and the transitions between cases and phases is based on the blockstatusses of all blocks.
Phases flowchart
In figure 2 the overall structure with the phases is shown. The different phases have the following goals:
Init phase
The init phase focuses on the initialisation of the program. This phase has one case and the flowchart of this phase is shown in figure 3.
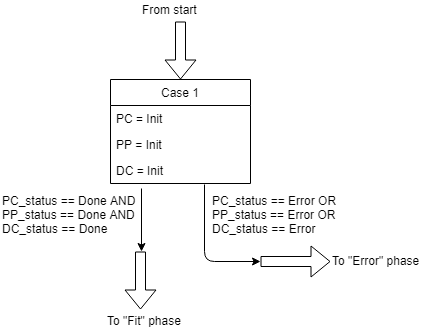
During the init phase the following actions are executed:
Fitting phase
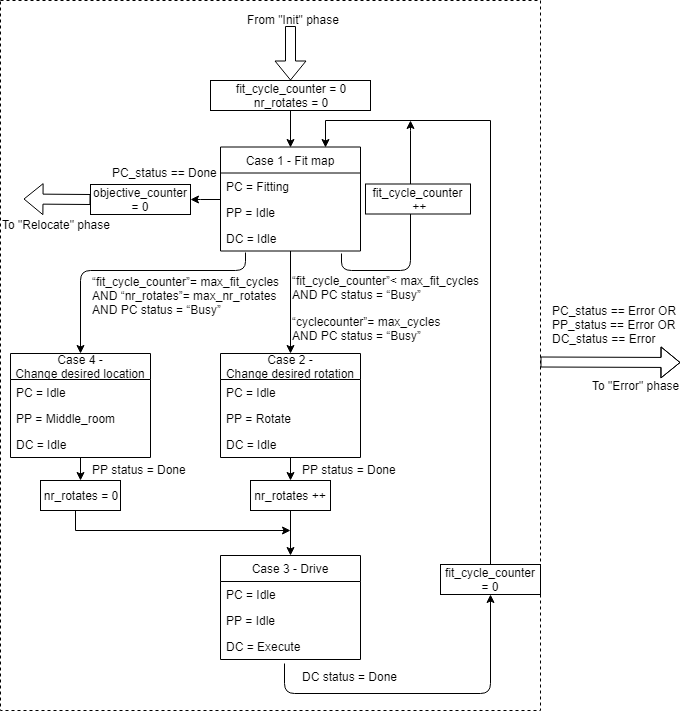
In the fitting phase the goal is to locate the robot relative to the given global map. This fitting is done in the perceptor by checking the laserdata, creating a local map and try to find a best fit between the local and global map. If this fit is successful the location of the robot is known and all new laser information can be used to update the location of the robot.
Relocate phase
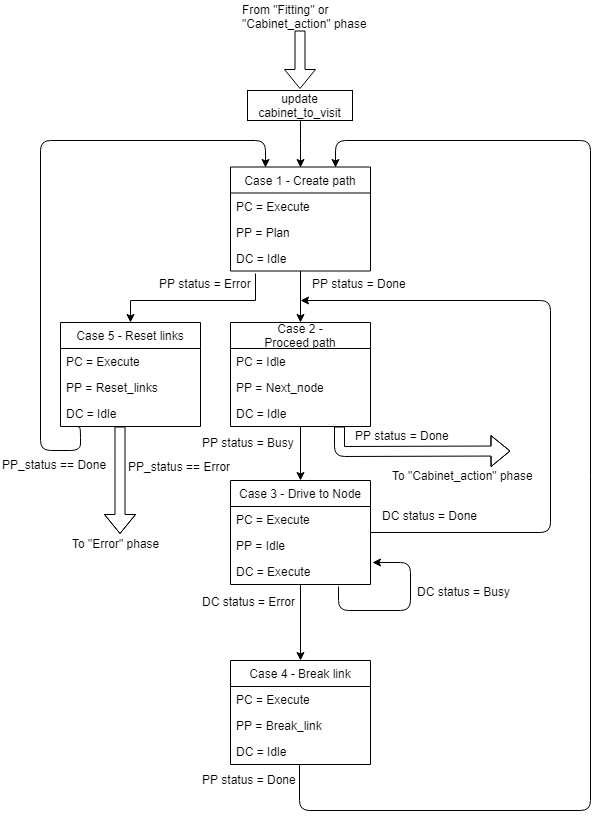
In the "Relocate" phase the goal is to drive the robot to the next cabinet. The driving involves the path planning, actuating the drivetrain of the robot and avoiding obstacles. During the driving the perceptor keeps updating the world map and keeps adding objects to the map is necessary. Also the fitting will be improved once more laserdata is obtained.
In figure 5 the overall flowchart is shown of the relocate phase. This phase contains the following cases:
Cabinet_action phase

During the cabinet action phase the robot can interact with the cabinet.
The required interaction is specified in the competition and is consisting of taking a snapshot of the current laserdata and play a sound.
The flowchart of this phase is shown in figure 6.
Error phase
The error phase is only visited if something unrecoverably went wrong in the program, e.g. a required file is missing. In this phase the output of the drive motors is set to zero and the error is displayed to the user. Then the program is terminated
Software blocks
Task manager
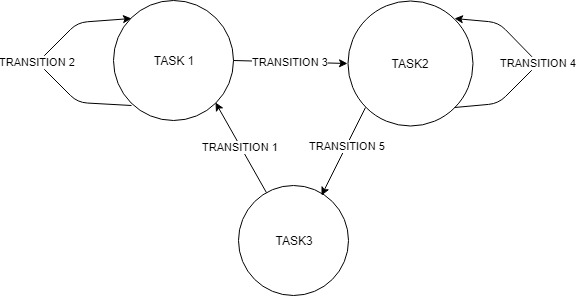
The task manager functions as a finite state machine which switches between different tasks/states. It focuses mainly on the behavior of the whole program rather than the execution. It determines the next operation phase and case based on the current phase, current case, current block statuses and counters in which the corresponding block modes of the perceptor, path planner and drive controller are set for the upcoming execution. It communicates with the other blocks via the World model.
Since the "Escape room challenge" and the "Hospital competition" require a complete different approach in terms of cooperation between the blocks, the task planner is completely rewritten for both challenges.
ESCAPE ROOM CHALLENGE
BASIC BLOCK DIAGRAM :
INITIALIZATION:
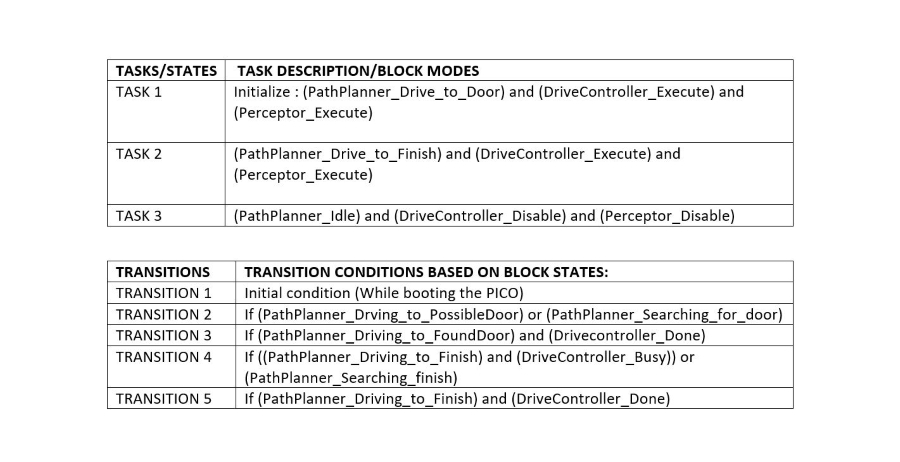
The path planner is given a command “Drive_to_door” while the drive controller and the preceptor are given a command “Execute” as a part of the initialization process.
EXECUTION:
The high-level tasks “Drive_to_door”, “Drive_to_exit”, “Execute”, “Idle” and “Disable” were given to appropriate blocks as shown below:
KEY:
HOSPITAL ROOM CHALLENGE
FLOW CHART :
The function description can be found here : File:TASK MANAGERfin.pdf
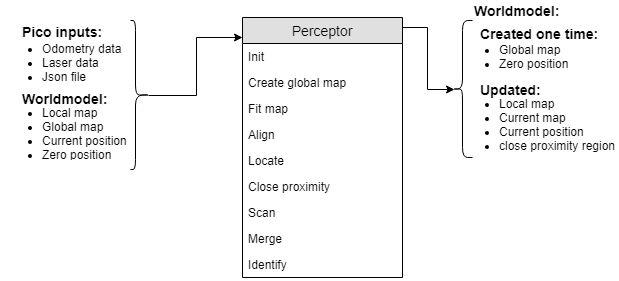
Perceptor
The perceptor receives all of the incoming data from the pico robot and converts the data to useful data for the worldmodel. The incoming data exists of odometry data obtained by the wheel encoders of the pico robot. The laserdata obtained by the laser scanners. A Json file containing the global map and location of the cabinets, this file is provided a week before the hospital challenge. Moreover, the output of the perceptor to the world model consists of the global map, a local map, a combined map, the current/zero position and a close proximity region. The incoming data is handled within the perceptor by the following functions. A detailed description on what each function does in the preceptor and more information about the data flow can be found here.
The inputs and outputs of the perceptor are shown in the following figure:
The data used in the perceptor:
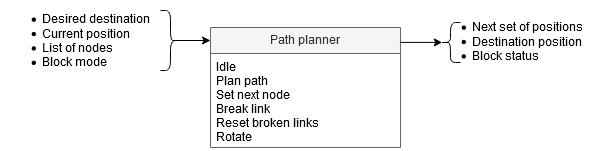
Path planner
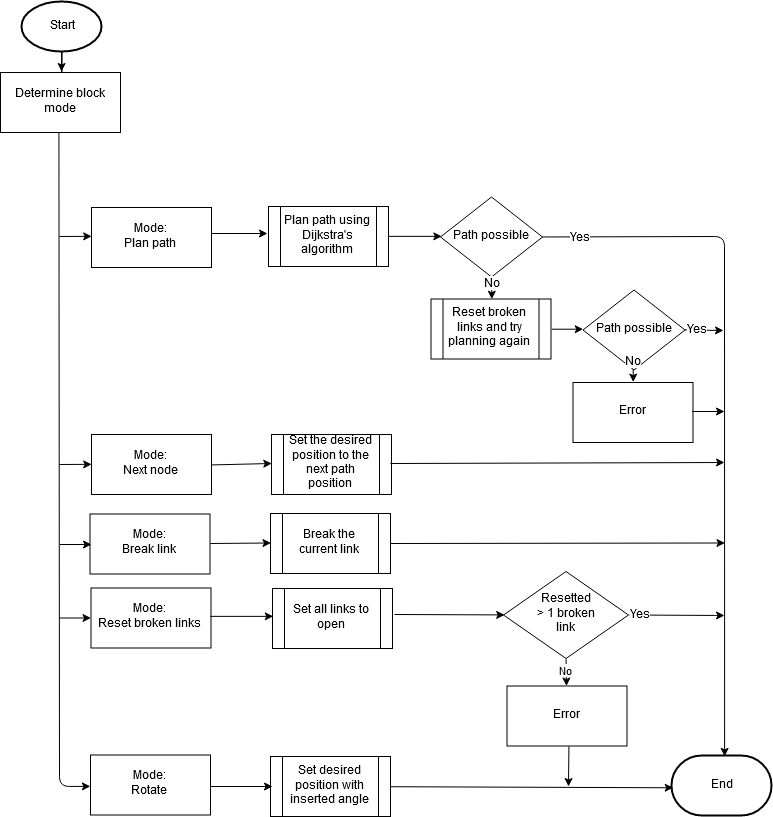
The path planner determines the path for the PICO robot based on the list of available nodes and the links between these nodes. For planning the optimal path, Dijkstra's algorithm is used and the distance between the nodes is used as cost. The choice for Dijkstra is based on it being sufficient for this application, the extra complexity of the Astar algorithm was not needed. The planned path is a set of positions that the PICO robot is going to drive towards, this set is called the ‘next set of positions’. This next set of positions is saved in the world model and used by the task manager to send destination points to the drive controller.
If the path planner is idle, it is waiting for the task manager to start planning. Once the path planner is planning the path from the position of the PICO robot towards a given destination.
The inputs, functions and outputs of the path planner are as follows:
A detailed description can be found here.
Drive controller
The drive controller software block ensures that the pico robot drives to the desired location. it receives the current and desired location and automatically determines the shortest path towards the desired location. While driving it also avoids small obstacles on it's path. If the object is too large, or the path is blocked by a door for example, the drive controller signals this to the path planner which calculated an alternative path.
To avoid obstacles a potential field algorithm is implemented in the drive controller. This algorithm uses two types of forces which are added and used to find a free direction. The first force is an attractive force towards the desired location. Secondly all the objects (walls, static and dynamic objects) that are close to the robot have a repellent force away from them. The closer the object, the larger the repellent force. All the forces are added together and the resulting direction vector is determined. This new direction is used as a desired direction at that time instance. In the gif shown here the repellent forces are visualised and it can be seen that Pico uses this to drive around an object in its path.
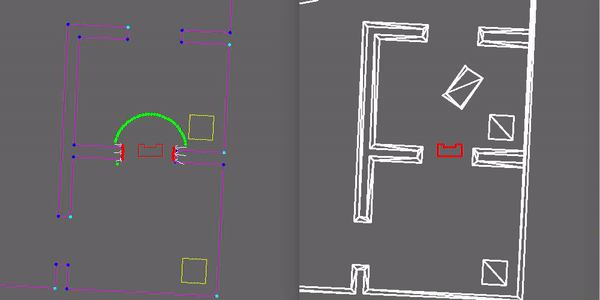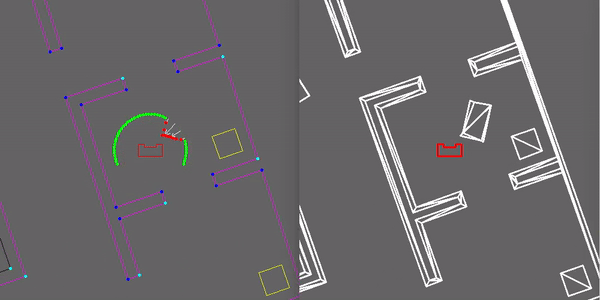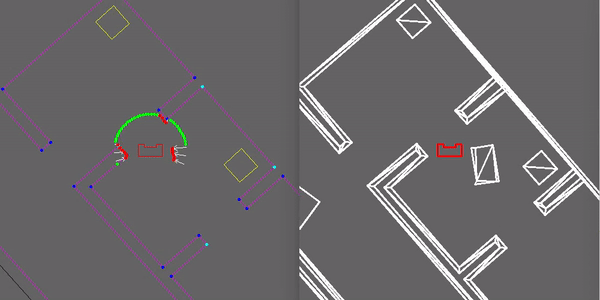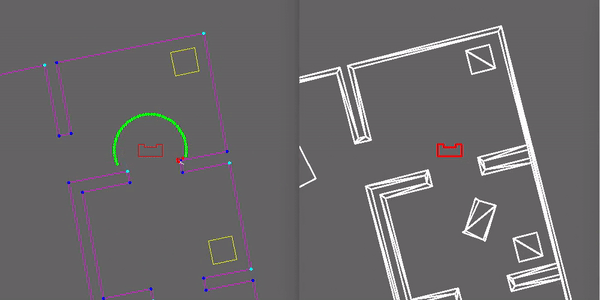
More details of the Drive Controller, including function descriptions can be found in the Drive Controller functionality description document found here.
Visualisation
To make it easy to debug the program, some time is invested in making a visualization class. This class makes it easy to visualize the defined objects and uses the properties of those objects to do so. Next to that there is a function to visualize a whole map (which is a vector of objects) with one command. The visualization makes use of the opencv library and a few of its basic functionalities such as imshow, newcanvas, Point2d, circle, line and putText.
Challenges
Escape Room Challenge
Our strategy for the escape room challenge was to use the software structure for the hospital challenge as much as possible. Therefore, the room is scanned from its initial position. From this location a local map of the room is created by the perceptor. Including, convex or concave corner points, doors and possible doors (if it is not fully certain the door is real). Based on this local map the task manager gives commands to the drive controller and path planner to position in front of the door. Once in front of the the possible door and verified as a real door the path planner sends the next position to the world model. Which is the end of the finish line in this case, which is detected by two lose ends of the walls. Also the robot is able to detect if there are objects in front of the robot to eventually avoid them.
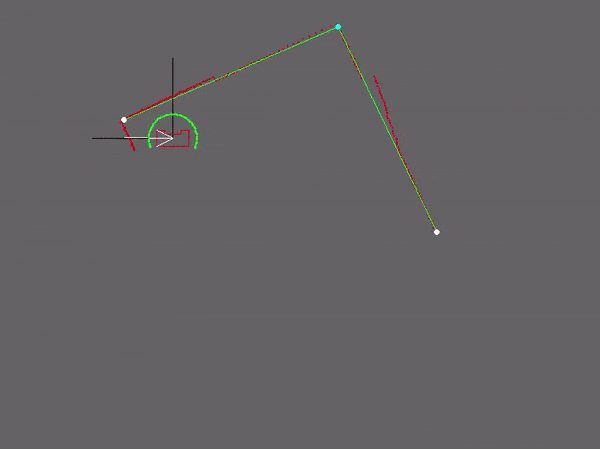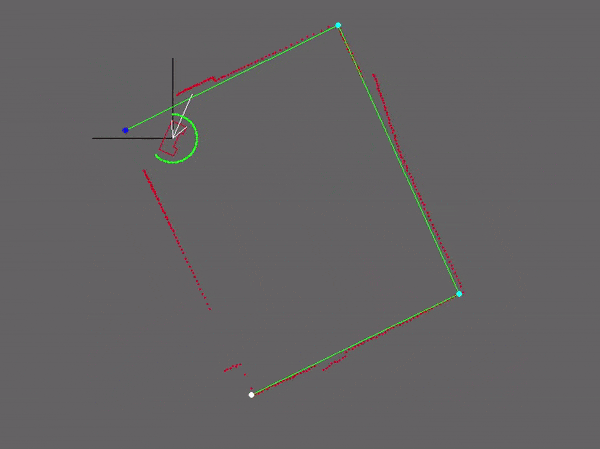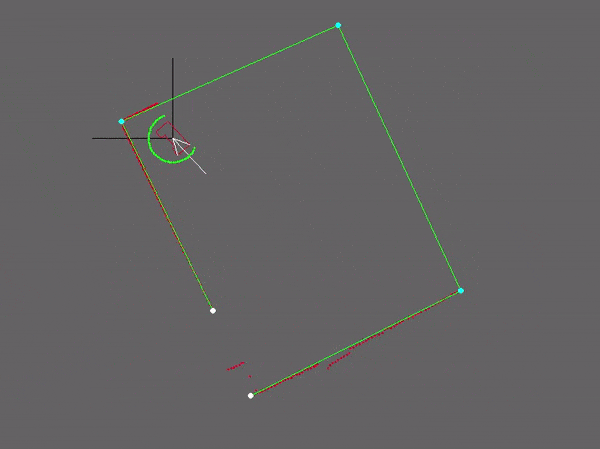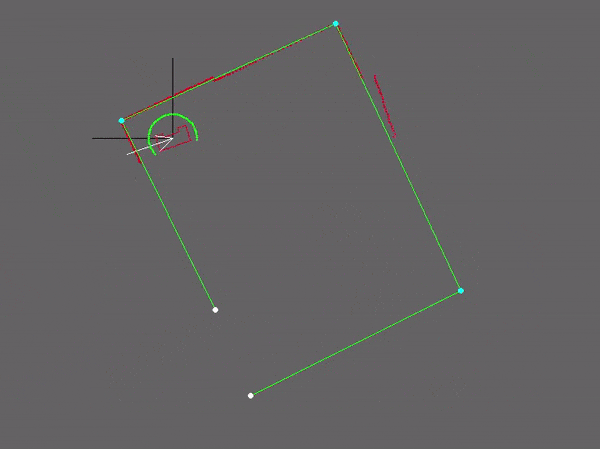
Simulation and testing
Multiple possible maps where created and tested. In most of the cases the robot was able to escape the room. However, in some cases such as the room in the escape room challenge the robot could not escape. The cases were analyzed but there was enough time to implement these cases. Furthermore, the software was only partly tested with the real environment at the time of the escape room challenge. Each separate function worked, such as driving to destinations, making a local map with walls, doors and corner points, driving trough a hallway and avoiding obstacles.
What went good during the escape room challenge:
The robot was made robust, it could detect the walls even though a few walls were placed under a small angle and not straight next to each other. Furthermore, the graphical feedback in from of a local map was implemented on the “face” of the Pico. The Pico even drove to a possible door when later realizing this was not a door.
Improvements for the escape room challenge:
Doors can only be detected if it consists of convex corners, or two loose ends facing each other. In the challenge it was therefore not able to detect a possible door. The loose ends were not facing each other as can be seen in the gif below. Furthermore, there was not back up strategy when no doors where found, other then scanning the map again. Pico should have re-positioned itself somewhere else in the room or the pico could have followed a wall. However, we are not intending to use a wall follower in the hospital challenge. Therefore, this does not correspond with our chosen strategy. Another point that can be improved is creating the walls. For now walls can only be detected with a minimal number of laser points. Therefore, in the challenge it was not able to detect the small wall next to the corridor straight away. This was done to create a robust map but therefore also excluded some essential parts of the map.
In the simulation environment the map is recreated including the roughly placed walls. As expected in this simulation of the escape room the pico did not succeed to find the exit, the reasons are explained above.
Hospital Challenge

During the hospital challenge a list of cabinets in a hospital must be visited to pick and place medicine. The given order of cabinets was 0, 1 and finally 3. Before this challenge a global map of the hospital with coordinates of the cabinets and walls was given. However there are doors that might be closed and unknown objects in the hospital. These objects can be either static or dynamic. The PICO robot must be able to handle these uncertainties.
The software for the hospital challenge is an improved version of the software used during the escape room challenge. The same block structure is used and as much as possible software is reused and adjusted where necessary. Major changes are done to the path planner and task manager since the complexity of the hospital challenge is much higher for those two blocks compared to the escape room challenge.
Video

The full and higher quality version of the video can be found here: Hospital challenge - video group 2 - 2019
What went well
The things that went well where being able to detect various objects such as walls and doors correctly. Next to that the closed door and static object were detected properly. Furthermore being able to plan a path around the closed door and static obstacles was no problem. Planning around objects is done by breaking the links between nodes, such that the path planning algorithm does not use these broken links anymore while planning a path. The broken links during the hospital challenge are visible in Figure 8 where all red lines between nodes indicate a broken link, white lines indicate a open link and the green lines indicate the planned path. Also did the localization work well, once it had determined the starting position correctly. This made it possible to determine the correct position of the PICO robot in the hospital during the challenge. Also was the localization robust against disturbances that were blocking it from detecting corners of rooms. This is also visible in Figure 8, where an object was blocking the top left corner of the room where PICO was in at that moment while visiting cabinet 1.
Improvements for the hospital challenge
The things that we would improve are improving the initial localization robustness since during the first try the localization was off, resulting in PICO getting stuck in the hallway. Luckily it did work correctly after a restart and we were able to finish. Also did we slightly hit the obstacle in the hallway, which was unexpected since a protection mechanism to avoid running into objects is implemented. Why this happened has to be investigated. The last improvement is reducing the total time to finish the challenge. The driving speed was lowered during the challenge to improve the accuracy of the localization, because the detected walls and doors were slightly off. If the robustness of the localization is improved, the driving speed can be increased as well to finish the hospital challenge faster. The time duration can also be decreased by removing the delay while waiting at a cabinet, since this delay was set to 5 seconds.