Designing the Opening Component: Difference between revisions
| Line 155: | Line 155: | ||
== Orientation / Location Finding == | == Orientation / Location Finding == | ||
'''Question: What kind of methods are there to position robots/carts/etc. and how do they work?''' | '''Question: What kind of orientation methods are there to position robots/carts/etc. and how do they work?''' | ||
* Parking Sensors | |||
<http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Parking_sensors> | <http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Parking_sensors> | ||
<http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Proximity_sensor> | <http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Proximity_sensor> | ||
<http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Position_sensor> | <http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Position_sensor> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
* Wireless Call & Receiver Units | |||
<http://www.google.com/patents/US7636621> | |||
<http://www.google.com/patents/US20130261870> | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
* Visual Tracking - | |||
<http://www.roborealm.com/tutorial/FIRST/slide030.php> Turning the drone to align with symbol | <http://www.roborealm.com/tutorial/FIRST/slide030.php> Turning the drone to align with symbol | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
Revision as of 14:20, 29 September 2014
Click to go to Opening.
There are many aspects that need to be considered when developing the mechanical system.
Planning
| Completion | Due Date *a little flexible | Stage |
|---|---|---|
| 29-Sept | Answered all Research Questions | |
| 29-Sept | List of Requirements the opening should fulfill | |
| 29-Sept | Set Specifications/Facts for tote & speed | |
| 1-Oct | Mechanisms and Design Decisions Done to get to final concept | |
| 6-Oct | Detailed Sketch(es) of Opening | |
| 6-Oct | Description of how it works & how to build | |
| 9-Oct | Build mini model? |
Facts
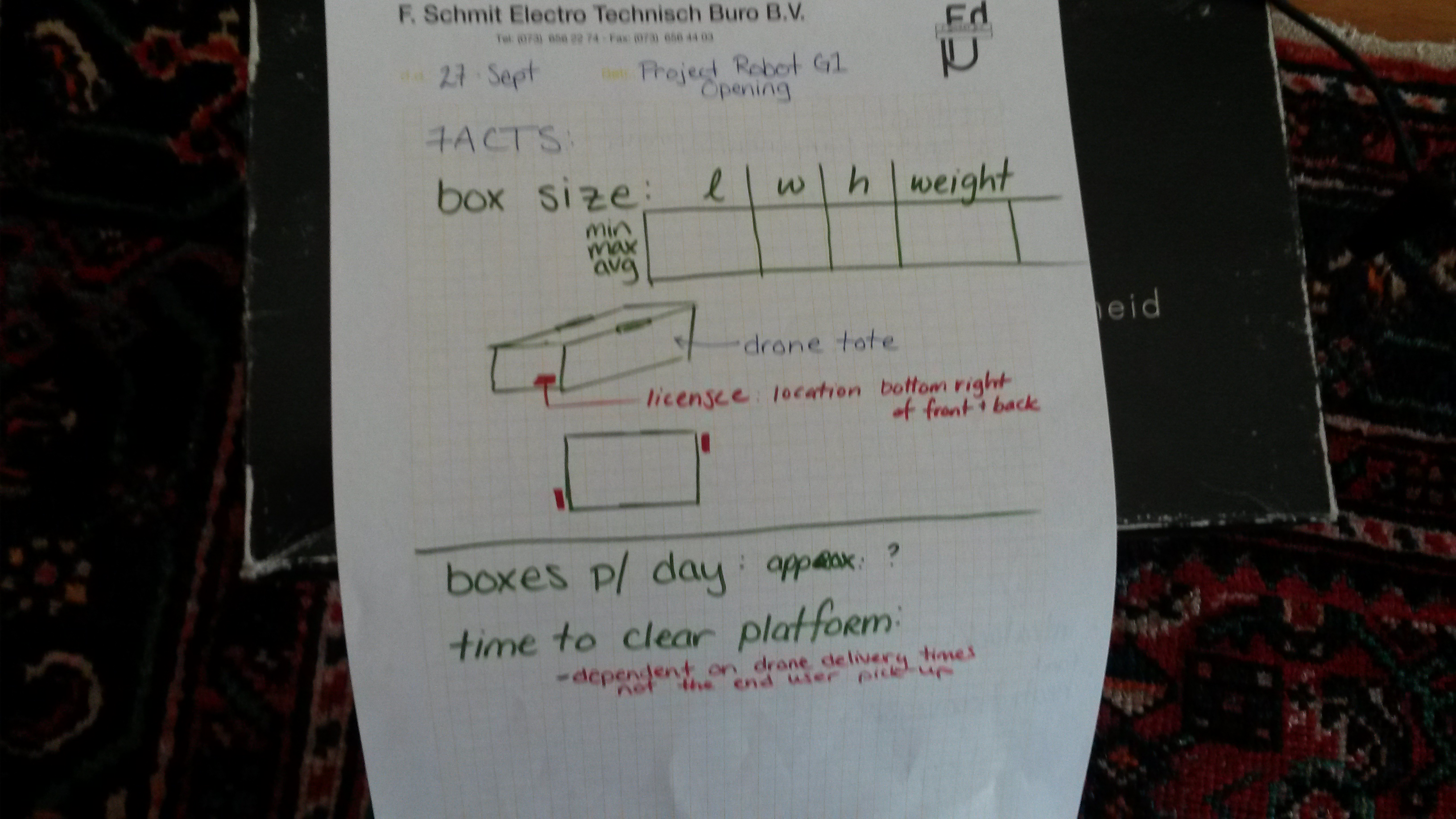
| Drone Tote | Height | Width | Depth | Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum | 0.2 kg | |||
| Maximum | 5 kg | |||
| Average | 12 cm | 15 cm | 26 cm | 2.5 kg |
Specs were estimated from looking at the Amazon Prime Air video since no real dimensions could be found, currently.
Tote has barcode located in bottom right corner of the tote on both the front and back face, simplifies orientation problem.
Totes expected to be handled p/day: 20 max
Time Spent handling a tote: 1 minute
Problem Description
Goal: The goal in this stage of the system is to receive a package from a drone, have it oriented in the appropriate position for further processing, and get it to the next stage of delivery.
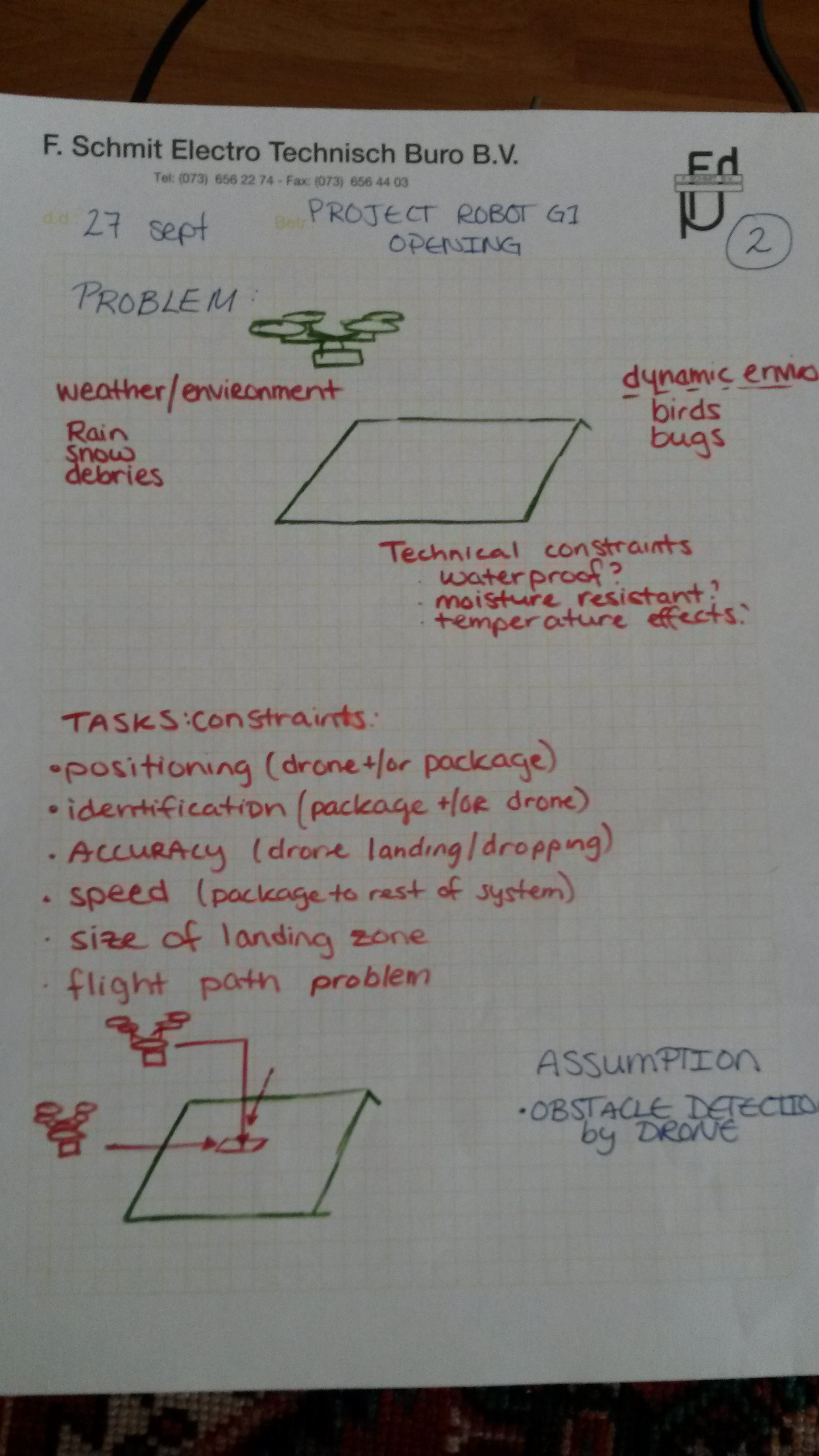
| Environmental Factors | Dynamic Factors | Technical Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Rain | Birds | Waterproofing? |
| Snow | Bugs | Moisture Resistance? |
| Debris | Temp. affects on function? |
| Task/Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Positioning | Drone+/or Package reaches the correct place for dropping the package or entering the system |
| Identification | package+/or drone needs to be identified by the system so that it can further handle the package |
| Accuracy | drone landing/dropping of the package should be accurately placed in the landing zone |
| Speed | The rate at which a package should be handled to the next stage of the system |
| Size of Landing Zone | The size may effect accuracy of package dropping (want to make this as large as possible) |
| Flight Path Problem | How many DoF does the drone have to approach the opening? |
Assumptions:
- Drone has Obstacle Detection to avoid objects in its way
Research Questions
Identification
Question: What kind of identification methods are there and how do they work?
- Radio Frequency ID (RFID)[1] - makes use of wireless electromagnetic fields to transfer data. It allocates tracking and identification of tags which are attached to items. This has been used in many different areas: Access Control for Hotel Rooms, Transportation and logistics in a distribution center, Track and trace of package deliveries.
- How it works: To make use of this identification methods it consists of two parts: a Tag and a Reader. The tag has the identification which can be transmitted. The reader sends a signal to the tag & then reads its response. The type of RFID system that is used is dependent on the tags and readers chosen to use.
- Used in Real Life: Drone Tracks Steel Products in Storage Yard [2] The drone is equipped with an RFID reader and steal bundles have the tags. Daily this drone hovers over various areas, reads tags and couples its own GPS location to this information and feeds it to a PC where the company keeps track of inventory.
- This could possibly be used on the platform design to get the package identified and then couple a cubby number to the package as it further proceeds through the system.
- Also good to note that RFID tags can be rewritten/relabeled after use [3]
(See | RFID Wiki for more information)
- Barcode Scanning [4] - makes use of a barcode and scanning devices that reads the barcodes. Barcodes are read via a light sensor which translates "optical impulses" into electrical ones, which decodes into the barcode's contents. Kinds of bar-code scanner that may be appropriate for our system.
- Omni-Directional Fixed Position Scanner - Can read poorly printed, wrinkled, or even torn barcodes. Often used in logistics to identify trays or pallets that need distribution to specific locations, or used in supermarkets. This type of scanner can be oriented in a position to read the barcodes off the package.
- Looking at possible barcode scanners that can be bought and their specifications I stumbled up Leuze Electronic. There I found a vast array of barcode scanners and detail in how they could be used. A Single Scanner, just 1 positioned however we want, could scan at high rates (industrial) but could only read a barcode from a specific orientation. A MPSi System, however, allowed the barcode to be read from any orientation. This was done by use for 2-3 scanners located in various positions. The cost of this kind of system, was definitely more pricey. Also to be noted is that each of these scanners require external power sources, or otherwise batteries that need replacement often. [5]
- Furthermore, there are various types of barcodes[6]: QR code, Universal Product Codes etc. Any of these would be appropriate for our system.
(See | Barcode Reader wiki for more information.)
What this research contributes to the design of this component:
From the research above, the RFID would be the better solution for the system:
- because it allows identification to be a continual process instead of requiring check points for scanning
- because it allows for re-writable totes, instead of having to sticker on a new barcode for every package
- because it creates more DoF in package orientation because a single receiver can located somewhere in the system, rather than placement of a scanner where the package has to pass by in the appropriate orientation
- Minor Considerations for the RFID: Security of the RFID/Interference with the RFID System
Orientation / Location Finding
Question: What kind of orientation methods are there to position robots/carts/etc. and how do they work?
- Parking Sensors
<http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Parking_sensors>
<http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Proximity_sensor>
<http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Position_sensor>
- Wireless Call & Receiver Units
<http://www.google.com/patents/US7636621>
<http://www.google.com/patents/US20130261870>
- Visual Tracking -
<http://www.roborealm.com/tutorial/FIRST/slide030.php> Turning the drone to align with symbol
What this research contributes to the design of this component:
(Make a selection as to which orientation method will be implemented (if any))
Ideas
-
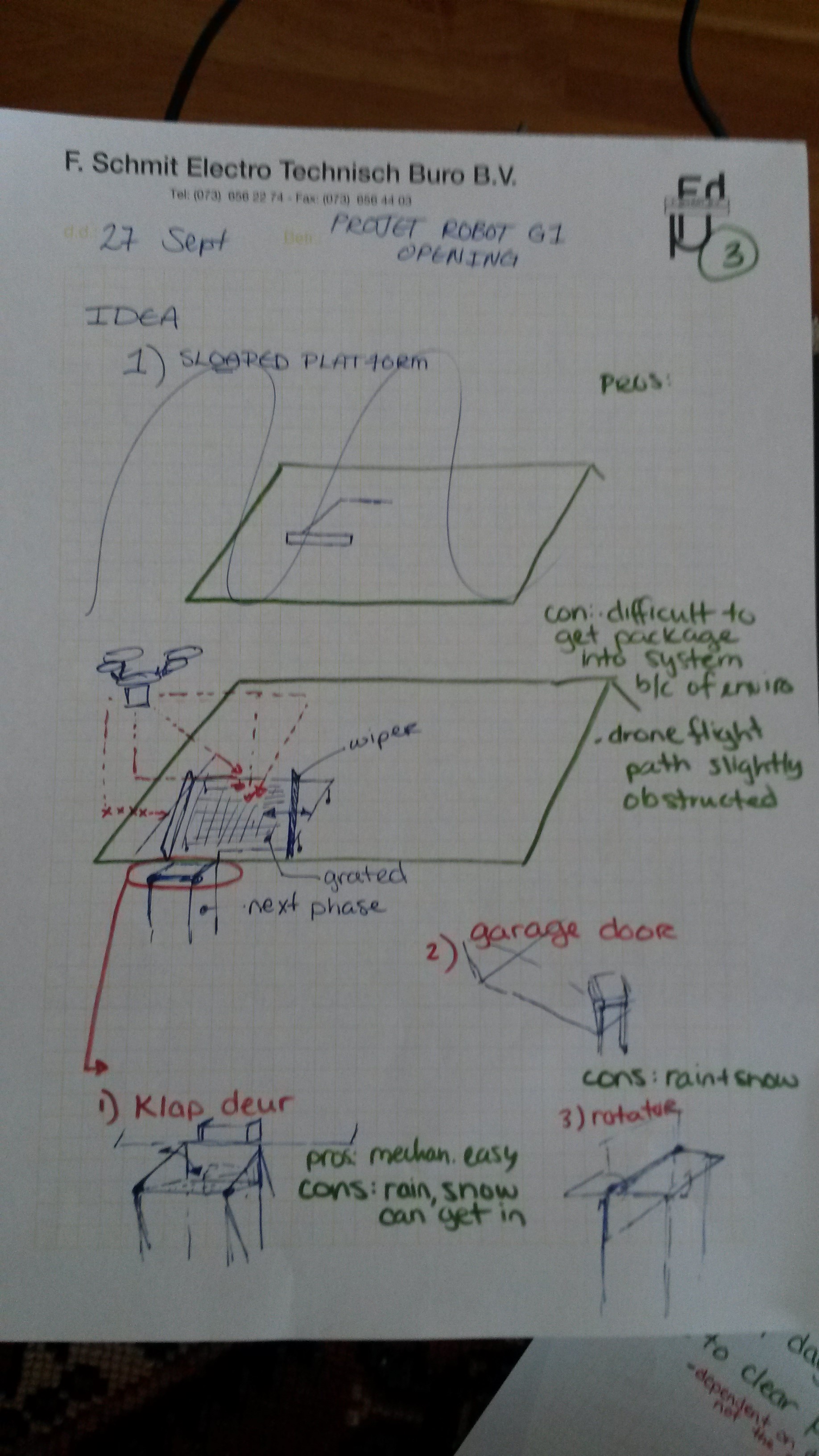
KS-OpeningP3-27-09
Sloped Platform & Door Ideas -
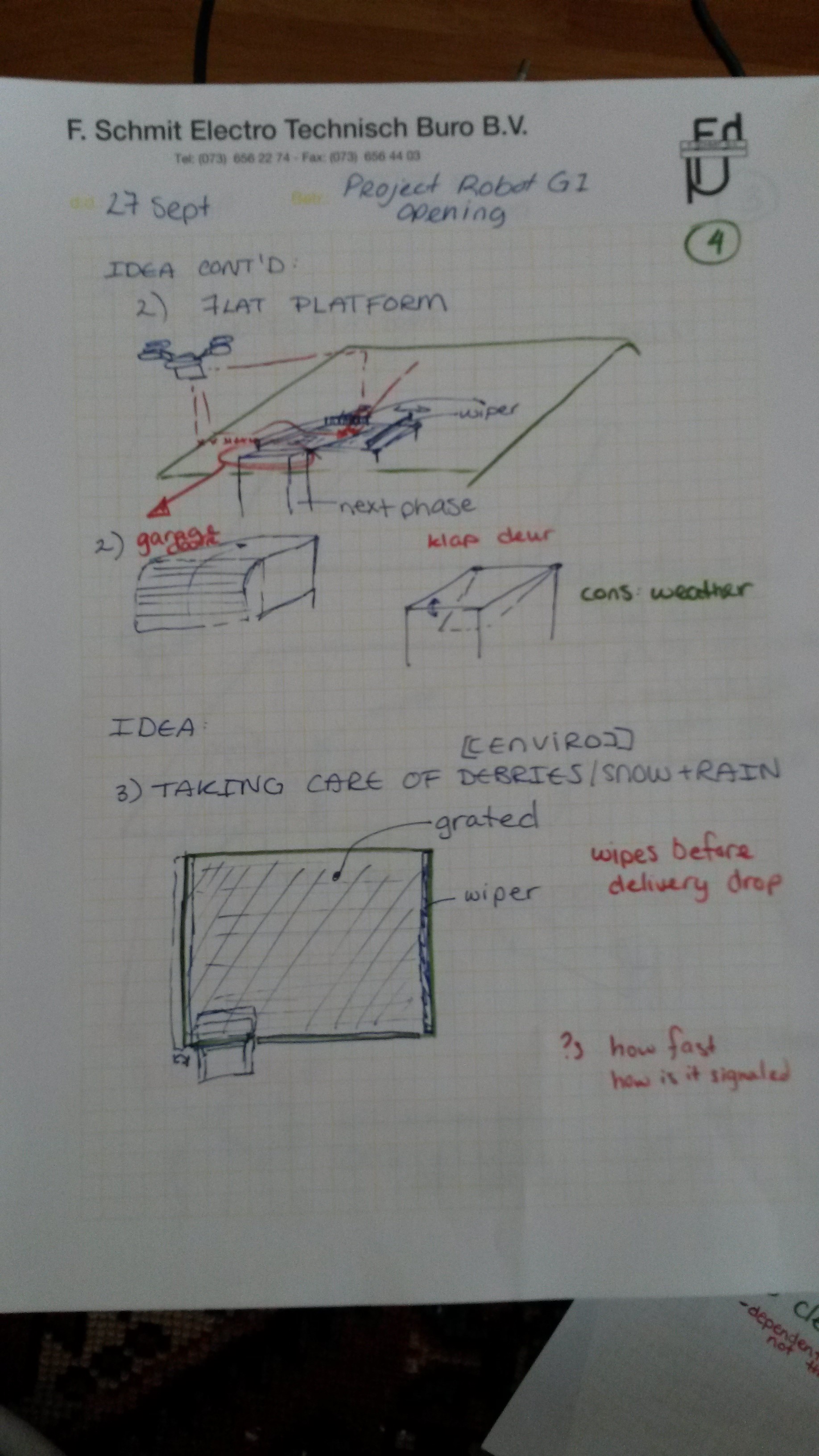
KS-OpeningP4-27-09
Flat Platform & Debris Ideas -
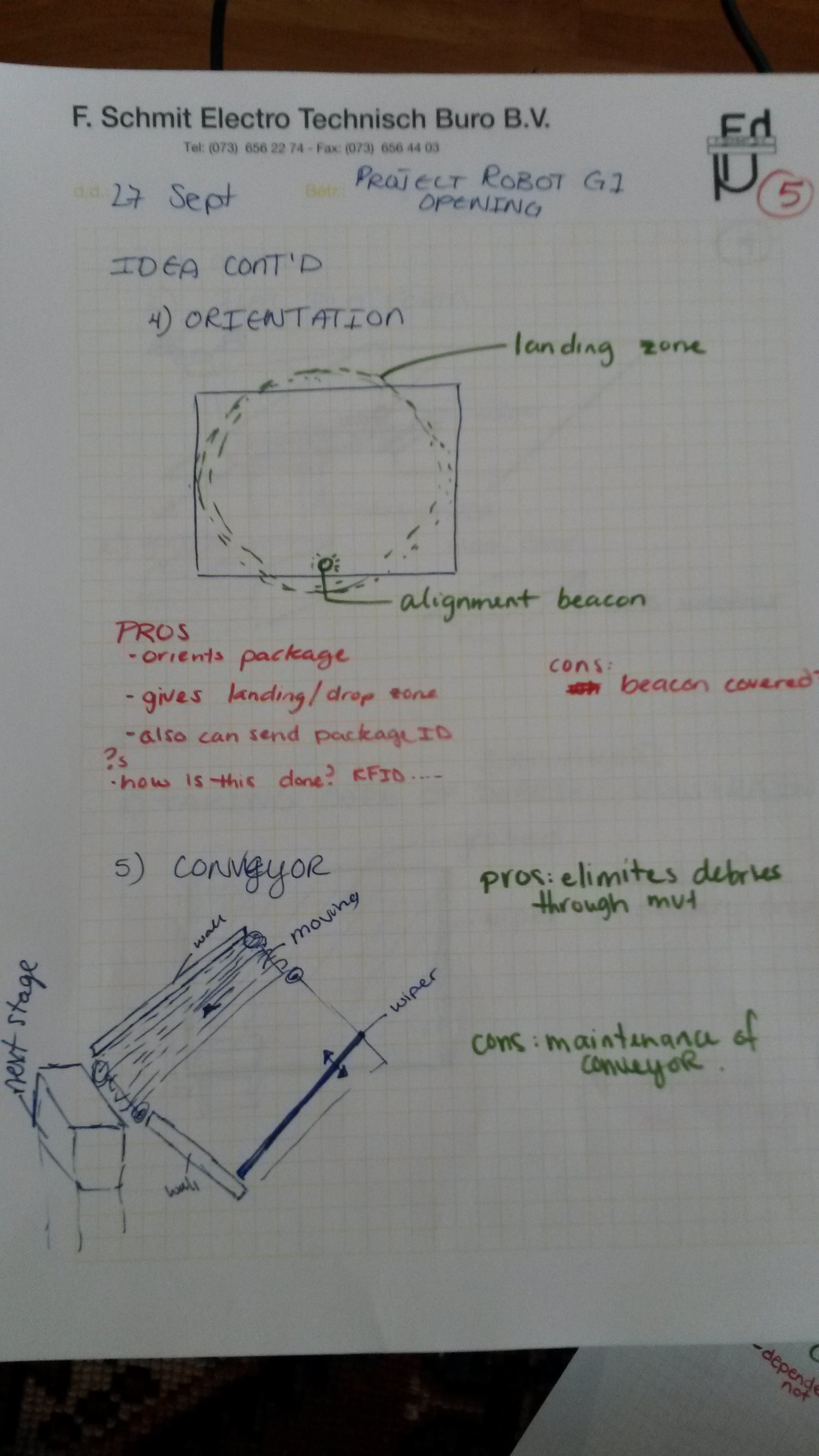
KS-OpeningP5-27-09
Orientation Idea & Conveyor Idea -
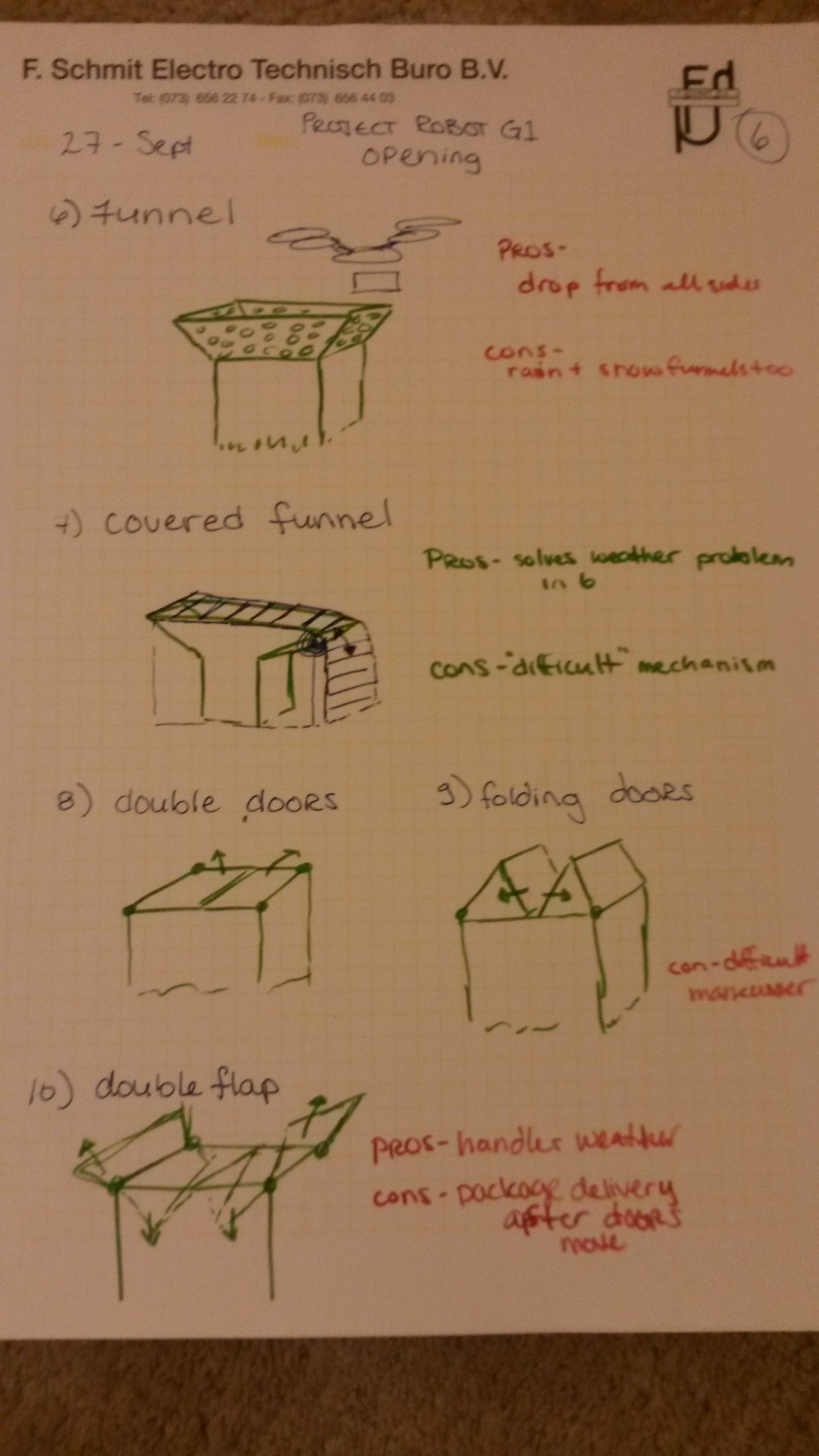
KS-OpeningP6-27-09
Funnel & Door Ideas
Drone Drop Zone
Sloped Platform
Labels: Drone Drop Zone
See page3 in gallery above for sketch.
| How it Works | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| As the name suggests, this set-up has a platform that is sloped with alignment to the roof. The slope allows for the package to be dropped and travel down with gravity towards the opening of the chimney. Also this system has a wiper which pushes the package in alignment after dropping. To make sure the package does not fall off the platform, there are guides. | Wiper can be used to clean off debris & snow. | Drone flight path slightly obstructed due to wiper & guides |
| Allows wide land/drop zone for the drone. | May look odd on buildings with flat roofs | |
| Drone can be oriented, but is not necessarily required b/c system aligns package after drop |
- See door mechanisms that could couple to this component to bring package into the system
- See orientation mechanisms that could couple to align package
Flat Platform
Labels: Drone Drop Zone
See page4 in gallery above for sketch.
| How it Works | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| This set-up has a platform that is flat and makes the use of two wipers. One in the x direction and one in the y direction, which will be used t align the package accordingly with the opening of the chimney. Guides prevents the package from falling off the platform. | Gets package oriented and to location | Flat less effective than slanted |
| Allows for big area land/drop zone | Drone flight path slightly obstructed by wipers & guides | |
- See door mechanisms that could couple to this component to bring package into the system
- See orientation mechanisms that could couple to align package
Conveyor
Labels: Drone Drop Zone See page5 in gallery above for sketch.
| How it Works | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Similar to the other two platforms above. This idea has a large landing platform but has a continual moving conveyor located on one side. A wiper pushes the package onto the grated conveyor which leads the package to the chimney. | Continual movement of conveyor limits debris and snow accumulation | Maintenance very important |
| Possible noise issues? | ||
- See door mechanisms that could couple to this component to bring package into the system
- See orientation mechanisms that could couple to align package
Funnel
Labels: Drone Drop Zone
See page6 in gallery above for sketch.
| How it Works | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Pro here | ||
| Pro here | ||
| Pro here |
Covered Funnel
Labels: Drone Drop Zone with Door Mechanism
See page6 in gallery above for sketch.
| How it Works | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Pro here | ||
| Pro here | ||
| Pro here |
Door Mechanisms
Garage Door
Labels: Door Mechanism
See page4 in gallery above for sketch.
| How it Works | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Pro here | ||
| Pro here | ||
| Pro here |
Double Doors
Labels: Door Mechanism
See page6 in gallery above for sketch.
| How it Works | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Pro here | ||
| Pro here | ||
| Pro here |
Folding Doors
Labels: Door Mechanism
See page6 in gallery above for sketch.
| How it Works | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Pro here | ||
| Pro here | ||
| Pro here |
Double Flap
Labels: Door Mechanism
See page6 in gallery above for sketch.
| How it Works | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Pro here | ||
| Pro here | ||
| Pro here |
Orientation
RF & Beacon
Labels: Orientation
See page5 in gallery above for sketch.
| How it Works | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| This is a possible solution for orientation & identification of the package. Through a radio frequency a drone can signal to the delivery system that it is in range (or vice versa). Over this RFID information can be sent about the size and location of the drone drop zone so that the drone can find it. Once hovering over it, the drone can then align itself with a light beacon located at a point on the platform. | Can transfer information about the package over the RFID as well | Beacon can be blocked by environmental obstacles |
| Allows specification of drone platform location and size of drone zone | Possible hacking? | |
Contrast Symbol
Labels: Orientation
See page5 in gallery above for sketch.
| How it Works | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| This is a possible solution for orientation & identification of the package. Through a symbol painted on the drone zone platform, the drone can perceive the contrast and orient itself accordingly to the symbol. | Simple Solution of painting a symbol | Paint can fade |
| Allows specification of drone platform size on basis of symbol | Not a method to help find the platform | |
Requirements
| Functional | Product | Process | External |
|---|---|---|---|
References
- ↑ Wikipedia. (2014). Radio-frequency identification. <http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Radio-frequency_identification>
- ↑ Swedberg, C.(2014, 26 Sept). RFID-Reading Drone Tracks Structural Steel Products in Storage Yard. RFID Journal. <http://www.rfidjournal.com/articles/view?12209>
- ↑ Roberti, M. (2014, 26 Feb). How Can I Program a Rewritable RFID Tag?. RFID Journal. <http://www.rfidjournal.com/blogs/experts/entry?10929>
- ↑ Wikipedia.(2014).Barcode reader.<http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Barcode_reader>
- ↑ N.A.(2014).Barcodeleser.Leuze Electronic GmbH.<http://www.leuze.com/en/deutschland/produkte/identifikation/barcode_identifikation/stationaere_barcodeleser/index.php>
- ↑ Wikipedia.(2014).Barcode.<http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Barcode#Types_of_barcodes>