Embedded Motion Control 2014 Group 6: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 138: | Line 138: | ||
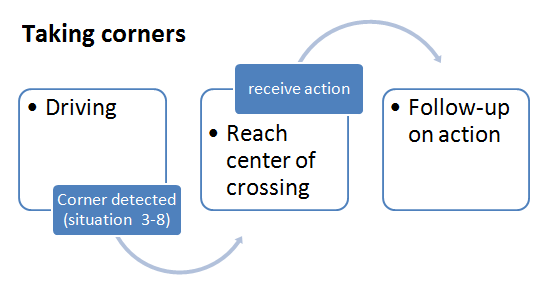
=== Taking corners === | === Taking corners === | ||
[[File:Taking_corners.png|center|thumb|1000px]] | [[File:Taking_corners.png|center|thumb|1000px]] | ||
== Decision node == | |||
The decision node is designed to act like a navigation tool. It tells the drive node where to go. The decision node does this by detecting which situation we are approaching (like corner left/right or T-crossing), taking into acount the information of the arrow node and previous turns and then tells the drive node where to go. | |||
=== Situation determination === | |||
In order to determine which situation we are approaching, we want to know 3 things: is there a corner to the left, is there a corner to the right and can we go straight ahead? | |||
We determine these 3 things by using the laser data. Unfortunately we will not always detect the corners and dead end at the same time, | |||
so when we detect one of these 3 we will drive to a fixed distance from the situation. In this time we drive we will determine if we also find the other two charateristics of the situation. Using the information we have we can determine the situation and publish it on the topic. | |||
=== Action determination === | |||
When we have published a situation, then the drive node makes sure we drive to the center of the situation. If we are in the center, we will determine if there are deadends in any turns, look if there are any arrows and then make a decision which way to go. | |||
Revision as of 12:33, 15 June 2014
Wout Laarakkers 0828580
Rik Boonen 0805544
Dhruv Khandelwal 0868893
Suraj Prakash 0870060
Hans Reijnders 0806260
Updates
- Include Bool action_done and Bool wall_close in topic drive for handshake (23 May)
Planning
Week 1 (2014-04-25 - 2014-05-02)
- Installing Ubuntu 12.04
- Installing ROS
- Following tutorials on C++ and ROS.
- Setup SVN
Week 2 (2014-05-03 - 2014-05-09)
- Finishing tutorials
- Interpret laser sensor
- Positioning of PICO
- having ore first meeting
Week 3 (2014-05-12 - 2014-05-16)
- Programming corridor competition
- Corridor competition
Week 4 (2014-05-19 - 2014-05-23)
- Creating basic structure for programming in Ros
- Planning
- Dividing tasks
* Drive node: Dhruv Khandelwal
* Decision node: Hans Reijnders, Rik Boonen
* Arrow node: Wout Laarakkers
- Programming individual parts
Week 5 (2014-05-26 - 2014-05-30)
- Programming individual parts
- Testing parts
- Integrating parts
Week 6 (2014-06-02 - 2014-06-06)
- Programming individual parts
- Testing parts
- Integrating parts
- Deadline for the nodes
Changes in group
Unfortunately Suraj Prakash has decided to quit the course, because he doesn't has enough time.
Corridor competition Software design
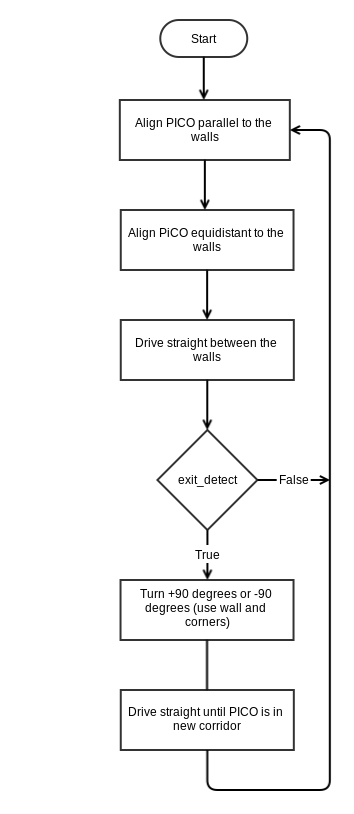
Software design
Structure
The first draft of the structure of nodes and topics is shown below.
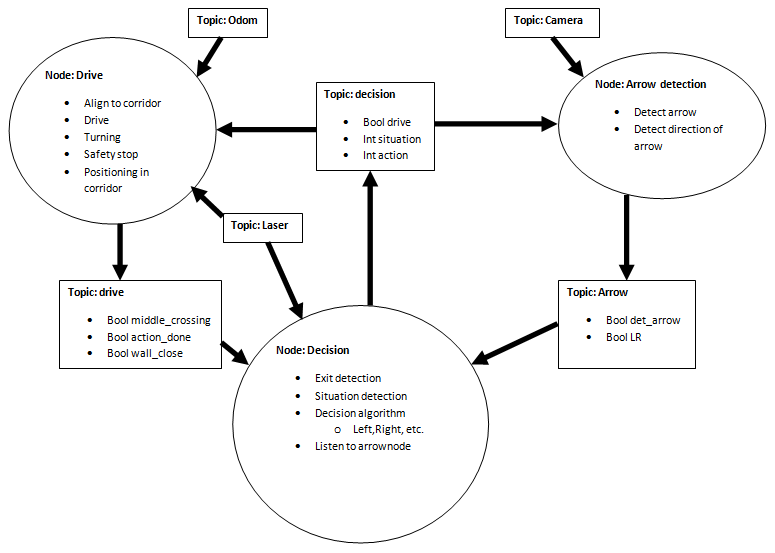
The integer 'situation' and 'action' have certain values corresponding to different cases. These cases are defined as shown below.
| Situation | |
| 1 | Detected corridor |
| 2 | Detected dead-end |
| 3 | Detected corner right |
| 4 | Detected corner left |
| 5 | Detected T-crossing (right-left) |
| 6 | Detected T-crossing (right-straight) |
| 7 | Detected T-crossing (left-straight) |
| 8 | Detected crossing |
| 9 | Unidentified situation |
.
| action | |
| 1 | Stop |
| 2 | Straight |
| 3 | Right |
| 4 | Left |
| 5 | Turn around |
| 6 | Follow left wall |
| 7 | Follow right wall |
Taking corners
Decision node
The decision node is designed to act like a navigation tool. It tells the drive node where to go. The decision node does this by detecting which situation we are approaching (like corner left/right or T-crossing), taking into acount the information of the arrow node and previous turns and then tells the drive node where to go.
Situation determination
In order to determine which situation we are approaching, we want to know 3 things: is there a corner to the left, is there a corner to the right and can we go straight ahead?
We determine these 3 things by using the laser data. Unfortunately we will not always detect the corners and dead end at the same time, so when we detect one of these 3 we will drive to a fixed distance from the situation. In this time we drive we will determine if we also find the other two charateristics of the situation. Using the information we have we can determine the situation and publish it on the topic.
Action determination
When we have published a situation, then the drive node makes sure we drive to the center of the situation. If we are in the center, we will determine if there are deadends in any turns, look if there are any arrows and then make a decision which way to go.