PRE2019 4 Group7: Difference between revisions
| Line 311: | Line 311: | ||
! Name !! Student number !! Time spent !! Break-down | ! Name !! Student number !! Time spent !! Break-down | ||
|-style="text-align: center;" | |-style="text-align: center;" | ||
| Eline Visser || 1375369 || | | Eline Visser || 1375369 || 8 hours || Research on app making. (2h) Practice with python and Kivy (3h) Documenting the process (1h) Editing the wiki (1h) More research in appypie and app makers after the meeting with tutor. (1h) | ||
|-style="text-align: center;" | |-style="text-align: center;" | ||
| Metten de Lange || 1240902 || hours|| | | Metten de Lange || 1240902 || hours|| | ||
Revision as of 14:12, 7 May 2020
Group members
Student Group
| Name | Student number | Bachelor | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eline Visser | 1375369 | e.a.l.visser@student.tue.nl | Applied Physics |
| Metten de Lange | 1240902 | m.m.d.lange@student.tue.nl | Applied Physics |
| Vera Holtmark van Dijkerhof | 1380893 | v.holtmark.van.dijkerhof@student.tue.nl | Applied Physics |
| Sterre Cuppens | 1387790 | s.cuppens@student.tue.nl | Psychology and Technology |
| Iris de Wit | 1258230 | i.c.d.wit@student.tue.nl | Psychology and Technology |
Problem statement
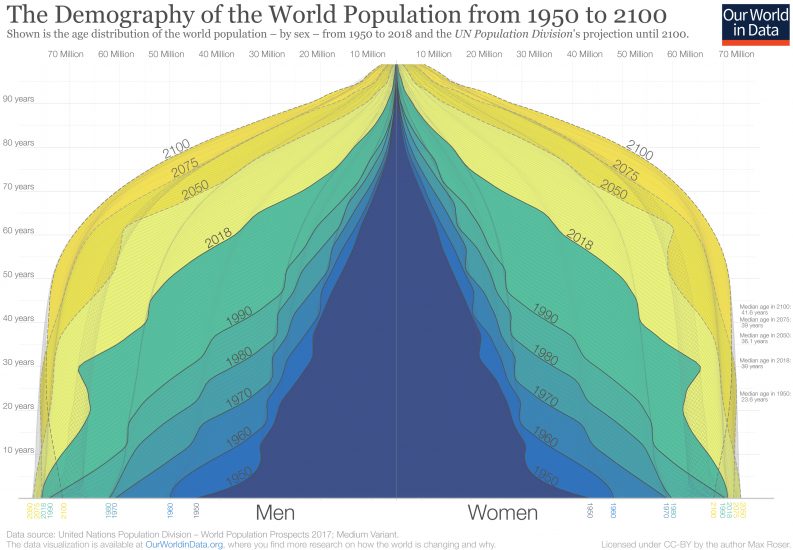
The current world population keeps expanding. In 1950 there were 2.5 billion people on Earth. In 2020 this number is 7.8 billion. [source: "World Population Clock: 7.8 Billion People (2020) - Worldometers". worldometers.info.] However, this is not the only change. There has also been a shift in the population age distribution. As can be seen in the image below, there used to be a pyramidal distribution of age, where there are relatively a lot of young people, and fewer elders. But in data of later decades and estimations for the near future, this distribution becomes more and more "block like". This means that at some point, there will be almost the same amount of elders alive as there are young people to care for them. It is estimated that this trend will continue to grow.
With that, the age-related decease rates will go up as well. Right now 50 million people are living with dementia. It is estimated that the portion of people over age 60 with dementia lies between 5 and 8 percent. The total number of cases is projected to grow to 82 million in 2030 and 152 million in 2050. [source:https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/dementia]
This leads to all sorts of detrimental effects for the care industry. Since there will be less and less spots available in nursing homes, elders with dementia will be expected to live at home longer. This demands the invention of new technology to aid them in day to day life.
Not only activities such as eating, taking medicine and staying active require attention, also the social live of elders with dementia is of great importance. As the person grows older, a large part of their social live will cease to exist. This can cause severe loneliness and even depression.
Objectives
The technology should be able to help older and demented people get through their daily lives. For them, many problems that most people never have to deal with are commonplace and they require lots of attention. However, giving this attention to everyone who needs it takes many people and much time, while it is not always possible to have enough caregivers for this. Technological solutions could provide an outcome.
Most importantly, the technology should be able to alleviate the loneliness of older or demented people. This is a problem that has been getting bigger and bigger, but technological solutions could provide an outcome.
Furthermore, the technology should be able to help demented people get through their daily lives. For them, even the most simple tasks like washing your hands require help from someone else. Robots or similar technology could help these people by guiding them through the process step by step, encouraging and correcting them where necessary.
Lastly, the technology should be able to contact help whenever necessary. For instance, when the user has fallen over and cannot get up, the help of someone else is needed. Because older people are more likely to get hurt, this is an important feature that can and should be included. The technology should be able to recognize when something has happened and contact outside help when needed.
Users
Types of users
Primary users
The primary users are the elderly people with dementia. With an elderly population that is set to more than double by 2050 worldwide, there will be an increased demand for elderly care. The shift in societal proportions will place new pressures on all aspects of elderly care. Loneliness, for instance, is a consequence of social, psychological and personal factors. Over half of people over the age of 75 live alone and 17% of older people see family, friends or neighbours less than once a week. A recent meta-analysis showed that the impact of loneliness and isolation carries the same mortality risk as smoking 15 cigarettes a day. This poses several impediments in the delivery of high-quality health and social care.[1] We want to focus especially on elderly with dementia. Because people with dementia experience progressive cognitive impairments that typically commence with short term memory problems but can encompass language deficits, difficulties initiating tasks, planning, monitoring and regulating behaviour, and visuospatial difficulties, agnosia (loss of ability to recognize familiar objects or people and apraxia (loss of ability to carry out complex purposive movements) [2]. For people with dementia it is extra hard to keep social connections with other people. Therefore, we want to make elderly people with dementia less lonely with our device.
Secondary users
Secondary users are the caretakers of the elderly people with dementia. They will have to cooperate with the device for the ultimate care for the elderly. The device should be a supporting tool for the caretakers, which makes the worry and care on daily tasks less. And it should be an addition to the care of the caretakers with the social aspect. It can give the elderly people the extra social interaction what caretakers sometimes can't give.
Tertiary users
Tertiary users of the device are the companies that create the product. Eventually, if there is a high enough demand for the product, companies will be producing the device. New technologies such as the device may create good business opportunities for newer companies and for both well-established companies. The companies will have to take the price of the device in account for the elderly people. They have to find a balance between an affordable device for the elderly people with dementia to reach a high enough demand. And the companies will have to make enough profit of the device to keep the production going.
User requirements
The following points are the user requirements. These user requirements are conditions or tasks that must be completed to ensure the completion of the project.
• The app should only contain the functions that are necessary for the app to reach its goal
• The functions of the app should all be visible and displayed in a orderly way by having as little text as possible and a maximum of 6 functions on the screen
• There should be consistency all throughout the app
• The app should be able to remind the user of information with help of notifications. The amount of information given should be customizable.
• The app should help to have social connections with other people by having a function to interact with other people. For instance, it should be able to (video) call relatives of the user.
• The app should have an option that provides help and support for using the app, for instance through hints that pop up during the use.
• The app should have the option to do cognitive training exercises
• The app should be able to be activated by an elderly with dementia alone
• The app should be able to make elderly with dementia feel at ease by having a relaxing and entertaining appearance
State of the Art
Assistive technology in elderly care
Recent developments in new technology are the subject of intensive research destined to make an important contribution to the care of older people, both in institutions and at home. Electronic sensors, video-monitoring, remote health monitoring and equipment such as fall detectors, door monitors, bed alerts, pressure mats and smoke and heat alarms can improve patients’ safety, security and ability to cope at home. Since care in the community is preferable to most patients and is usually less expensive than in care homes, system using advanced technology to support people at home could benefit both patient and care provider. [3]
Loneliness and new technologies in a group of Roman adolescents
Those who use Internet most often declared having more friends who go on-line. This finding can be discussed in two perspectives. During adolescence friendship is often established on the basis of common interests and shared activities. In this case, the use of Internet could constitute an element able to launch and to facilitate the beginning of a friendship between two or more persons and to contribute toward greater cohesion in an already existing friendship. On the other side, the push toward homogeneity and similar behaviours, which often characterises groups of adolescents, could be considered a motivational factor in the use of this technology.It also emerged that those who use Internet more hold that as a result they neglect their friends and their scholastic commitments. A new technology may initially absorb time and attention usually dedicated to other things; the progressive disappearance of the novelty element could, instead,bring attention back to interests that existed prior to the new technology.The data from this research do not allow us to indicate a direction in the relationship between loneliness and the use of Internet. Due to the type of communication characterised by Internet, it could produce greater loneliness in adolescents who make greater use of it. However, it cannot be excluded that the large use of this technology is only an unsuccessful strategy put into action to face pre-existing loneliness, or that other variables intervene in the relationship between the use of Internet and loneliness. [4]
Socially Assistive Robots in Elderly Care: A Systematic Review into Effects and Effectiveness
The ongoing development of technology, specifically robots, against the background of a decreasing number of care personnel raises the question of what the potential contribution of robotics could be in rationalizing and maintaining, or even improving the quality of elderly care. Robots can contribute to health care support in terms of capacity, quality (performing very accurately and task specific), finance (support or even take over tasks of trained personnel), and experience (e.g., increased feeling of autonomy and self management). The idea of robotics playing a role in health care was launched some decades ago and has mainly been developed for physical training in rehabilitation as well as personal assistance for tasks of activities of daily living. Robotic applications supporting social behavior are a more recent development. So far, systems have been developed supporting child’s play and care for elderly with dementia. However, the uptake of these systems in care practice has been limited. One of the reasons is that there appears to be a mismatch between what is technically developed and the perceived needs within care environments.The term SIR was introduced to distinguish these robots from other robots that involve “conventional” human robot interaction, such as in tele-operation scenarios. In SIR, the robot’s goal is to develop close and effective interactions with a human for the sake of interaction itself. In contrast, in SAR, these systems are not designed to help the human being performing work tasks or saving time in routine activities, but to give assistance through social interaction to achieve progress in, for example, convalescence,rehabilitation, and learning. As such, SAR is a subsection of SIR. [5]
Scoping review on the use of socially assistive robot technology in elderly care
With an elderly population that is set to more than double by 2050 worldwide, there will be an increased demand for elderly care. The shift in societal proportions will place new pressures on all aspects of elderly care. Loneliness, for instance, is a consequence of social, psychological and personal factors. Over half of people over the age of 75 live alone and 17% of older people see family, friends or neighbours less than once a week. A recent meta-analysis showed that the impact of loneliness and isolation carries the same mortality risk as smoking 15 cigarettes a day. This poses several impediments in the delivery of high-quality health and social care. Socially assistive robot (SAR) technology could assume new roles in health and social care to meet this higher demand. These are robots adept at completing a complex series of physical tasks with the addition of a social interface capable of convincing a user that the robot is a social interaction partner. Five roles of SAR were identified: affective therapy, cognitive training, social facilitator, companionship and physiological therapy. [1]
Technology and loneliness in old age
In an attempt to contribute to a better understanding of the link between modern technology and loneliness in old age, this paper points to the vital role of individual dispositions. A construct sensitive to both technological as well as societal change, perceived obsolescence was shown to influence the way personal and telephone contacts were responded to. With low social contacts and high obsolescence being detrimental to feelings of social and societal integration in their own rights, their combination may compound feelings of loneliness far beyond additivity. Going further, feelings of being out of step with modern times were found to mediate the effects impact of low technological competence on loneliness. Given the accelerated obsolescence of both technological devices and user know-how, to keep up with technological progress may become a challenge not only for those persons who never learned how to use a computer. Thoughtful design and implementation of technology is needed to assure access to and orientation within modern society despite varying technological backgrounds and competences. [6]
Technology Implementation and Workarounds in the Nursing Home
As new systems have been explored to support medication administration, technology has become a critical part of these discussions. In response to ongoing patient safety challenges, health care organizations have implemented a variety of technological mechanisms to reduce medication errors such as computerized physician order entry, electronic medication administration record, and clinical decision support systems. However, implementation of technology has not been without risk. As technology has been developed and tested, new types of medical error and risk for error have occurred. Workarounds have been defined as “informal temporary practices for handling exceptions to normal work flow”. Exploration of WA, blocks, and the risk to patient safety is an important consideration as technology implementation moves forward in health care. As the literature has unveiled hidden risks associated with technology implementation, there is a need to understand the manner in which health care professionals interact with new technology and how work processes are adjusted as a result of technology implementation. Understanding these WA as a means of first-order problem solving is an important consideration to understanding the risk to medication safety. As new technologies are introduced, continued monitoring to identify work flow is needed so appropriate changes can be made to address the underlying problems that create work flow blocks ultimately leading to potential WA. Additionally, as technology is implemented, organizational processes that will interface with the technology must be carefully re-engineered to reduce the unintended consequences of change. [7]
Technology in dementia care
People with dementia experience progressive cognitive impairments that typically commence with short term memory problems but can encompass language deficits, difficulties initiating tasks, planning, monitoring and regulating behaviour, and visuospatial difficulties, agnosia (loss of ability to recognize familiar objects or people and apraxia (loss of ability to carry out complex purposive movements). Whilst drugs have for some time been used and approved by health organizations for the treatment of mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease, these drugs do not cure, reverse or tackle the underlying root problem causing the dementia. Therefore in the absence of a cure, more innnovative approaches need to be developed to help promote independence and maximise quality of life. In this context, assistive technologies offer much potential and can make a very significant difference to the lives of people with dementia and to their primary caregivers. Indeed it has been noted that technologies should be part of a home package and should be provided in a thoughtful, sensitive ethical way. Technologies can assist people to maintain their independence improve quality of life. The overall opportunities technology can create for people with dementia however have to date not been fully maximised. [2]
Computerized multi-domain cognitive training reduces brain atrophy in patients with amnestic mild cognitive impairment
Multi-Domain Cognitive Training (MDCT) is a training programs that may protect people of the lost of grey matter volume in the brain. This could be a non-pharmacological intervention to slow the progress of dementia. The training program has two sessions a week and each session was 1h. Every session the tasks would challenge three out of the following six cognitive domains; reasoning, memory, visuospatial skills, language, calculation and attention. Every week every domain would be tested and trained within the tasks. At the end of two weeks of training, the grey matter volume of the participants was increases by 6.14% on average and a significantly positive correlation between the volume and scores on cognitive function tests was found. [8]
The Impact of Computer Technology on the Elderly
When designing technology for elderly users it is important to take some changes humans experience in mind. These changes are either sensory and motor changes, cognitive changes or social changes. Sensory and motor changes are the changes that the body experiences, such as decreasing in vision, hearing and motor skills. The cognitive changes cause the rate at which the users can learn and remember the new technology and “computer skill” to decrease. These changes cause elderly people to have difficulty with navigating through out the computer and remembering how to do things they have already done before on the computer. The social environment has a big influence in the technology that elderly people use. The traditional WIMP (Windows, Icons, Menus and Pointers) don’t consider these changes and when designing for elderly it is important to adapt the WIMP’s. [9]
Loneliness, health and social network among elderly people
Over a span of 10 years residents of nursing homes with a cognitive impairment where asked about feeling alone and the satisfaction with social contacts. There was an initial visit and three follow-ups after that. The people participating in the study where all cognitive impaired, which raised the question if it was ethical to use these participants for research while they didn’t understand the initial information of the study. The researchers included cognitively impaired elderly because it was important to the study and the end goal is to improve the future life quality of them. The questions asked in the interviews with the participants where about experiencing loneliness, being satisfied with social contact, living alone and having good friends to talk to. The percentage of the participants that said to not experience loneliness and where satisfied with social contacts increased over the follow-up visits. The percentage of people living alone steadily decreases over the course of the follow-ups, as could be expected. The percentage of people having a good friend to talk to decreased. Another inside that the study gave was that sever cognitively impaired participants experienced loneliness more often, while they more frequent visits then less cognitively impaired participants. [10]
Pain in Cognitively Impaired Nursing Home Patients
The findings of the study confirm that pain is common in cognitive impaired elderly homes. 60% of the patients that were able to make the complaints know said to experience pain. The participants of this study were disabled and most had difficulty performing daily activity, whether they did or did not experience pain. The results show that the pain management in skilled nursing homes is limited and only partially successful. 25% of the patients received physical therapy and apart from that only a few patients were given any other pain management. Cognitive impairment is a barrier in assessing and managing the pain complaints, 21% of the patients weren’t able to make their needs known. 17% wasn’t able to indicate the level off pain with the scales. This study concludes that pain assessment and management strategies for elderly with cognitive impairment need constant and frequent assessment of pain at that moment. The existing scales to measure the pain might need some adjustment to make up for the disabilities of the patient. [11]
Assistive Technology for Memory Support in Dementia
This review analyses the available Assistive Technology for elderly with dementia. A wide range of these Assistive Technology devices, that supports people with memory loss is commercially available nowadays. The only thing that is missing is a systematic review of studies that focus on the efficacy of these devices for supporting people with memory loss. The study primarily focusses on the efficacy of the assistive technology for memory support. This is researched in terms of level of dependency, daily performance of personal and instrumental activities of daily living and de admission to the care in the long term. The secondary objective that the review tests is the impact of the assistive technology on the users in terms of autonomy, usefulness and user-friendliness, adoption of the assistive technology. The conclusion of the review was that there needs to be more research about the effectiveness of the current assistive technology to support people with cognitive impairments with their memory loss. [12]
The use and acceptance of new media entertainment technology by elderly users: Development of an expanded technology acceptance model
Among older people, the barrier to start using technology is rather high, especially compared to younger people who grow up surrounded by technology. The two main factors contributing to the decision for older people to use a given technology are Perceived Usefulness (PU) and Perceived Ease of Use (PEOU). Previous experience with technology makes the barrier to start using it lower. It is important to note that the actual usefulness or ease of use is not that impactful, but rather how the user perceives it to be, even if they haven’t used it yet. Previous failures also contribute to the barrier for elderly people to pick up a new technology. [13]
Intelligent Assistive Technology Applications to Dementia Care: Current Capabilities, Limitations, and Future Challenges
Dementia is a growing problem in our society. Demented people are hard to care for and need lots of help with even the most basic tasks. This care is expensive and hard to provide, but technology may offer solutions. These solutions are broad in scope and range from sensors to memory aids. In the latter category the aids vary from cooking aids that guide the patients through a recipe to glasses that provide active reminders based on the surroundings or cameras that take photos that can later be used to remember things. The sensors are the most common can be divided into three categories: Physiological, environmental and advanced integrated sensors. The physiological sensors measure things ranging from the patients conditions or if they have fallen, based on which it can alert caretakers. Environmental sensors can be used to detect things that may be a danger to the patients. The advanced integrated sensors can help with the largest variety of things, from simply helping with home security to guiding a patient through washing their hands. While the technologies show promise, this is still an emerging research field and much work still needs to be done. However, these technologies could prove to be very useful in tackling dementia-related issues. [14]
The Use of Technology by the Elderly
The use of technology and its’ providing information allows the elderly to face more easily the difficulties of modern life, trespassing the limits of their social and emotional isolation, thus achieving a more qualitative living. The purpose of this research was to explore whether the elderly were familiar with modern technology. Education of the untrained elderly is the most essential step in order to become familiar with new technologies. More in detail, this can be accomplished through specifically designed education programs that teach elderly the way new technologies work. Furthermore, these programs should be also addressed to individuals who belong to the supportive environment of the elderly such as the younger members of the family. It would be beneficial if the younger helped them to familiarize with each object, removing fears of using high technology devices. [15]
The Use of Everyday Technology by People with Dementia Living Alone
While the technological development available to society is taking quantum leaps, we have little knowledge of how people with mild dementia manage to cope with familiar technology at home, such as television and electronic household machines, or new technology, such as remote controls, cell phones and computers. As this technology represents a potential problem area, the aim of this qualitative, exploratory study was to identify and characterize difficulties with and hindrances to using everyday technology, as they appeared in data, for persons with early stage dementia. The barriers to everyday technology use appeared in four domains: As interfering conditions related to the person, the context and the design of the artefacts, and as limitations in the participants’ knowledge of the technology and its potential, and as difficulties in direct technology use, characterized by communication problems both in understanding and in the administration of the technology. The participants’ use of instructions for use formed the fourth domain.[16]
Technology to Reduce Social Isolation and Loneliness
Large numbers of individuals, many of them senior citizens, live in social isolation. This typically leads to loneliness, depression, and vulnerability, and subsequently to other negative health consequences. This research focused on understanding the communication needs of people in environments associated with social isolation and loneliness, and how technology facilitates social connection. It consists of successive iterations of field studies and technology prototype design, deployment, and analysis. Particular attention is paid to seniors in retirement communities and in long-term care settings (nursing homes). [17]
Loneliness matters: A theoretical and empirical review of consequences and mechanisms
As a social species, humans rely on a safe, secure social surround to survive and thrive. Perceptions of social isolation, or loneliness, increase vigilance for threat and heighten feelings of vulnerability while also raising the desire to reconnect. Implicit hypervigilance for social threat alters psychological processes that influence physiological functioning, diminish sleep quality, and increase morbidity and mortality. The purpose of this paper is to review the features and consequences of loneliness within a comprehensive theoretical framework that informs interventions to reduce loneliness. We review physical and mental health consequences of loneliness, mechanisms for its effects, and effectiveness of extant interventions. Features of a loneliness regulatory loop are employed to explain cognitive, behavioral, and physiological consequences of loneliness and to discuss interventions to reduce loneliness. Loneliness is not simply being alone. Interventions to reduce loneliness and its health consequences may need to take into account its attentional, confirmatory, and memorial biases as well as its social and behavioral effects. [18]
What do community-dwelling people with dementia need? A survey of those who are known to care and welfare services.
The aging society will bring an increase in the number of people with dementia living in the community. This will mean a greater demand on care and welfare services to deliver efficient and customized care, which requires a thorough understanding of subjective and objective care needs. This study aims to assess the needs of community-dwelling people with dementia as reported by themselves and by their informal carers. The study also aims to give insight into the service use and gaps between needs and the availability of services. [19]
Intelligent Technology for an Aging Population: the Use of AI to Assist Elders with Cognitive Impairment
This article surveys new technologies that incorporate artificial intelligence techniques to support older adults and help them cope with the changes of aging, in particular with cognitive decline. [20]
Older Adults' Reasons for Using Technology while Aging in Place
Problem: the use of technology varies considerably among older adults. current models of technology acceptance are missing essential predictors specific to community-dwelling older adults. [21]
Problem: With aging, the risk of dementia, especially Alzheimer’s disease (AD), markedly increases (prevalence of more than 20% at age larger or equal to 80 years). Social activities are most heavily affected by spatial disorientation, which increases the risk of getting lost and exhibiting wandering behavior. Consequently, patients reduce outdoor mobility leading to a more sedentary lifestyle and social isolation, with a primary worsening of the quality of life and with a secondary negative impact on cognitive functions, cardiovascular tone, brain plasticity, and mood. A situation-aware Information and communication technology (ICT) requires a flexible fine-tuning by stakeholders of system usability and complexity of function, and of user safety and autonomy. It should operate by artificial intelligence/machine learning and should reflect harmonized stakeholder values, social context, and user residual cognitive functions. ICT services should be proposed at the prodromal stage of dementia and should be carefully validated within the life space of users in terms of quality of life, social activities, and costs. [22]
The effects of information and communication technologies on informal caregivers of persons living with dementia: A systematic review.
Up to 75% of people living with dementia in the United States are cared for by family members in their homes ICT interventions can improve decision confidence, reduce emotional strain, improve spousal relationship conflict, decrease activity restriction, increase self-efficacy, and decrease caregiver burden. A range of ICT interventions including, telephone-, video-, and computer-based interventions appear to be successfully targeting caregiver support for a range of affective caregiver outcomes, including burden, depression, and anxiety. Telephone technology can be used effectively as a stand-alone intervention or in tandem with other ICTs. [23]
The Use of Information and Communication Technology in Elderly and Patients with Dementia
The goal of this study was to summarize the most common ICT tools, and present the results of the most important clinical studies regarding the use of ICT methods in elderly and in patients with dementia. All findings are documented in two tables. Most notable for us (for reducing isolation/strengthening social network) [24]
Building an app
Snappy appypie
https://snappy.appypie.com/user/app/9537aa4c8602 This is the link to a free app developer. You don't need to write code for this. You can choose from different templates and there can be a lot of editing. Here's an example:
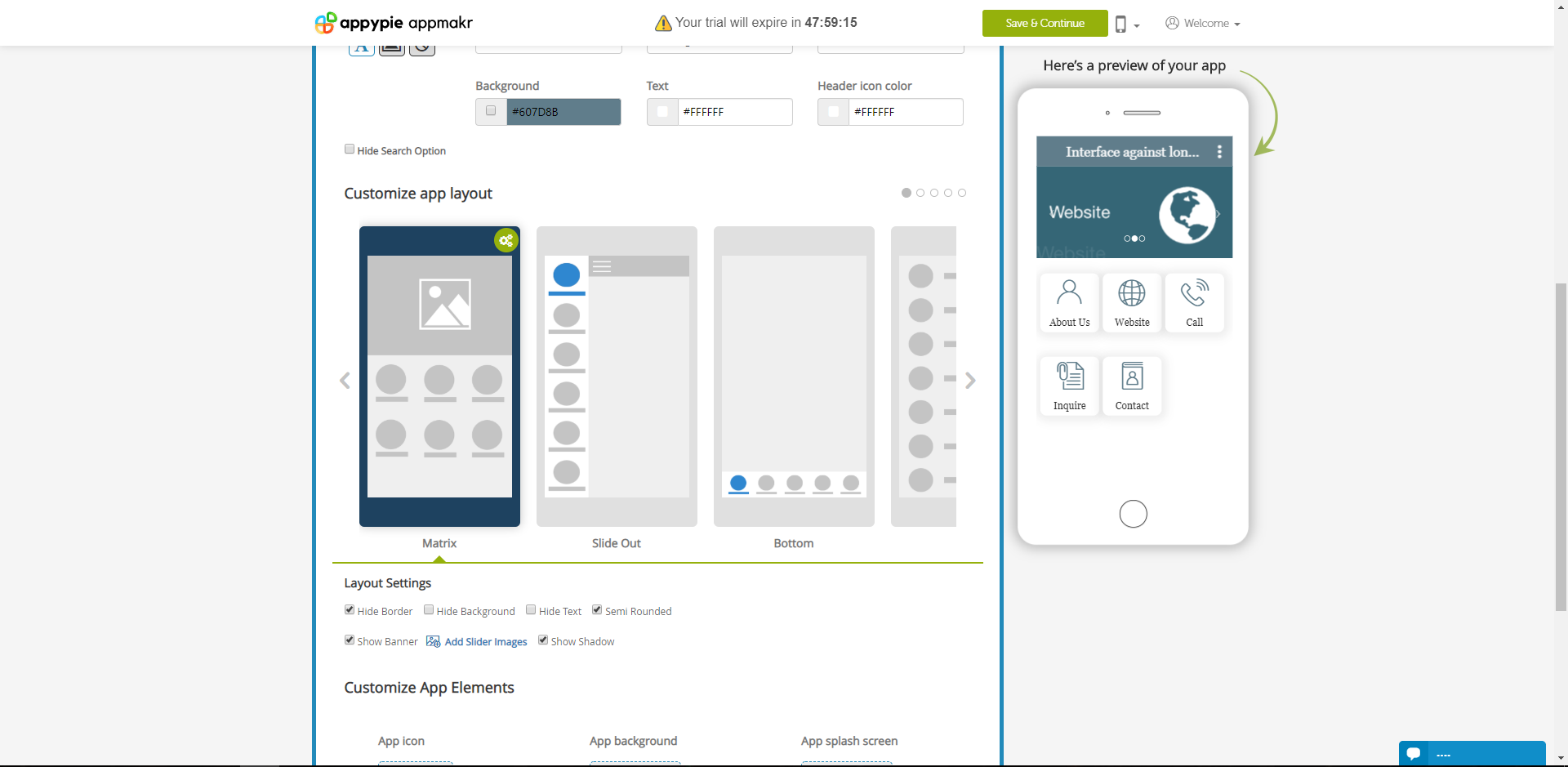
It costs 18 euros per month to use and to develop your app in the App store or Google play. I thought it was a free app developer (apart from the App stores) but it turned out you have to pay 18 euros per month for just developing the app as well.
As stated in one of the articles we found, it is hard for people with dementia to remember how to use the technology. It should be designed as simple as possible. Therefore there should be a "simple" design. We still have to research what this exactly means and conduct user-tests. What we also found was that people with dementia are really sensitive to stress. The design should be as "calm" as possible with no jumping/moving or pop-up objects in the screen. We should also make it as realistic as a physical button for example. So the user should get feedback as it pushes a real button. This could be achieved by changing color or sensation of the screen. It could for example vibrate and change color when the button is pressed. In the article this is stated as 'lack of embodiment of technology'. Older people for example are more used to the movement of writing a letter than typing on a keyboard.
These adjustments might be too hard to achieve in this app developer, because you cannot code it yourself. Therefore it might be more advantageous to work with an app developer that uses simple code.
Adobe Phonegap
In this video Cite error: Invalid parameter in <ref> tag with explanation, the person uses Adobe Phonegap to make an app that you can instantly see on your device. You can edit multiple things and link it to a phone to download.
I tried downloading it twice and it was not working and the desktop application kept loading forever, so this is not an option in my opinion. I looked at forums and a lot of people had the same problems so this seems like an unreliable program.
Good Barber
Good barber is a app maker similar to appypie. It seems to have more customizability though. There is a 30 day trail in which you can test the app and develop it. For us those 30 days are enough so we do not have to get the payed version. Here is a link https://www.goodbarber.com/. And a review https://apptooltester.com/reviews/goodbarber/.
Kivy and python code
In my research, I found multiple sources that used Kivy and then used python code to code a mobile app. Kivy is an open source Python library for rapid development of applications that make use of innovative user interfaces, such as multi-touch apps. Website: https://kivy.org/#home
The advantages of coding your own app are that it is highly customizable and you do not have to deal with other parties like another app develop website when making the app. An advantage of using Kivy is that is allowes the app to display well on every screen size. You can alter the dimensions and the widgets will automatically stay centered. A disadvantage is that none of us have worked with this before. However, I took some time and found a couple tutorials that will help a lot.
The first video Cite error: Invalid parameter in <ref> tag is part of a series by Tech with Tim on YouTube which takes you through all the little steps of app making. The second helpful tutorial Cite error: Invalid parameter in <ref> tag helped in setting up the programs that you need and together the two tutorials allowed me to make the first steps of an app.
Details
I needed Python version 3.7.1 for this to work. I also downloaded Pycharm for the code. This is what both videos use. This is a texteditor where you can write the code. You need to know object oriented programming to do this. On the Kivy website there was some info about that and the first video from Tech With Tim mentions that he has some tutorials as well on his page.
Progress
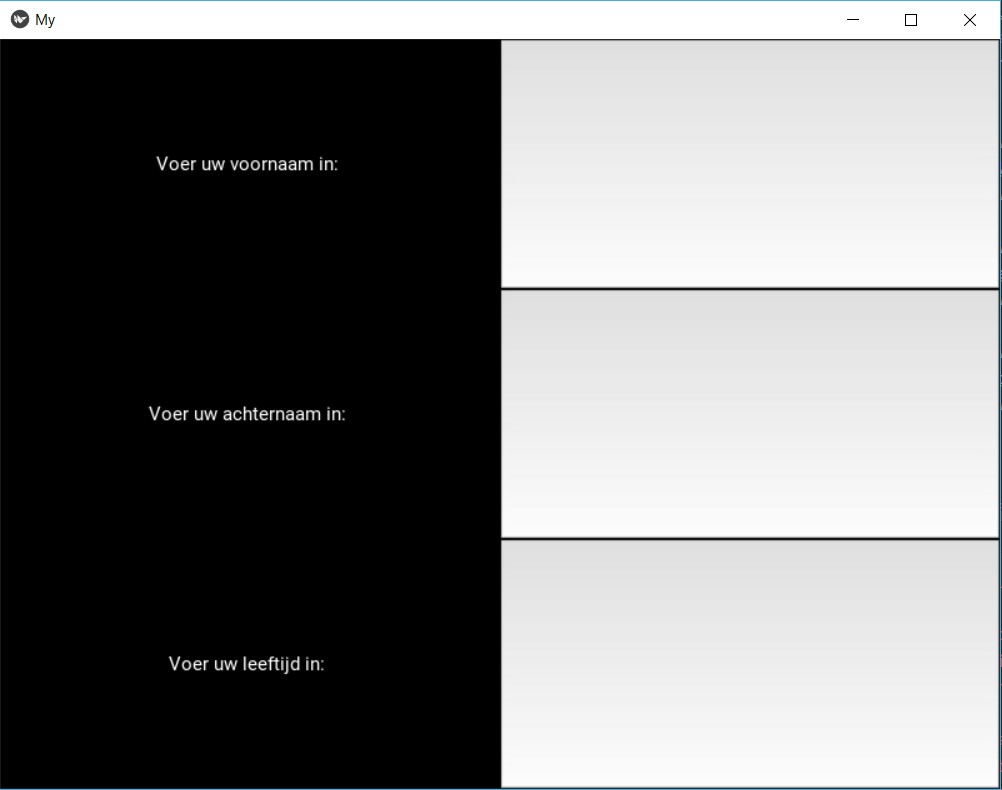
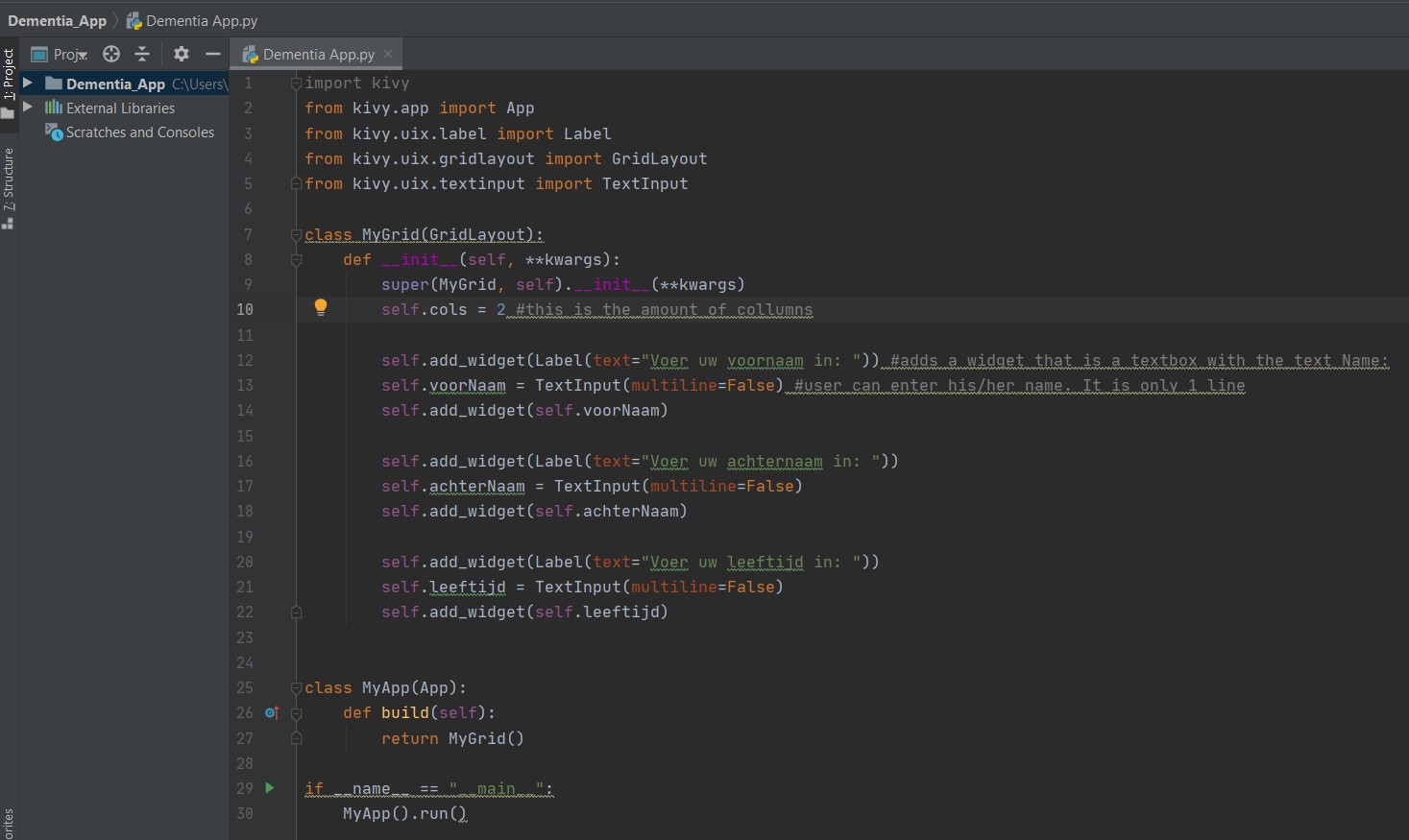
At the end of the second tutorial I was able to make an app that allows the used to put in his or her personal information in text boxes. The following images show the app screen and the code.
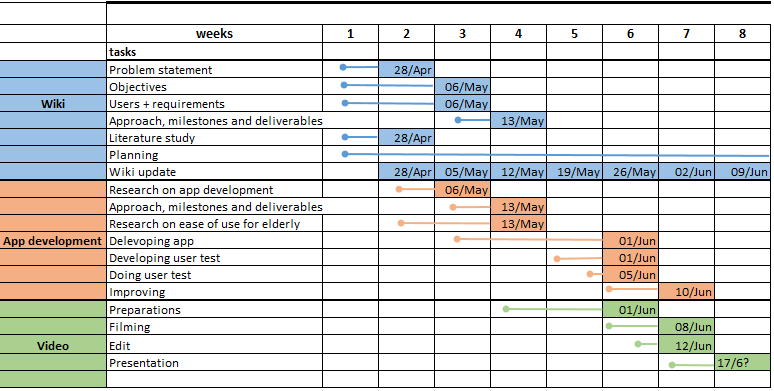
Planning
| Week | Tasks to start | Intermediate Deadlines | All | Eline | Iris | Metten | Sterre | Vera |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (20-4) / 26-4) | Articles - First plan | Articles - First plan | Read and summarize at least 25 papers, set up first plan | Wiki update | ||||
| 2 (27-4 / 3-5) | Research on app development - Research on ease of use for elderly | First plan worked out | Wiki update | Problem statement | Planning | Objectives | Users and requirements | State of the Art update |
| 3 (4-5 / 10-5) | Approach, milestones and deliverables - Developing App | Objectives worked out | Wiki update | Information and plan for building an app | Information and plan for building an app | Improving Objectives | Improving Objectives | Improving Objectives |
| 4 (11-5 / 17-5) | Preparations video | Approach, milestones, deliverables - Research ease of use for elderly | Wiki update | |||||
| 5 (18-5 / 24-5) | Developing user test | Wiki update | ||||||
| 6 (25-5 / 31-5) | Analysis and improve app - Filming and later on edit | App finished - User tests done - Preparations video done | Wiki update | |||||
| 7 (1-6 / 7-6) | Preparing presentation | Improving done, Video finished | Wiki update | |||||
| 8 (8-6 / 14-6) | Presentation | Wiki update |
Time management
Week 1:
| Name | Student number | Time spent | Break-down |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eline Visser | 1375369 | 11 hours | Introductory meeting and study guide + group formation (2h) 2 group meetings (1.5h) Think of ideas and do research + read old wikis (2.5h) Learn how to edit wiki and make start on page (0.5h) 5 articles literary study and summary (4.5h) |
| Metten de Lange | 1240902 | hours | |
| Vera Holtmark van Dijkerhof | 1380893 | 13 hours | Introductory meeting and study guide + group formation (2h) 2 group meetings (1.5h), reading wiki pages of previous groups (1.5h), reading 5 articles (6h), summarizing articles (2h) |
| Sterre Cuppens | 1387790 | 11 hours | Introductory meeting and study guide + group formation (2h) 2 group meetings (1.5h), Literature research (5 h), Summarize articles, (2 h) Update wiki (0.5 h) |
| Iris de Wit | 1258230 | 11 hours | Introductory meeting and study guide + group formation (2h) 2 group meetings (1.5h), reading wiki pages of previous groups (1.5h), reading 5 articles (6h), summarizing articles (2h) |
Week 2:
| Name | Student number | Time spent | Break-down |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eline Visser | 1375369 | 6 hours | Summaries on articles (1h) Wiki problem statement (3h) Meeting tutor + Group (1h) Watch videos on how to make an app (1h) |
| Metten de Lange | 1240902 | hours | |
| Vera Holtmark van Dijkerhof | 1380893 | 5 hours | Updating summaries and references of articles (2h), meeting with group and tutor (1h), reading article and rewriting requirements with obtained information (2h), |
| Sterre Cuppens | 1387790 | 9 hours | Meeting (1 hrs), Updating references and summaries of articles (1 h), Types of users (3 h), User requirements (3 h), Update wiki (1 h) |
| Iris de Wit | 1258230 | 6 hours | Meeting (1 hrs), Updating references and summaries of articles (1 h), making three different plannings (one over all, one for tasks and one scheme in Wiki) (3 h), Update wiki (1) |
Week 3:
| Name | Student number | Time spent | Break-down |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eline Visser | 1375369 | 8 hours | Research on app making. (2h) Practice with python and Kivy (3h) Documenting the process (1h) Editing the wiki (1h) More research in appypie and app makers after the meeting with tutor. (1h) |
| Metten de Lange | 1240902 | hours | |
| Vera Holtmark van Dijkerhof | 1380893 | hours | |
| Sterre Cuppens | 1387790 | 8 hours | Meeting (1 h), Read articles again (2 h), Improve user requirements (4 h), Update wiki (1 h) |
| Iris de Wit | 1258230 | hours |
References
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Cahilla, S., Macijauskieneb, J., Nygårdc, J., Faulknera, J., & Hagend, I. (2007). Technology in dementia care. Technology and Disability, 19, 55–60. Retrieved from https://content.ios.press.com/download/technology-and-disability/tad00227?id=technology-and-disability%2Ftad00227.
- ↑ Miskelly, F. (2001). Assistive technology in elderly care. Age and Ageing, (30), 455–458. Retrieved from https://watermark.silverchair.com/300455.pdf.
- ↑ Prezza, M., Pacilli, M. G., & Dinelli, S. (2004). Loneliness and new technologies in a group of Roman adolescents. Computers in Human Behavior, 20(5), 691–709. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2003.10.008.
- ↑ Bemelmans, R., Gelderblom, G. J., Jonker, P., & de Witte, L. (2012). Socially Assistive Robots in Elderly Care: A Systematic Review into Effects and Effectiveness. Journal of the American Medical Directors Association, 13(2), 114-120.e1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jamda.2010.10.002.
- ↑ Kaspar, R. (2004). Technology and loneliness in old age. Gerontechnology Journal, Vol 3(No 1), 42–48. Retrieved from https://journal.gerontechnology.org/archives/324-326-1-PB.pdf.
- ↑ Vogelsmeier, A. A., Halbesleben, J. R. B., & Scott-Cawiezell, J. R. (2008). Technology Implementation and Workarounds in the Nursing Home. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association, 15(1), 114–119. https://doi.org/10.1197/jamia.m2378.
- ↑ Zhang, H., Wang, Z., Wang, J., Lyu, X., Wang, X., Liu, Y., … Yu, X. (2019, January 31). Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6355814/.
- ↑ van de Watering, M. Retrieved from http://marekvandewatering.com/texts/HCI_Essay_Marek_van_de_Watering.pdf.
- ↑ Ferrel, B.A. Ferrel, B.R. Rivera, L. (1995, November 8).
- ↑ Van der Roest, H.G. Wenborn, J. Pastink, C. Dröes, R. Orrell, M. (2017, June 11). Retrieved from https://www.cochranelibrary.com/cdsr/doi/10.1002/14651858.CD009627.pub2/abstract.
- ↑ Dogruel, L., Joeckel, S., & Bowman, N. D. (2015). Retrieved from https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/0144929X.2015.1077890
- ↑ Ashok J. Bharucha, Vivek Anand, Jodi Forlizzi, Mary Amanda Dew, Charles F. Reynolds, Scott Stevens, Howard Wactlar (2009) Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2768007/
- ↑ Roupa, Z., Nikas, M., Gerasimou, E., Zafeiri, V., Giasyrani, L., Kazitori, E., & Sotiropoulou, P. (2010). The use of technology by the elderly.Retrieved from Health Science Journal.
- ↑ L. Nygård Ph.D. & S. Starkhammar (2007) The use of everyday technology by people with dementia living alone: Mapping out the difficulties, Aging & Mental Health, 11:2, 144-155, DOI: 10.1080/13607860600844168.
- ↑ Hawkley, L. C., & Cacioppo, J. T. (2010). Loneliness matters: A theoretical and empirical review of consequences and mechanisms. Retrieved from Annals of Behavioral Medicine. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12160-010-9210-8
- ↑ .. Van Der Roest, H. G., Meiland, F. J. M., Comijs, H. C., Derksen, E., Jansen, A. P. D., Van Hout, H. P. J., … Dröes, R. M. (2009). What do community-dwelling people with dementia need? A survey of those who are known to care and welfare services. Retrieved from International Psychogeriatrics. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1041610209990147
- ↑ Pollack, M.E. (2005). Intelligent Technology for an Aging Population: The Use of AI to Assist Elders with Cognitive Impairment. Retrieved from AI Magazine, 26, 9-24.
- ↑ (cite: Peek S, T, M, Luijkx K, G, Rijnaard M, D, Nieboer M, E, van der Voort C, S, Aarts S, van Hoof J, Vrijhoef H, J, M, Wouters E, J, M: Older Adults' Reasons for Using Technology while Aging in Place. Retrieved from Gerontology 2016;62:226-237. doi: 10.1159/000430949) https://www.karger.com/Article/FullText/430949
- ↑ Lucero, R. J., Fehlberg, E. A., Patel, A., Bjarnardottir, R. I., Williams, R., Lee, K., Ansell, M., Bakken, S., Luchsinger, J. A., & Mittelman, M. (2018). The effects of information and communication technologies on informal caregivers of persons living with dementia: A systematic review. Alzheimer's & dementia (New York, N. Y.), 5, 1–12. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trci.2018.11.003 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6315277/
- ↑ Retrieved from https://www.researchgate.net/publication/326323900_The_Use_of_Information_and_Communication_Technology_in_Elderly_and_Patients_with_Dementia