PRE2018 4 Group6: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
=== Interview === | === Interview === | ||
The interview questions can be found and the minutes of the interview can be seen in [[PRE2018_4_Group6_Interview|here]]. | We will try to interview do an interview with someone from Rijkswaterstaat, so that we can present our ideas and receive feedback for our idea. The interview questions can be found and the minutes of the interview can be seen in [[PRE2018_4_Group6_Interview|here]]. | ||
== Problem statement == | == Problem statement == | ||
Revision as of 20:01, 25 May 2019
Group members
| Name | Student ID | Department |
|---|---|---|
| Tom Vredenbregt | 1221775 | Applied Physics |
| Jur Kappé | 1252895 | Applied Physics |
| Jannes van Poppelen | 1238120 | Applied Physics |
| Yannick de Jong | 1250663 | Applied Physics |
| Thom Smits | 1227659 | Applied Physics |
Organizational Matters
Task division & Planning
A planning has been made which we are supposed to stick to during the project. In this planning most of the things we have defined to be important/crucial for this project are mentioned. Aside from work on the wiki page, which everyone will do, the tasks are mostly divided amongst the group. The main focusses of the group are:
- Yannick: The simulation and making the solution smart.
- Thom: Analysis of the USE stakeholders, ethics.
- Tom: Mathemathics of the solution and creating of the model.
- Jur: Finding data, and analysing it, helping out Yannick.
- Jannes: Responsibility, Law, analysis use stakeholders.
Minutes
Throughout the course the group will have official meetings. A summary (minute) of what has been said/achieved in every meeting will be made. These summaries can be found here.
Agendas
Like the minutes, the agendas made by the chair will be published. The agendas for the meetings can be found here.
Interview
We will try to interview do an interview with someone from Rijkswaterstaat, so that we can present our ideas and receive feedback for our idea. The interview questions can be found and the minutes of the interview can be seen in here.
Problem statement
The implementation of smart traffic lights in big cities reduces the travel time substantially. Whilst this makes the traffic flow more efficiently in the cities, a different solution has to be found to improve the traffic flow on highways. The ever increasing amount of traffic jams during the peak hours in the Netherlands(https://www.anwb.nl/verkeer/nieuws/nederland/2019/april/lichte-filegroei-in-eerste-kwartaal) is a call to arms to find solutions to this time-consuming phenomenon known as traffic congestion. One of these solutions is the routing of navigation systems that changes based on the activity on the highways. Traffic jams would be avoided by rerouting the navigation to go around the traffic jams, should it be the faster alternative. Of course, this solution is one of many, and it will contribute minimally on its own to the general problem. A different potential solution could be to simply add more lanes to each highway. Not only would this be very excessive outside of the peak hours, but it also would not be very cost- nor time efficient. For this reason, we propose to look for a solution in which we would optimize and change the current highways to a state in which it can, in fact, improve traffic flow in general. This solution we are proposing is the so-called "smart road". These lanes will adapt dynamically to the activity of both sides of the highway, as will be clarified visually later on. During morning peak hours, lanes highways towards big cities are usually very busy, whereas the lanes on the opposite side aren't that busy at all. Being able to distribute the lanes such that both sides would have a sufficient amount of lanes would benefit the traffic flow. The opposite directions would apply for evening peak hours. This solution would not only improve the traffic flow on highways during peak hours, but it would serve as a basis for the traffic flow outside of the peak hours. Coincidentally, this would also substantially reduce the emission that cars produce in traffic jams by continuously stopping and driving off. Central to this problem would be to research the question: Is the introduction of "smart roads" on the Dutch highways a viable solution to traffic congestion on Dutch highways?
Approach
Producing an actual prototype for a smart road in 8 weeks seems rather unlikely. Instead, the problem will be tackled by literature analysis, as well as a simulation of a smart road using a mathematically developed model. The final product for the project would, therefore, be a combination of a report about the literature analysis, together with the analyzed simulation of the smart road.
The literature analysis will include the USE aspects of the selected problem and an analysis of the present state of smart roads. In-depth analyses for user, society and enterprise stakeholders will be made. Since smart roads are designed to accommodate the users' needs, the focus will be on the user, its needs, and how to satisfy them.
The simulation of the smart road will be constructed using a mathematical model. Central in this mathematical model is a constructed norm which determines the orientation of the smart road. This norm is based on lane occupation on each side of the highway, as well as the time of the day to account for the peak hours. Whenever this norm is exceeded, the smart road will change in such a way that this norm is no longer exceeded. There is a couple of things that need to be accounted for in the simulation. One of which is the possibility of accidentally ending up on the wrong side of the highway as a result of the smart road adapting to its surroundings.
Rough description of the USE stakeholders
In the case of smart roads, the following stakeholders in the USE frame can be defined. The stakeholders in the case of smart roads are:
Users
- Commuters (people who use the roads to go from their residence to their work)
- Leisure traffic (people who use the road for travels to the vacation or a day out)
- Public transport (as example buses and taxis)
- Residents living next to the roads (requirement: good traffic flow for a minimum noise problem)
Societity
- Government (the Dutch government is responsible for the maintenance and construction of the roads)
- Rijkswaterstaat
- Environment action groups
Enterprise
- Transport (transport of goods with use of lorries or other heavy traffic)
- Rijkswaterstaat (the active maintenance of the roads)
Requirements
The defined stakeholders and users in the list above have certain requirements in the case of smart roads. The requirements for each stakeholder can be found in the list below.
USERS
Commuters -> Commuters need well-maintained roads with enough lanes such they roads won't get jammed at rush-hour. Commuters use the roads to get to work. In the case that the roads get jammed, the commuters will be late on work or have to depart much earlier. But options are temporary, so the requirements for commuters are well accessible well-maintained roads which won't get jammed at rush-hour (between 07:00-09:00 and 17:00-19:00).
Leisure traffic -> Leisure traffic is traffic which uses the roads for pleasure purposes. The requirements for leisure traffic is the same as the requirements for commuters. The only difference is when the roads are needed. For leisure traffic, the roads need to be accessible around the weekends and vacation days.
Public transport Again the requirements are the same as the requirements mentioned above.
To conclude the requirements for the USER stakeholders are in general the same. The requirements for the USER are well accessible and well-maintained roads.
Society
Goverment -> Because roads are constructed from taxes money, is it key to keep it as cost efficient as possible. Another requirement for the government is that roads are well-useable. (ik heb echt geen idee)
Environment action groups -> These groups are fighting for less emission which is better for the milieu. This can be obtained by fewer cars on the (which isn't likely to happen) or better traffic flow such that there is less emission.
Enterprise
Transport traffic -> The requirements for transport traffic are well-maintained and accessible roads. An important note is that an important requirement for transport traffic is that it won't bother other road users. If transport traffic bothers road users, then the requirements of the above-mentioned users become in danger.
Rijkswaterstaat -> The requirements of for the maintenance of the road (rijkswaterstaat is responsible for the maintenance) is that the smart won't be too expansive to construct and not too expansive to maintain. So it is a requirement to keep the smart roads as simple as possible. If the smart road is simple, then maintance and the construction is in the scope of the construction workers.
Exact description of the USE stakeholders
As described in the section above ("rough description of the USE stakeholders") there are many groups of stakeholders which use the road. In this section, there is a better description and clarification of the defined stakeholders. The determined stakeholders are based on the sources about the chosen road and on defined stakeholders in section "rough description of the USE stakeholders". The percentages of the road users can be seen in figure (nog toevoegen).
Stakeholder
The first major stakeholders are commuters. Commuters are people who have to travel their living place to their workplace. Form the literature (bron toevoegen) it can be seen that (gekozen weg) is the connection between Amsterdam and the rest of the Netherlands. So it can be concluded that between 07:00 - 09:00 and from Monday up to and including Friday the road would be mainly used in the direction of Amsterdam (bron tegen aan gooien). The second important time period commuters use the road is around 17:00-19:00 on the same days. In this period most commuters will travel away from Amsterdam. As can be seen in the literature, the traffic jam (spits) causes by commuters is solvable through a simple solution (as for example an extra lane with gates at both ends). By designing the "'smart road" it is advisable to take these solutions into account. It is also advised to not defined the commuters as the main stakeholders by designing the "smart roads"
The second major stakeholders are traffic caused by transport. As can be seen in the literature the most common form of transport traffic is (heb hier bronnen voor nodig).
The third group of stakeholders are public transport. For the "smart road" public transport can be divided into two groups: scheduled transport, unscheduled transport. The first group (scheduled transport) is the larges group. The first group is the easiest in the problem of "smart roads", because of the schedule it easy to takes these into account. Secondly, public transport (like busses) are divided on the road. Because of the schedule of buses, it shouldn't be that multiple busses are presented at the same location at the same time. These two arguments based on the schedule it can be concluded scheduled public transport would not be the main focus by designing "smart roads". The second group is a negligible small group.
An important group of stakeholders are the people going on vacation. Here we have "heavy" vacation traffic and "light" vacation, here "heavy" vacation traffic are caravans and motorhomes. The "light" vacation traffic is the remaining vacation traffic. Because (gekozen weg) has a speed limit of 130 km/h "heavy" vacation traffic has a speed limit of at most 90 km/h. This speed is substantially different. In the case that a large group of "heavy" vacation traffic is going on the road at the same time (as for an example the dutch "zwarte vrijdag"), the road can get clogged. Vacations days are planned, this makes it possible to make a rough estimation. A possible case is that a large group of "heavy" vacation traffic and "light" vacation going on the road at an unpredictable time. By designing the "smart roads" vacation traffic is an important group to look at.
A common group of stakeholders are day trippers or other people who use the road for their own purpose. This group of stakeholder can be seen as negligible. The mentioned group of stakeholder is not likely to get on the road at a great density. Because of this, this group of stakeholders would not load the traffic flow in such a way that the road becomes stuck because of them
Last important stakeholder is the government. The Dutch government is responsible for maintaining and to construct the roads. It is important to take into account that the designed solution is not too expansive and not to technology hard to maintain. A too expansive "smart road" is not a feasible solution. An expansive "smart road" is possible for small local roads, but not for roads of large highways. For this research, it is looked at (gekozen weg) and the possibility of implementing the "smart road" on comparable roads. Secondly, the roads are paid form tax money. Impossible expansive roads would cost the taxpayer too much, such that the taxpayer would not accept it.
For the maintenance of the roads is Rijkswaterstaat. A road which is completely based on technology would require highly skilled maintenance staff (which again would be expansive to obtain). Also, the maintenance of the road would take a lot of time. At the moment road maintenance is (note this is a heavy simplified view) depositing concrete and painting the road stripes. When technology is heavy blended with technology, it would require a lot more preparation time (determining where what is) and more refined work. Form this is important that the "smart road" is designed such that it isn't technological to difficult.
Constraints
Form the described stakeholders above (see the section Exact description of the USE stakeholders) there constraints on which the "smart road" should obey. These constrain are important by designing the "smart road". The two major stakeholders form which constraints can occur are the governments (the law) and the maintainer of the road (rijkswaterstaat). These two are coupled.
Constraints from the law
The in the Netherlands there are certain laws and rules about the infrastructure and highways. One of these laws is the so-called wegenverkeerswet, form these laws the following list of constraints arise
- The maximum and minimum speed at highways. The maximum possible speed at highways is 130 km/h the minimum accepted speed for road users is 50 km/h (from https://www.rijksoverheid.nl/onderwerpen/verkeersregels/vraag-en-antwoord/wat-is-de-minimumsnelheid-voor-het-wegverkeer and https://wetten.overheid.nl/BWBR0001948/2017-09-01). Form this the speed constrain arise, the solution should not go faster than the minimum speed. If barrier change has a speed higher than the minimum speed, some road users can get in problems when for instance they try to overtake other road users. So form this it can be concluded that
v_(barrier) < v_(minimum)
With v_(barrier) the speed the barrier changes lanes and v_(minimum) the lowest accepted speed on highways.
- The second constrain arise from the wegenverkeersweg article 14 (see https://wetten.overheid.nl/BWBR0001948/2017-09-01).
Constraints from the maintainer
The interview questions can be found and the minutes of the interview can be seen in here.
(These constraints will get clearer after the interview with the maintainer (rijkswaterstaat). These will be contacted after the meeting of 20-5-2019, after which the focussed road will be chosen).
(Het is mij niet helemaal duidelijke waar de wetten kunnen gaan schuren, ik zou dit morgen even na vragen tijdens de tutor meeting)
Driver analysis
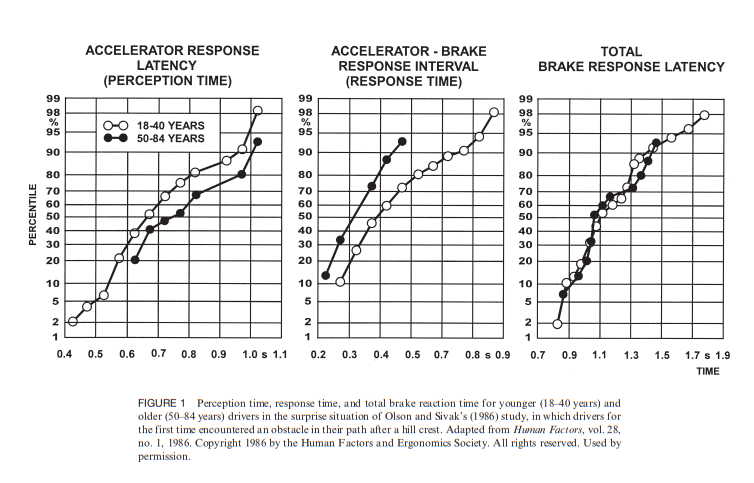
To simulate a road with traffic, a general idea of a basic human driver has to be implemented in code. In this simulation, it is assumed that everybody has an average response time with a slight (random) deviation each time. This response time is set to 1.4 seconds which is the 90th percentile according to this figure:
The random deviation that is taken is between -0.3 and 0.3 seconds, resulting in a final response time between 1.1 and 1.9 seconds
Improving traffic flow
Several concepts could be implemented to improve traffic flow on highways. Some are dynamic, meaning that the lane division of the road will change with the amount of vehicles on each side of the road, whereas other are stationary, thus will not the change the lane division, and don't exhibit any kind of element a smart road would have. Several of these concepts will be analysed below. This analysis will provide a basis for the quality of each concept (to what extent the concept actually solves the problem). Moreover, it will also demonstrate that our selected option is the most viable one around. One thing to note considering the problem is that adding more and more lanes on either side of the road is not a solution. This would be quite an expensive and environmental irresponsible alternative, which is not desired.
Carpool lanes
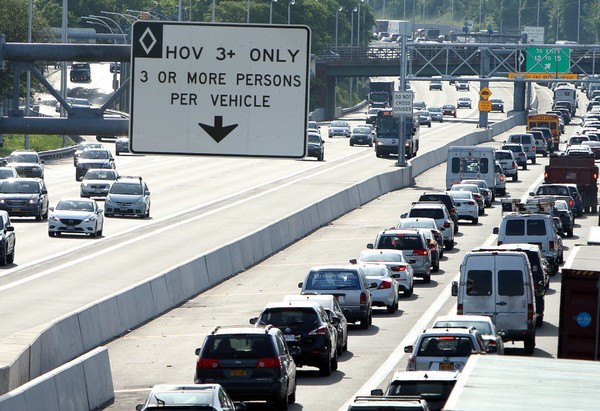
Carpool lanes (also sometimes called HOV-lanes) have already been around for a long time. They originate from the United States and Canada, but have also been present in Europe for quite a while (A1 Highway Netherlands, 1993). Their purpose is to minimize traffic congestion by allowing an extra lane for cars having multiple passengers. With the introduction of carpool lanes was also the intention to reduce the distance travelled by vehicles and thus minimize air pollution. It does not change the lane distribution, but instead adds an extra lane. It therefore would be a stationary solution to the main problem.
Figure ... Current day carpool lane on a busy interstate in the United States.
Since it has been around for quite some time we will not have to speculate about its effictiveness. The introduction of carpool lanes in the United States was said to reduce traffic congestion, but to what extent is this actually the case? Analysis of traffic data obtained in California disproves the claim [21]. Whilst this is just one example, it certainly is not the only one. First and probably most crucial is the fact that carpool lanes are heavily underutilized. Traffic flow and lane capacity during peak hours(the amount of vehicles passing a detector per hour per lane) is substantially lower than what is promoted. California Department of Transportation consider the traffic flow to be 1650 vehicles per hour per lane, but 80% of the samples are a marginable amount below this. So much less vehicles drive on carpool lanes compared to regular lanes. Furthermore, travel time that is saved by utilizing carpool lanes is rather small.
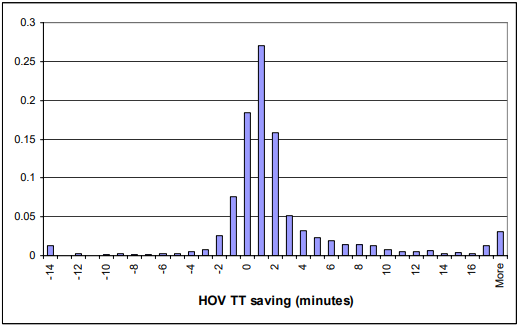
Figure ... Probabilty distribution of HOV travel time savings over a 10-mile route.
As can be seen from the figure above, the time save is minimal. The mean time saved is only 1.7, which is not so desirable as it will bare have an impact. A more desirable time save would be anywhere between five and ten minutes. However, the probability for the time save to be greater than 4 minutes is only 0.19, which is not that promising. On top of that, the small time save obtained by carpool does not encourage others to start carpooling. The analysis also concludes that the reduction of traffic congestion by the carpool lanes is almost negligible if regular lanes are allowed to be loaded with cars.
Carpool lanes therefore a rather poor solution to traffic congestion. They are merely usuable during the peak hours, as they lose their purpose outside of them, whenever it is not busy on the highways. Carpool lanes are a rather costly investment that would reduce congestion minimally and therefore would definetly not be the most optimal way to tackle the problem.
Stationary road barrier (slagboom-ish)
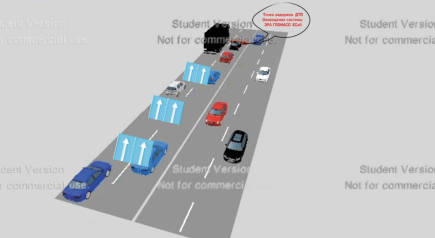
A different approach to reducing traffic congestion could be a stationary road barrier on each side of the road. Eventhough the barrier itself would be stationary, it will still have dynamic elements. Its implimentation is being experimented with in the United States already (apparently. bron + plaatje zoeken ). This system works well because of one lane that is in the middle of both sides of the road. This lane can be made available for either side whenever it is necessary to do so. Think for example about its use during peak hours. The extra available lane that is provided by this system for the direction in which it is necessary could improve traffic flow to such an extent that it will prevent any traffic jams.
(hier schets van systeem toevoegen)
This system (assuming one long extra lane) could theoretically also work in both directions of the road, just as carpool lanes do, but there is just one lane available. The edge this system has on carpool lanes is that it only requires the availability of one extra lane, instead of two lanes, which will reduce its cost substantially. Like carpool lanes, its most optimal use would be during peak hours, when it is quite busy on the roads. This system can also be used outside of the peak hours. It is not the most optimal, however. As only one side of the road can use the extra available lane at the time, the transition of the driving direction on the extra lane will not be the smoothest. To do this, first the lane has to be closed off for the side of the road it is made available for. Following that, the entiterity has to be cleared. Only after that has been done, the barrier for the other side can be opened. This process is quite time consuming, and thus is not the most optimal.
One way this could be solved would be to divide the lane into parts. This would allow for both directions to utilize the lane at the same time, at different locations. Eventhough the problem of transitioning is still there, the time it takes could be substantially reduced, which would allow for a more efficient traffic flow.
This system certainly can be a viable solution to the problem. It has the possibility to prevent traffic jams (or at least minimize the length of traffic jams), during and even outside of the peak hours. For the latter still a smooth way of transitioning has to be come up with but it certainly has potential. While it would be a better solution than carpool lanes, it still is not the most optimal one.
Movable barrier system
Movable barrier systems are a very promising dynamical solution to lane management on highways. These barriers are designed in such a way that they increase the capacity on the road by using the existing lanes and redistributing them, all whilst minimizing traffic congestion. This system is similar to the stationary barrier in the sense that both sides of the road can utilize the same lane, but at different times. Both sides of the road are seperated by a movable line of concrete barriers. These barriers can be moved in such a way that an extra lane will be made available to the side which needs it.
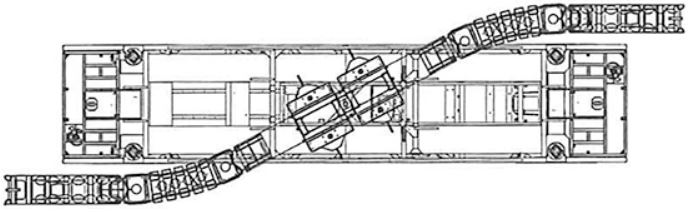
Figure... A barrier moving machine in action.
Currently, the only way to move these barriers is by using big machinery. The barriers are T-shaped concrete blocks, which are linked together. The machine then lifts the barriers up from the road, and passes them through its conveyor part.
The conveyor part can transfer up to 7.3 meter of barrier at once. When the part of the barrier is at the desired location, the barrier is gently placed on the road, such that it will not get damaged.
Instead of just having one lane to divide between both sides of the roads, this system can be used much more freely, as shown below.
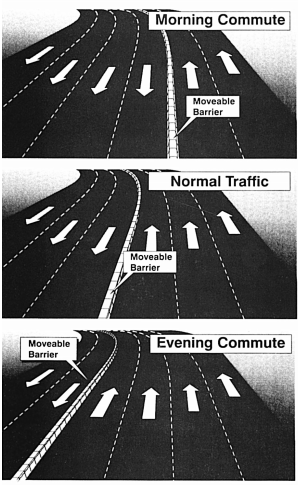
Figure... Visualisation of the freedom of the barrier movement system. Credit: Rob Bain (http://www.robbain.com/Moveable%20Barrier.pdf)
In the picture, three different lane distributions can be seen, depending on the time of the day. The barrier can be moved in such a way that it accomodates both directions of the road. Starting the redistribution timely can completely prevent any traffic congestion during peak hours. For this to work, the road needs to have a lot of lanes. An example of such a road would be the A2 between Utrecht and Amsterdam. The system could also be applied outside of peak hours to improve the traffic flow. Since the behaviour on the road is hard to predict, the speed of the machine matters a lot.
If instead of big machines, this barrier system could be automated, it could also be applied over much longer distances, and it would happen much faster. Automation of the barrier system will cut the time it takes to redistribute the lane tremendously. Since the movable barrier system has not been introduced for a long time, automation will be a long term goal in the future and thus might take a while.
The movable barrier system has a lot of potential. When the system is used on time for the bigger highways it can seriously improve traffic flow. The only drawback it has from being actively used is the amount of time it takes to move the barriers. As of now, this process is rather slow, but once it speeds up, this system can be a good solution to traffic congestion.
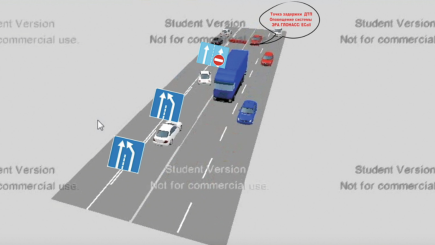
Flexible lines
A somewhat similar solution to the movable barriers is using flexible lines. These are lines that can be changed from straight to broken lines, and vice versa, to indicate the lane distribution of the road. A straight line would indicate where the travelling directions are seperated, and broken lines would be used to indicate where the lanes are seperated from eachother, just like what is currently the case, too. A visualisation can be seen below.
Figure ... Visualisation of a road with flexible lines. The effect of the flexible lines can not yet be seen.
A system like this will be superiour to the movable barrier system in a lot of ways. The time it takes to move the lines is substantially lower than the time it takes to move the barriers. This would already solve one of the problems that the movable barrier had. The short time it will take to the redistribute the lane makes the flexible lines very flexible. One instance this could be used is to timely indicated any obstacles on the road for example.
Figure ... Visualisation of a road which had its lines changed in order to redistribute the lanes.
Since the presence of the obstacle can be detected on time, the lines can be changed in such a way that the car can avoid it on time, thus preventing any possible congestion.
Just like all other mentioned systems, the flexible line system can be used to redistribute the lane division during the peak hours, to prevent any congestion and to improve the traffic flow. Even outside of the peak hours this system can be used to improve traffic flow at areas where it needs improvement.
The introduction of a system as such does come with its disadvantages. The barrier system had a barrier two seperate both the directions of travelling traffic. Since this system can redistribute the road into any configuration, the travelling directions can not be seperated but by a line. This ofcourse is rather dangerous on a road where vehicles move with high speeds. A different issue is to determine what the lines will be made of. It needs to be something which does not take a long time to change. Concrete barriers will not work. One possibility could be using lights. This again would impose some difficulties. Using lights would only work whenever it is dark outside. A different alternative would have to be found during the day, which still passes all constraints.
Flexible lines are a promising solution. It is definetly one of the better solutions against traffic congestion, but it comes with its difficulties. If a solution to these difficulties has been found it will surely be the better solution out of all the ones previously mentioned.
Final solution
Solution description
During the meeting on 17-05, we eliminated some potential solutions for the congestion problem. Neither carpool lanes, nor the stationary road barrier seemed like the most optimal solution for this problem. Instead, the latter two out of four have been chosen, an best of both solutions are combined to create what we believe will be the most optimal way to decrease traffic congestion.
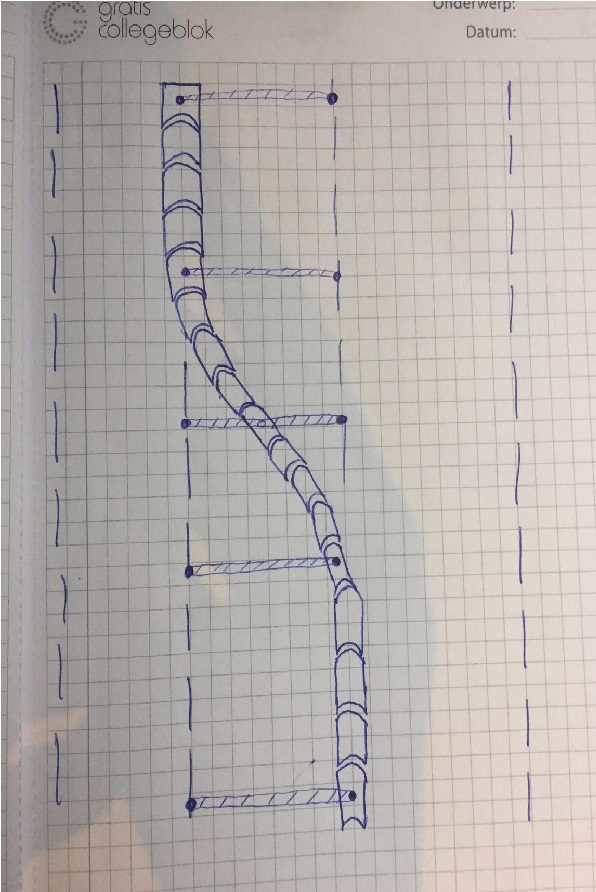
The design combines the concepts of the flexible lines and the movable barrier system. One flaw that was present in the flexible lines concept was how to actually draw the lines between the lanes. We figured that implementing the concrete barriers, the same ones as from the movable barrier system, could work out quite well. This would also mean that the big machine that moves the barriers would be obsolete. We wanted the barriers to move independently. The barriers, again with dimensions like such[1], would be placed on some sort of rails in between the lanes. A visualization of the concept can be found below.
Some parts of the barrier (pivots), would be able to move horizontally over the road, which would cause the other barriers, attached to these pivot barriers, to follow them. The barriers would sort of move like a snake in between the roads. After the pivot barriers move horizontally and have reached their destination, the barriers lock in place.
A concept like this is very dynamical, in the sense that it can be applied according to the situations on the road. Its application is not just limited to peak hours, but it can even be used to reduce congestion outside of them, when applied timely. It takes best of both of our concepts, and combines them to create the most optimal solution. It is very flexible, and it can be used much more faster, and thus also more efficient than the big machine that would independently move the barriers, at a rather slow pace. This concept also comes with its constraints:
- The number of lanes for which this concept can be applied is at least 3. In this case it would only have one extra lane to divide between both sides of the road. The distribution of the lanes will be more optimal if there are more roads available which the system can be used.
- The system needs to be powered. The concrete barriers can not move by themselves. Since we no longer want them to be moved by a big machine, they need to be powered, and some movement mechanism has to be come up with.
- The speed at which the barriers move must be below maximal value. When the speed at which the barriers move is too fast, other vehicles can be cut off, which could cause dangerous situations.
Ethics & Responsibility
Ethical consideration
In order to take the considerations of the users into account, ethical consideration is made. This is done such that by designing the smart road, the users' constraints and requirements are not forgotten. For the other stakeholders, it is possible to get contact and obtain their requirements and constraints. With the use of the coming ethical consideration (on the basis of the utilism and Kantism) it possible to view what is possible and what isn't possible in other to keep the users in mind.
Utilism
A short recap of utilism: in utilism, it is the goal to perform an action such that it leads to the happiness of most people. A short sidenote: the quality of happiness is also important in the consideration which action to do. In general, an utilist would want a road which is designed in such a way that most people who use the road the most often would like and be happy with this road. It is important to look at the most often users of the road, this is because this group of users are having to deal the most with the designed solution (think by these users of transport traffic, commuters etc.). For these stakeholders, it is important that the road user-friendly such that is pleasant to ride the road (no speedbumps or low-quality roads (like the Belgian roads). Secondly, it is important that it is clear how to uses the road (with respect to the designed smart road). If the road is unclear how to use, it would lead to people who get irritated or unhappy with the designed road. An utilst would disapprove this because it (in this case) does not lead to the most happiness for the most people. So when designing the smart road and the users are approached by a utilitarian way of thinking, it is important to keep in mind that the most important stakeholders are the users who use the road the most often and that the solution would lead to the most happiness of most people (an important: the most happiness in the group of the most often users).
Kant
State-of-the-Art (Literature Study)
Evaluation of a movable barrier concrete system
- This report reviews the cost, safety, and effectiveness of a movable barrier system used on highways. This system is not used for our specific use case (creating a flexible and reconfigurable road) but is used for road maintenance. The report analyses specific traffic accidents involving this system, as well as the advantages and disadvantages of the system overall. Eventually, the report states that the system performs adequately in the use case as described in the report.
Moveable Barrier Solves Work-Zone Dilemma
- This article describes a movable barrier system used temporarily during the renovation of a bridge. In this instance three lanes are used, where the middle lane is used based on traffic needs. It also highlights the advantages and disadvantages of this and other types of systems.
Conclusion
In conclusion of the ethical consideration, it can be concluded that virtue ethics is not useful to take into account by design the smart road. Virtue ethics does not necessarily lead to constraints of requirements form the stakeholders. It will display the virtue of road users like the speeding limit (from https://www.universiteitleiden.nl/binaries/content/assets/customsites/study-abroad-exchange-students/road_traffic_signs_and_regulations_jan_2013_uk.pdf) or how should I use the road. Form this, it won't become clear what the constraints would be, but form virtue ethics it is possible to determine some requirements road users needed. The needs/requirements and constraints of the users can be best explained with the use of the ethical consideration, where the Virtue (only the requirements), Utilitarian and Kant's ethics are combined. Here the Utilitarian is the most important view to use because it is the easiest to use, but also it gives the most disguised requirements and constraints for the user stakeholders. With the use of this ethical consideration, the link between the designed smart road and the road users is made. With this section, the user's stakeholders are explained and given a voice such that these stakeholders aren't ignored and are considered. With this, the designed road will be the best possible solution for all the stakeholders.
Simulation
The simulation will be made using the Unity3D software package. This software package will allow for relatively easy 3D simulations using ready-made models. It also includes physics simulations and scriptable interfaces.[2]
References
1. Bielli, M., Ambrosino, G., & Boero, M. (1994). Artificial Intelligence Application in Traffic. Retrieved 4 mei 2019, van https://books.google.nl/books?hl=en&lr=&id=3cEEdaHrykAC&oi=fnd&pg=PA3&dq=artificial+intelligence+in+traffic&ots=0qYOXTFD1B&sig=akDTYf3nqHL0U26K8-rPSvZnP6k&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q=artificial%20intelligence%20in%20traffic&f=false
This Article provides information about the development and the applications of AI in traffic and transport. All difficulties of discerning the role and worth of the AI techniques are discussed. The algorithm provides solutions in the area's from traffic control, logistics and highway management.
2. Li, L., Lv, Y., & Wang, F. (2016a, 10 Juli). Traffic signal timing via deep reinforcement learning - IEEE Journals & Magazine. Retrieved 4 mei 2019, from https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/7508798
In this paper the author writes about a set of algorithms to designs signal timing plans via deep reinforcement learning. This approach is usefull in order to set up a deep neural network which can learn from the sampled traffic state/control input and the corresponding traffic system performance output. Using this most idealized network the best signal timing policies can be decided. in this paper provides possible benefits of this approach and will discuss the relation between the already existing approaches.
3. Contreras, S., Kachroo, P., & Agarwal, S. (2016, 1 maart). Observability and Sensor Placement Problem on Highway Segments: A Traffic Dynamics-Based Approach - IEEE Journals & Magazine. Retrieved 4 mei 2019, from https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/7317783
This source is about ways to collect data of the road as efficient as possible using sensors. This data may then be used to reduce traffic congestion. The sensors has to maximize the information collected and minimize monetary cost. This journal will talk about the observability problem in terms of sensor placement and then present a method for comparing different scenario's for different sensor placement.
4. Satyanarayana, M. (1970, 1 January). Intelligent Traffic System to Reduce Waiting Time at Traffic Signals f. Retrieved 4 mei 2019, from https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-981-10-7868-2_28
The research of this conference paper is about how to control the traffic issues in developing countries as India. The enormous amount of cars adding each day plus the path of emergency service vehicles are a hugh problem in the countries. This papar will provide better solutions for these two problems based in the latest technology called the Internet of Things.
5. NDW (z.d.). Documenten - Nationale Databank Wegverkeersgegevens. Retrieved 4 mei 2019, from https://www.ndw.nu/documenten/nl/
A Database from the "National Databank Wegverkeersgegevens" with information about the dutch roadways. With for example the measuring locations, travel times, speeds and intensities of the cars.
6. NDW, C. B. S. (2018, 1 maart). CBS Statline. Retrieved 4 mei 2019, from https://opendata.cbs.nl/#/CBS/nl/navigatieScherm/zoeken?searchKeywords=*&page=1&theme%5B%5D=422
This cite provides several databases related to the traffic flows and important data about the users driving behavior. It also has an important database for which kind of traffic is on the road.
7. Walraven, E. (2016, 1 June). Traffic flow optimization: A reinforcement learning approach. Retrieved 4 mei 2019, from https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0952197616000038
Traffic congestion causes important problems such as delays, increased fuel consumption and pollution. This paper will provide a way to formulate any traffic problem as a Markov Decision Process. From that a Q-learning algorithm will learn a policy dictating the maximum driving speed such that traffic congestion is reduced. This solution will not only take into account the existing approaches, but it will also take traffic predictions into account. And as a final point the author will show you using a simulation experiment that the predicted optimal speed limits will help reducing the traffic congestion.
8. Nguyen T. (2018, 16-19 Sept.). Ahead of the Curb: Smart Roads. Retrieved 5 May 2019, from https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8656667
This article tries to improve the road quality using Big Data, new technology and on-demand information. Two ideas 'Smart Road technology' and 'Dynamic Road Markings' will be explored in order to revolutionize these roads by creating an on-demand system adjesting lanes to any vehicle, bike or pedestrian traffic. The quality will be improved on points as mobility, sustainability, safety and accessibility.
9. El-Wakeel A., Li J., Rahman M. (2017, 14-16 Nov). Monitoring road surface anomalies towards dynamic road mapping for future smart cities. Retrieved 5 May 2019, from https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8309076
The development of Smart Cities aims to transform city infrastructures and services through the use of information and communication technologies. One aspect of Smart City applications is the demand for more efficient and safe transportation systems. Specifically, road anomalies are some of the challenges that contribute to the increase in vehicle damage and decrease in driver safety. This paper proposes a road surface condition monitoring system that utilizes low cost MEMS acceleration sensors and GPS receivers within a tablet to detect and localize road surface anomalies.
10. Arbi Z., Belkahla O., Sbai M.K. (2017, 17-19 Feb). A multi-agent system for monitoring and regulating road traffic in a smart city. Retrieved 5 May 2019, from https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8071843
This paper designs a multi-agent system to monitor road traffic in a smart city and dynamically adjust, in a distributed manner, traffic lights duration to traffic densities at different road sections. This will done in order to minimize both locally and globally waiting times by the anticipating abilities of modern agents and their communication abilities.
11. Wang C., David B., Chalon R. (2014, 1-3 May). Dynamic road lane management: A smart city application. Retrieved 5 May 2019, from https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6864085
12. Hausknecht M.m, Au T., Stone P., Fajardo D., Waller T. (2011, 5-7 Oct.). Dynamic lane reversal in traffic management. Retrieved 5 May 2019, from https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6082932
13. Amditis A., Bimpas M., Thomaidis G., Netto M. (2010, 8 July). A Situation-Adaptive Lane-Keeping Support System: Overview of the SAFELANE Approach. Retrieved 5 May 2019, form https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/5504223
14. Chen Y., Krumm J. (n.d.). Probabilistic Modeling of Traffic Lanes from GPS Traces. Retrieved 5 May 2019
15. Yi R. (2016, 23 Jan). A Probability-Based Model of Traffic Flow. Retrieved 5 May 2019
16. Calvert S.C., Taale H., Snelder M., Hoogendoorn S.P., (2012, June). Probability in traffic: a challenge for modelling. Retrieved 5 May 2019
17. Caprani C., (2005, 10 Jan). Probalistic analysis of highway bridge traffic loading. Retrieved 5 May 2019
18. Li J., Gong S., Xiang T. (n.d.). Global Behaviour Inference using Probabilistic Latent Semantic Analysis. Retrieved 5 May 2019
19. Summala, Heikki. (2000). Brake Reaction Times and Driver Behavior Analysis. Transportation Human Factors. 2. 217-226. 10.1207/STHF0203_2. Retrieved 11 May 2019 from https://www.researchgate.net/publication/233039156_Brake_Reaction_Times_and_Driver_Behavior_Analysis
20. Olson, P. L., & Sivak, M. (1986). Perception-Response Time to Unexpected Roadway Hazards. Human Factors, 28(1), 91–96. https://doi.org/10.1177/001872088602800110
21. Kown, J., Varaiya, P. (2008). Effectiveness of California's High Occupancy Vehicle (HOV) system. Retrieved 10 May 2019 from https://www.researchgate.net/publication/222817805_Effectiveness_of_California's_High_Occupancy_Vehicle_HOV_system