Embedded Motion Control 2018 Group 3: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
=Initial Design= | =Initial Design= | ||
Revision as of 15:10, 9 May 2018
Group Members
| TU/e Number | Name | |
|---|---|---|
| 0848904 | Luc (L.L.M.) van den Aker | l.l.m.v.d.aker at student.tue.nl |
| 0852908 | Thomas (T.) Neilen | t.neilen at student.tue.nl |
| 0909434 | Jeroen (J.W.) van de Valk | j.w.v.d.valk at student.tue.nl |
| 0896947 | Nourdin (N.) Kaai | n.kaai at student.tue.nl |
| 0883056 | Peter (P.) van Dooren | p.v.dooren at student.tue.nl |
| 0861750 | Ties (T.J.) van Loon | t.j.v.loon at student.tue.nl |
Initial Design
Requirements:
- PICO should make no collisions with any walls
- PICO cannot stand still for 30 seconds or longer
- For the escape room challenge, the robot should leave the room within 5 minutes
- For the hospital challenge, within 5 minutes, mapping, reverse parking and obtaining the object should be done
- Its surroundings should be made visible in a map
- PICO should be able to reach every position in the room
- PICO should be able to leave every room
- PICO should make distinction between the hall and rooms
- It should run autonomously, so in each challenge there should be no additional input
- To start your software, only one executable has to be called
- PICO should be able to recognize an object and stand still close to it
Functions:
- PICO should be able to drive in any direction
- PICO should be able to turn around
- It should be able to detect walls
- PICO has to know its own position within the mapped map
- PICO is able to construct a map
- It should be possible to create a trajectory to a room
- PICO should be able to recognize an object
Components:
- Sensors:
- Laser Range Finder (LRF)
- Wheel encoders (odometry)
- Actuator:
- Holonomic base (omni-wheels)
- Computer:
- Intel i7
- Ubuntu 16.04
Specifications:
- Translation maximum: 0.5 m/s
- Rotation maximum: 1.2 rad/s
- Range of Laser Range Finder is assumed to be bigger than maximum room dimension
- The field of view of the Laser Range Finder is from -2 rad to 2 rad, divided in pieces of 0.004004
- The Laser Range Finder can only measure at one height
Interfaces:
The interfaces of the initial design are shown in Figure 1:
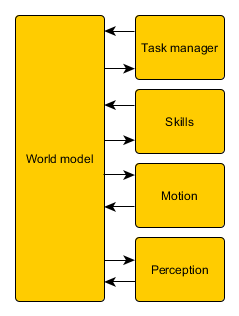
As shown in Figure 1, a world model is the link between all other parts. The tasks represent the highest level, meaning the most global work PICO has to do. The skills are needed to complete these tasks and some motions together form a skill. The perception contains the sensors, the continuous data. Below an overview of the different parts are given:
World model:
- Compose map
- Object recognition
Tasks:
- Mapping of the environment
- Backward parking at the specified location
- Searching for the object
Skills:
- Planning a trajectory
- Collision avoidance
- Backward parking
- Navigate
- Positioning in front of a opening
- Compose maps
Motion:
- Translation
- Rotation
Perception:
- Odometry
- Laser Range Finder
- Controll effort