PRE2017 1 Groep1: Difference between revisions
| Line 358: | Line 358: | ||
== Robot Communication == | == Robot Communication == | ||
=== Flowchart === | |||
To get a better understanding of what the robot is proposed to function like we made some flowchart to simulate part of the decision making process. | To get a better understanding of what the robot is proposed to function like we made some flowchart to simulate part of the decision making process. | ||
====The robot==== | ====The robot==== | ||
The robots decision making process starts with a simple check if the robot is still upright. If this fails the robot will send an error message. After the robot has been determined itself to be upright it checks if its camera returns a functional videofeed. If this is not the case the robot will try and clean the camera itself. When this fails the robot will report an error stop. If the camera can properly view the robots surroundings it will use its depth perception camera to observe any objects (or persons) and map this onto an accessible area map. And separately map the people in its field of view to a map. When the items from a given timeframe are mapped to their designated maps the next input is used. The IR camera is checked in the same way the other camera was checked. If the camera is functioning correctly the field of view is checked for fires and if there are any they are added to the obstacle map. The information from the IR camera and the people map are cross referenced to be certain that the people being perceived are real warm blooded humans. If they are low to the ground they are kept on the obstacle list and otherwise they are removed from the obstacle list. When all people in the instance are reviewed the robot attempts to send the created maps to the controller and reattempts of contact is not established. The controller processes all maps and the robot receives its optimal path with updated maps. The robot then updates its path and maps accordingly. | The robots decision making process starts with a simple check if the robot is still upright. If this fails the robot will send an error message. After the robot has been determined itself to be upright it checks if its camera returns a functional videofeed. If this is not the case the robot will try and clean the camera itself. When this fails the robot will report an error stop. If the camera can properly view the robots surroundings it will use its depth perception camera to observe any objects (or persons) and map this onto an accessible area map. And separately map the people in its field of view to a map. When the items from a given timeframe are mapped to their designated maps the next input is used. The IR camera is checked in the same way the other camera was checked. If the camera is functioning correctly the field of view is checked for fires and if there are any they are added to the obstacle map. The information from the IR camera and the people map are cross referenced to be certain that the people being perceived are real warm blooded humans. If they are low to the ground they are kept on the obstacle list and otherwise they are removed from the obstacle list. When all people in the instance are reviewed the robot attempts to send the created maps to the controller and reattempts of contact is not established. The controller processes all maps and the robot receives its optimal path with updated maps. The robot then updates its path and maps accordingly. | ||
| Line 371: | Line 371: | ||
|[[File:Proposed_C_flowchart(15-10).jpg|thumb|510px|right|Proposed flowchart for the cotroller]] | |[[File:Proposed_C_flowchart(15-10).jpg|thumb|510px|right|Proposed flowchart for the cotroller]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
=== State diagram === | |||
In reality, robot operations almost inevitably fail to go according to plan. There may occur events that are not thought of, and thus the robot would maybe not be capable of handling these. Also the robot can have mechanical, electrical of software problems. Sensors and actuaters can misbehave. In a flow chart, a nominal plan of action can be acurately and clearly described. However, fail states are harder to describe in the format. | |||
This is where the state diagram comes in. In the state diagram, different problems can be described, and tell the user/robot what to do. It is a clear method because the robot can asses in which state it finds itself in, and can plan action according to the state's conditions. | |||
The state diagram for our robot can be seen in the figure below. | |||
== Police thoughts == | == Police thoughts == | ||
Revision as of 17:38, 22 October 2017
| Members of group 1 | |
| Bern Klein Holkenborg, Mechanical Engineer | |
| Sjoerd van Heesbeen, Mathematician | |
| Luke van Unen, Software Scientist | |
Introduction
In this project, problems are solved from a societal perspective. Engineers usually look at engineering problems, but fail to notice that either the problem is of no issue for the user or society, or the problem may be irrelevant for the problem the user or society has. This project explores the utility of just that: looking from a user's need. For the course a problem is posed which is be detailed below.
Problem Definition
Crowd Theory
Today, there are several different psychological theories on crowds. There is Gustave Le Bon's theory, Sigmund Freud's theory, Ralph Turner’s theory, Henri’s Tajfel’s theory and many more.. Each of these theories have a different perspective on the psychology of a crowd and its members. It is important to look at these theories when designing a crowd management solution. The psychology of a crowd tells about the interaction between individuals, thoughts of the masses and tells about the (unpredictable) actions of these crowds. Knowing the inner processes in a crowd explains the origin of all kinds of problems within a crowd, such as uproar, violence, mass rallying, panic and so on. Therefore theories mentioned earlier will be looked into, as to investigate why or where a robot can best help interacting and managing a crowd.
Irrational theory
First off, Gustave Le Bon's Theory is looked into. Gustave Le Bon wrote ‘Mind of the Crowd’ and with that started the psychology of masses department in psychology, which now-a-days branches to politics, conventional and social media and many other. In this ‘Mind of the Crowd’, Le Bon argues that individuals are no longer themselves. Would an individual been alone, he would kept himself under restraint. Le Bon says ‘he is no longer conscious of his acts’. His argument is that a crowd is irrational. It does not think for itself, it only acts. An important quote from his work: We see, then, that the disappearance of the conscious personality, the predominance of the unconscious personality, the turning by means of suggestion and contagion of feelings and ideas in an identical direction, the tendency to immediately transform the suggested ideas into acts; these, we see, are the principal characteristics of the individual forming part of a crowd. He is no longer himself, but has become an automaton who has ceased to be guided by his will.
In other words, rationality translates to irrationality by contagion of feeling and ideas in identical direction. And irrationality leads to immediate acting upon ideas, thus the individual started being an actor incapable of reason instead of a rational being.
Although in the 1960’s the theory of irrational crowds was widely rejected, now-a-days this theory is taken in consideration again in some behalf. Take the Burnley Riots in England 2001. Young people were discontent about their living conditions. There was unemployment, poverty, crime and other conditions. In 2001, these youngsters started looting shopping centers and setting cars alight. Initially, law enforcement tried to communicate with the rioters, however soon noticed the riot and its members were irrational, and in no way able to negotiate. Homes were petrol bombed, families were attacked, and ofcourse law enforcement got attacked. Petrol bombs, stones and other projectiles were hurled at the police. People joined the riots just for the sake of looting or for violence. The riot eventually caused over 300 officers to be hurt. So how could robots have helped the law enforcement? A mobile barrier between rioters and law enforcement could have probably prevented many officer injuries, and could have created safe areas in critical zones. Robots could have literally provided this mobile barrier and even more. Robots could have acted as riot control unit equipped with water guns and/or cameras.
Secondly, Sigmund Freud’s theory. Sigmund Freud is a well-respected psychologist published ‘Group Psychology and the Analysis of the Ego’ in 1921. In fact, this is the base for his most famous published work ‘The Ego and the Id’. In his ‘Group Psychology and the Analysis of the Ego’, Freud also argues that the individuals in large groups form an irrational crowd acting on suggested ideas. However, the reasoning is different. Freud suggests that the so called ‘super-ego’, the part of the ego that is conscious and responsible for our inner reasoning is overthrown in a group. The intensification of emotion in a group by contagion is not accounted for by the super-ego. Freud argues that through a crowd, the super-ego’s restraints on a person’s behavior is minimalized and these restraints are replaced by impulses from, for example a charismatic crowd leader creating simple emotions instead of complex ones, as simple ones are easier to interpret for the restraint super-ego. This is for example how dictators like Hitler manipulated crowds he believes. The difference here between Le Bon and Freud is that people not merely stop thinking, but are overwhelmed in contagious emotion. Though the conclusion is similar, the individual starts being an actor incapable of reason instead of a rational being. Because the conclusion of this theory is the same, the same principles can be applied for using a robot riot support unit. One note on that however, Freud suggests that charismatic leaders have an extra effect on the actions of a crowd. Identifying and recognizing these individuals would be an almost impossible task for robots. However what support they could provide is whenever such a person is identified by law enforcement, robots can provide a way to penetrate the crowd and lead in law enforcement to enable arrest.
Emergent norm theory
Although Le Bon and Freud argue for an irrational crowd, Ralph Turner argues for a largely rational crowd. He published his ‘emergent norm theory’ just after Freud’s theory. He argues that people initially, in all types and sizes of crowds, do not know how to behave. Because social interaction, people start behaving like the norms of people around them. Important is that this, in contrary to the other theories, makes this crowd theory dependent on situational factors. Essentially Ralph Turner argues that social order and rationality guide behavior. This means that still, charismatic leaders will create norms that guide crowds, however these norms might not be acceptable for the individual in the crowd. The norms formed by the individual can be explained by anonymity, stimulation, emotion, contagion, legality and much more. Modern individual theories like Henri Tajfel’s social identity theory argue that individuals are not guided by the crowd, but by norms set by their social identity. This means that individuals are dictated in their morals and norms by groups to whom they are primarily are related to. These can be religious, cultural, politically or any other form of group that sets morals and norms. This way crowds are more versatile than in other theories. This theory argues that because of these crowds formed by social identity, people feel united, have a high self-esteem and have pride for this group. This causes prejudiced views of other groups or non-members, and depending on the groups moral/norms, can cause violence or other problems. This theory argues that also, crowds are largely irrational, since the prevailing cause of action is the norms set by a group. To illustrate these two theories, take the Baltimore 2015 riots. The Baltimore 2015 riots came about when Baltimore Police arrested Freddie Gray. Gray died from injuries to his neck and back, caused by his arrest by 6 officers. His arrest caused uproar in the black Baltimore society. Why this riot is interesting is because the stages of escalation. First peaceful protests were held against police violence. Peaceful norms were abided. However, more people joined the protests, and naturally the occasional arrests were made. Some protesters started harassing police offers, and later many followed. A new norm was set by the crowd, in which emotion, contagion and anonymity played part. The protests intensified because of the fact that Freddie Gray was black, which many protesters identified with. Finally a full scale riot happened with over 200 fire incidents to houses and vehicles. Also many looting occurred. In the end, thousands of officers were deployed to contain the riots, and resulted in many police injuries. Again, a mobile barrier and additional information could have prevented looting, fires and injuries from happening. It wouldn’t have prevented the riot from happening, but it would have contained the damage it has done.
Concluding from these theories is that riots can be prevented in some cases, through communication and picking the out the people that are influencing the crowd in a wrong way. Still there will be some riots and therefore our robot will make sure there are less victims afterwards from both sides, police and rioters. When analyzing the theory, it becomes clear the crowd start as heterogeneous whole with lots of law abiding people, not ready to throw rocks and projectiles at the police, but after a while some aggressive minority gets the overhand and will change the crowd to a homogeneous one. This crowd will be ready to go against the police, resulting in victims on both sides. That is where the robot comes in, first of all a robot can’t be harmed, only parts will be broken, but can be repaired. Next to that the robot can act on the situation very swiftly, as they make decisions in a split second. But the robot will not be there as a replacement of the current mobile unit, they will be a tool used by the police. Still some human police officers must be present to instruct the robots and make arrests, but they are in less danger, so the risk of getting harmed is significantly decreased. Another advantage of robots over humans is that robots will not get aggressive, while humans react to swearing or getting hit, robots will keep doing what they doing, resulting in less victims at the crowd side.
When thinking of this problem and the solution we think is best, there is also the thought of a device controlled by humans, for example a bulldozer with a shield upfront, it is a lot easier to make and will have the same effect on first sight. But there are some things that can’t be done by such a machine or humans. The advantage of robots is they are all single-controlled, every robot can do his own action. So when bumping into an obstacle, the robot is able to find a way to avoid it. Next to that, the robots can communicate and make decisions a lot faster than humans can. Also data can be easily communicated, making sure the most accurate plan of action is made. Furthermore, the robot can help by picking out the black sheep in the crowd by making a way through the crowd, where a police officer is able to arrest them. So all by all robots can definitely impact riots positively, they could possibly lower the chance of escalation, but most likely lower the chance of damage and injury. This will eventually become clear in the process. A robot that could act as barrier, riot control unit or information system can definitely prevent harm to police, and thus also to rioters and non-partaking individuals.
Objective
As described above, to keep up with population growth, the police force has to evolve to a (partly) automated force. The objective for the project is just that. A robot should be created to automate an otherwise employee intensive police task. Without bringing user or society at risk. The robot should be safe to interact with, useful and be able to cope with every situation it faces. There are already "real" police robots providing assistance to citizens (Dubai). However they are often seen as lacking in most capabiltiies compared to human officers. The scope of the project would be far to great to design such a complete officer replacement robot. Instead in this project we will try tackling a specific police task. Some examples of such a tasks would be: Speeding control, a mobile robot could check wherever, whenever for speeding cars. Or an automated alchohol check, a robot could be set up to automatically check if a driver is allowed to drive or not. Or a robot that monitors a vehicle chase, a mobile robot unit might be faster, cheaper and more varsetile than a police helicopter.
Approach
To tackle a good problem, we would like to investigate how and why a police task is performed and how this could be improved upon by utilizing robots. We would like to be in contact with dutch police staff to define these tasks, and also narrow it down to a single well defined problem. The task should be investigated in detail by means of real world examples. As before, why and how it is done in its current way, what rules there are, what is vital to keep in mind for a good result, how people respond to the actions being taken, and if all this permits for robots to enhance the tasks being performed. When all these parameters are well defined, a robot can be designed both technically and functionally. After designing the robot, the design has to be verified by both the police and users which can be done by enquete, interview and maybe even a prototype test.
Scenario
Current practice
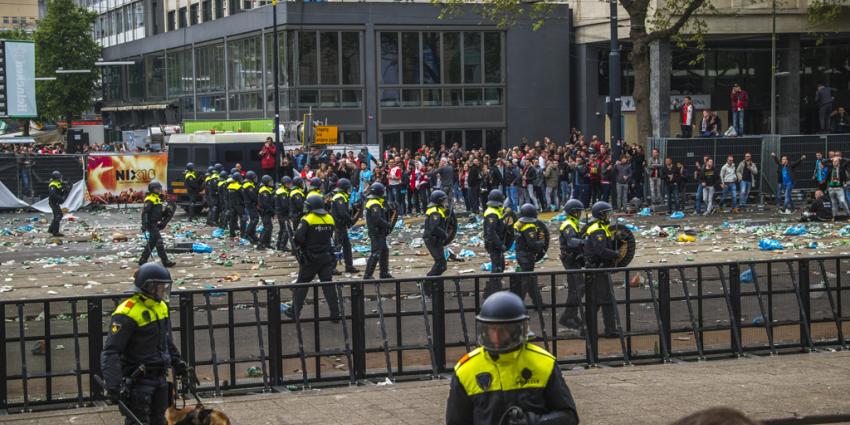

I fine example of predictable rioting is what happened in Rotterdam at the 7th of May 2017 when soccer fans turned against the police when their team did not win the match to secure the Dutch championship. Police forces were prepared and on standby to secure the sites were the disgruntled fans had gathered and forcibly did so making many arrests in the process. Even though the clearing of the Stadhuisplein went over quite well officers were pelted with bottles and rocks and hooligans where forcibly removed creating a situation where officers, bystanders and the culprits of the violence were all at risk. There is some video material of violent hooligans being driven away, but there also were some isolated cases of people trying to talk to the M.E. officers whom then still have to forcebly move them of the square. The advance can not just simply be stopped for a chat. All of this takes a long time while police lines shift forward all the while angry fans constantly release their frustration upon the officers. After some time the officers and their colleges on horseback ended the altercations after about a hundred arrests were made. In the end manier culprits got community service punishments to make amends for the damages and harm done to the police.
Ideal solution
Because of the knowledge of the locations where the fans will meet to watch a match a response is prepared in advance. Officers are placed nearby these locations and if altercations arise they are sent in to clear the areas where violent masses have gathered, breaking them apart and moving them away. But because officers are not made of metal advance is usually slow, dangerous. All the while violent culprits only get more chances to release their anger upon the officers. In our ideal situation the front line of shields is supported by robotic units. The robots are deployed nearby in advance in unison with officers to be ready when needed. These robots are moved on command by the officer in charge and are capable of moving the crowds in the same way a line of shielded officers would. With the advantage of the robot not feeling pain or needing to protect its body from harm like an officer needs to. Having a sturdy robot get hit by a bottle or fireworks may not only protect officers from bodily harm but is also less likely to give the adrenalin junkies among the crowd the same satisfaction thus breaking part of the crowd’s intent for engagement. The robots are thus filling a more dangerous position while officers can focus on other tasks like apprehending violent offenders trying to take out the worst elements of the crowd. So while the robot steadily advance officers can focus on the more difficult tasks hopefully enabling a steadier advance compared to when they also have to look out for their own and their colleagues’ safety. Because of the swifter action less constant violence can be applied to the crowd thus defusing the situation even further. In this scenario the quicker advanve would leave less time for property or personal damages to befall. (And my personal hopes would be that such a riot is no longer seen as an opportunity to fight the cops and thus become less attractive for manier violent elements all together)
Deliverable
Now the problem is stated, a target has to be set for us to work to. This target has to be concise, clear and measurable. The target for this project will be to deliver a robot design that reinforces the police force during riots. For the design, requirements are set for the robot, as well as constraints, as to make sure the feasibility of this project. The process of this design will be elaborately explained, supported by literature claims, police and user interview(s). Finally the functionally will be validated by again literature, a case study and police feedback. Each of these targets will be explained in further detail below.
Firstly, the target has to be concise, clear and measurable. What is meant with this is that the deliverable will be designed to a set of design goals that clearly state each individual function and capability it has to adhere. Also it is stated which functionality will not be possible or wished. The goals have to be not only clearly stated, also they have to be measurable. To be concise in your goal, a numerical value has to be attached to you as to define when the goal is met or not. It can also then be easily evaluated if the design goal was too high of a standard, or too low. This evaluation can then be taken in account for the next project.

As for our target, in this project we opt for a robot design that reinforces police officers in riot situations. This however is very broad, thus the functionality has to be specified. As stated in the problem description, officers equipped with full body protection, shields and batons stand in line, forming the front of conflict as can be seen in the figure XX. They themselves form the barrier that contains violence, and come in direct contact with this violence. Is this nowadays really still necessary you could ask? This projects design goal would be to replace these human officers with robots, as to have a mechanical initial barrier, instead of a human one. These robots will communicate together to form a solid barrier. These robots will be instructed by police where to go, however the robots will operate this order themselves. The robots will navigate his route, whilst able to hold formation. It will be able to overcome obstacles (of specified proportions stated in the requirements) and know when to navigate around the obstacle. The robot will be constructed so that it is stable and hard to knock over. The robot will be able to withstand significant projectile impact, like bricks or petrol bombs. Should a robot be incapable of moving because of it is knocked over, or destroyed, the managing officer will be notified by the robot. … The robot will also prevent itself from doing serious human harm. The robot can communicate with the crowd via speakers.???? … With these functionalities, the robot will be capable of being an initial barrier between law enforcement and the violent crowd. This barrier will prove to be safer for both police and crowd. This is however further explained in … The problem definition??? ….
To make these functional requirements measurable, requirements are set. Also constraints are given to make sure the design is mechanically feasible.
Requirements
- Movement and stability
- The robot has the ability to move forward and backwards.
- Note that for stability, the robot will be rather heavy.
- The robot has the ability to make zero radius turns.
- Being able to move anywhere from any position can be crucial for keeping formation
- The robot has the ability to reach 10 kilometers an hour.
- This is two times the average speed of human walking. In most situations, the robot will move at less than walking speed, however, in some situations it might be required to charge.
- The robot has the ability to climb obstacles of 30 cm high.
- This is 10cm over the average street curb height in the Netherlands. This would also be sufficient for running over most riot debris.
- The robot has the ability to climb 10-degree slopes
- In the Netherlands, the steepest roads are only almost 10-degree averagely, and 15-degree at their steepest points. This means that besides a few select roads, this robot will be able to drive each road in the Netherlands.
- The robot has to be able to withstand some significant forces thus needing to be quite stable.
- This stability can be achieved by keeping the center of gravity proportional to the weight or by making a wider base for the robot to stand on. Different shapes will warrant different parameters and optimal design needs further research.
- Traction on the propulsion mechanism is also required while making sure that people cannot get caught on it is imperative.
- The robot can manouver on all street surfaces.
- Both on sidewalks consisting of bricks and plain road surfaces made out of tarmac.
- The robots should move over these surfaces without seriously damaging them.
- The robot has the ability to move forward and backwards.
- Functionality:
- Has a shield for both defending and pushing.
- The robot should afford itself some protection with its shield, enabling some passive defense to the projectiles mentioned in durability.
- The shield should be able to rotate freely, as ot should be facing the right direction as the robot is turning.
- The shield should be able to withstand the force of multiple people kicking and beating it and even using improvised arms i.e. pipes or branches.
- The edges of the shield when drawn close to those of other robots should be close together enough that an adult cannot fit through.
- The shield's edges should be unubtrisive so that anyone in front of it cannot simply fall against them and seriously injure themselves.
- Force feedback sensor to determine how hard it is being pushed, giving officers an idea how bad it is for the people up front.
- The robot has situational awareness.
- Accurate use of GPS and local positioning. SO the control can keep track of the robots and the robots can accuratly coordinate their movement together.
- Being able to see its surroundings (all 360-degrees) with depth.
- Having multiple camera’s as one might be too easy to disable by means of for instance spray paint. Thus, keeping visuals as consistent as possible.
- Recognition for officers and other robots. (Could be visual or by other recognition methods).
- Imaging external back-up. To make sure that any criminal offenses being commited are recorded.
- Obstacle recognition, to avoid for instance streetlights and garbage bins.
- Control capabilities tablet
- There is are a list of formations by which the robots can complete their task.
- Settings for movement speed both forward and backwards.
- Emergency shut-down in case of need. If an emergency occurs the robots should either stop immediately or split up their formation.
- GPS and street map retrieval. If the system is to be portable, it should be able to adapt to new locations by retrieing the local map and implementing it.
- Modularity (to be further discussed)
- Communication speaker, to tell the people to leave and what repercussions staying will have.
- Water cannon, as a manner of dispersing the crowd.
- Has a shield for both defending and pushing.
- Durability:
- The robot is waterproof.
- The robot has the ability to sustain both heavy rain and misaligned water cannon bursts (thus IPX5 is necessary).
- The robot is fire proof.
- Not simply put blaze by any incendiary means (i.e. Molotov’s).
- The robot is fitted to withstand minor explosions.
- Fire crackers and other hand thrown explosives should not simply break the robot.
- The robot can with stand physical damage.
- Being hit or kicked by people even to the point of them using improvised arms (as mentioned before).
- Getting hit by bottles or rocks should prove irrelevant.
- Propulsion mechanism should not be susceptible to tampering on the field.
- The robot should perform in the field even when its driving through glass or being assaulted like mentioned above to preserve functionality.
- The robot is waterproof.
Constraints
- Safety
- Propulsion
- The robots should be aware of objects moving at higher speeds avoiding collisions.
- The propulsion should be designed in a way such that getting caught in or under should be nigh impossible.
- Emergency stop or backing up should be readily available.
- Force detection to inform officers of possible crushing’s.
- Stability
- The robot should not be able to be toppled over on top of someone.
- Whilst moving the robot should be stable enough to move itself in non-obtrusive way to its surroundings.
- Shape
- While being a robust robot thin hard edges and other parts prone to blunt trauma should be on the rear side keeping safety first.
- Propulsion
- Usability
- Intuitive control scheme. Selecting formation and advancement speeds should make sense to the users.
- Portability to different locations. Being able to adapt to new settings.
- Reliability, parts should be as durable as possible as in action repairs are unrealistic.
- Surroundings
- Area’s where the robots are to be deployed should not be left with permanent damages because of them.
The design of the robot will be explained per functionality. To realize a functionality, state of the art sensors, actors and methods will be combined. It will be described by text and illustration how these sensors, actors and methods will work together to realize the particular function. If there is time, a realization of functions could be worked out, however is probably too ambiguous and thus optional. Finally, a sketch of the final robot will be given.
To validate the design, a case study will be given. Also police feedback and user feedback will evaluate the design. The goal for the case study is analyzing an actual riot that happened (preferably in the Netherlands). Conclusions will be given what has happened, why, and how the riot could have been handled better. Then with this information, we introduce our robots to the riot, and analyze how probably the riot would have happened. As said before, we want the stakeholders to evaluate the design and its usability. With both the feedback and the case study a conclusion will be drawn about how the robot would fare in society.
USE cases
USE CASES Robots
In a riot there is most of the time a lot going on, at one place they are throwing rocks, while they are starting a fire on the other side. The robot has to act on all these circumstances in the best way possible, below there are some events listed where is explained how to handle in every situation, about what the robots see and communicate to the other robots and control unit and the other way around.
- There is a rioter on the ground
- Robot recognizes obstacle (depth camera)
- Robot recognizes the obstacle as a living human form (IR camera)
- Robot recognizes that the human is below height threshold
- Robot presuming it is either a child, or a wounded adult the robot should perceive it as an obstacle to be avoided
- Robot updates the obstacle map accordingly
- Robot navigates around the 'obstacle'
- In this case it is important that the robots make the way clear for the policesquad, as they can pick the person up and give them first aid if needed. But it also necessary to keep the line intact, as the riot still has to be contained.
- A robot has a malfunction whereby the controller can no longer communicate with it
- Control unit loses contact with robot for more than three communication cycles
- Control unit recognizes robot as currently inactive
- Control unit resisters the broken robot as an obstacle
- Control unit determines new trajectory for the other robots accordingly
- A replacement robot takes the place of the broken one if available
- If the robot reconnects
- When it is still close to the formation it should move to regroup with them
- If it is left far behind the robot is deactivated
- Though a robot malfunctions, the line has to be hold within a small amount of time, therefore the control unit checks three times and then moves on to with the other robots, this way the line will be held.
- One of multiple cameras aren’t working correctly anymore
- Check if there is connection to the camera
- If the camera report it is functioning:
- Spray camera glass with cleaner agent
- Whipe camera glass
- Check if camera's view is improved
- If the camera view improves yet is not yet cleared clean again
- If the camera view is cleared revert to normal
- If the camera view does not improve send go to camera not responding
- If the camera is not responding
- Robot sends an alert to the Control Unit that the camera is malfunctioning
- Control Unit recognizes robot as malfunctioning
- Control Unit sets the robot as an obstacle in the map
- Control unit determines new trajectory for the other robots accordingly
- Camera's are critical to the robot functioning safely in its environment. Thus measures must be taken proportionately in case of camera failures.
- There is a big fire in front of a robot
- IR camera recognizes the immense heat
- Robot recognizes the immense heat using its IR camera
- Robot updates its obstructions map accordingly to the location of the heat source
- Robot navigates around the 'obstacle'
- It is important that the robot recognizes fire as it can seriously damage the robot and moving toward and or through it can result into people being pushed into it.
- Emergency stop
- Control unit recognizes the emergency stop has been set
- Control unit reports all robot a new goal at their current position, stopping the robots where they are
- Robots can be further set to full shutdown where they will no longer try to stay where they are and the shield no longer moves
- In crucial situations the robots might need to stopped immediately by the user.
- Losing communication with Control Unit
- Control unit loses contact with robot for more than three communication cycles
- Control unit recognizes robot as inactive
- Control unit maps the uncommunicative robot as an obstacle
- Control unit determines new trajectory for the other robots accordingly
- When losing communication with the control unit
- Propulsion malfunction
- Robot recognizes it cannot propel itself in the desired direction
- Robot sends an alert to the control unit that its propulsion is malfunctioning
- Control unit recognizes robot can no longer propel itself forward
- Control unit recognizes robot as inactive
- Control unit sets the robot as an obstacle in the map
- Control unit determines new trajectory for the other robots accordingly
- This is the same as a malfunctioning robot.
- Police officers need space to move through the line (for instance to make arrests)
- Police officer sets a new formation and sets the destination to the current position
- Control unit determines new trajectory for the robots accordingly
- The robots adapt to the new path set for them making space for the officers
- The robot may be needed to make space in their lines to provide an opportunity for actions to be taken they can not perform. Specifying tis in the formation leaves the robots to create this space themselves preventing the need for manual control.
- When the control unit is unable to plan a trajectory to the goal
- Control unit cannot currently determine a path through the obstacles
- Control unit notifies user the robots cannot proceed
- Control unit
- User responds b
- There are some extraordinary cases where the control unit can’t find a correct trajectory, in this case the police has to take over to get them out of this situation
- The robot get pushed
- The robot evaluates the force feedback
- If the feedback gives an extraordinary high value, alert the police officer
- Otherwise continue with its trajectory
- The crowd will eventually resist the robots, as they get too forceful, the police must help them, for example by arresting persons
- The crowd is pushing forward as a singular mass with possible crushing of individuals
- Robots reports the force value, determined be the sensor attached to the shields connecting point, when it exceeds normal values over a longer period of time
- User evaluation of camera feed and the strength of the force applied to the robots to determine the extent of the dangers of the situation
- User determines there is a serious safety concern and adapts the formation to make space for people to pass through
- User determines there is no need for concern yet and keeps receiving data from the robot as the situation evolves
- If the crowd is large enough to and fully envelops the robots front side in multiple rows the risk of crushing might arise. The robot must return feedback to the user so they can act accordingly.
USE CASES Police
There are also some cases where the robot can’t make any decisions, but the police have to. These decisions can be really hard as it can lead to escalation or to harmed people. Below there are some of these difficult cases explained with their pitfalls.
1. The riot is in a starting phase, distance between the robots and the crowd is ten meters, people are talking to each other and some of the members are throwing some bad language to the police. In the middle of the crowd a woman is injured and needs first aid but the crowd won’t let them through.
In this case there are two options: the robots charge and make way for the first aid and doing nothing, hoping they will let them through eventually. The charge option sounds very interesting, but charging can make the riot escalate when it is not even started. Doing nothing will keep the riot at the same level, but the woman doesn’t get the help needed. When making the choice of charging, the police will set as goal to get to a certain point in the crowd and the robots will use their tactics to get there and make way for the first aid.
2. The riot is in a critical phase and in the middle of the crowd there is a fire.
The same options hold for this, but the risk are different. When charging the fire can get extinguished, but there is the risk people get stuck between the crowd and the line, resulting in people who are getting choked. But doing nothing will have risks for the people around that fire. Here the police has to make the choice which risk is greater and more dangerous.
USE
User aspect
While dealing with police work, there are two main users involved. Firstly the peacekeepres themselves, they are the would be users of our proposed design. The police undoubtebly has needs and wishes for such a design, therefore we are approaching them to discuss what they want and what we can offer them. This is one of the main focusses of our project. The robot will also have to deal with members of the public both bystanders and others. For bystanders the robots are also in a way part of the security forces keeping them safe and should thus make that come true in their point of view. They must have a safe feeling in the presence of these robots and clearly see why it is needed to enhance everyones safety. And next to the bystanders there are the troublemakers whom must be handled with care, according to law and common decency. They should not feel overly threaten yet still feel the need to adhere to the the robot "will" as set by the police.
Society aspect
These robots are aimed to have a positive impact on society. Riots will be easier deal with and there is an oppertunity for less people to get hurt in the process. Keeping both officers and members of the public further away from harm. Society fells its own judgement upon the robots and their intended and percieved goals. The robots must act within the law, it must have a well defined reason to harm people or any other action involving people. This part will be elaborately handled in this report, as there are a lot of ethical rules and there are different ways to applicate them.
Enterprise aspect
The enterprise aspect of our design can handled in two ways, the first one is that the police continues working on the design of the robot as there will be plenty left to research and to develop. The second option is that the design is further developed in the private sector and they will be sold to the police. Eventhough this is a very interesting part of a robots design there is still little presedent to begin with so design takes a higher focus.
Functional Investigation
State of the Art
Crowd control has been an issue for decades. There is less chance of being arrested in a large group of people, thus naturally, crowds often are unpredictable and violent for the environment and crowd control force. And since there are a lot of people now, and in the past, sharing a common thought, crowds gathering is of daily occurence. Because of this, researchers and engineers have already tried to investigate how to minimise damage of such crowds by optimising crowd control techniques and preventing crowds from harming the controlling agents by, for example replacing the human agents with robotic ones. An analysis of such robotic crowd control techniques is presented here to investigate different techniques, possibilities and tricks to keep in mind for the design of our own robot.
Drivetrain
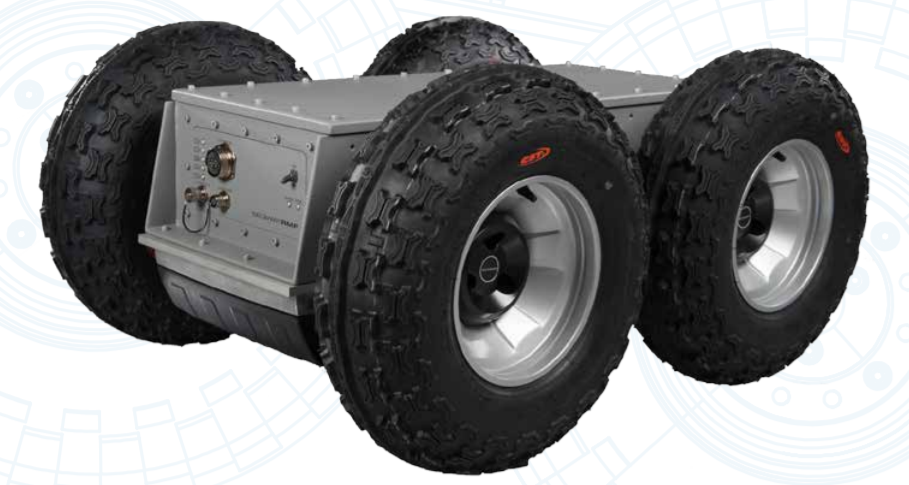
Segway RMP440
The Segway RMP440 is a 4 wheel off-road flexible transportation robot. The Segway RMP440 is designed so it can navigate loose, rough and steep terrain. It does that with this 4 big wheels, driven by a powerful DC motor per wheel, allowing it to drive upto 29km/h and deliver 100N-m torque. It can drive through 250mm of water and traverse slopes of 30 degrees. It is controlled by user input from control software from a PC. The robot is designed to handle 90kg of payload through rough terrain. The type of payload is upto the user, this can vary from carrying equipment upto weapons (or waterguns as seen in the figure below). The battery lasts 8 hours at operating power.
 |
 |
The Segway RMP440 is in many ways effective for the goal we set for crowd control management. The robot is powerful, can drive fast, though rough terrain, lasts long, is strong, and most importantly: it is flexible. It can be mounted with waterguns, shields, guns or any other tool needed for crowdcontrol. Also, the cost is relatively low since the design does not include really advanced hardware. This relatively low cost is important: When multiple robots are purchased and then set up to connect to each other, these things could be driven by an autonoum program that navigates multiple of these robots simultaniously, performing known crowd control techniques for optimal crowd control. Since the control software is already written, it would only have to be modified and adapted for autonomous control.
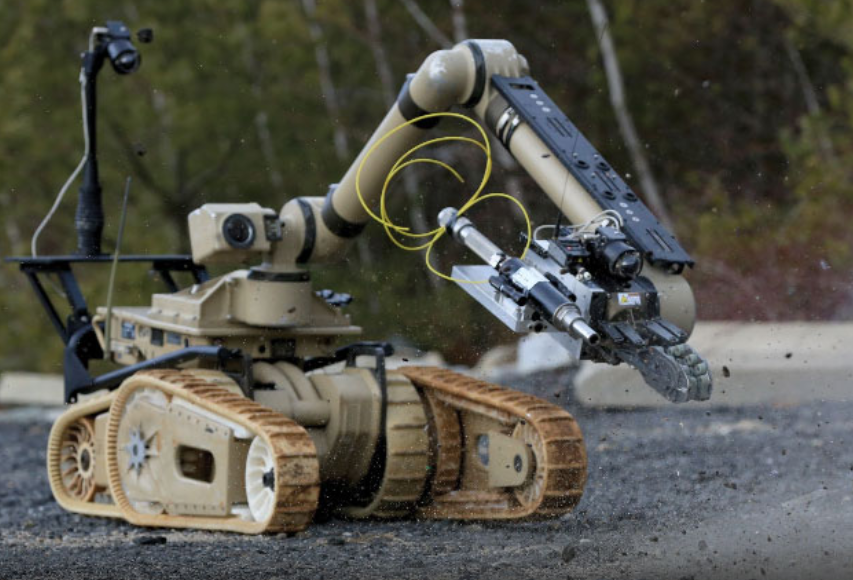
Endeavor Robotics Kobra
The Kobra from Endeavor Robotics is like the Segway RMP440 an off-road flexible transportation robot. From their specification sheet:
The Kobra was designed to provide unmatched strength, power and payload support in an easy to operate robot package. Kobra has a lift capacity of 330 pounds (150 kg) and integrates numerous payloads to expand your operational area. Kobra can reach over 11.5’ feet (3.5 m), easily climb stairs, fit through doorways or down aisle-ways and store or deploy directly from the back of a small 4x4 vehicle. Able to achieve sustained speeds of 8 mph (12.9 km/h) while carrying 150-pound payloads, the Kobra maintains mobility on rough terrain in all weather conditions.
It can climb 55 degrees slopes, even steeper than the Segway RMP440. It also comes with four cameras, radio repeater compatible with the Endeavor Robotics software, and can be expanded with multiple accessories, sensors and disruptors (guns). Also it's runtime is 10 hours at operating conditions.
 |
 |
What makes this robot especially viable for our goal is the special caterpillar capability illustrated in the figure on the right. The robot has four caterpillars which can move independently. This results in optimal grip on all terrains, can deal with sudden changes in elevation (such as sidewalk curbs). It also enables for flexible movement and zero radius turns.
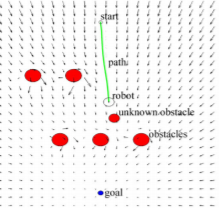
Evolutionary Artificial Potential Field
This method of robot control focusses on single robot control, but is probably a good option to expand for multiple robot control. The Evolutionary Artificial Potential Field (EAPF) method in general deal with motion planning that includes two different but complementary tasks: plath planning and motion planning. Path planning is responsible for generating a set of positions in the workspace that can drive the robot from it's initial position to the target position. Motion planning takes in account the path plan, but translates this to how the robot should actuate this path.
The EAPF is actually an optimisation of the Artifical Potential Field (APF) method. The APF method is illustrated in the figure below:
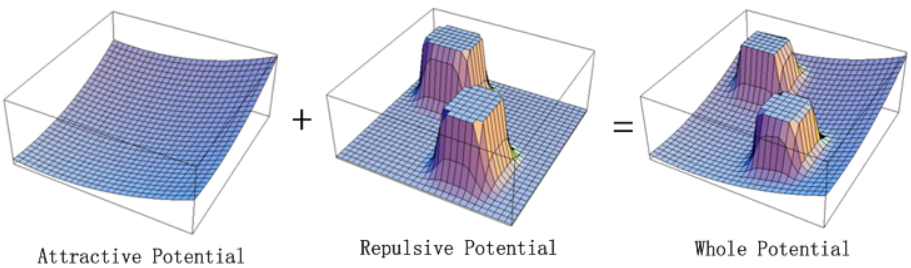
The robot in this figure prefers low rather than high potential, thus moves from the right to the left meanwhile avoiding the repulsive pillars. This method seems fine, however there is a massive drawback: the robot could be trapped in a local minimum of potential and get stuck. The problem is the robot checks the potential locally, and when it has navigated to a minimum it has no way of knowing how to proceed since locally, the potential is worse in every direction. This is illustrated in the APF Local Minimum figure.
It also turns out the system has difficulties in dynamic situations where obstacles change position or suddenly appear.
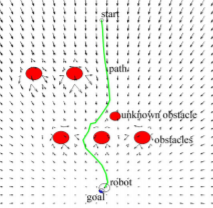
To solve the minimum problem of APF, EAPF was designed. EAPF attaches a cost to the potential. The EAPF method then tries to find a path to the goal that minimizes this cost. Only information on the position of the robot, obstacles and the goal is needed for this method. This way, a global planning is implemented to solve the local planning issue of local minima.
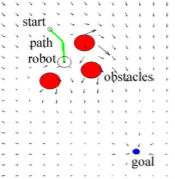
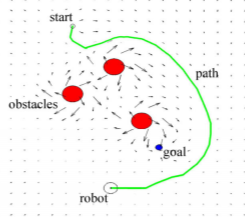
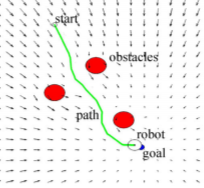
In the paper Optimal Path Planning Generation for Mobile Robots using Parallel Evolutionary Artificial Potential Field cited in the sources chapter, an even better method is proposed which uses the EAPF and adds Generic Algorithms to improve the path planning for dynamic environments with less computational power and a bigger workspace. Experiments in the paper show some promosing results shown in the figures below. The most important thing is that it can handle a dynamic environment, since the crowd control robots will experience this; there is no predefined map of the situation.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Crowd control technique
In the US Army Field Manual, different crowds are described on which to use different tactics. The Manual describes 3 crowd types: Public disorder, Public disturbance and Riot. With Public disorder being non-violent crowds, Public disturbance is where crowds start chanting and singing collective opinions. Some individuals will disturb the normal flow of things. A riot is the most extreme type of crowd, where crowds turn violent and actively try to defeat authorities and the controlling force.
For the control of a crowd, it is important to know it's type so control forces can react accordingly. To identify it's type, background information is needed. An assesment can be made by asking questions:
- Who are they? What is the identity of the crowd? Are they strikers, ethnic factions or social protesters?
- What are their goals?
- What are they capable of doing?
- What are their traditional behaviors?
- When and where will they assemble?
- Where will they go?
- What are the possible targets of violence?
- What is the worst case scenario?
- When and where will they disperse?
Knowing these questions is essential to decide on the tactic to control the crowd with. Too offensive can react to unnecessary violence, whereas too soft can react to an out of control situation.
For a public disorder, often it is enough to stand by and watch for disturbance. Public disturbance and riot often needs more advanced tactics. First of all, when a riot is started, it is important to deter people from joining or leaving the riot. This by for example extensive patrolling, or proclamate the illigality of the riot. Alert, agressive patrolling of the disturbance area deters the gathering of crowds, it also allows for information to be collected, and it creates the psychological impression of the control force being everywhere at once. The use of vehicles provide adds to that effect: The control force is better equipped than the crowd. Varying patrol routes and times keep lawbreakers from being able to pick a safe place or time to act. Proclamating the illigality of the riot makes people aware of the individual and how he is acting illigal. In a crowd, a feeling of shared responsibility causes people to behave different compared to when people are aware of the responsibility they themselves have. Making people aware of themselves and the illigalities they do by proclamation can stop this shared responsibility and deter people. Also warnings can be verbally proclamated like warnings of lootings: "During a disturbance, criminal activity is at it's peak. Your house may be getting looted now, return to your homes!" However, to really try to control the crowd, forces have to either disperse, or contain the crowd.
Containment is the process of limiting a crowd to the area they are presently occupying. It is a suitable option when the crowd must be prevented from spreading to surrounding areas and communities. Perimeter patrols and barriers have to be set up to contain the crowd. However, containment has to be acted upon with caution, to avoid the "fight or flight" syndrome common to people feeling trapped with no escape. Containment contains a lot of coördination. Barriers have to be set up at specified locations. Vehicles or forces have to be traveling at close interval in formation. Dispersion is the process of taking deliberate actions to fragment an assembled crowd in order to prevent the destruction of property or prevent injury. Dispersion is done by proclamations, show of force and moving in crowd control formations. The difficulty of dispersion is channeling the dispersion route. The dispersed crowd should preferably take a chosen route where the crowd can safely and calmly leave the area. Dispersing crowds into wide-open areas for example is unwanted since a new gathering can occur. The crowd should be kept moving, but not too hurried to avoid panic.
This projects opts for Civil Disturbance Formations executed partly by robots. Especially the front of each formation should be operated by robots to minimise damage to the control force. There are different formations (A,B,C, are the squad members, other signs are leaders etc. in the figures below):
- Line formation is the most used formation because it's offensive and defensive applications. As offensive, the line is used to push or drive crowds straight back across an open area or street. Defensive to hold the crowd or deny acces to a certain area.
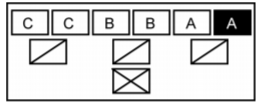
- Echelon formation is an offensive formation to drive crowds away from buldings, fences and walls.
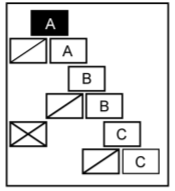
- Wedge formation is an offensive formation to penetrate and split crowds into smaller groups.
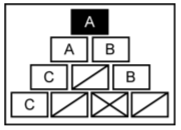
- Diamond formation is a defensive formation that offers all-around security when in an open area.
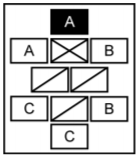
Ideally, the robot designed for this project would be able to execute these formations. The robots should be communicating with eachother sharing location and sensor information to execute this.
Robot Communication
Flowchart
To get a better understanding of what the robot is proposed to function like we made some flowchart to simulate part of the decision making process.
The robot
The robots decision making process starts with a simple check if the robot is still upright. If this fails the robot will send an error message. After the robot has been determined itself to be upright it checks if its camera returns a functional videofeed. If this is not the case the robot will try and clean the camera itself. When this fails the robot will report an error stop. If the camera can properly view the robots surroundings it will use its depth perception camera to observe any objects (or persons) and map this onto an accessible area map. And separately map the people in its field of view to a map. When the items from a given timeframe are mapped to their designated maps the next input is used. The IR camera is checked in the same way the other camera was checked. If the camera is functioning correctly the field of view is checked for fires and if there are any they are added to the obstacle map. The information from the IR camera and the people map are cross referenced to be certain that the people being perceived are real warm blooded humans. If they are low to the ground they are kept on the obstacle list and otherwise they are removed from the obstacle list. When all people in the instance are reviewed the robot attempts to send the created maps to the controller and reattempts of contact is not established. The controller processes all maps and the robot receives its optimal path with updated maps. The robot then updates its path and maps accordingly.
The controller
The controller checks if the goal for the formation has been changed. If so its goal paramaters need to be edited accordingly. During a cycle the robot receives maps from the robots. It will then check if all active robots have sent their data. If it has not happened consecutively for a given boundary of times the controller will simply assume the previous data to still hold. If it happens more often the robot will be presumed to be lost and it will from now on be an obstacle. If a robot respondes that has been considered lost the system will try to reïntergrate it. The maps are then concatenated and the goal and available space are used to derive an optimal path if possible. If these are found the robots are updated. But if it is not able to keep going an error is sent and the robots await a new goal.
 |
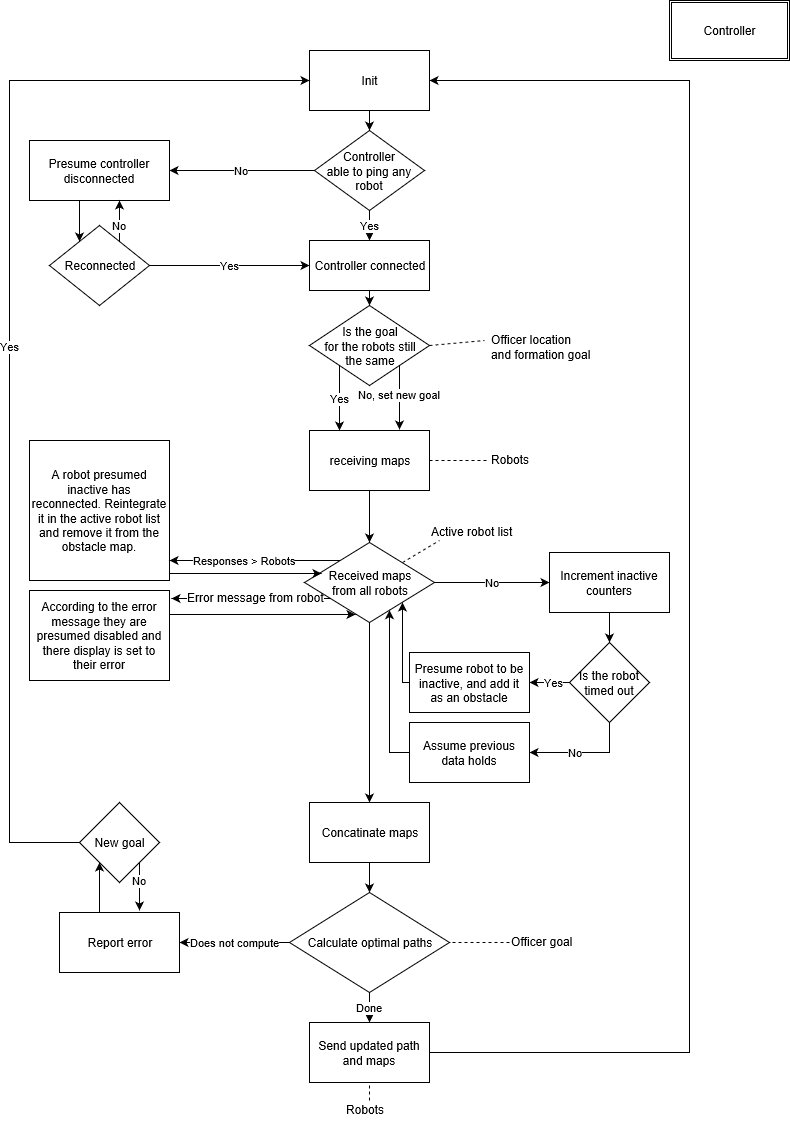 |
State diagram
In reality, robot operations almost inevitably fail to go according to plan. There may occur events that are not thought of, and thus the robot would maybe not be capable of handling these. Also the robot can have mechanical, electrical of software problems. Sensors and actuaters can misbehave. In a flow chart, a nominal plan of action can be acurately and clearly described. However, fail states are harder to describe in the format. This is where the state diagram comes in. In the state diagram, different problems can be described, and tell the user/robot what to do. It is a clear method because the robot can asses in which state it finds itself in, and can plan action according to the state's conditions.
The state diagram for our robot can be seen in the figure below.
Police thoughts
User thoughts
Design
Requirements
To design this kind of robot there are three sorts of requirements that have to be met. First of all the robot needs to meet some technical requirements, it must have the tools to accomplish something. Then there are two sorts of functional requirements, first there are the requirements about the decision making of the robot. Second there are ethical requirements, while there are a lot of ethical rules when you treat with people.
Decision making: During a riot, people must be driven to a safer place, the robot has to make a decision when to push the people and to what place. Therefore the robot need to have contact with the other robots and riot police, together they have to make a choice what the best option is. The robot also need to make decisions when it comes to signaling crimes, so they can arrest them.
Technical requirements: The robot has to sustain a lot of violent people, so it needs to be made out of sustainable, hard materials. Next to that it has to stand solid as people will try to push it over, it must hold over 10 people pushing against the robot. Furthermore it must have the ability to arrest people, so it has to have a mechanism to hold people. For making the decisions the robot must see, it has to have an overview of the situation, it must detect people, actions and safer places.
Ethical requirements: Because you are dealing with people there are a lot of ethical rulings you have to take in mind. You can't assault a troublemaker without any reason, also the means are restricted by these ethics. Shooting is easily ethical irresponsible, you also can't hold a person without reason. These ethical decisions will have to be implemented in the decision making, in a further stage of the project we will discuss the ethical restrictions and possibilities.
Functional
Technical
Validity of design
Police thoughs
User tests
prototype?
Sources
Endeavor Robotics Kobra http://endeavorrobotics.com/products#710-kobra Endeavor Robotics Kobra Spec Sheet http://endeavorrobotics.com/media/docs/English%20Specs/Endeavor%20Robotics%20PackBot%20Spec%20Sheet.pdf Segway RMP440 Spec Sheet http://rmp.segway.com/downloads/RMP440LE.pdf PEAPF Navigation technique https://link-springer-com.dianus.libr.tue.nl/content/pdf/10.1007%2Fs10846-014-0124-8.pdf Crowd Control Technique https://fas.org/irp/doddir/army/fm3-19-15.pdf Gustave Le Bon, The mind of Crowds http://www.gutenberg.org/files/445/445.txt Freud Group Psychology http://freudians.org/wp-content/uploads/2014/09/Freud_Group_Psychology.pdf Social identity theory and other social theories https://www.simplypsychology.org/social-identity-theory.html Irrational riots http://news.ku.dk/all_news/2013/2013.4/riots_create_irrational_behaviour/ Crowd behavior research Groningen http://www.rug.nl/research/portal/files/14565232/02c2.pdf
1. catagorizeren papers
2. Lezen
3. Probleemstelling opstellen: Waarom is onze robot nodig?
4. Definiëren wat we gaan inleveren/deliveren.
Papers and articles:
- Human Robot Interaction
- (1) Humanoid robots state of the art, and human reaction (book) https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007%2F978-0-387-85349-9.pdf
- Psychology of Rioting
- (2) Crowd action as intergroup process: Introducting the police perspective http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com.dianus.libr.tue.nl/doi/10.1002/(SICI)1099-0992(199807/08)28:4%3C509::AID-EJSP877%3E3.0.CO;2-C/abstract
- (3) Cops and Chaos: A Historical Examination of the Police Role in Riot Control http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/19361610.2015.1069532?scroll=top&needAccess=true
- (4) Crowd theory and the management of crowds: A controversial relationship http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/0011392113486443
- (5) Contemporary understanding of riots: Classical crowd psychology, ideology and the social identity approach http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/0963662516639872
- Conflict escalation
- Riot Simulation
- (6) Analysis of a riot in Burnley http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/10439460410001674956
- Crowd Management
- (7) Interactive Control of Large-Crowd Navigation in Virtual Environments Using Vector Fields http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/4670099/
- Robot utility in riots
Citations and information from articles
Crowd action as intergroup process: Introducting the police perspective
Treating the crowd as an homogeneous whole plays an important role in escalating
Conflict occurs where crowds gather because it is in the very nature of crowds to be conflictual
The police officers see the crowd as an heterogeneous whole
Some of those, I am sure, the vast majority were good law abiding people under normal circumstances. But when you are in a group like that, I am sure that, the fever of the cause, the fever of the day, the throwing and everything else, they get locked together and think ``oh we are part of this. – Chief inspector during the poll tax riots
Only one black sheep in the herd, with law abiding people, can stir the whole crowd up
However heterogeneous crowd composition might be, once people get together in the crowd homogenizing processes take over. Everybody is potentially violent and, once violence actually starts, everybody is liable to join in.
When trouble occurs and the police intervene, their tactics are generally aimed at getting rid of the threat entirely: dispersing the crowd, driving it in a particular direction, dividing it and containing it
Pc 8: `You haven't got the discussion time'. Pc 10: `No, you are talking about a split second decision'. Pc 8: `your main aim in that situation is not to make arrests but to clear the streets and stop a public order situation. You are running through, you have got to make very quick assessments of people. It is just a quick and difficult assessment and you will make wrong assessments' (Grp. 2, BTb).
When going in without violence you wouldn’t come out alive.
Cops and Chaos: a historical examination of the police role in riot control
The first thing law enforcement officials can do to control collective violence is to be professional in their daily dealings with the people they serve. History has shown that people everywhere demand to be treated fairly.
While it is clear that the police are not singlehandedly responsible for the enormity of slavery, segregation, and discrimination, the police are representatives of the government and society at large.
As noted by the U.S. Department of the Army (2014, pp. 2–6), winning in a crowd control mission “is not like winning in combat. (...) Winning in this environment is about seizing and holding the moral high ground.”
For starters, rather than wearing riot gear, officers should wear standard uniforms or perhaps even, depending upon the weather, casual uniforms such as knit shirts and short pants. Having officers prepare for a protest by means of donning riot gear complete with helmets, shields, and batons at the ready may psychologically prep the officers and the crowd for conflict (Madensen & Eck, 2006; Masterson, 2012). In contrast, having officers meet, greet, shake hands, and make small talk with crowd members can help forge “a psychological bonding with the crowd that pays real dividends. It is very difficult to fight the police if you’ve just been friendly with some individual officers”
This does not mean that, at the first sign of trouble, police officers in riot gear need to form a phalanx with their shields locked and batons drawn and advance toward the crowd. Research suggests that such synchronized actions nourish aggression.
A critical analysis of the Burnley riot
Through being undermanned, the white youth became only more confident about, so the situation began to escalate.
First, the police were present in insufficient numbers given the likely magnitude of the brewing confrontation; and second, the key decision to withdraw officers from a scene of growing white racist hostility outside the Baltic Fleet signalled to the Asian communities that, since the police were apparently unwilling or ill-prepared to defend them, they would have to take their safety into their own hands.
Team progress
28-9-2017: Through reading of the articles a clear problem description was defined in a discussion and will be elaborated by Bern. Furthermore the deliverable is chosen:
- RPC's
- Case study
- Design
The wishes for the RPC and design will be elaborated by Sjoerd and the case study by Luke.