PRE2016 3 Groep1: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 240: | Line 240: | ||
https://www.festo.com/cms/en_corp/14014.htm | https://www.festo.com/cms/en_corp/14014.htm | ||
=='''Visiting van den Borne'''== | ==='''Fertilization'''=== | ||
There are some different aspects in the fertilization process that are currently improved by the use of robots. Four of the main aspects are soil Electrical Conductivity mapping systems, GIS services, precision sampling and precision fertilization. Those four aspects will be discussed below. | |||
===='''soil Electrical Conductivity mapping systems'''==== | |||
Soil Electrical Conductivity (EC) is a measurement that correlates to soil properties affecting crop productivity including soil texture, cation exchange capacity, drainage conditions, organic matter level, salinity (salt level) and subsoil characteristics. This information is used to make a fertilization plan. Soil EC is one of the simplest and least expensive ways of soil mapping for precision fertilization. Some examples of soil EC mapping systems are the EM38-MK2 sensor (left) and the Dualem 21s sensor (right). | |||
Below, the result of a Soil EC measurement is given, this map is made by dragging the sensor across the field. The sensor measures how good the different patches of soil conduct electricity and the needed data can then be determined from this information. | |||
===='''GIS services'''==== | |||
GIS is short for Geological Information System. GIS services use satellites to analyze all sorts of geological information. With the aid of GIS, maps of fields or farms are created with different layers (yield map, EC map, soil sampling, remote sensing, etc.), allowing the precise application of fertilizer (and other inputs) according to the variability of the field. Some examples of GIS services are Google Earth and esri. | |||
===='''Precision sampling'''===== | |||
Precision sampling is soil sampling with the use of global positioning system (GPS), which allows to precisely locate position in the field. First the field is mapped, after which a grid is placed over the field, dividing the field in smaller sections. In those grids sample sections are chosen, more sample sections means more accurate sampling, but also higher costs. GPS is then used to accurately take the samples. Finally the soil is analyzed in a lab and the outcomes are displayed on a map. | |||
Above is an example of a sampling grid. With this particular way of sampling the distribution of the sampling sections gives the most accurate outcome. It is called a diamond sampling pattern, since the sampling sections are in a diamond shape, as can be seen above. | |||
===='''Precision fertilization'''==== | |||
==='''Visiting van den Borne'''=== | |||
We visited one of the most advanced precision farms in the Netherlands, where a lot of new techniques for precision agriculture are being used. The name of the farm is van den Borne potatoes. | We visited one of the most advanced precision farms in the Netherlands, where a lot of new techniques for precision agriculture are being used. The name of the farm is van den Borne potatoes. | ||
Revision as of 18:05, 19 February 2017
Presentation 1:
Problem description Model the economical and ecological impact of using robots (drones) in agriculture.
Objectives
The system must
- use drones to acquire data
- analyze the data
- react to the results of the analysis
approach
-research state of the art
-abstract from state of the art
-contact with user
-Create model
-analyze impact
USE aspects
-Societal problem of hunger
-Cheaper food for user
-Cheaper then workers in the long run
Group members
- Guus van Dongen 0960106
- Johan Somers
- Teun de Groot 0951139
- Jur Bartels
- Laurence Keijzer
- Bastiaan Wuisman
Project Description
Use Aspects
It is important to check what the USE aspects are when we want to locate the problem and try to invent something for it.
- Primary Users: the primary users for the drones are the farmers. They are going to work with the technology as a tool for the work process.
- Secundary Users:
- Tertiary Users:
- Society:
- Enterprise:
Project Planning
Week 1
- Create presentation
- Determine concept idea of drones helping for agriculture
- Research about state of the art
Week 2
- Finish the state of the art [milestone]
- Weeding
- Seeding
- Fertilize
- Harvesting
- Irrigation
- Crop protection
- Contact with User
- Definition of the problem
- Visiting van den Borne [milestone]
- Create presentation
- Create planning
- Re-create scenario
Week 3
- Contact with User
- Contact with 'Jan Staal adviesbureau' made (Has contact with many farmers)
- Contact with 'Johannes Strever' (Uses GPS a lot)
- Contact with University Team (Are developing a drone for van den Borne)
- Formulate concept [Milestone]
- Start of the model [Milestone]
- Search for essential information (data)
- Economical
- Ecological
- Company scale
- Global scale
- Software: what software are we going to use
- Update wiki
Week 4
- Implementing the model in software [Milestone]
- Update wiki
Week 5
- Finished model of application in the Netherlands [Milestone]
- Update wiki
Week 6
- Finished model global scale [Milestone]
- Update wiki
Week 7
- Testing the models [Milestone]
- Changing the models
- Update wiki
Week 8
- Finished Wiki [Milestone]
- Formulated advise [Milestone]
- Prepare Presentation
- Giving Presentation
State of the art automated agriculture
Weeding
There are some quite exciting technological developments going on in the area of automated weeding. The most important technologies will be discussed below.
Deepfield Weeding Robot
The first far-developed technology is the Deepfield Weeding robot of Bosch, see below.
This robot has GPS navigation to move through the fields with a 90% electrical efficiency. A row of linear actuators is attached to the bottom of the robot. When the robot detects weed is punched one of the actuators in the ground the destroy the little plant. The company claims that the positions accuracy is 2 mm and that it can remove 20 weeds per second. Given 40 weeds per square meter, the robot can process a hectare in three hours. The machine will cost about the same as a midsized tractor (http://www.dairyherd.com/news/german-company-demonstrates-automated-weeding-machine).
Advantages of this design:
- Herbicide-free farming
- Relative fast operation
Disadvantages of this design:
- Only suitable for small weeds
- Only suitable for field with small crops
There is also an other variant of this machine under development. This machine looks almost the same, but it does use herbicides. A greater working with of six to seven meters is possible with foldable booms. This machine will still lead to massive herbicide savings, but with a much bigger capacity potential.
LettuceBot
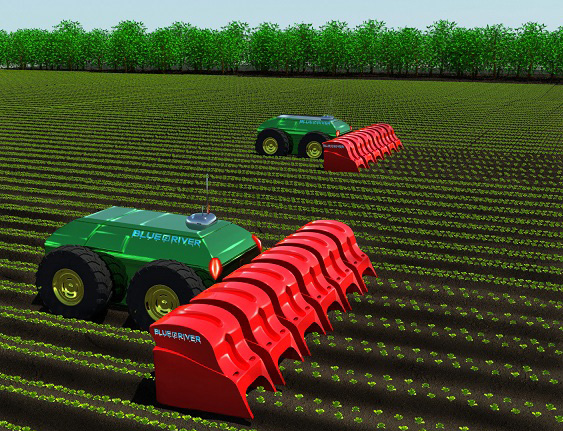
A company called Blue River created a robot which can identify weed and excess planted lettuce plants with the use of image recognition. When it is determined which plants need to be removed, the robot sprays a little amount of herbicide on it. This can result in a 90% reduction of use of pesticides. Currently the robot is towed behind a conventional tractor, but Blue River is working on an fully automated version of the LettuceBot.
While driving four miles per hour the precision is a quarter of an inch. The machine can process 40 acres per day and can cared for up to 5000 plants per minute. The machine also collects data about the plants when driving through the field to keep track of the growth and health of the plants.
Advantages of this design:
- It is already a fully functioning machine
- It is really fast
Disadvantages of this design:
- It can only be used on lettuce
- It isn't fully autonomous yet
Naïo Technologies
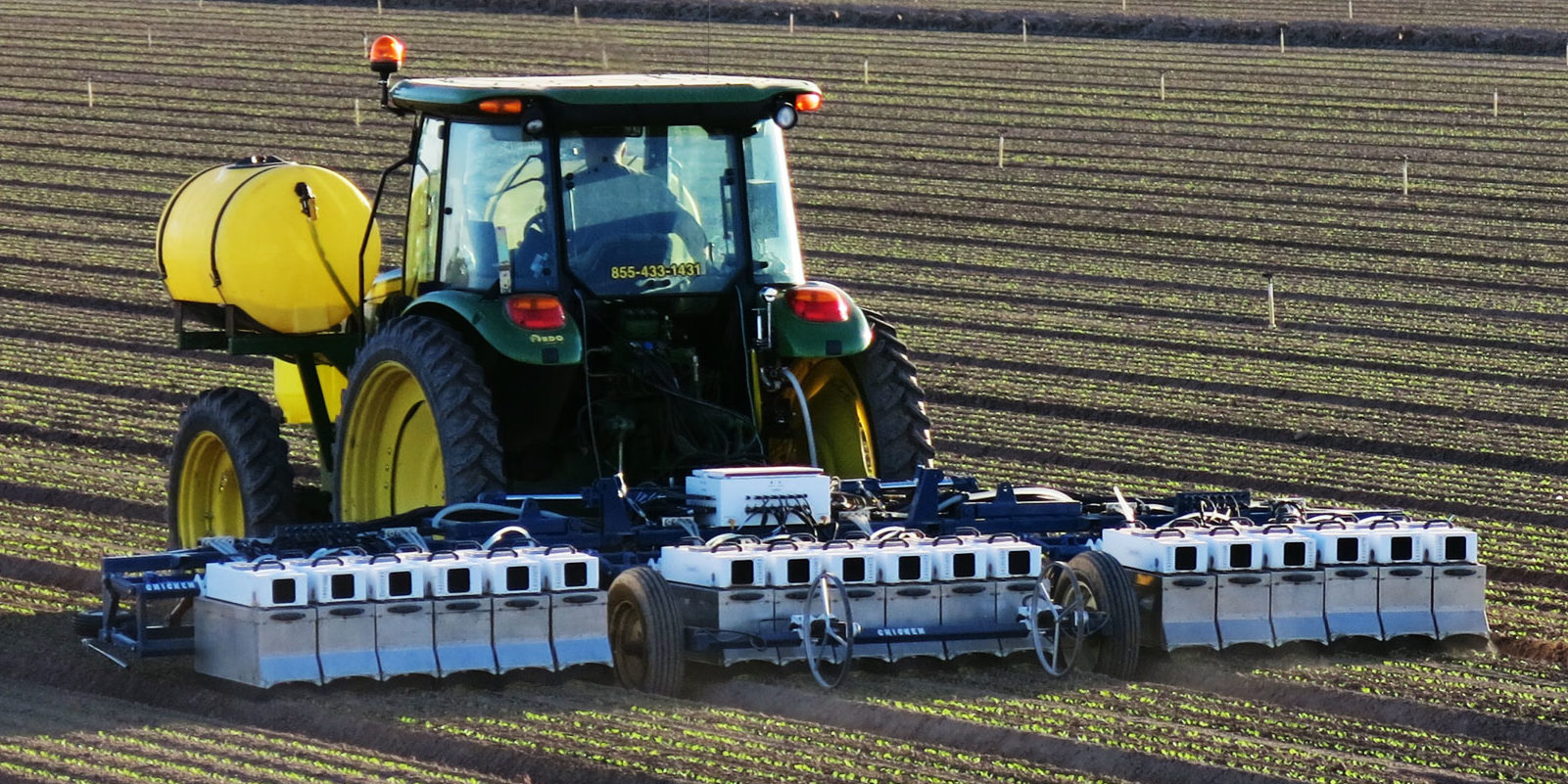
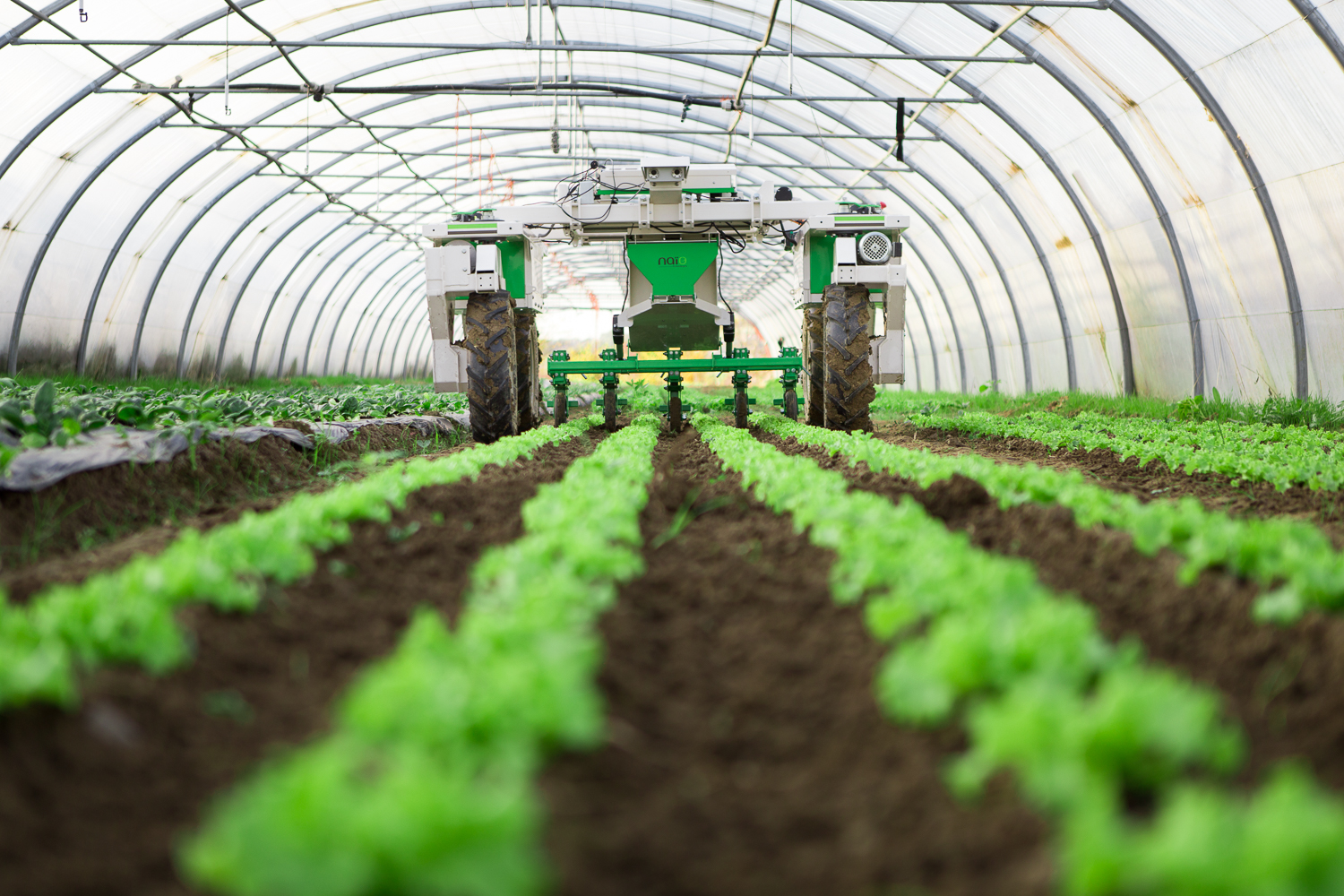
Naïo Technologies is a company that produces different types of weeding robots. They are suitable for different kinds of users and crops. The one thing that the different robots have in common is that they remove weeds by hoeing. This lets the robots stand out to the opposing companies and robots. The most important robots of Naïo technologies can be seen below.
The first robot is called 'Oz' and is suitable for smaller fields. The small battery driven robot has a maximum moving speed of 1.3 kilometers per hour. It follows the mounds via different optical sensors and RTK GPS. The robot can turn itself around to start independently with a new mound. It only uses about one euro worth of electricity to weed one hectare.
The second robot is created for bigger farms and uses the same techniques as the Oz robot.
The third robot is called 'Ted' and is used to weed vineyard. The maximum speed is four kilometer per hour and it can maintain a surface of about 25 hectares. This robot also shares the most techniques used in the other robots. The company is working on extending the capabilities of the robot with adding functionalities as mowing, leaf thinning and trimming.
Seeding Machine
There are two kinds of seeding machines, the normal one and the precision machine.
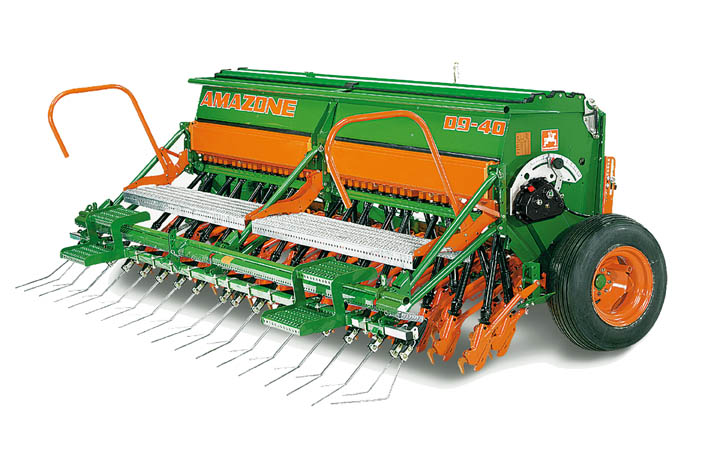
Normal seeding machine
A seeding machine is a device that is able to sow the seeds by metering out the individual ones. The machine positions the seeds in a soil and covers them to a certain average depth. The machines makes sure that the seeds are placed at equal distances and depths. Eventually the machine covers the seeds with soil so they can’t be eaten by birds.
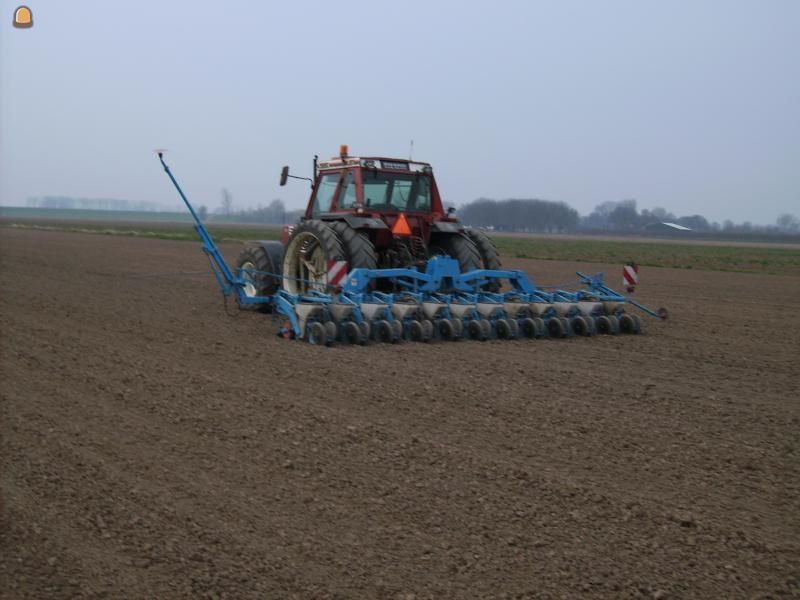
Precision Agriculture
For the precision agriculture there is a new design for seeding machines. This model makes use of GPS. This makes it possible that the machine exactly knows where to drop the seeds.
Automated Seeding machines
In 2006 an Australian company designed a machine that is able to plant 6 rows at a time. Eventually the machines have been sold to England and Dutch farmers as well.

Field robot event
In 2016 there was a robot event in Hassfurt, Germany. One of the games they played there was a seeding game on the field. The robots have to operate on an area of 10 x 1 meters. The robot should take wheat seeds from a station and has to sow them on the area. There were no specific rules how the machines should complete the task. The robots had to distributes the seeds as even as possible and cover them with soil.
Other kinds of mini robot seeders:
Harvesting
There already are a few robots designed for the harvesting of crops. Due to the difference in the way certain crops should be picked, robots that harvest crops are often designed for one specific crop, such as bell pepper, cucumber or any other crop.
Sweeper
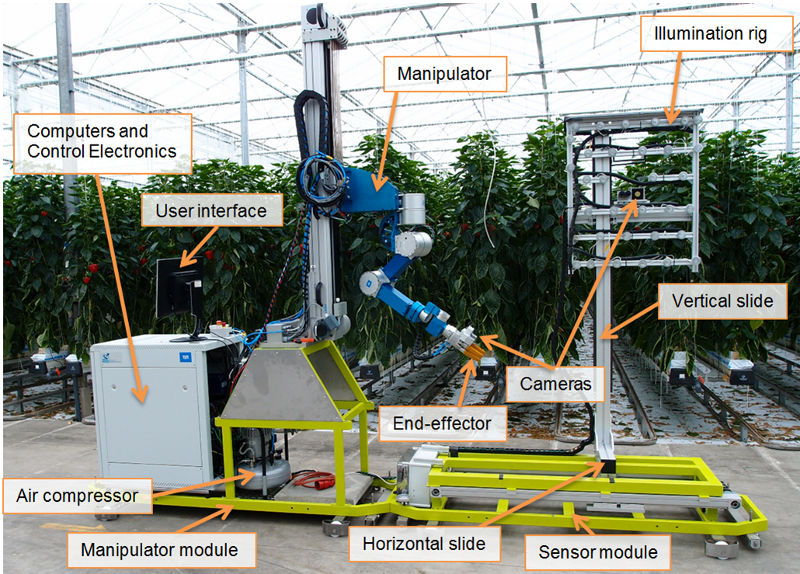
The Wageningen University and Research center developed a robot for picking bell peppers in collaboration with a group of bell pepper growers. The robot is displayed below.
The robot picks the crops using a mechanical arm (The manipulator) and then places the crops into a container. To locate the peppers it uses multiple cameras to build a 3D picture, while trying to eliminate potential obstructions such as leaves. It has a special lighting rig to prevent bad light from being an issue. This robot was tested successfully in 2014, but was limited to slower speeds at that time due to fear that higher speeds may damage the crops.
http://www.crops-robots.eu/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=22&Itemid=22
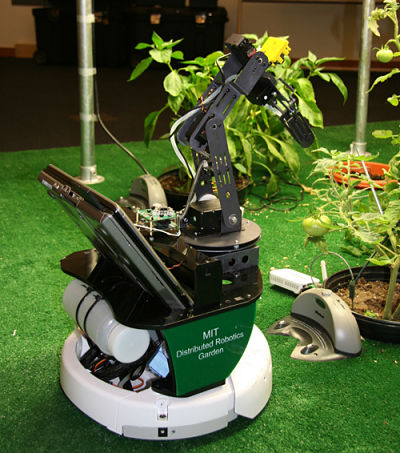
MIT Robot Gardener
MIT developed its own gardening robot in 2009. The robot has a mechanical arm for picking the crops and a watering pump to water them. A difference with the usual approach here is that the robot does not contain any sensors to analyze the plants, the sensors are placed on the plants themselves. Using sensors that can detect soil humidity and other techniques borrowed from botanical science, the sensors broadcast the need per plant, giving this technique a high precision in picking and watering the plants.
Agrobot SW6010
The Agrobot SW6010 is a commercial berry picking robot. It features a rather large truck-like design, but is fully capable of autonomous harvesting of berries such as strawberries. To pick crops it utilizes a set of precision arms, with five arms on each side. Using the multiple arms, the robot can reach multiple plants and pick crops more efficiently. There is space for two passengers to check and sort berries that the machine collects. To identify the berries, the system uses the companies patented AGvision system, which supposedly determines the ripeness of the fruit by analyzing the color and form.
Cucumber harvester
Another project of the Wageningen University and Research center is a robot for cucumber harvesting, which utilized a double camera system and a mechanical manipulator arm to detect and harvest ripe cucumbers. They built and tested a prototype in 2001 and were able to detect 95% of the ripe cucumbers, and successfully picked 75% of those. The vision techniques developed by this robot can be found in multiple modern harvesting robots.
Berry Nice
This machine is a berry picking machine developed by the Japanese Shibuya corporation. It features robots that move on rails in contrast to most autonomous robots which use wheels. Using rails increases stability and speed, but makes adapting the system more difficult as the robot can only move to where the rails are. It also uses 3D stereo cameras to determine ripeness.
CROPS solution
The CROPS solution is a modular adaptable robot to harvest ripe fruits, the project is sponsored by the European Union. The goal of the project is to develop a robot that can not only harvest one, but multiple types of crops easily. It uses FinRay fingers, which are adaptable grippers to hold a fruit, and a knife to cut the fruit off the plant. To detect ripeness, cameras and color and humidity sensors are used.
https://www.festo.com/cms/en_corp/14014.htm
Fertilization
There are some different aspects in the fertilization process that are currently improved by the use of robots. Four of the main aspects are soil Electrical Conductivity mapping systems, GIS services, precision sampling and precision fertilization. Those four aspects will be discussed below.
soil Electrical Conductivity mapping systems
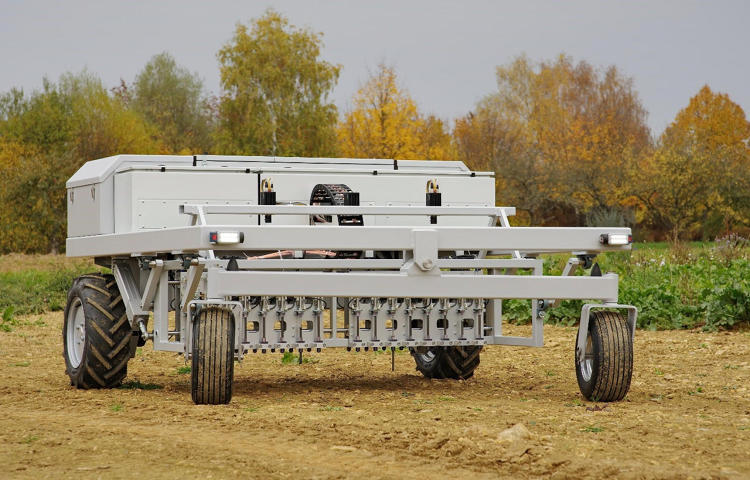
Soil Electrical Conductivity (EC) is a measurement that correlates to soil properties affecting crop productivity including soil texture, cation exchange capacity, drainage conditions, organic matter level, salinity (salt level) and subsoil characteristics. This information is used to make a fertilization plan. Soil EC is one of the simplest and least expensive ways of soil mapping for precision fertilization. Some examples of soil EC mapping systems are the EM38-MK2 sensor (left) and the Dualem 21s sensor (right).
Below, the result of a Soil EC measurement is given, this map is made by dragging the sensor across the field. The sensor measures how good the different patches of soil conduct electricity and the needed data can then be determined from this information.
GIS services
GIS is short for Geological Information System. GIS services use satellites to analyze all sorts of geological information. With the aid of GIS, maps of fields or farms are created with different layers (yield map, EC map, soil sampling, remote sensing, etc.), allowing the precise application of fertilizer (and other inputs) according to the variability of the field. Some examples of GIS services are Google Earth and esri.
Precision sampling=
Precision sampling is soil sampling with the use of global positioning system (GPS), which allows to precisely locate position in the field. First the field is mapped, after which a grid is placed over the field, dividing the field in smaller sections. In those grids sample sections are chosen, more sample sections means more accurate sampling, but also higher costs. GPS is then used to accurately take the samples. Finally the soil is analyzed in a lab and the outcomes are displayed on a map.
Above is an example of a sampling grid. With this particular way of sampling the distribution of the sampling sections gives the most accurate outcome. It is called a diamond sampling pattern, since the sampling sections are in a diamond shape, as can be seen above.
Precision fertilization
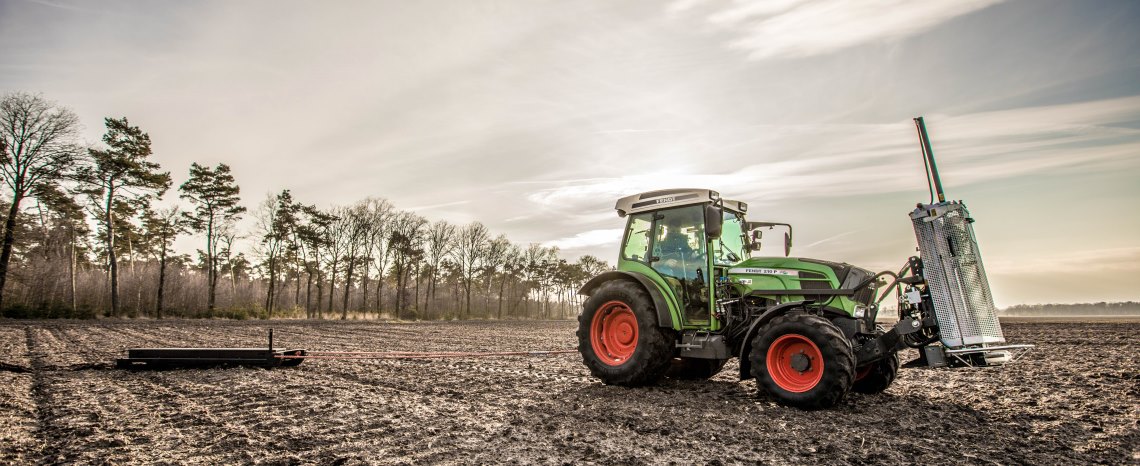
Visiting van den Borne
We visited one of the most advanced precision farms in the Netherlands, where a lot of new techniques for precision agriculture are being used. The name of the farm is van den Borne potatoes. The biggest difference on their farm is that almost everything they do with the potatoes is done by precise machines. They are able to work with a precision of 6x6 meters.
We had a conversation with Jacob in which we talked about the pros and cons of precision farming and the usage of new technologies.
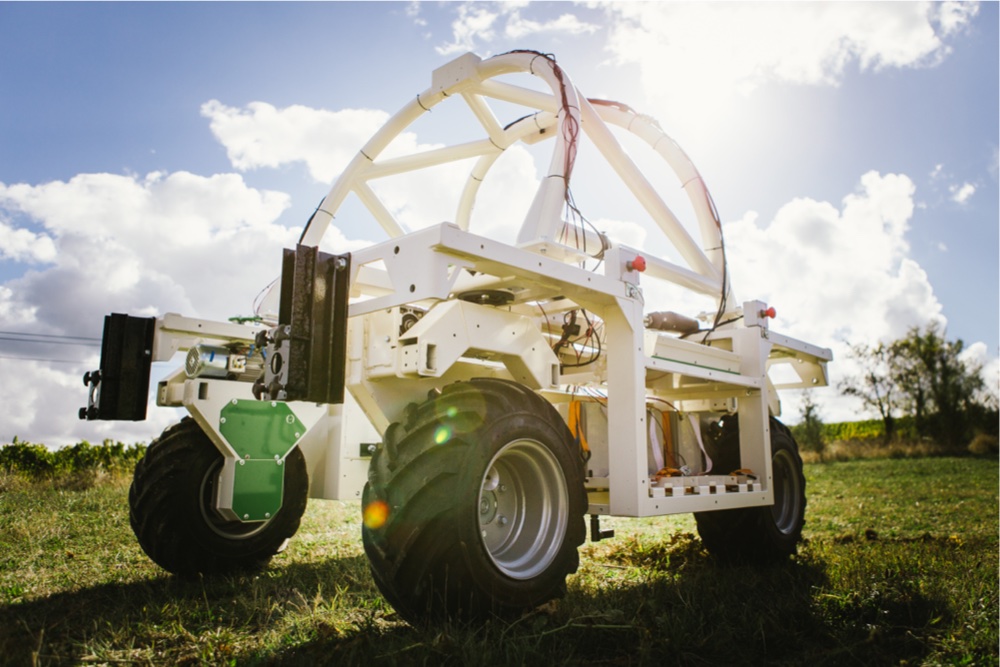
He explained to us that by using new technologies you will get more work, but it is worth it because of the higher yield gained. The investment in technologies costs a lot of money. But because of the precise measurement and management of the plant, you are able to reduce the overlap, meaning that there are less resources used. This saves a lot of money if you are a big farmer. The biggest problems he struggles with are the legal restrictions. There are many rules for flying with drones which makes it hard to work with this technology.
The cameras they are using are able to collect a lot of data. One of the cameras measures 5 different spectra, the standard RGB and the extra close-infrared and normal infrared. The pictures made with this camera are stitched together, so one big picture is gained. This picture is then analyzed. With the pictures of another drone with a normal camera, they are also able to make a 3d model of the farmland.
Jacob explained that the precision farming is mostly used with corn, wheat and grass. Van den Borne grows potatoes, because potatoes have a high efficiency. He also explained to us that if the bottom of your farming land exists of sand, you have to add liquid manure. When working with the precision agriculture concepts on sand the results are much better.
All machines that are required for executing the process of growing potatoes are designed for operating with GPS. Everything that happens on the land of van den Borne will be actuated by a computer.
The only part that is difficult with the technology is that it is simple to measure all kinds of things, but it is difficult to process the 'raw data' to data you can work with. It will always stay hard to exactly tell, out of a picture, where you should change something for optimizing the grow process.
The current project he is working with right now, is that of a building team that tries to build a new drone. And because of the legal restrictions he is observing the possibilities for using drones that fly with a fixed power cable.
References
-Company that makes ground scans and 3D scans with drones: https://3dr.com/ -Drones made for agriculture: https://www.sensefly.com/applications/agriculture.html -Drones that also map the ground: http://www.precisionhawk.com/ -Examples of agriculture robots: https://www.intorobotics.com/35-robots-in-agriculture/ -Some facts and companies analyzed: https://www.therobotreport.com/news/ag-in-transition-from-precision-ag-to-full-autonomy -Benefits analyzed: https://www.geospatialworld.net/article/drones-and-robots-future-agriculture/ -Professors etc. giving their views: http://fruitworldmedia.com/index.php/featured/robots-huge-potential-robotics-agriculture-industry/ -Japanse company that founded a fully autonomous indoor farm: http://spread.co.jp/en/sustainable-farming/ -Project of the EU for percision lifestock farming: http://www.eu-plf.eu/index.php/publications/ -eLeaf technology: http://www.eleaf.com/products-showcase-fruitlook#technology-pimapping -Automated precision weeding: http://www.bluerivert.com/ -Case study of drones in argiculture https://blog.dronedeploy.com/case-study-ce39c9f44e48#.tsnfhikpp -Mechanical weeding robot http://link.springer.com/article/10.1023%2FA%3A1015674004201?LI=true -Seeding and fertilazation robot goo.gl/s2ehLC -Machine-to-machine communication goo.gl/UVJDFS -Framework for argicultural systems goo.gl/RGzsuo -Farmer in the Netherlands which uses the drone: http://www.loonbedrijfthijssen.nl/contact/ -An other farmer in that uses drones: http://www.vandenborneaardappelen.com/ -Bosch Weeding Robot: https://www.deepfield-robotics.com/en/Weeding.html