E-box/Install manual: Difference between revisions
| Line 209: | Line 209: | ||
Download the manual via this [[Media:BuidingRunningSimulink.pdf|link]]. | Download the manual via this [[Media:BuidingRunningSimulink.pdf|link]]. | ||
Revision as of 09:36, 6 July 2011
This page contains the neccesary step to install a realtime linux system with EtherCAT
Installing a linux distribution
Ubuntu 10.04 LTS
Ubuntu is an operating system developed by the Ubuntu community. Based on Linux and GNU software Ubuntu is perfect for most PC's and laptops. It contains all the applications you need, a modern web browser, email package, programs for photo editing and important to us: all the tools for programming. Ubuntu is developed with focus on security. LTS (Long Term Support) versions will be three years provided with security updates. These LTS versions are free and available for everyone. Upgrades to new versions of Ubuntu will always be free.
This part describes how to install and configure Ubuntu 10.04LTS with rt-kernel. The last LTS (Long Term Support) version with rt support during the writing of this document is Ubuntu version 10.04 (Lucid Lynx). It is also possible to install Ubuntu Studio. This version for audio- and video editing is still equipped with the Linux kernel-rt
Download and install ubuntu-desktop-amd64.iso 10.04.2 (64 bits) or ubuntu-10.04.2-desktop-i386.iso (32 bits):
http://www.ubuntu-nl.org/getubuntu/download/LTS or http://releases.ubuntu.com
Download the latest updates via the Synaptic Package Manager. Package updates are allowed. Do not upgrade e to a higher Ubuntu version eg 10.10.
Download and install Linux-rt via the Synapic Package Manager.
Restart Ubuntu and repeatedly press the Shift button. You'll come into the Grub boot manager menu. Select the rt kernel version.
Check the kernel version in a terminal with:
uname -r
respons: kernelversion-rt
2.6.31-11-rt
Change standard kernel to start by installing the package startupmanager
Embedded pc's
A manual for installing Ubuntu on embedded pc's can be found here: Install manual for Ubuntu on embedded pc
Required packages
Download and install via the Synaptic Package manager:
Nautilus file browser. (This is useful as superuser) gcc and g++ 4.1 (For Matlab 2007b) java-1.6.0-sun or sun-java6-bin (using Matlab and smartSVN) smbfs (for connection to Windows shares)
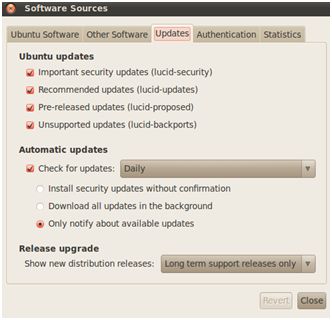
Some packages are not available with the default settings. Check also: Pre-released updates (lucid Proposed) and unsupported updates.
Check java version:
java -version
Two versions of gcc and g++ are installed. These are gcc and g++ 4.1 and 4.3. The default version is probably the highest 4.3. Matlab2007b MEX only works with gcc and g++ version 4.0 to 4.2.
Check the default used version:
gcc --version g++ --version
Force a symbolic link to version 4.1 in the /usr/bin directory:
cd /usr/bin ln -sf gcc-4.1 gcc ln -sf g++-4.1 g++
Installing Matlab
Currently two versions of Matlab are supported: 2007b and 2010a (experimental support only). Choose a supported version.
Installing Matlab 2007b
Matlab 2007b is availiable at:
\\wtbfiler\Software\Unix-Software\matlab2007b
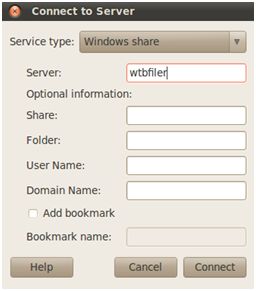
Use samba to the connect the wtbfiler:
taskbar, places, connect to server, windows share (samba)
Type server wtbfiler, leave the other fields empty and connect. Domain Name, Username and Password should be filled on the next page otherwise it will not work.
Copy the Matlab folder temporarily to your Home directory.
Check your permissions:
ls -l
Make sure the installation files are executable and change your permissions if necessary:
chmod 755-R /home/username/matlab2007b
Create a new directory:
mkdir /usr/local/matlab75
copy the licence.dat in this directory.
It's possible to do this on the commandline. It is more convienient to use the Nautilus file browser. Open a new terminal start nautilus and copy the file:
sudo nautilus Password:
Open a terminal and install Matlab2007b:
sudo ./install
Create a symbolic link for matlab in /usr/bin (Matlab starts from any directory):
sudo su Password: cd /usr/bin ln -s /usr/local/matlab75/bin/./matlab /bin/matlab
Start Matlab:
matlab
If your matlab code is invisible set the visual effects in Ubuntu to none:
System, Preferences, Appearance, Visual Effects
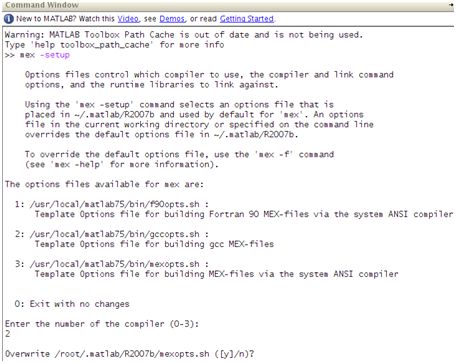
For MEX we need g++ and gcc 4.1. Force matlab to use the gcc compiler by:
>> mex -setup
Option 2: gcc MEX files
Matlab is installed and configured.
Getting the software
It is possible to obtain the current software via our svn-server
What is svn? Svn, in full: Subversion is a tool to exchange files between members of a team. It ensures that all team members always have the latest versions of all project files available. With svn precious work is not lost: you can always fall back on earlier versions of your project. There are dozens svn clients. All open-source. Smartsvn is a handy java based svn client available at:
http://www.syntevo.com/smartsvn/index.html
check out the following url into your svn client:
https://e-box.wtb.tue.nl/svn/e-box/trunk/src/E-box/
Link to the svn install-manual pdf: link title
Copy the folders and files in:
/home/ebox/svn/trunk/src/E-box/
Open a terminal and start matlab as a superuser:
sudo matlab password:
After updating your local copy, run
make_all_clean make_all_install
in Matlab to obtain a fresh copy of the latest verion.
What does make_all_install?
The Libs Timer_posix, ec, and Coin are build and the symbolic links are created
Soem EtherCAT master library C files are build. Output directory in:
/usr/src/soem
Tagets:
C mex files through are build by make.m
subsequently the target mexglx files be installed in:
/usr/local/matlab75/rtw/c/ectarget/sfunctions
Ectarget is installed in:
/usr/local/matlab75/rtw/c
Building and running a Simulink model in the external mode with eclib
Download the manual via this link.