Group2 19-1 Week2: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (11 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
== Week 2 Logbook == | == Week 2 Logbook == | ||
Requirements: | === Requirements: === | ||
The requirements are based off of what the vehicle will encounter on its journey to and on Europa. The global actions are listed under 'The Goal'. Under 'steps' all challenges that come with these global actions are outlined in more detail. | The requirements are based off of what the vehicle will encounter on its journey to and on Europa. The global actions are listed under 'The Goal'. Under 'steps' all challenges that come with these global actions are outlined in more detail. | ||
The goal: | ==== The goal: ==== | ||
Search for life, signs of life, or conditions that would allow for life on Europa | Search for life, signs of life, or conditions that would allow for life on Europa | ||
It is unlikely that a fly-by mission can find out all there is to know about Europa | It is unlikely that a fly-by mission can find out all there is to know about Europa | ||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
*3 This lander should tell us more about Europa itself and the possibility for it to harbor life | *3 This lander should tell us more about Europa itself and the possibility for it to harbor life | ||
Steps: | ==== Steps: ==== | ||
*0.1 Not cost too much | *0.1 Not cost too much —› Can, in the end, costs be decreased? | ||
*1.1 Leave Earth | *1.1 Leave Earth —› The tools necessary to leave Earth’s orbit | ||
*1.1.1 Liftoff capacity | **1.1.1 Liftoff capacity —› Maximum weight for the mission | ||
*1.1.2 Liftoff fuel | **1.1.2 Liftoff fuel —› Fuel necessary to carry weight off Earth | ||
*1.2 Traverse space to Europa | *1.2 Traverse space to Europa —› Fuel necessary to make the journey to Europa | ||
*1.3 Land on Europa | *1.3 Land on Europa —› Fuel necessary to make a safe landing on Europa | ||
*1.3.1 Brake systems | **1.3.1 Brake systems —› Fuel necessary to move around on Europa’s surface | ||
*2.1 keep contact with the command centre | *2.1 keep contact with the command centre —› Long-range communication | ||
*2.2 Survive Europan surface, t.w. | *2.2 Survive Europan surface, t.w. —› How do we keep the lander working on Europa? | ||
*2.2.1 Iono- & Magnetosphere (electromotor?) | **2.2.1 Iono- & Magnetosphere (electromotor?) —› Is Europa’s magnetosphere of influence? https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1029/97JE03556 | ||
https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1029/97JE03556 | **2.2.2 Low gravity —› How do we cope with low gravity? Calculations of non-uniform gravity https://www.reddit.com/r/askscience/comments/1okc05/what_would_happen_if_i_started_my_car_in_zero/ (This one was mainly to get a general idea of things to consider about zero gravity. Please note that this is about 0 gravity, rather than low gravity.) | ||
*2.2.2 Low gravity | **2.2.3 Low atmospheric pressure —› Is Europa’s atmospheric pressure of influence? Oxygen densities of around 10^-10 that of earth (~1.801*10^23 cm^-2)(see also calculation: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Barometric_formula) 3D-Plasma source-sink model: https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1029/97JE03556 Spectrometry model: https://www-nature-com.dianus.libr.tue.nl/articles/373677a0.pdf Monte Carlo model: http://people.virginia.edu/~rej/papers05/shema_sdarticle.pdf | ||
Calculations of non-uniform gravity | **2.2.4 Low temperatures —› How do we cope with the low temperatures? 86-132 K http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.962.8753&rep=rep1&type=pdf | ||
https://www.reddit.com/r/askscience/comments/1okc05/what_would_happen_if_i_started_my_car_in_zero/ (This one was mainly to get a general idea of things to consider about zero gravity. Please note that this is about 0 gravity, rather than low gravity.) | ***2.2.4.1 Brittleness materials —› How do we cope with materials getting brittle? | ||
*2.2.3 Low atmospheric pressure | ***2.2.4.2 Freezing of fluids —› How do we prevent internal fluids from freezing? | ||
Oxygen densities of around 10^-10 that of earth (~1.801*10^23 cm^-2)(see also calculation: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Barometric_formula) | **2.2.5 Possibly rough or slippery surface —› How do we provide enough traction on the surface? | ||
3D-Plasma source-sink model: | **2.2.6 Withstand tectonic activity —› How do we protect the lander against tectonics? | ||
https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1029/97JE03556 | *2.3 operate partially autonomously —› What should the lander do on its own? | ||
Spectrometry model: | *2.4 operate for preferably several years, Either: —› How to maximize the longevity of the lander’s life? | ||
https://www-nature-com.dianus.libr.tue.nl/articles/373677a0.pdf | **2.4.1 carry enough energy —› Bigger batteries/fuel capacities? | ||
Monte Carlo model: | **2.4.2 Produce energy there (sulfuric compounds/ sun/ magnetic field??) —› Harvest fuel on-site? | ||
http://people.virginia.edu/~rej/papers05/shema_sdarticle.pdf | |||
*2.2.4 Low temperatures | |||
86-132 K | |||
http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.962.8753&rep=rep1&type=pdf | |||
*2.2.4.1 Brittleness materials | |||
*2.2.4.2 Freezing of fluids | |||
*2.2.5 Possibly rough or slippery surface | |||
*2.2.6 Withstand tectonic activity | |||
*2.3 operate partially autonomously | |||
*2.4 operate for preferably several years, Either: | |||
*2.4.1 carry enough energy | |||
*2.4.2 Produce energy there (sulfuric compounds/ sun/ magnetic field??) Harvest fuel on-site? | |||
*3.1 Examine Europan surface | *3.1 Examine Europan surface —› How will we perform research on the surface? | ||
*3.1.1 Move around | **3.1.1 Move around —› How will we move from one spot to another? | ||
*3.1.2 Take pictures (cameras) | **3.1.2 Take pictures (cameras) —› The tools to create pictures on-site | ||
*3.1.3 Chemical analysis | **3.1.3 Chemical analysis —› The tools to analyze materials on-site | ||
*3.1.4 Orientation on the surface (no accelerometer; maybe gyroscope?) | **3.1.4 Orientation on the surface (no accelerometer; maybe gyroscope?) | ||
*3.2 Examine Europan core? | *3.2 Examine Europan core? —› Will we dig below the surface to perform research? | ||
*3.2.1 Dig and sail under water | **3.2.1 Dig and sail under water —› How do we get/move below the surface? | ||
*3.2.2 Take pictures | **3.2.2 Take pictures —› As 3.1.2 | ||
*3.2.3 Chemical analysis | **3.2.3 Chemical analysis —› As 3.1.3 | ||
*3.2.4 Stay in contact with outside world (maybe not possible at depth) Communication necessary at depth? | **3.2.4 Stay in contact with outside world (maybe not possible at depth) —› Communication necessary at depth? | ||
*3.3 Look for signs of life | *3.3 Look for signs of life —› Determine whether life or traces of it is present | ||
*3.3.1 Find microbes (microscope) | **3.3.1 Find microbes (microscope) —› Possibly using microscope for small evidences | ||
*3.3.2 Chemical analysis | **3.3.2 Chemical analysis —› As 3.1.3 and 3.2.3 | ||
*4.1 While we’re there | *4.1 While we’re there —› Future research or side-research? | ||
*4.2 Research towards other moons/Jupiter | *4.2 Research towards other moons/Jupiter —› New information about Jupiter and its moons? | ||
=== Planning === | |||
==== Week 1: ==== | |||
*General research | |||
*Define Users | |||
==== Week 2: ==== | |||
*Determine objective | |||
*Select design choices based on requirements | |||
*Find solutions to the problems in requirements | |||
*Make a planning | |||
==== Week 3: ==== | |||
*Further research design choices | |||
*Finish up solutions to requirement problems | |||
==== Week 4: ==== | |||
*Combine design choice | |||
*Define potential problems and try to solve them | |||
==== Week 5: ==== | |||
*Revise design | |||
==== Week 6: ==== | |||
*Update design | |||
*Conclusion | |||
*Discussion | |||
==== Week 7: ==== | |||
*Finalize wiki | |||
*Make presentation | |||
==== Week 8: ==== | |||
*Presentation | |||
=== Possible report chapters === | |||
*Introduction | |||
*State of the art | |||
*The users and their needs | |||
*Potential problems | |||
*User contact & aspect of interest | |||
*Requirements | |||
*New innovative designs | |||
*Objectives | |||
*Approach | |||
*Stakeholders | |||
*Method | |||
*Design | |||
*User Contact | |||
*Conclusion | |||
*Discussion | |||
=== Possible solutions === | |||
==== 2.2.2 & 2.2.5: Gravity and grip ==== | |||
Lunar rover: | |||
https://www.lpi.usra.edu/lunar/documents/NTRS/collection2/NASA_TR_R_401.pdf | |||
https://www.lpi.usra.edu/lunar/documents/NTRS/collection2/NASA_TM_X_66816.pdf | |||
Due to the lower gravity, the normal force that a vehicle experiences is significantly smaller than it would on a similar surface on earth. | |||
This produces no problem for the vehicle’s ability to climb hills, as the force of gravity to be overcome is proportionally smaller. | |||
However, if the vehicle picks up speed, it is more likely to slip due to reduced friction. —› Low velocities | |||
Furthermore, in case of a collision with an immovable object, the vehicle is more likely to overturn because the force of gravity keeping it grounded is less strong. —› Low velocities & Low COM & proper collision detection | |||
Something in the autonomy that helps it regain traction once in a slip? | |||
The non-uniform gravity field means that orienting w.r.t. the surface is more difficult. | |||
[[File:Net_Surface_Gravity_on_Europa.jpg|frame|left|Combined gravity of Europa and Jupiter on the surface of Europa. θ=0 is the sub-Jovian side of Europa.]] | |||
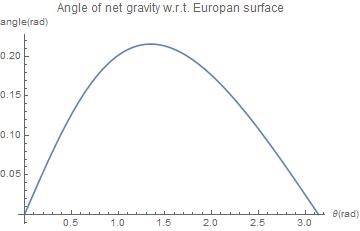
[[File:Surface_gravity_angle_Europa.jpg|frame|right|The angle under which the gravitational field on Europa's surface is tilted due to Jupiter's gravity. θ=0 is the sub-Jovian side of Europa.]] | |||
As seen on the left, the component of gravity perpendicular to the surface (gy) increases as you move from the sub-Jovian to the anti-Jovian side of Europa. This happens because on the sub-Jovian side, Jupiter is pulling you away from Europa, whereas on the anti-Jovian side, it is pulling you through Europa. | |||
The component of gravity parallel to Europa's surface (gx) peaks halfway between the Jovian poles. | |||
On the right you can see that the angle that the total gravitational field makes with the Europan surface is biggest at θ a little bit smaller than π/2. | |||
However, the graphs show that at every point between the Jovians, the gravitational force is uniquely defined (i.e. there is no point where the direction AND strength of gravity are both equal to another point on Europa), so that using a combination of a gyroscope (spinning in the orbital plane of Europa) and accelerometer, the vehicle should be able to determine where it is on Europa. This is both useful information for mapping Europa, as well as for making sure that the vehicle knows what is the actual up. The indiscrepancy between the gravitational and geographical up might otherwise form problems for the vehicle's risk assesment (in particular against overturning). | |||
http://www.apostolyuk.com/files/papers/Springer.pdf | |||
Problem: The vehicle should be able to traverse snow without sinking in too deep; we don’t know how thicc the snow layers on Europa are and thus can’t determine if the vehicle can afford to sink all the way through the layer. Furthermore, the vehicle should get enough traction on slabs of water ice, possibly also covered in a thin layer of snow. Lastly the wheels should not wear too much in sand or on rocks. | |||
If the wheels are hollow they should not fill up with sand and snow as this will make it harder to rotate them. Holes in the tires/ tracks should allow anything that gets in to get out. | |||
Caterpillar tracks have the benefit of more traction on snow and sand as well as ice, but are much less durable (between 8- and 10 thousand km (around Europa once)) and far less efficient. | |||
http://www.pan-ol.lublin.pl/wydawnictwa/TMot5/Gardynski.pdf | |||
Both caterpillar tracks and regular wheels can be equipped with spikes or studs of some sort. These, however, wear down quickly and go at the cost of some efficiency. | |||
To overcome this problem, low disturbance spikes can be used. | |||
https://patents.google.com/patent/US4332424A/en | |||
Or this alternative solution claiming to have the advantages but not the disadvantages. | |||
https://patents.google.com/patent/US4909576A/en | |||
==== 2.2.6 Tectonic activity ==== | |||
Considering the forces at work in the shifting of tectonic plates, it is unlikely that current human technology can save a vehicle trapped in a tectonic crevasse. It is thus sensible to try and avoid this at all costs. | |||
Tectonic activity can be measured with a seismometer. It is difficult to determine in advance how one can predict whether the vehicle is in a dangerous zone from a particular spike in seismic activity. However, the seismometer can be used to map out where Europa is most geologically active. | |||
[In the case of ridge formation, there are possibly 2 dangerous zones, one of which can in fact possibly be survived if the vehicle is properly equipped for it. At rover velocities, if (chaos territory or) a ridge forms right below the vehicle, there is little chance of it escaping, in particular with the edges possibly collapsing. However, if the ridge forms a distance away from the vehicle, it might get covered in snow or water. Neither of these would be good for the vehicle, but it can be given systems to survive this, such as shielding of all electronics to prevent short circuiting or something to melt the layer of snow on top of it.] | |||
==== 2.2.3, 2.2.4 The effect of temperature and pressure on the functioning of the vehicle ==== | |||
Many STP liquids are solid at Europan temperatures but will due to the low pressure sublimate immediately. Fluids can most likely only be kept in pressurised containers. | |||
The low pressure can pose a significant problem concerning the cooling of the vehicle, as there will be little air to lose heat to. The air will be super cold to create a significant temperature differential, but super thin as well which reduces conductive cooling. Furthermore, the low air temperature reduces convective cooling. | |||
If gains and losses are properly balanced, it might actually be possible to keep the body of the vehicle at a significant temperature with the thermonuclear battery heating it up. Model: Insulation vs source | |||
Very rough simulation of temperature in the rover after an extended period of time. Centre contains a 100 kW power source and outside temperature is 100 K. | |||
A benefit is that at these temperatures electric resistances in wiring will be significantly lower. If proper materials are chosen, it might even be possible to acquire superconducting wires at these temperatures. | |||
The largest problem is rooted in lubricants. These will be exposed to the environment far away from the body of the vehicle, possibly close to the ground where thermal conduction is largest. Use ball bearings? | |||
Maybe use large wheels. These will keep their axes (which need to be lubricated and thus warm) far away from the ground so they will stay warmer. | |||
Suggestions for Calisto exploration; exploration at cryogenic temperatures | |||
https://ntrs.nasa.gov/archive/nasa/casi.ntrs.nasa.gov/20030063128.pdf | |||
==== 2.4.1 Functioning of an RTG on Europa ==== | |||
Thermoelectric generator (TEG) is impeded by strong magnetic fields (presumably starting at fields weaker than Jupe-Jupe’s) | |||
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1503.05764.pdf | |||
TEG power output drops at lower temperatures (even with similar temperature differentials) | |||
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0196890412001896 | |||
But maybe not? | |||
https://www.osti.gov/servlets/purl/5579376 | |||
Okay so the thing is, some sources say that TEGs lose efficiency at ~100 K, due to changing of material properties and the thermoelectric effect not working at too low electron energies, whereas some say they become more efficient because resistivity of the materials decreases and relative electron energy differences increase. Either way, a TEG could possibly work on Europa, but it depends strongly on how much heat the vehicle produces and the rate at which it loses this heat. In other words: whether it is able to sustain a sufficient temperature differential. If the outward shape of the vehicle is taken into account, it might actually be possible to adapt it to accommodate this temperature difference. | |||
---- | ---- | ||
[[PRE2019_1_Group2|Back to the main page]] | [[PRE2019_1_Group2|Back to the main page]] | ||
Latest revision as of 13:45, 15 September 2019
Notulen Tutor Meeting
- Bekijken of de Rover wel het ideale voertuig is voor een missie op Europa
- Starten vanuit objectives en vanuit daar de missie ontwerpen
- Specifiek zijn/kiezen wat het echte doel van het onderzoek wordt
- Beschrijven bij welke requirements aan welke wensen van welke gebruikers voldaan wordt
- Overwegingen over resilience van onderdelen van het voertuig
- Waar in het systeem de interactie met de gebruikers plaatsvindt
- Planning maken, milestones
- Criteria opstellen voor de kwaliteit van de milestones en deliverables
- Opdeling van het project reviseren
- Kans op succes vergroten bij onzekerheid
- Waar lander/rond rijden? Daar het voertuig op aanpassen
- Waar zoeken naar leven? Welke experimenten daar uitvoeren? Wat voor equipment daarvoor nodig?
- Zorgen dat onze individuele stukken in elkaar passen en een mooi geheel vormen
- Meer gebruikmaken van de mogelijkheden die de wiki biedt
Presentatie: 20 minuten; 5 minuten vragen, mogelijk 5 minuten iets laten zien
Week 2 Logbook
Requirements:
The requirements are based off of what the vehicle will encounter on its journey to and on Europa. The global actions are listed under 'The Goal'. Under 'steps' all challenges that come with these global actions are outlined in more detail.
The goal:
Search for life, signs of life, or conditions that would allow for life on Europa It is unlikely that a fly-by mission can find out all there is to know about Europa
- 1 Hence, a lander mission is required
- 2 Furthermore, it should be able to survive on Europa
- 3 This lander should tell us more about Europa itself and the possibility for it to harbor life
Steps:
- 0.1 Not cost too much —› Can, in the end, costs be decreased?
- 1.1 Leave Earth —› The tools necessary to leave Earth’s orbit
- 1.1.1 Liftoff capacity —› Maximum weight for the mission
- 1.1.2 Liftoff fuel —› Fuel necessary to carry weight off Earth
- 1.2 Traverse space to Europa —› Fuel necessary to make the journey to Europa
- 1.3 Land on Europa —› Fuel necessary to make a safe landing on Europa
- 1.3.1 Brake systems —› Fuel necessary to move around on Europa’s surface
- 2.1 keep contact with the command centre —› Long-range communication
- 2.2 Survive Europan surface, t.w. —› How do we keep the lander working on Europa?
- 2.2.1 Iono- & Magnetosphere (electromotor?) —› Is Europa’s magnetosphere of influence? https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1029/97JE03556
- 2.2.2 Low gravity —› How do we cope with low gravity? Calculations of non-uniform gravity https://www.reddit.com/r/askscience/comments/1okc05/what_would_happen_if_i_started_my_car_in_zero/ (This one was mainly to get a general idea of things to consider about zero gravity. Please note that this is about 0 gravity, rather than low gravity.)
- 2.2.3 Low atmospheric pressure —› Is Europa’s atmospheric pressure of influence? Oxygen densities of around 10^-10 that of earth (~1.801*10^23 cm^-2)(see also calculation: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Barometric_formula) 3D-Plasma source-sink model: https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1029/97JE03556 Spectrometry model: https://www-nature-com.dianus.libr.tue.nl/articles/373677a0.pdf Monte Carlo model: http://people.virginia.edu/~rej/papers05/shema_sdarticle.pdf
- 2.2.4 Low temperatures —› How do we cope with the low temperatures? 86-132 K http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.962.8753&rep=rep1&type=pdf
- 2.2.4.1 Brittleness materials —› How do we cope with materials getting brittle?
- 2.2.4.2 Freezing of fluids —› How do we prevent internal fluids from freezing?
- 2.2.5 Possibly rough or slippery surface —› How do we provide enough traction on the surface?
- 2.2.6 Withstand tectonic activity —› How do we protect the lander against tectonics?
- 2.3 operate partially autonomously —› What should the lander do on its own?
- 2.4 operate for preferably several years, Either: —› How to maximize the longevity of the lander’s life?
- 2.4.1 carry enough energy —› Bigger batteries/fuel capacities?
- 2.4.2 Produce energy there (sulfuric compounds/ sun/ magnetic field??) —› Harvest fuel on-site?
- 3.1 Examine Europan surface —› How will we perform research on the surface?
- 3.1.1 Move around —› How will we move from one spot to another?
- 3.1.2 Take pictures (cameras) —› The tools to create pictures on-site
- 3.1.3 Chemical analysis —› The tools to analyze materials on-site
- 3.1.4 Orientation on the surface (no accelerometer; maybe gyroscope?)
- 3.2 Examine Europan core? —› Will we dig below the surface to perform research?
- 3.2.1 Dig and sail under water —› How do we get/move below the surface?
- 3.2.2 Take pictures —› As 3.1.2
- 3.2.3 Chemical analysis —› As 3.1.3
- 3.2.4 Stay in contact with outside world (maybe not possible at depth) —› Communication necessary at depth?
- 3.3 Look for signs of life —› Determine whether life or traces of it is present
- 3.3.1 Find microbes (microscope) —› Possibly using microscope for small evidences
- 3.3.2 Chemical analysis —› As 3.1.3 and 3.2.3
- 4.1 While we’re there —› Future research or side-research?
- 4.2 Research towards other moons/Jupiter —› New information about Jupiter and its moons?
Planning
Week 1:
- General research
- Define Users
Week 2:
- Determine objective
- Select design choices based on requirements
- Find solutions to the problems in requirements
- Make a planning
Week 3:
- Further research design choices
- Finish up solutions to requirement problems
Week 4:
- Combine design choice
- Define potential problems and try to solve them
Week 5:
- Revise design
Week 6:
- Update design
- Conclusion
- Discussion
Week 7:
- Finalize wiki
- Make presentation
Week 8:
- Presentation
Possible report chapters
- Introduction
- State of the art
- The users and their needs
- Potential problems
- User contact & aspect of interest
- Requirements
- New innovative designs
- Objectives
- Approach
- Stakeholders
- Method
- Design
- User Contact
- Conclusion
- Discussion
Possible solutions
2.2.2 & 2.2.5: Gravity and grip
Lunar rover: https://www.lpi.usra.edu/lunar/documents/NTRS/collection2/NASA_TR_R_401.pdf https://www.lpi.usra.edu/lunar/documents/NTRS/collection2/NASA_TM_X_66816.pdf Due to the lower gravity, the normal force that a vehicle experiences is significantly smaller than it would on a similar surface on earth. This produces no problem for the vehicle’s ability to climb hills, as the force of gravity to be overcome is proportionally smaller. However, if the vehicle picks up speed, it is more likely to slip due to reduced friction. —› Low velocities
Furthermore, in case of a collision with an immovable object, the vehicle is more likely to overturn because the force of gravity keeping it grounded is less strong. —› Low velocities & Low COM & proper collision detection Something in the autonomy that helps it regain traction once in a slip?
The non-uniform gravity field means that orienting w.r.t. the surface is more difficult.

As seen on the left, the component of gravity perpendicular to the surface (gy) increases as you move from the sub-Jovian to the anti-Jovian side of Europa. This happens because on the sub-Jovian side, Jupiter is pulling you away from Europa, whereas on the anti-Jovian side, it is pulling you through Europa. The component of gravity parallel to Europa's surface (gx) peaks halfway between the Jovian poles.
On the right you can see that the angle that the total gravitational field makes with the Europan surface is biggest at θ a little bit smaller than π/2.
However, the graphs show that at every point between the Jovians, the gravitational force is uniquely defined (i.e. there is no point where the direction AND strength of gravity are both equal to another point on Europa), so that using a combination of a gyroscope (spinning in the orbital plane of Europa) and accelerometer, the vehicle should be able to determine where it is on Europa. This is both useful information for mapping Europa, as well as for making sure that the vehicle knows what is the actual up. The indiscrepancy between the gravitational and geographical up might otherwise form problems for the vehicle's risk assesment (in particular against overturning). http://www.apostolyuk.com/files/papers/Springer.pdf
Problem: The vehicle should be able to traverse snow without sinking in too deep; we don’t know how thicc the snow layers on Europa are and thus can’t determine if the vehicle can afford to sink all the way through the layer. Furthermore, the vehicle should get enough traction on slabs of water ice, possibly also covered in a thin layer of snow. Lastly the wheels should not wear too much in sand or on rocks. If the wheels are hollow they should not fill up with sand and snow as this will make it harder to rotate them. Holes in the tires/ tracks should allow anything that gets in to get out. Caterpillar tracks have the benefit of more traction on snow and sand as well as ice, but are much less durable (between 8- and 10 thousand km (around Europa once)) and far less efficient. http://www.pan-ol.lublin.pl/wydawnictwa/TMot5/Gardynski.pdf Both caterpillar tracks and regular wheels can be equipped with spikes or studs of some sort. These, however, wear down quickly and go at the cost of some efficiency. To overcome this problem, low disturbance spikes can be used. https://patents.google.com/patent/US4332424A/en Or this alternative solution claiming to have the advantages but not the disadvantages. https://patents.google.com/patent/US4909576A/en
2.2.6 Tectonic activity
Considering the forces at work in the shifting of tectonic plates, it is unlikely that current human technology can save a vehicle trapped in a tectonic crevasse. It is thus sensible to try and avoid this at all costs. Tectonic activity can be measured with a seismometer. It is difficult to determine in advance how one can predict whether the vehicle is in a dangerous zone from a particular spike in seismic activity. However, the seismometer can be used to map out where Europa is most geologically active. [In the case of ridge formation, there are possibly 2 dangerous zones, one of which can in fact possibly be survived if the vehicle is properly equipped for it. At rover velocities, if (chaos territory or) a ridge forms right below the vehicle, there is little chance of it escaping, in particular with the edges possibly collapsing. However, if the ridge forms a distance away from the vehicle, it might get covered in snow or water. Neither of these would be good for the vehicle, but it can be given systems to survive this, such as shielding of all electronics to prevent short circuiting or something to melt the layer of snow on top of it.]
2.2.3, 2.2.4 The effect of temperature and pressure on the functioning of the vehicle
Many STP liquids are solid at Europan temperatures but will due to the low pressure sublimate immediately. Fluids can most likely only be kept in pressurised containers. The low pressure can pose a significant problem concerning the cooling of the vehicle, as there will be little air to lose heat to. The air will be super cold to create a significant temperature differential, but super thin as well which reduces conductive cooling. Furthermore, the low air temperature reduces convective cooling. If gains and losses are properly balanced, it might actually be possible to keep the body of the vehicle at a significant temperature with the thermonuclear battery heating it up. Model: Insulation vs source
Very rough simulation of temperature in the rover after an extended period of time. Centre contains a 100 kW power source and outside temperature is 100 K. A benefit is that at these temperatures electric resistances in wiring will be significantly lower. If proper materials are chosen, it might even be possible to acquire superconducting wires at these temperatures.
The largest problem is rooted in lubricants. These will be exposed to the environment far away from the body of the vehicle, possibly close to the ground where thermal conduction is largest. Use ball bearings? Maybe use large wheels. These will keep their axes (which need to be lubricated and thus warm) far away from the ground so they will stay warmer.
Suggestions for Calisto exploration; exploration at cryogenic temperatures https://ntrs.nasa.gov/archive/nasa/casi.ntrs.nasa.gov/20030063128.pdf
2.4.1 Functioning of an RTG on Europa
Thermoelectric generator (TEG) is impeded by strong magnetic fields (presumably starting at fields weaker than Jupe-Jupe’s) https://arxiv.org/pdf/1503.05764.pdf TEG power output drops at lower temperatures (even with similar temperature differentials) https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0196890412001896 But maybe not? https://www.osti.gov/servlets/purl/5579376 Okay so the thing is, some sources say that TEGs lose efficiency at ~100 K, due to changing of material properties and the thermoelectric effect not working at too low electron energies, whereas some say they become more efficient because resistivity of the materials decreases and relative electron energy differences increase. Either way, a TEG could possibly work on Europa, but it depends strongly on how much heat the vehicle produces and the rate at which it loses this heat. In other words: whether it is able to sustain a sufficient temperature differential. If the outward shape of the vehicle is taken into account, it might actually be possible to adapt it to accommodate this temperature difference.