Embedded Motion Control 2019 Group 8: Difference between revisions
| Line 75: | Line 75: | ||
== Route planning == | == Route planning == | ||
== State machine == | |||
== Object detection/avoidance == | == Object detection/avoidance == | ||
In order to be able to drive from waypoint to waypoint without any collisions, there are two different options hardcoded. The first option is when driving in open space and the second options is when driving through a narrow opening, such as a door. Each case will be explained below. | |||
=== Open space object avoidance === | |||
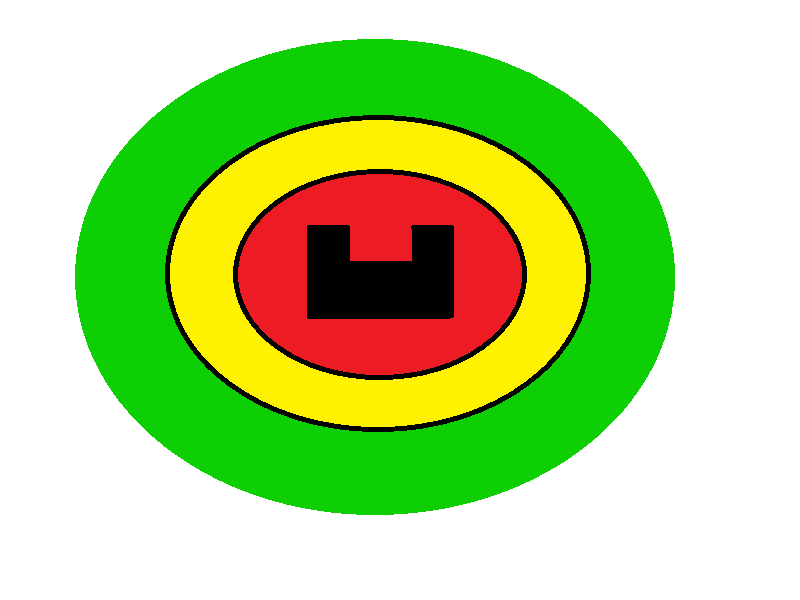
In the open space, objects can be encountered, which could be either dynamic objects, such as people walking around, and static objects, such as cupboards. In order for PICO to know how to act upon sensing an object nearby, an area around PICO is taken as seen in Figure | |||
[[File:openspace.png]] | |||
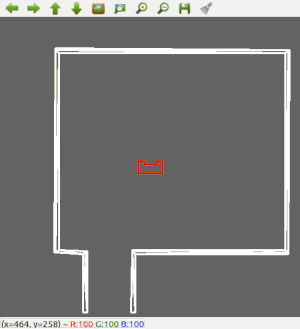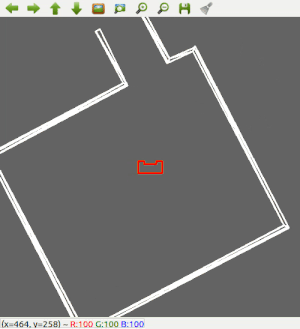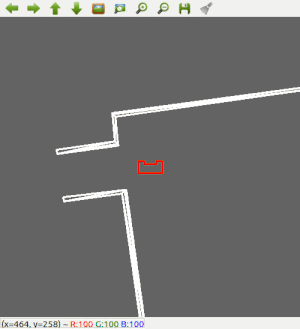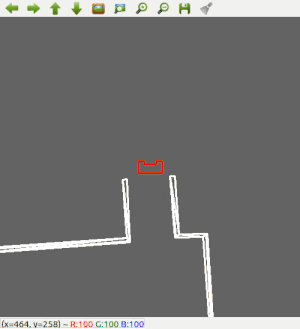
=== Narrow way object avoidance === | |||
[[File:Object_detect_narrow.png]] | [[File:Object_detect_narrow.png]] | ||
Revision as of 10:18, 14 June 2019
Group Members
| Name | Student ID | |
|---|---|---|
| Stan (C.M.) den Hartog | 0953184 | c.m.d.hartog@student.tue.nl |
| Elise (E.D.T.) Verhees | 0950109 | e.d.t.verhees@student.tue.nl |
| Rob (R.J.G.) Dorussen | 0968849 | r.j.g.dorussen@student.tue.nl |
| Gosse (G.) Bijlenga | 0950642 | g.bijlenga@student.tue.nl |
| Max (M.J.) van Haren | 0953564 | m.j.v.haren@student.tue.nl |
Introduction
In the course Embedded Motion Control (EMC) the software design of an autonomous robot is given as an objective. The implementation of the software skills to fulfill real-life robotic tasks in real-time situations, takes into account both planning and basic programming. For this assignment, two challenges are given.
The first challenge is the Escape Room Challenge, in which the robot is placed in a room with a single exit with a random orientation. Upon placement, the robot should autonomously find the exit, move towards the exit and exit the room without touching the surroundings. The second challenge is the Hospital Challenge, in which the robot should autonomously function within a hospital, based on a specific map. The goal for the robot is to go from cabinet to cabinet, while on the way encountering random disturbances as deemed normal in a hospital.
This wiki page will give an overview of the designs for both the Escape Room and Hospital challenges.
Escape Room Challenge
Design Document
For the Escape Room Challenge a design document has been made. Hererin, the requirements, specifications, components, interfaces and functions can be found within. The file can be found here.File:Design document.pdf
Escape Room Execution
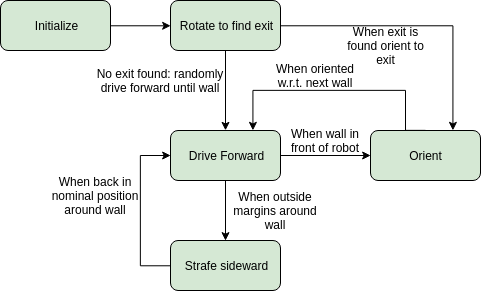
A short summary of the actions the robot will undertake can be seen in the State machine showed below.
Wall Following
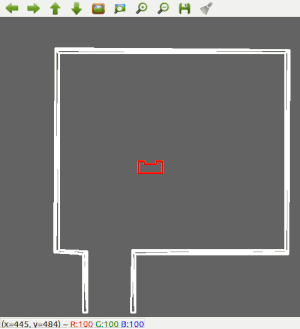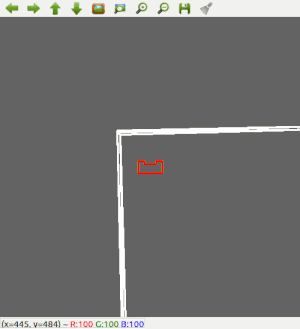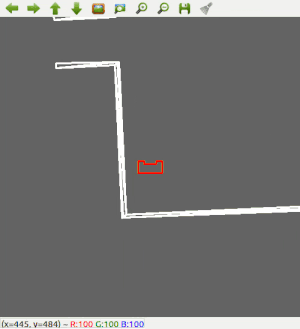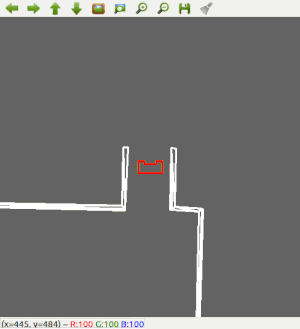
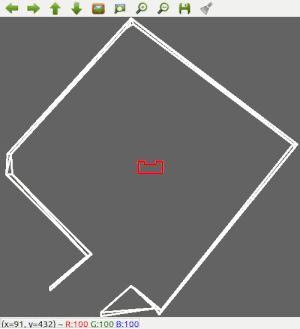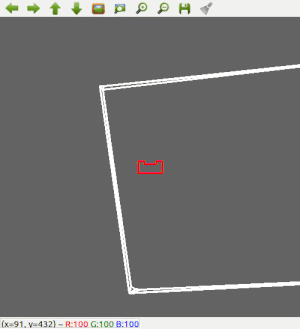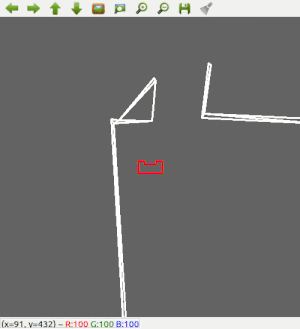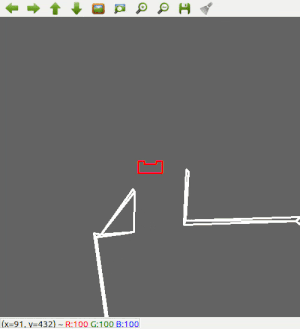
Since the most robust solution is to follow a wall, this is chosen to be implemented first. The decision has been made to make the robot always keep the wall on its left side. Good results are achieved in the 2 random maps that are shown below.
Scanning for an exit
Next, the robot is made a bit 'smarter'; It will first scan the room for an exit. If an exit is found, it will stop rotating, rotate a bit back, to make sure it will head for the left wall, start heading for the exit, and then continue with the wall following procedure to exit the corridor. The result for this can be seen below.
Escape Room Result
Hospital Challenge
Hospital Challenge Brainstorm Session
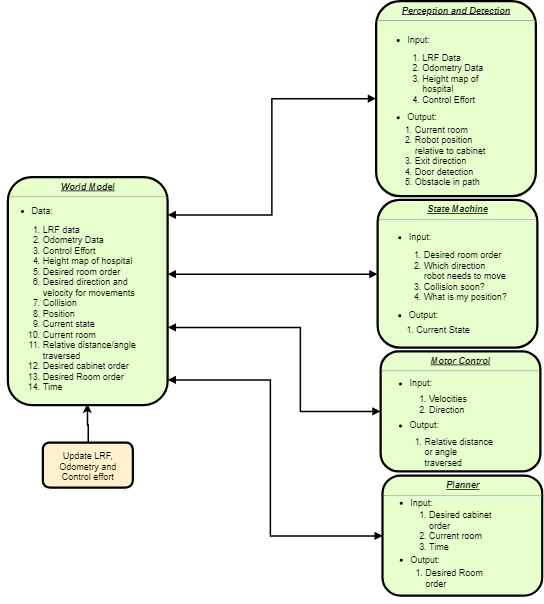
To prepare for the hospital session, a brainstorm session is done and several new requirements, specifications, functions and components are thought of.
The following diagram is the result of this brainstorm session.
Localization
Route planning
State machine
Object detection/avoidance
In order to be able to drive from waypoint to waypoint without any collisions, there are two different options hardcoded. The first option is when driving in open space and the second options is when driving through a narrow opening, such as a door. Each case will be explained below.
Open space object avoidance
In the open space, objects can be encountered, which could be either dynamic objects, such as people walking around, and static objects, such as cupboards. In order for PICO to know how to act upon sensing an object nearby, an area around PICO is taken as seen in Figure