Embedded Motion Control 2018 Group 6: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 161: | Line 161: | ||
result for world model: | result for world model: | ||
setpoint angle and velocity of robot | setpoint angle and velocity of robot | ||
[[File:Interface_PICO.png|900px]] | |||
Revision as of 15:05, 10 May 2018
Group members
| Name: | Report name: | Student id: |
| Thomas Bosman | T.O.S.J. Bosman | 1280554 |
| Raaf Bartelds | R. Bartelds | add number |
| Bas Scheepens | S.J.M.C. Scheepens | 0778266 |
| Josja Geijsberts | J. Geijsberts | 0896965 |
| Rokesh Gajapathy | R. Gajapathy | 1036818 |
| Tim Albu | T. Albu | 19992109 |
| Marzieh Farahani | Marzieh Farahani | Tutor |
Initial Design
Requirements and Specifications
Use cases for Escape Room
1. Wall and Door Detection
2. Move with a certain profile
3. Navigate
Requirements for Escape Room
R1.1 The system shall detect walls without touching them
R1.2 The system shall detect the goal/door
R1.3 The system shall log and map the environment
R2.1 The system shall move slower than 0.5 m/s translational and 1.2 rad/s rotational
R2.2 The system shall not stay still for more than 30 seconds
R3.1 The system shall find the goal
R3.2 The system shall determine a path to the goal
R3.3 THe system shall navigate to the goal
R3.4 THe system shall not touch the walls
R3.5 The system shall complete the task within 5 minutes
Use cases for Hospital Room
(unfinished)
1. Mapping
2. Move with a certain profile
3. Orient itself
4. Navigate
Functions, Components and Interfaces
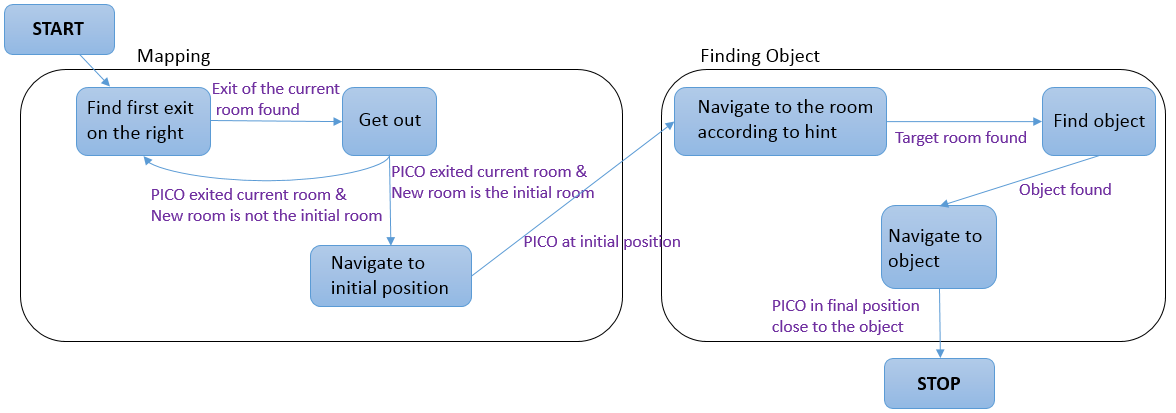
The program which will be running on the Pico can be categorized in four different components: perception, monitoring, plan and control. They exchange information through the world model, which stores all the data. Below, the functions of the four components are described.
Perception:
ERC:
input: lrf-data
process (filter) the laser-readings
result for world model:
distances to objects
HC: input: lrf-data, odometry process both sensors with gmapping process (filter) the laser-readings result for world model: map, distances+angles to objects
Monitoring:
ERC:
input: distances to objects
process distances to determine situation: following wall, (near-)collision, entering corridor, escaped room
result for world model:
state of situation
HC: input: map, distances to objects process distances and map to determine situation: following path, (near-)collision, found object result for world model: state of situation
Plan:
ERC:
input: state of situation
determine next step: prevent collision, continue following wall, stop because finished
result for world model:
state of next step
HC: input: state of situation determine next step: goto new waypoint, continue following path, prevent collision, go back to start, stop because finished determine path to follow result for world model: state of next step
Control:
ERC:
input: distances+angles to objects, state of next step
determine setpoint angle and velocity of robot
result for world model:
setpoint angle and velocity of robot
HC: input: state of next step, path to follow determine setpoint angle and velocity of robot result for world model: setpoint angle and velocity of robot