PRE2016 3 Groep16: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
* Local security and criminals detection | * Local security and criminals detection | ||
* Inspection of insulation materials in houses (not directly "human recognition", but considered a valuable research) | * Inspection of insulation materials in houses (not directly "human recognition", but considered a valuable research) | ||
==Problem Statement== | |||
Due to turbulent geopolitical times in parts of Africa, thousands of people try to get a safe better life in Europe. Conflicts in countries such as Somalia and the violation of human rights in countries with strict regimes such as Eritrea force certain groups in those countries to move elsewhere. The safest place that is reachable to them is Europe, however to make it to Europe the Mediterranean Sea needs to be crossed. The crossing is often done with old small boats that were originally intended for much less passengers than they are currently loaded with. The result is the sinking of many boats resulting in many drownings. In 2016 there were 4,218 known deaths in the Mediterranean with drowning as cause. In the first month of 2017 the death count as cause of drowning was already 377 migrants. | |||
Up until November 2014 Italy had its own rescue operation called Mare Nostrum to find refugees which were victims of boat accidents. The rescue mission was successful, about 160,000 people were saved from drowning. However, the use of seven ships, two helicopters, three planes and the help of the marine, coastal guard and Red Cross costed €9,5 million per month which was to expensive and the mission stopped. Moreover it was thought that the rescue operation would encourage refugees to take their chances to cross the sea, as they would be rescued anyway when they would get in trouble. The result of stopping with the operation resulted in a ten fold of casualties. | |||
The search for refugees is currently done with the use of helicopters and planes equipped with cameras, however these aerial vehicles are very expensive to keep in the air. The cost of the assistance of a C-130 turboprop plane used in rescue missions, for example, costs more than €6,000 per hour. The main purpose for these aircrafts is to spot refugees, after which a boat will get them out of the water. | |||
In order to make rescue operations such as Mare Nostrum stay in action costs have to be cut. Since the aircraft division of those operations are one of the most expensive aspects, another solution must be invented. The usage of the promising drone technology could be a very good solution since they are a lot cheaper to keep flying. Moreover they could be used in large numbers to cover large water surfaces making rescue operations much more efficient. Therefore, this wiki will discuss the feasibility of the deployment of drones within refugee rescue missions. Since drones are currently relying on rather weak power sources, batteries in particular, the equipment of the drones should be minimal. The use of a thermal camera will therefore be investigated because apart from the fact that it is small and lightweight, the automatic detection of organisms, in this case human refugees, can be easily implemented since humans have a warmer body temperature than the surrounding water. Moreover, since the thermal cameras are not dependent on visible light, the cameras can also be used at night increasing operational hours of the drone. | |||
== Objectives == | == Objectives == | ||
Revision as of 13:13, 7 March 2017
Group members
| Student ID | Name |
| 09 | M.D Visser |
| 09 | G. Marzano |
| 09 | R. Schalk |
| 09 | T. Jansen |
| 09 | J. Van Galen |
| 09 | B.G.M Hopman |
Introduction
This is the Wiki page for the project Robots everywhere (0LAUK0) of group 16. The subject chosen is "Detection of people by using drones equipped with IR/heat sensors and Camera". Developing such a technology would make an impact due to the several applications it carries along. In the first phase of the project, after brainstorming, the following applications emerged:
- Find refugees in open sea
- Local security and criminals detection
- Inspection of insulation materials in houses (not directly "human recognition", but considered a valuable research)
Problem Statement
Due to turbulent geopolitical times in parts of Africa, thousands of people try to get a safe better life in Europe. Conflicts in countries such as Somalia and the violation of human rights in countries with strict regimes such as Eritrea force certain groups in those countries to move elsewhere. The safest place that is reachable to them is Europe, however to make it to Europe the Mediterranean Sea needs to be crossed. The crossing is often done with old small boats that were originally intended for much less passengers than they are currently loaded with. The result is the sinking of many boats resulting in many drownings. In 2016 there were 4,218 known deaths in the Mediterranean with drowning as cause. In the first month of 2017 the death count as cause of drowning was already 377 migrants. Up until November 2014 Italy had its own rescue operation called Mare Nostrum to find refugees which were victims of boat accidents. The rescue mission was successful, about 160,000 people were saved from drowning. However, the use of seven ships, two helicopters, three planes and the help of the marine, coastal guard and Red Cross costed €9,5 million per month which was to expensive and the mission stopped. Moreover it was thought that the rescue operation would encourage refugees to take their chances to cross the sea, as they would be rescued anyway when they would get in trouble. The result of stopping with the operation resulted in a ten fold of casualties. The search for refugees is currently done with the use of helicopters and planes equipped with cameras, however these aerial vehicles are very expensive to keep in the air. The cost of the assistance of a C-130 turboprop plane used in rescue missions, for example, costs more than €6,000 per hour. The main purpose for these aircrafts is to spot refugees, after which a boat will get them out of the water. In order to make rescue operations such as Mare Nostrum stay in action costs have to be cut. Since the aircraft division of those operations are one of the most expensive aspects, another solution must be invented. The usage of the promising drone technology could be a very good solution since they are a lot cheaper to keep flying. Moreover they could be used in large numbers to cover large water surfaces making rescue operations much more efficient. Therefore, this wiki will discuss the feasibility of the deployment of drones within refugee rescue missions. Since drones are currently relying on rather weak power sources, batteries in particular, the equipment of the drones should be minimal. The use of a thermal camera will therefore be investigated because apart from the fact that it is small and lightweight, the automatic detection of organisms, in this case human refugees, can be easily implemented since humans have a warmer body temperature than the surrounding water. Moreover, since the thermal cameras are not dependent on visible light, the cameras can also be used at night increasing operational hours of the drone.
Objectives
General
- Showing that drones can be implemented in substitution of regular surveillance vehicles/cameras, consequently reducing costs and risks for operators.(Principle of Unnecessary Risk-PUR )
- Autonomous movement (User)
Application 1: Refugees search
- Reducing costs for refugee search in open sea (Society)
- Increase relative number of rescued refugees (Society)
Application 2: Surveillance & Security Drones
- Reduce the number of crimes (Society)
- Have a better understanding of crime distribution (Society)
- Make surveillance cheaper and more efficient (Enterprise & Society)
- Large scale surveillance
Application 3: Insulation in houses
- Verify heat losses in buildings
- Increased efficiency of procedure (analyze multiple living units & buildings at same time)
- Reduction of costs for maintenance and related time
Approach
General
- Determine the demands and benefits for user, society & enterprise.
- Divide group in subgroups working on different aspects of the project.
- Make a detailed planning.
Technical
- Equip the drone with a thermal camera (considering that a drone can be provided by TU/e).
- Program the drone and tune the sensors (e.g. find the threshold voltages) to detect the different values.
- Link the obtained data to an environmental structure (e.g. environment heat model).
- Adjust program in order to map properly the perimeters and consider the external heat deviations.
- Act on the environment under inspection (e.g. transmitting signal to operator).
Literature Study
For the literature study of our project the article titled ‘feasibility study of inexpensive thermal sensors and small UAS deployment for living human detection in rescue missions application scenarios’ was found. This article mentions how there are two critical phases in which geospatial imaging for rescuing purposes can be very useful. Namely for the detection of humans and secondly for the confirmation whether a detected human is dead or alive. Moreover the article elaborates on the “proof of concept for using small UAVs equipped with infrared and visible diapason sensors for detection of living humans in outdoor settings”. In which “Electro-optical imagery was used for the research in optimal human detection algorithms”.
Quite a lot of useful information about thermal imaging came forward in this research. Already in the introduction a human psychological aspect comes forward which says that “the human tendency to disregard opportunity costs when the life of identifiable individuals are visibly threatened. Due to this fact, we may observe operations when hundreds of people and multiple sets of equipment are deployed to save only one human life”. Moreover Rudol et al, already introduced human body detection via positioning algorithms using visible and infrared imagery in 2008. Follow up research in this field realized analysis algorithms that detect breathing and heartbeat rates through 15 cm of rubble.
In our research we were already aware of the fact that manned aerial vehicles for rescuing purposes are quite expensive. However something that came forward in this article and was not considered by us is that for manned aerial vehicles “very strict requirements are needed for areas of take-off and landing, and these areas are often far from the search and rescue area”. Moreover we found out that there exist several classes of UAVs, however we will adapt to the drone that can be provided by TU/e.
The research article conducted their research on human dummy objects and real humans. Experimental results showed that “various types of boundaries created by changes in feature signs such as color and texture, bringing a lot of difficulties in automated image processing. Thus, a potentially reliable algorithm needs to consider all combination of different types of image attributes together in order to provide correct segmentation of real natural images”. The conclusion following up on this result made clear that living humans can be detected in a reliable way in positive (13 °C) as well as negative (-5 °C) temperature surroundings.
Reference: Levin, E., Zarnowski, A., McCarty, J. L., Bialas, J., Banaszek, A., & Banaszek, S. (2016). Feasibility Study of Inexpensive Thermal Sensors and Small Uas Deployment for Living Human Detection in Rescue Missions Application Scenarios. ISPRS-International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, 99-103.
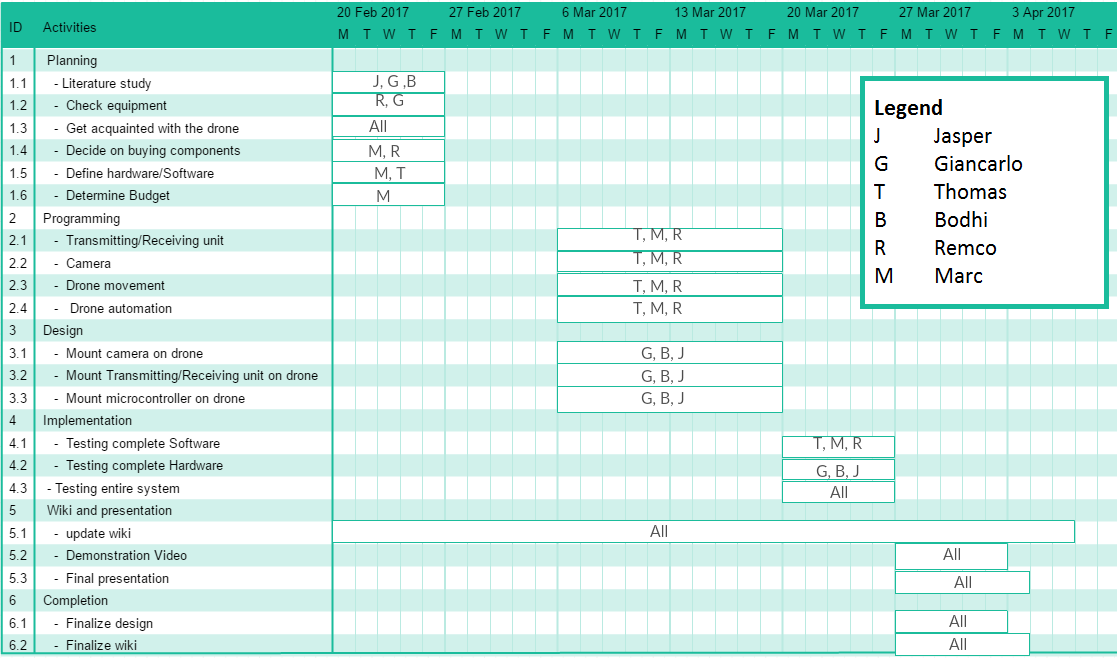
Planning
To organize the workload of the project a planning is required, where the main requirements and deadlines are set, together with the task division (starting from week 3 of the quartile e.g. 20th Ferbuary 2017).
Logbook
Weekly the progress of the group is going to be reported in this logbook. The purpose is to keep the full group up to date with the progress of each sub group. Moreover, it is useful to be always able to compare the actual progress with the planning.
Week 1
Week 2
During week 2 the group had to present the subject of the project, with the relative objectives and approach. Based on the feedback received, the group starts to focus on one of the application presented: """"""APPLICATION""
USE analysis of the application
User
Society
Enterprise
State of the art
(Boat)refugee drone Avy
The use of drones is a development that has not been around for decades. This directly implies that research on drones for application in specific domains is not largely spread and therefore there are few state-of-the-art systems that are comparable with the idea that this group wants to develop. Nevertheless, there has been developed a drone that is specifically designed for refugees. Avy is the drone that has been receiving publicity lately, as it focusses on delivering goods (a huge floater) to the refugees on open see. After dropping the floater, the location of the refugees is directly known and the emergency services can move to the area with the gathered knowledge. The weakness of this design is that the drone does not focus on the detection of refugees, as the location that is transmitted comes down to the location at which the floater is dropped. For dropping a floater, one must be able to detect the refugees by some means, as dropping a floater randomly will not help the current problem. A thermal camera, with which our design will be equipped, will ensure detection of refugees on open see, even at night conditions. Many other elements of Ivy are very hopeful and inspirational to our development, such as the design of the Avy. This design focused on traveling large distances overseas, which is not doable with a 'regular' quadcopter drone. This, however, is not directly interesting for our project, as the main focus is on the detection by using the thermal camera instead of designing a drone that is able to cover large distances. Even though the design of Avy focussed on large distance travelling on high speeds (around 200 km/h), it is still able to take-off and land vertically. Moreover, the design is fully electric driven with propulsion, able to fly (nearly) autonomously and able to carry a payload of around 10 kg.
Dubai
Week 3
In preparation for the presentation of this week, the group defines the deliverables of the project
Deliverables
- A working drone equipped with thermal-sensing camera capable of detecting humans
- Complete wiki with all relevant information on the project. This includes an introduction, a context analysis (state of the art), problem statement, research with an accent on the USE perspective, and finally a conclusion with some ideas for further improvement.