Ultra Wide Band System - Trilateration: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
* Positioning using Bluetooth beacons | * Positioning using Bluetooth beacons | ||
* Positioning using image processing | * Positioning using image processing | ||
=== Trilateration using a Laser Range Extender === | |||
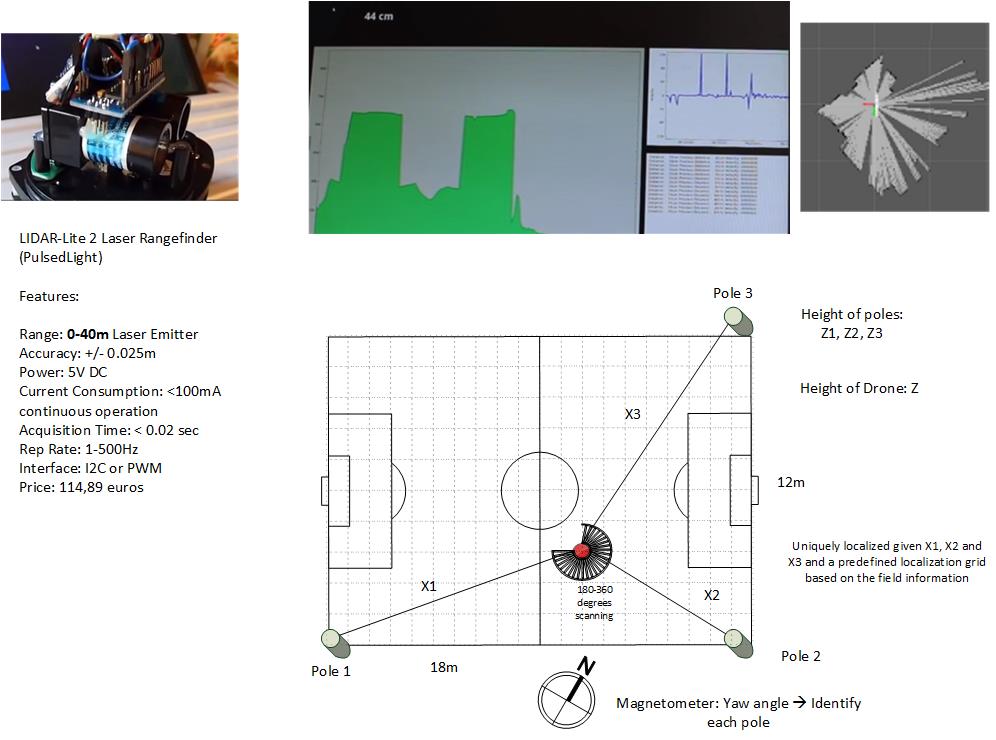
A laser range extender can be used to determine the distance between the laser itself and an object reflecting the beam. A company was found that produces, small lightweight laser range extenders that can rotate. By placing three poles at known positions around the field, and measuring the distance to those poles, the drone can be positioned using trilateration. Trilateration is a type of positioning algorithm, an easy way of understanding is that if a circle with the distance between each pole and the drone were to be drawn around every pole, only one intersection point would remain. If the height is also known, the drone state is thus known. Unfortunately, the sensor was out of stock for the duration of the project, and no alternative was found at it is an emerging technology. As such this concept was abandoned. | |||
[[File:LaserSolution.jpg|600px|thumb|left|Overview Laser Range Extender Concept]] | [[File:LaserSolution.jpg|600px|thumb|left|Overview Laser Range Extender Concept]] | ||
=== Trilateration using Ultra-Wideband Beacons | |||
Similar to the previous concept are Ultra-Wideband Beacons. These are small sensors communicating with one another over the ultra-wide band radio spectrum. Given the time between sending and receiving, the distance can be estimated with a promised accuracy of around 10 centimeters. By placing at least three beacons at known positions and placing one beacon on the drone, trilateration can again be applied to find the drone position w.r.t. to the stationary beacons. The beacons around the field are referred to as anchors and the beacon on the drone is referred to as the tag. Multiple tags can be in the system as well as more than three anchors providing more accuracy through redundancy, making it a very extendable concept. This method is very new, and only a few manufacturers are available. Ready-to-use systems are still rare. There is a company, DecaWave, offering evaluation kits that are instantly usable without additional development, but these are expensive and maybe too fragile for use on a drone. | |||
Revision as of 13:23, 31 March 2016
One of the most important building blocks for the drone referee is a method for positioning. At all times, the drone state, namely the set {X,Y,Z,Yaw}, should be known in order to perform the refereeing duties. Of the drone state, Z and the Yaw are measured by either the drone sensor suite or other programs as they are required for the low-level control of the drone. However, in order to localize w.r.t. the field and to find X and Y, a solution has to be found. To this end, several concepts were composed. Of those concepts, trilateration using Ultra Wide Band Anchors (UWB) was realized. First, the rejected concepts are shortly listed, followed by a detailed explanation of the UWB system.
Concepts
The positioning system must provide an accurate enough signal at a high enough sample rate for position control. As ball out of pitch detection is to be detected using image processing, an accuracy of 0.5 meters was chosen as minimum accuracy for the positioning system. This means that a circle with a radius of half a meter designate the position of the drone. For the sample rate a minimum of 10 measurements per second was chosen. However, as most of the technologies listed here are very new or still in development, this information could not be obtained for all of them. The following concepts will be discussed:
- Trilateration using a Laser Range Extender
- Trilateration using ultra-wideband beacons
- Positioning using Bluetooth beacons
- Positioning using image processing
Trilateration using a Laser Range Extender
A laser range extender can be used to determine the distance between the laser itself and an object reflecting the beam. A company was found that produces, small lightweight laser range extenders that can rotate. By placing three poles at known positions around the field, and measuring the distance to those poles, the drone can be positioned using trilateration. Trilateration is a type of positioning algorithm, an easy way of understanding is that if a circle with the distance between each pole and the drone were to be drawn around every pole, only one intersection point would remain. If the height is also known, the drone state is thus known. Unfortunately, the sensor was out of stock for the duration of the project, and no alternative was found at it is an emerging technology. As such this concept was abandoned.
=== Trilateration using Ultra-Wideband Beacons Similar to the previous concept are Ultra-Wideband Beacons. These are small sensors communicating with one another over the ultra-wide band radio spectrum. Given the time between sending and receiving, the distance can be estimated with a promised accuracy of around 10 centimeters. By placing at least three beacons at known positions and placing one beacon on the drone, trilateration can again be applied to find the drone position w.r.t. to the stationary beacons. The beacons around the field are referred to as anchors and the beacon on the drone is referred to as the tag. Multiple tags can be in the system as well as more than three anchors providing more accuracy through redundancy, making it a very extendable concept. This method is very new, and only a few manufacturers are available. Ready-to-use systems are still rare. There is a company, DecaWave, offering evaluation kits that are instantly usable without additional development, but these are expensive and maybe too fragile for use on a drone.