PRE2015 3 Groep2 week4: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
== Way flying == | == Way flying == | ||
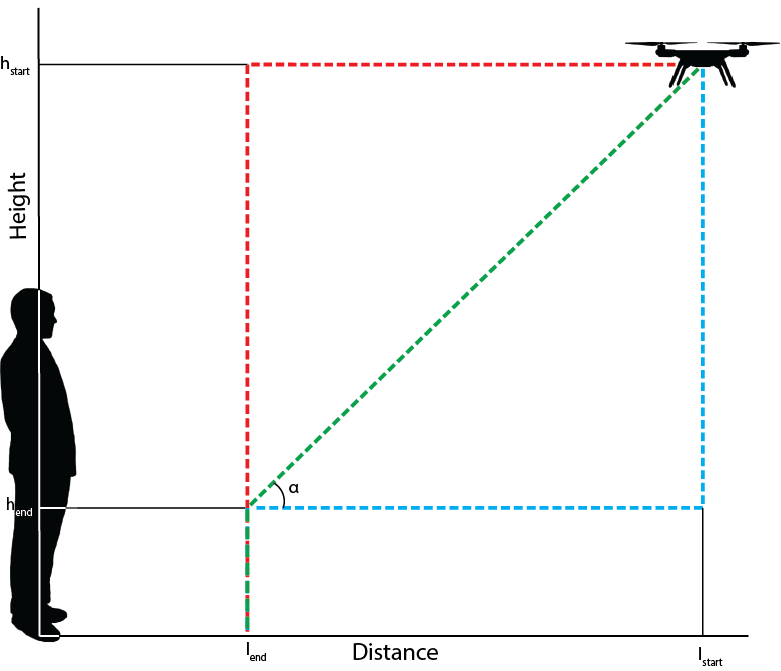
;Situation A | |||
:The drone flies horizontally to a certain distance l<sub>end</sub> then the drone land vertically. | |||
;Situation B | |||
:The drone flies diagonally to a certain point l<sub>end</sub> en h<sub>end</sub>. Then the drone lands vertically. | |||
;Situation C | |||
:The drones lowers itself vertically to a certain height h<sub>end</sub>. It then flies horizontally to a certain distance l<sub>end</sub> before it lands vertically on the ground. | |||
[[File:FlightPathCombained.png|thumbnail|upright=2.5|Schematic representation of the experiment setup. Situation A, displayed in red. Situation B, displayed in green. Situation C, displayed in blue.]] | [[File:FlightPathCombained.png|thumbnail|upright=2.5|Schematic representation of the experiment setup. Situation A, displayed in red. Situation B, displayed in green. Situation C, displayed in blue.]] | ||
Revision as of 12:18, 29 February 2016
experiment
Approaching Users
Multiple factors can play a role, for the user to feel safe and comfortable with the drone approaching him. So far little research has been done regarding approaching people in a user friendly way, as can be seen in Research from week 3. In order to be able to potato
Way flying
- Situation A
- The drone flies horizontally to a certain distance lend then the drone land vertically.
- Situation B
- The drone flies diagonally to a certain point lend en hend. Then the drone lands vertically.
- Situation C
- The drones lowers itself vertically to a certain height hend. It then flies horizontally to a certain distance lend before it lands vertically on the ground.