Mobile Robot Control 2023 Rosey: Difference between revisions
(→Global Navigation: added extra documentation) |
m (Minor additions) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Welcome to the group page of team Rosey! | Welcome to the group page of team Rosey! This page is currently under construction. | ||
===Group members table=== | ===Group members table=== | ||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
[[File:Midterm presentation Rosey.pdf|thumb|Midterm Presentation|none]] | [[File:Midterm presentation Rosey.pdf|thumb|Midterm Presentation|none]] | ||
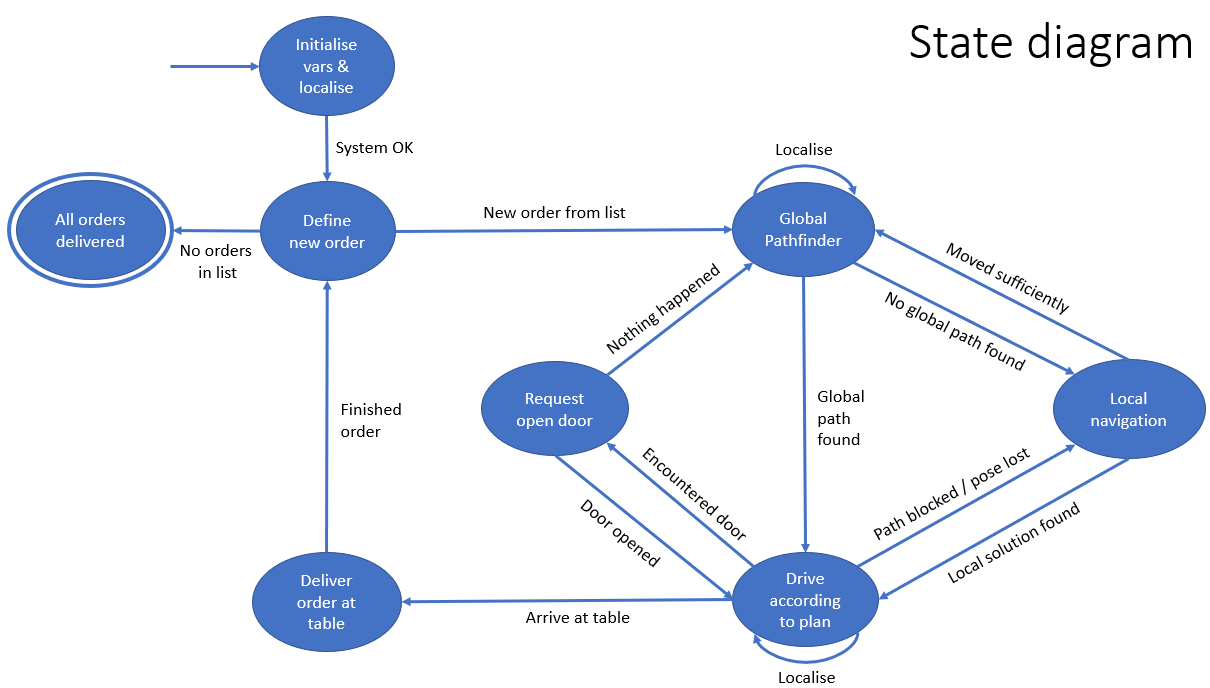
===Current state diagram=== | ===Current state diagram=== | ||
[[File:StateDiagramRosey.png|thumb|441x441px|Current state diagram, reflected in the main.c file. ( | [[File:StateDiagramRosey.png|thumb|441x441px|Current state diagram, reflected in the main.c file. (Version 2 as of 17-06-2023)|none]]*Final version with sub-state diagram to be added. | ||
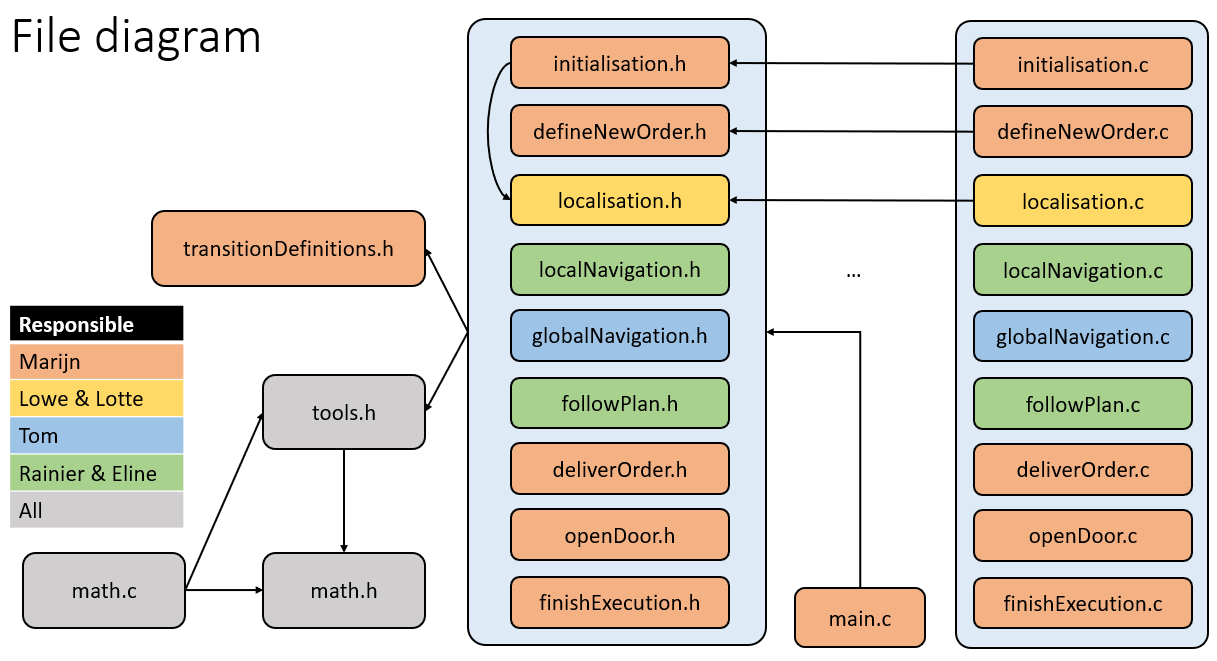
===File structure=== | ===File structure=== | ||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
'''Used algorithm and predefined knowledge''' | '''Used algorithm and predefined knowledge''' | ||
The global navigation uses the A* algorithm to find the shortest path to from a starting node to a goal node. The A* algorithm uses a predefined grid of nodes. This grid is applied by a JSON file, generated with Matlab. With Matlab, the grid nodes with their connections are manually chooses in the known map. On top of that, we were inspired by the lecture about Safe navigation in a hospital environment to introduce some context-aware navigation into our model, by means of semantics. Each node contains some semantic information about its environment, described by a integer. The following semantic integers are included: 0 = table 0, 1= table 1, ..., 49 = table 49, 50 = door, 99 = empty (meaning no semantic information present). This information is also included in the JSON file | The global navigation uses the A* algorithm to find the shortest path to from a starting node to a goal node. The A* algorithm uses a predefined grid of nodes. This grid is applied by a JSON file, generated with Matlab. With Matlab, the grid nodes with their connections are manually chooses in the known map. On top of that, we were inspired by the lecture about Safe navigation in a hospital environment to introduce some context-aware navigation into our model, by means of semantics. Each node contains some semantic information about its environment, described by a integer. The following semantic integers are included: 0 = table 0, 1= table 1, ..., 49 = table 49, 50 = door, 99 = empty (meaning no semantic information present). This information is also included in the JSON file. | ||
'''Preparation phase''' | '''Preparation phase''' | ||
| Line 59: | Line 59: | ||
In <code>globalNavigation(),</code> there are a few steps which has to be taken for determining the best path as node sequence. | In <code>globalNavigation(),</code> there are a few steps which has to be taken for determining the best path as node sequence. | ||
# First, the robot determines its own position in its map and the closest node is found. One assumed that there is no complete blocking object as a wall in between the robot and the closest node, i.e. sufficient nodes has to be properly placed. | #First, the robot determines its own position in its map and the closest node is found. One assumed that there is no complete blocking object as a wall in between the robot and the closest node, i.e. sufficient nodes has to be properly placed. | ||
# The goal node is found by finding the corresponding semantic number of the destination table | #The goal node is found by finding the corresponding semantic number of the destination table | ||
# The <code>aStar()</code>is executed to find the best path - In case the output is [-1], there is no path available with the provided information. Possibly causes: connections are not correctly defined are essential connections are removed. - the output with the sequence of nodes to (and including) the goal node is written to the global<code>*pathNodeIDs</code>variable | #The <code>aStar()</code>is executed to find the best path - In case the output is [-1], there is no path available with the provided information. Possibly causes: connections are not correctly defined are essential connections are removed. - the output with the sequence of nodes to (and including) the goal node is written to the global<code>*pathNodeIDs</code>variable | ||
# The main function returns whether a path is found | #The main function returns whether a path is found | ||
'''Cutting connections in case of blocking objects or close doors''' | '''Cutting connections in case of blocking objects or close doors''' | ||
Revision as of 15:28, 25 June 2023
Welcome to the group page of team Rosey! This page is currently under construction.
Group members table
| Name | Student ID |
|---|---|
| Eline Wisse | 1335162 |
| Lotte Rassaerts | 1330004 |
| Marijn Minkenberg | 1357751 |
| Rainier Heijne | 1227575 |
| Tom Minten | 1372300 |
| Lowe Blom | 1266020 |
Midterm presentation
File:Midterm presentation Rosey.pdf
Current state diagram
*Final version with sub-state diagram to be added.
File structure
Work division
We identified three 'major parts' of the assignment. These are the localisation, the global and local navigation of the robot. We additionally saw use for an overseeing role, which should ensure that the interfaces between the functions are clear. The work is divided as follows:
- Marijn : System architecture & overview
- Tom : Global navigation (A*)
- Eline & Rainier : Local navigation (potential fields + open space)
- Lowe & Lotte : Localisation
Used algorithm and predefined knowledge
The global navigation uses the A* algorithm to find the shortest path to from a starting node to a goal node. The A* algorithm uses a predefined grid of nodes. This grid is applied by a JSON file, generated with Matlab. With Matlab, the grid nodes with their connections are manually chooses in the known map. On top of that, we were inspired by the lecture about Safe navigation in a hospital environment to introduce some context-aware navigation into our model, by means of semantics. Each node contains some semantic information about its environment, described by a integer. The following semantic integers are included: 0 = table 0, 1= table 1, ..., 49 = table 49, 50 = door, 99 = empty (meaning no semantic information present). This information is also included in the JSON file.
Preparation phase
Create JSON with the provided Matlab script. The script has a visualization tool for plotting the position of all nodes.
---include grid placement of the final assignment map when available---
Initiation phase (run once)
The json file is imported with the loadConfigFile()and the grid is constructed withconstructGrid().
Global path finder phase
In globalNavigation(), there are a few steps which has to be taken for determining the best path as node sequence.
- First, the robot determines its own position in its map and the closest node is found. One assumed that there is no complete blocking object as a wall in between the robot and the closest node, i.e. sufficient nodes has to be properly placed.
- The goal node is found by finding the corresponding semantic number of the destination table
- The
aStar()is executed to find the best path - In case the output is [-1], there is no path available with the provided information. Possibly causes: connections are not correctly defined are essential connections are removed. - the output with the sequence of nodes to (and including) the goal node is written to the global*pathNodeIDsvariable - The main function returns whether a path is found
Cutting connections in case of blocking objects or close doors
---Write when local navigation is finished---