RoPod/Tutorials/Installing Ubuntu (Linux Part): Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
TUe\20172455 (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (5 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
[[File:WifiSettings.png|250px|thumb|center|Figure 1. Wi-Fi settings.]] | [[File:WifiSettings.png|250px|thumb|center|Figure 1. Wi-Fi settings.]] | ||
An entire overview to setup the wireless TUe-WPA2 connections is given [http://www.quzart.com/notes/5-tue-wpa2-linux-wifi/index.xhtml here]. | |||
= Rename ethernet device = | = Rename ethernet device = | ||
In Ubuntu 16.04 the ethernet naming convention changed. To avoid possible incompatibilities with the examples and tutorials used in the project, we can rename the ethernet device to the standard name “eth0”. | In Ubuntu 16.04 the ethernet naming convention changed. To avoid possible incompatibilities with the examples and tutorials used in the project, we can rename the ethernet device to the standard name “eth0”. | ||
Get the MAC address of your ethernet | Get the MAC address of your ethernet device: | ||
<pre> ifconfig </pre> | <pre> ifconfig </pre> | ||
| Line 37: | Line 24: | ||
<pre> sudo gedit /etc/udev/rules.d/10-rename-network.rules </pre> | <pre> sudo gedit /etc/udev/rules.d/10-rename-network.rules </pre> | ||
with the following content: | with the following content: (Replace ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:f by the MAC address of your device.) | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
SUBSYSTEM=="net", ACTION=="add", ATTR{address}=="ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff", NAME="eth0" | SUBSYSTEM=="net", ACTION=="add", ATTR{address}=="ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff", NAME="eth0" | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
You need then to restart your computer. Verify that the name indeed changed running ifconfig again. | You need then to restart your computer. Verify that the name indeed changed running ifconfig again. | ||
Latest revision as of 11:51, 25 March 2021
Info
RoPod Configuration
Other
Setup network connection
If not done yet, plug in a networkcable or setup your network settings as follows (using your own username and password):
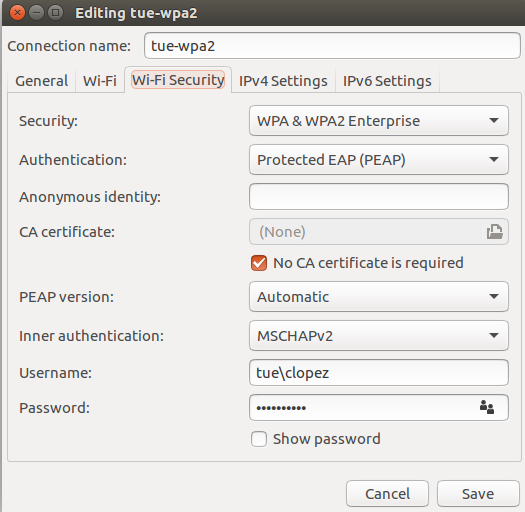
An entire overview to setup the wireless TUe-WPA2 connections is given here.
Rename ethernet device
In Ubuntu 16.04 the ethernet naming convention changed. To avoid possible incompatibilities with the examples and tutorials used in the project, we can rename the ethernet device to the standard name “eth0”. Get the MAC address of your ethernet device:
ifconfig
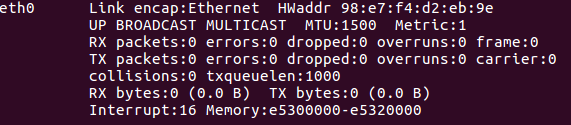
If you see eth0 listed in your devices, then you do not have to change it. Otherwise, create the following file “/etc/udev/rules.d/10-rename-network.rules”:
sudo gedit /etc/udev/rules.d/10-rename-network.rules
with the following content: (Replace ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:f by the MAC address of your device.)
SUBSYSTEM=="net", ACTION=="add", ATTR{address}=="ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff", NAME="eth0"
You need then to restart your computer. Verify that the name indeed changed running ifconfig again.
Several tips for customizing Ubuntu are given on this page of the Embedded Motion Control course.
Once you have Linux up-and-running, we are going to install GitHub.