PRE2020 3 Group8: Difference between revisions
| Line 125: | Line 125: | ||
==== Stakeholder analysis ==== | ==== Stakeholder analysis ==== | ||
A stakeholder analysis of an issue consists of finding the equilibrium of different demands from different perspectives. The stakeholder map shows which stakeholders will be considered, moreover, it will help to identify the interests and mechanisms of the stakeholders to influence other stakeholders, key people, competitors and to reduce potential risk. | |||
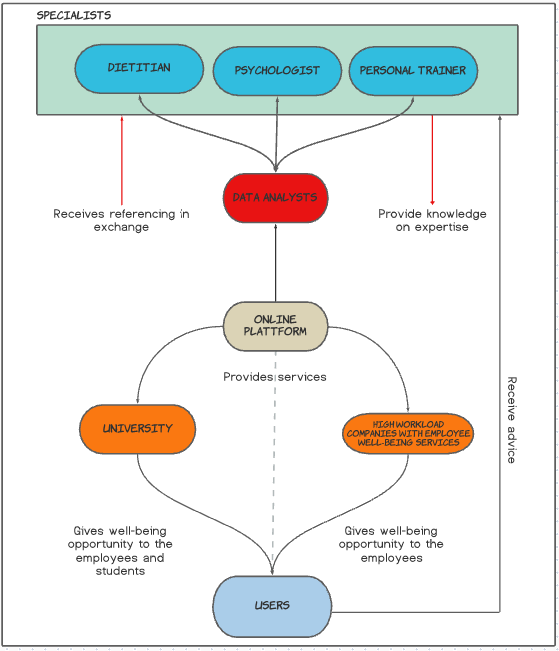
The center is the online platform in the center which connects every stakeholder and provides access to the AI assistant. The main target group is the users, described above. With the marketing, the first targeting would reach the bigger associations, companies or universities, furthermore individuals who personally are interested. The idea is to include specialists, such as dietitians, psychologists and personal trainers. The data analysts are mainly members in our current team who could work in collaboration with the specialist as an exchange in knowledge and expertise. Our team would provide referencing to the specialists by our customers in case the users wish to use the help of physical specialists, e.g. receive a proper diet plan from a dietitian, set a bigger goal for weight loss with a personal trainer or get better help from a psychologist. The help of the specialists could be included in the watch. | |||
The collaboration with bigger companies e.g. IT companies where the employees are required to work long with a busy schedule or to do night-shifts would give an opportunity to help to maintain health goals for the employees. Universities could also profit from the services and help the well-being of their students and employees. | |||
[[File:Stakeholder_map.png]] | |||
==== Business plan and development ==== | ==== Business plan and development ==== | ||
Revision as of 12:16, 23 February 2021
Group description
Abstract
A pure software end-user application that supports people in their need to socialize while motivating self-improvement. Anthropomorphism is intentionally used to increase user commitment and experience. Machine learning techniques are used to process user's data and provide feedback, and to facilitate the anthropomorphized interface.
Conceptualized Idea
Hypothetical idea: A webpage/application, that will motivate its users into a more (mentally) healthy way of living life. The user can put in any preferences to be motivated on and set its own goals. Numeric data of the user will be tracked in a communicative way rather than filling in forms, is stored and compared to older data, and reflection of this comparison will be given in a personalized way back to the user.
On this page, the concept of this motivating coaching system will be presented. This system combines specialized monitored and self-measured data from its user with individual and reference knowledge to give its users an overview (and recommendations). The system will keep track of one’s daily life structure, translate and summarize the numerical input into recommendations in a continuous personalized motivating coaching dialogue taking into account the needs and preferences of each user individually.
Members
(in alphabetical order):
- Edwin Steenkamer (1006712)
- Emi Kuijpers (1227154)
- Fanni Egresits (1316400)
- Morris Boers (1253107)
- Lulof Pirée (1363638)
Task division
Machine Learning: Lulof & Edwin
User Interface: Morris
User-centered design: Emi & Fanni
GitHub Page:
Logbook
See the page logbook_group_8
Problem statement and objectives
Problem Statement
Often loneliness is associated with elderly people living unintentionally in social isolation due to unfortunate circumstances. However, the reality is that loneliness is experienced by all ages and almost all humans. [1] Humans are social animals [2] ), and we humans influence each other by merely existing together. Loneliness is seen as a severe public health issue due to its association to increased risk of morbidity and mortality [3]. A study by Luhmann & Hawkley [4] suggests that the prevalence rates of loneliness are highest for young adults (<30 years).
Needs
Two needs arise from the problem statement above. Firstly, to reduce biases in the decision-making process due to falsely remembered memories, people need to be provided with an objective summary of their past events. Secondly, the net amount (both intensity and frequency) of negative emotions and lack of motivation experienced due to a lack of social interaction must be decreased to fill the lack of external motivation.
Goals
To reach the needs stated above, the software application has two main requirements:
- Firstly, the system's main aim is to provide users with insight in parts of their behavioural patterns that are unknown to them. Humans tend to rely heavily on their intuitions, which can often strongly deviate from its true value. The system will serve as a non-biased evaluation tool, which will result in the user discovering behavioural patterns after a fixed period based on their objective data, rather than intuitions and memory.
- Secondly, to increase the motivation of the user to put in data, and to enhance positive changes in behavioural patterns, anthropomorphic features will be used while designing the system. Using a human-like question generator to let the user put in data rather than a non-interactive (for example, a questionnaire), the user will perceive a need to answer the system rather than merely filling in the data. The aim here is to increase motivation and overall well-being by presenting the data's reflection in a personalized way.
Beyond the scope
The following features are probably valuable additions to the product, but they are beyond the scope of what can be achieved in one quartile:
- Voice recognition, natural language text inputs (natural language processing is too much to add within the given timespan)
- Animated anthropomorphized interface (e.g. simulated face)
User description
Primary Target Audience
The application will be designed to be used by technology-oriented adults (mainly focusing on minus 30 years), who interact with computers and smartphones on a daily basis. The main target for this system are students who spend most of their time alone in their student accommodation. This can both be due to contemporary COVID-19 pandemic stay-at-home regulations, but also for users who live abroad for a short time, for example.
The focus will also be on people who want to improve their daily structure and overall well-being in any way but have no idea what would be best for them. Therefore, the system will provide its user with objective data to discover clear behavioural patterns that might have lead to certain events. Users are more extensively described at the user analysis-section. %refer to user analysis on the wiki. If wiki still unavailable, delete sentence. The application will likely not be suitable for children due to its design constraints, or for elderly people who are not technology-oriented and adapted to new technologies.
User requirements
To engage positive behaviour in people using an AI application, an accessible and practical user-interface is critical. An irresponsive, unintuitive or unfinished interface may discourage users from using the application, let alone be positively nudged by the application. Users need to perceive social engagement and be positively motivated by the system to change its behaviour.
Approach, milestones and deliverables
Milestones
The project milestones are divided into three main parts: Implementing a human-centered design approach, the system's economical value and the software milestones.
User-centered Design
Target User-perspective: Human-Centered design
- Perform user analysis
- Describe the potential main users and their needs
- Provide several persona scenario's.
- Define boundaries for user requirements
- Research needs to be conducted on how different system features will motivate its users and trigger them to change their behaviour in a non-intrusive, engaging way.
- Secondary end-users and stakeholders (developers, the scientific community) need to be defined and described.
Potential Ethical Threats
- Negative anthropomorphism: By adding human-like features to non-human agents, it is essential to consider possible threats of cognitive deception. The user must be (and stay) aware that the responses are computationally generated.
- Paternalism: The system is designed to provide its user's insight into their behaviour and motivate them objectively to make positive changes. Hence, the system is deliberately nudging the user. A sufficient amount of care must be taken not to exploit this capability to act against the user's interest.
- Intruding one's privacy: Research has to be investigated to find an optimum amount of tradeoff between the user trusting the system enough to give a sufficient amount of data without negatively intruding the user.
Comparative advantage, product innovation and improving Quality of life of its users
- Essence and uniqueness of the project need to be defined.
- Describe current state-of-the-art, combining it with essence and uniqueness to state comparative advantages.
- Define the actual perceived gain of the end-user.
Economical perspective
Economical value
In this section, the preferences of the given users are described that determine the economical value of our product. This can be defined by a survey/questionnaire or by market-research.The economical value of the product is the benefit that the costumers receive from the usage of the AI software. In the case of the specific device we develop, this could be the motivation, joy, health,fun..etc. This value is not an objective characteristic, but rather subjective, since it differs by its user's needs and expectations. Because of this diversity, our proposal is a survey conduction before the start of the program to collect enough information for a fully personalized service. On this way, the economical value to the customers (EVC) can be determined and the market price of the software can be quantified. \\ After the market-research, we plan to create a competitor-analysis which helps us to see which additional tools we need to implement and what the essence and uniqueness our product could be compare to our competitors. This step will also help us to narrow or extend the list of stakeholders we want to approach. This information will enable us to create a value network,a cash-flow for the upcoming semester and to develop a business plan.
Stakeholder analysis
A stakeholder analysis of an issue consists of finding the equilibrium of different demands from different perspectives. The stakeholder map shows which stakeholders will be considered, moreover, it will help to identify the interests and mechanisms of the stakeholders to influence other stakeholders, key people, competitors and to reduce potential risk. The center is the online platform in the center which connects every stakeholder and provides access to the AI assistant. The main target group is the users, described above. With the marketing, the first targeting would reach the bigger associations, companies or universities, furthermore individuals who personally are interested. The idea is to include specialists, such as dietitians, psychologists and personal trainers. The data analysts are mainly members in our current team who could work in collaboration with the specialist as an exchange in knowledge and expertise. Our team would provide referencing to the specialists by our customers in case the users wish to use the help of physical specialists, e.g. receive a proper diet plan from a dietitian, set a bigger goal for weight loss with a personal trainer or get better help from a psychologist. The help of the specialists could be included in the watch.
The collaboration with bigger companies e.g. IT companies where the employees are required to work long with a busy schedule or to do night-shifts would give an opportunity to help to maintain health goals for the employees. Universities could also profit from the services and help the well-being of their students and employees.
Business plan and development
- Cash-flow
- Business model
Software milestones
Startup
- Research what technologies are feasible to implement, and potentially applicable to reach the requirements
- Division in modules with (relatively) independent functions that can be developed and tested independently
- Create specific requirements for different modules
- Create designs for various modules
- Define interfaces between modules
Rough Scattered Prototype
- A functional yet limited user interface is present, without taking into account human factors design.
- Working content-generating networks have been implemented, but the output does not yet need to be fine-tuned or adaptive to input
Connected Prototype
- A basic database is operational
- The interface can accept inputs, pass the input information to the database. Human factor design will be implemented into the interface.
- The decoder can read the database and generate output in the UI. The output does not yet need to be perfectly adjusted to the database’s content.
- The Question-generator can generate output to be displayed in the UI
Rough Complete Prototype
- Users are able to select which variables will be logged.
- Users are able to delete data
- Users can request transparency of the data gathered (whether this is just a textual description, direct access to the database, or otherwise)
- The Question-generator produces human-like questions that align with the input fields
- The decoder produces outputs that correctly reflect nontrivial information in the database.
Literature Review (separate file)
Due to bugs in the installation of the LaTeX engine of the wiki, mathematical expressions cannot be shown here. See the following Overleaf file for the literature review, and references: Literature review Overleaf file.
Overview
Work-in-progress-page
See the page WIP group 8 for an actively edited file of notes.
User guide
TODO...
Software documentation
TODO...
References
- ↑ Hammond, C., Qualter, P., Victor, C., & Barretto, M. (2018). Who feels lonely? The results of the world's largest loneliness study.
- ↑ Baumeister, R. F. & Bushman, B. J. (2008), Social Psychology and Human Nature. 2nd edition, Wadsworth, Cengage Learning, 436-441
- ↑ Cacioppo, J. T., & Cacioppo, S. (2018). The growing problem of loneliness. Lancet, 391, 426. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30142-9
- ↑ Luhmann, M., & Hawkley, L. C. (2016). Age differences in loneliness from late adolescence to oldest old age. Developmental psychology, 52(6), 943.